Catalyst is a PyTorch framework for Deep Learning Research and Development.
It focuses on reproducibility, rapid experimentation, and codebase reuse
so you can create something new rather than write yet another train loop.
Break the cycle – use the Catalyst!
Getting started
pip install -U catalystimport os
from torch import nn, optim
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
from catalyst import dl, utils
from catalyst.contrib import MNIST
model = nn.Sequential(nn.Flatten(), nn.Linear(28 * 28, 10))
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=0.02)
train_data = MNIST(os.getcwd(), train=True)
valid_data = MNIST(os.getcwd(), train=False)
loaders = {
"train": DataLoader(train_data, batch_size=32),
"valid": DataLoader(valid_data, batch_size=32),
}
runner = dl.SupervisedRunner(
input_key="features", output_key="logits", target_key="targets", loss_key="loss"
)
# model training
runner.train(
model=model,
criterion=criterion,
optimizer=optimizer,
loaders=loaders,
num_epochs=1,
callbacks=[
dl.AccuracyCallback(input_key="logits", target_key="targets", topk_args=(1, 3, 5)),
dl.PrecisionRecallF1SupportCallback(
input_key="logits", target_key="targets", num_classes=10
),
],
logdir="./logs",
valid_loader="valid",
valid_metric="loss",
minimize_valid_metric=True,
verbose=True,
load_best_on_end=True,
)
# model evaluation
metrics = runner.evaluate_loader(
loader=loaders["valid"],
callbacks=[dl.AccuracyCallback(input_key="logits", target_key="targets", topk_args=(1, 3, 5))],
)
assert "accuracy01" in metrics.keys()
# model inference
for prediction in runner.predict_loader(loader=loaders["valid"]):
assert prediction["logits"].detach().cpu().numpy().shape[-1] == 10
features_batch = next(iter(loaders["valid"]))[0]
# model stochastic weight averaging
model.load_state_dict(utils.get_averaged_weights_by_path_mask(path_mask="./logs/*.pth"))
# model tracing
utils.trace_model(model=runner.model.cpu(), batch=features_batch)
# model quantization
utils.quantize_model(model=runner.model)
# model pruning
utils.prune_model(model=runner.model, pruning_fn="l1_unstructured", amount=0.8)
# onnx export
utils.onnx_export(model=runner.model.cpu(), batch=features_batch, file="./logs/mnist.onnx", verbose=True)Step-by-step Guide
- Start with Catalyst — A PyTorch Framework for Accelerated Deep Learning R&D introduction.
- Try notebook tutorials or check minimal examples for first deep dive.
- Read blog posts with use-cases and guides.
- Learn machine learning with our "Deep Learning with Catalyst" course.
- And finally, join our slack if you want to chat with the team and contributors.
Table of Contents
Overview
Catalyst helps you implement compact but full-featured Deep Learning pipelines with just a few lines of code. You get a training loop with metrics, early-stopping, model checkpointing, and other features without the boilerplate.
Installation
Generic installation:
pip install -U catalystSpecialized versions, extra requirements might apply
pip install catalyst[ml] # installs ML-based Catalyst
pip install catalyst[cv] # installs CV-based Catalyst
# master version installation
pip install git+https://github.com/catalyst-team/catalyst@master --upgrade
# all available extensions are listed here:
# https://github.com/catalyst-team/catalyst/blob/master/setup.pyCatalyst is compatible with: Python 3.6+. PyTorch 1.3+.
Tested on Ubuntu 16.04/18.04/20.04, macOS 10.15, Windows 10, and Windows Subsystem for Linux.
Features
- Universal train/inference loop.
- Configuration files for model and data hyperparameters.
- Reproducibility – all source code and environment variables are saved.
- Callbacks – reusable train/inference pipeline parts with easy customization.
- Training stages support.
- Deep Learning best practices: SWA, AdamW, Ranger optimizer, OneCycle, and more.
- Workflow best practices: fp16 support, distributed training, slurm support, DALI loaders.
- Any hardware backend supported: AMP, Apex, DeepSpeed, FairScale, XLA.
Tests
All Catalyst code, features, and pipelines are fully tested. We also have our own catalyst-codestyle and a corresponding pre-commit hook.
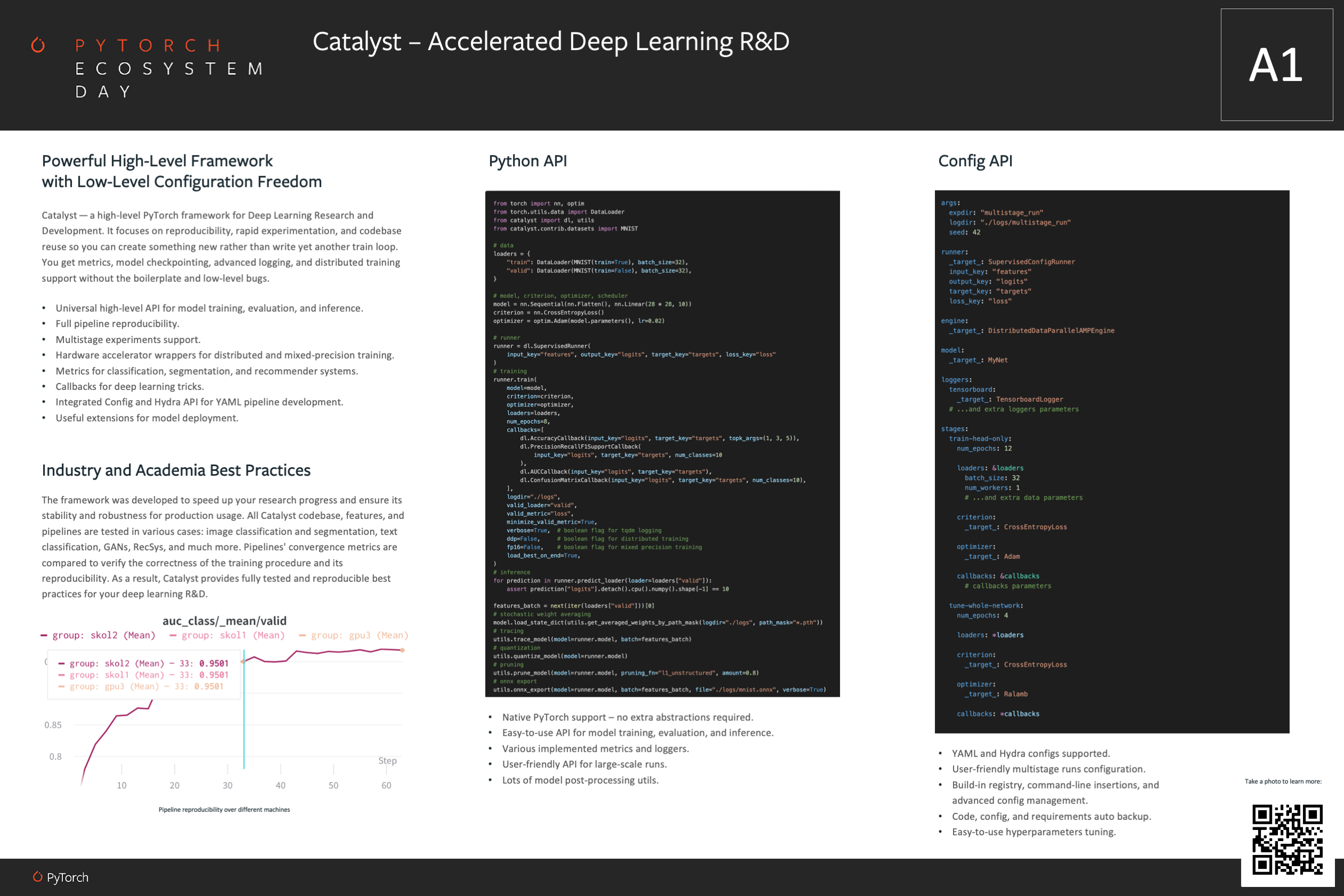
During testing, we train a variety of different models: image classification, image segmentation, text classification, GANs, and much more. We then compare their convergence metrics in order to verify the correctness of the training procedure and its reproducibility.
As a result, Catalyst provides fully tested and reproducible best practices for your deep learning research and development.
Catalyst
Documentation
Minimal Examples
Introduction tutorial "Customizing what happens in
train"Demo with customization examples
Reinforcement Learning with Catalyst
CustomRunner – PyTorch for-loop decomposition
import os
from torch import nn, optim
from torch.nn import functional as F
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
from catalyst import dl, metrics
from catalyst.contrib import MNIST
model = nn.Sequential(nn.Flatten(), nn.Linear(28 * 28, 10))
optimizer = optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=0.02)
train_data = MNIST(os.getcwd(), train=True)
valid_data = MNIST(os.getcwd(), train=False)
loaders = {
"train": DataLoader(train_data, batch_size=32),
"valid": DataLoader(valid_data, batch_size=32),
}
class CustomRunner(dl.Runner):
def predict_batch(self, batch):
# model inference step
return self.model(batch[0].to(self.device))
def on_loader_start(self, runner):
super().on_loader_start(runner)
self.meters = {
key: metrics.AdditiveMetric(compute_on_call=False)
for key in ["loss", "accuracy01", "accuracy03"]
}
def handle_batch(self, batch):
# model train/valid step
# unpack the batch
x, y = batch
# run model forward pass
logits = self.model(x)
# compute the loss
loss = F.cross_entropy(logits, y)
# compute the metrics
accuracy01, accuracy03 = metrics.accuracy(logits, y, topk=(1, 3))
# log metrics
self.batch_metrics.update(
{"loss": loss, "accuracy01": accuracy01, "accuracy03": accuracy03}
)
for key in ["loss", "accuracy01", "accuracy03"]:
self.meters[key].update(self.batch_metrics[key].item(), self.batch_size)
# run model backward pass
if self.is_train_loader:
loss.backward()
self.optimizer.step()
self.optimizer.zero_grad()
def on_loader_end(self, runner):
for key in ["loss", "accuracy01", "accuracy03"]:
self.loader_metrics[key] = self.meters[key].compute()[0]
super().on_loader_end(runner)
runner = CustomRunner()
# model training
runner.train(
model=model,
optimizer=optimizer,
loaders=loaders,
logdir="./logs",
num_epochs=5,
verbose=True,
valid_loader="valid",
valid_metric="loss",
minimize_valid_metric=True,
)
# model inference
for logits in runner.predict_loader(loader=loaders["valid"]):
assert logits.detach().cpu().numpy().shape[-1] == 10ML - linear regression
import torchx
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader, TensorDataset
from catalyst import dl
# data
num_samples, num_features = int(1e4), int(1e1)
X, y = torch.rand(num_samples, num_features), torch.rand(num_samples)
dataset = TensorDataset(X, y)
loader = DataLoader(dataset, batch_size=32, num_workers=1)
loaders = {"train": loader, "valid": loader}
# model, criterion, optimizer, scheduler
model = torch.nn.Linear(num_features, 1)
criterion = torch.nn.MSELoss()
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters())
scheduler = torch.optim.lr_scheduler.MultiStepLR(optimizer, [3, 6])
# model training
runner = dl.SupervisedRunner()
runner.train(
model=model,
criterion=criterion,
optimizer=optimizer,
scheduler=scheduler,
loaders=loaders,
logdir="./logdir",
valid_loader="valid",
valid_metric="loss",
minimize_valid_metric=True,
num_epochs=8,
verbose=True,
)ML - multiclass classification
import torch
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader, TensorDataset
from catalyst import dl
# sample data
num_samples, num_features, num_classes = int(1e4), int(1e1), 4
X = torch.rand(num_samples, num_features)
y = (torch.rand(num_samples,) * num_classes).to(torch.int64)
# pytorch loaders
dataset = TensorDataset(X, y)
loader = DataLoader(dataset, batch_size=32, num_workers=1)
loaders = {"train": loader, "valid": loader}
# model, criterion, optimizer, scheduler
model = torch.nn.Linear(num_features, num_classes)
criterion = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters())
scheduler = torch.optim.lr_scheduler.MultiStepLR(optimizer, [2])
# model training
runner = dl.SupervisedRunner(
input_key="features", output_key="logits", target_key="targets", loss_key="loss"
)
runner.train(
model=model,
criterion=criterion,
optimizer=optimizer,
scheduler=scheduler,
loaders=loaders,
logdir="./logdir",
num_epochs=3,
valid_loader="valid",
valid_metric="accuracy03",
minimize_valid_metric=False,
verbose=True,
callbacks=[
dl.AccuracyCallback(input_key="logits", target_key="targets", num_classes=num_classes),
# uncomment for extra metrics:
# dl.PrecisionRecallF1SupportCallback(
# input_key="logits", target_key="targets", num_classes=num_classes
# ),
# dl.AUCCallback(input_key="logits", target_key="targets"),
# catalyst[ml] required ``pip install catalyst[ml]``
# dl.ConfusionMatrixCallback(
# input_key="logits", target_key="targets", num_classes=num_classes
# ),
],
)ML - multilabel classification
import torch
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader, TensorDataset
from catalyst import dl
# sample data
num_samples, num_features, num_classes = int(1e4), int(1e1), 4
X = torch.rand(num_samples, num_features)
y = (torch.rand(num_samples, num_classes) > 0.5).to(torch.float32)
# pytorch loaders
dataset = TensorDataset(X, y)
loader = DataLoader(dataset, batch_size=32, num_workers=1)
loaders = {"train": loader, "valid": loader}
# model, criterion, optimizer, scheduler
model = torch.nn.Linear(num_features, num_classes)
criterion = torch.nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss()
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters())
scheduler = torch.optim.lr_scheduler.MultiStepLR(optimizer, [2])
# model training
runner = dl.SupervisedRunner(
input_key="features", output_key="logits", target_key="targets", loss_key="loss"
)
runner.train(
model=model,
criterion=criterion,
optimizer=optimizer,
scheduler=scheduler,
loaders=loaders,
logdir="./logdir",
num_epochs=3,
valid_loader="valid",
valid_metric="accuracy",
minimize_valid_metric=False,
verbose=True,
callbacks=[
dl.BatchTransformCallback(
transform=torch.sigmoid,
scope="on_batch_end",
input_key="logits",
output_key="scores"
),
dl.AUCCallback(input_key="scores", target_key="targets"),
# uncomment for extra metrics:
# dl.MultilabelAccuracyCallback(input_key="scores", target_key="targets", threshold=0.5),
# dl.MultilabelPrecisionRecallF1SupportCallback(
# input_key="scores", target_key="targets", threshold=0.5
# ),
]
)ML - multihead classification
import torch
from torch import nn, optim
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader, TensorDataset
from catalyst import dl
# sample data
num_samples, num_features, num_classes1, num_classes2 = int(1e4), int(1e1), 4, 10
X = torch.rand(num_samples, num_features)
y1 = (torch.rand(num_samples,) * num_classes1).to(torch.int64)
y2 = (torch.rand(num_samples,) * num_classes2).to(torch.int64)
# pytorch loaders
dataset = TensorDataset(X, y1, y2)
loader = DataLoader(dataset, batch_size=32, num_workers=1)
loaders = {"train": loader, "valid": loader}
class CustomModule(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_features: int, out_features1: int, out_features2: int):
super().__init__()
self.shared = nn.Linear(in_features, 128)
self.head1 = nn.Linear(128, out_features1)
self.head2 = nn.Linear(128, out_features2)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.shared(x)
y1 = self.head1(x)
y2 = self.head2(x)
return y1, y2
# model, criterion, optimizer, scheduler
model = CustomModule(num_features, num_classes1, num_classes2)
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = optim.Adam(model.parameters())
scheduler = optim.lr_scheduler.MultiStepLR(optimizer, [2])
class CustomRunner(dl.Runner):
def handle_batch(self, batch):
x, y1, y2 = batch
y1_hat, y2_hat = self.model(x)
self.batch = {
"features": x,
"logits1": y1_hat,
"logits2": y2_hat,
"targets1": y1,
"targets2": y2,
}
# model training
runner = CustomRunner()
runner.train(
model=model,
criterion=criterion,
optimizer=optimizer,
scheduler=scheduler,
loaders=loaders,
num_epochs=3,
verbose=True,
callbacks=[
dl.CriterionCallback(metric_key="loss1", input_key="logits1", target_key="targets1"),
dl.CriterionCallback(metric_key="loss2", input_key="logits2", target_key="targets2"),
dl.MetricAggregationCallback(metric_key="loss", metrics=["loss1", "loss2"], mode="mean"),
dl.OptimizerCallback(metric_key="loss"),
dl.SchedulerCallback(),
dl.AccuracyCallback(
input_key="logits1", target_key="targets1", num_classes=num_classes1, prefix="one_"
),
dl.AccuracyCallback(
input_key="logits2", target_key="targets2", num_classes=num_classes2, prefix="two_"
),
# catalyst[ml] required ``pip install catalyst[ml]``
# dl.ConfusionMatrixCallback(
# input_key="logits1", target_key="targets1", num_classes=num_classes1, prefix="one_cm"
# ),
# dl.ConfusionMatrixCallback(
# input_key="logits2", target_key="targets2", num_classes=num_classes2, prefix="two_cm"
# ),
dl.CheckpointCallback(
logdir="./logs/one",
loader_key="valid", metric_key="one_accuracy", minimize=False, save_n_best=1
),
dl.CheckpointCallback(
logdir="./logs/two",
loader_key="valid", metric_key="two_accuracy03", minimize=False, save_n_best=3
),
],
loggers={"console": dl.ConsoleLogger(), "tb": dl.TensorboardLogger("./logs/tb")},
)ML – RecSys
import torch
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader, TensorDataset
from catalyst import dl
# sample data
num_users, num_features, num_items = int(1e4), int(1e1), 10
X = torch.rand(num_users, num_features)
y = (torch.rand(num_users, num_items) > 0.5).to(torch.float32)
# pytorch loaders
dataset = TensorDataset(X, y)
loader = DataLoader(dataset, batch_size=32, num_workers=1)
loaders = {"train": loader, "valid": loader}
# model, criterion, optimizer, scheduler
model = torch.nn.Linear(num_features, num_items)
criterion = torch.nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss()
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters())
scheduler = torch.optim.lr_scheduler.MultiStepLR(optimizer, [2])
# model training
runner = dl.SupervisedRunner(
input_key="features", output_key="logits", target_key="targets", loss_key="loss"
)
runner.train(
model=model,
criterion=criterion,
optimizer=optimizer,
scheduler=scheduler,
loaders=loaders,
num_epochs=3,
verbose=True,
callbacks=[
dl.BatchTransformCallback(
transform=torch.sigmoid,
scope="on_batch_end",
input_key="logits",
output_key="scores"
),
dl.CriterionCallback(input_key="logits", target_key="targets", metric_key="loss"),
# uncomment for extra metrics:
# dl.AUCCallback(input_key="scores", target_key="targets"),
# dl.HitrateCallback(input_key="scores", target_key="targets", topk_args=(1, 3, 5)),
# dl.MRRCallback(input_key="scores", target_key="targets", topk_args=(1, 3, 5)),
# dl.MAPCallback(input_key="scores", target_key="targets", topk_args=(1, 3, 5)),
# dl.NDCGCallback(input_key="scores", target_key="targets", topk_args=(1, 3, 5)),
dl.OptimizerCallback(metric_key="loss"),
dl.SchedulerCallback(),
dl.CheckpointCallback(
logdir="./logs", loader_key="valid", metric_key="loss", minimize=True
),
]
)CV - MNIST classification
import os
from torch import nn, optim
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
from catalyst import dl
from catalyst.contrib import MNIST
model = nn.Sequential(nn.Flatten(), nn.Linear(28 * 28, 10))
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=0.02)
train_data = MNIST(os.getcwd(), train=True)
valid_data = MNIST(os.getcwd(), train=False)
loaders = {
"train": DataLoader(train_data, batch_size=32),
"valid": DataLoader(valid_data, batch_size=32),
}
runner = dl.SupervisedRunner()
# model training
runner.train(
model=model,
criterion=criterion,
optimizer=optimizer,
loaders=loaders,
num_epochs=1,
logdir="./logs",
valid_loader="valid",
valid_metric="loss",
minimize_valid_metric=True,
verbose=True,
# uncomment for extra metrics:
# callbacks=[
# dl.AccuracyCallback(input_key="logits", target_key="targets", num_classes=10),
# dl.PrecisionRecallF1SupportCallback(
# input_key="logits", target_key="targets", num_classes=10
# ),
# dl.AUCCallback(input_key="logits", target_key="targets"),
# # catalyst[ml] required ``pip install catalyst[ml]``
# dl.ConfusionMatrixCallback(
# input_key="logits", target_key="targets", num_classes=num_classes
# ),
# ]
)CV - MNIST segmentation
import os
import torch
from torch import nn
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
from catalyst import dl
from catalyst.contrib import IoULoss, MNIST
model = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(1, 1, 3, 1, 1), nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(1, 1, 3, 1, 1), nn.Sigmoid(),
)
criterion = IoULoss()
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=0.02)
train_data = MNIST(os.getcwd(), train=True)
valid_data = MNIST(os.getcwd(), train=False)
loaders = {
"train": DataLoader(train_data, batch_size=32),
"valid": DataLoader(valid_data, batch_size=32),
}
class CustomRunner(dl.SupervisedRunner):
def handle_batch(self, batch):
x = batch[self._input_key]
x_noise = (x + torch.rand_like(x)).clamp_(0, 1)
x_ = self.model(x_noise)
self.batch = {self._input_key: x, self._output_key: x_, self._target_key: x}
runner = CustomRunner(
input_key="features", output_key="scores", target_key="targets", loss_key="loss"
)
# model training
runner.train(
model=model,
criterion=criterion,
optimizer=optimizer,
loaders=loaders,
num_epochs=1,
callbacks=[
dl.IOUCallback(input_key="scores", target_key="targets"),
dl.DiceCallback(input_key="scores", target_key="targets"),
dl.TrevskyCallback(input_key="scores", target_key="targets", alpha=0.2),
],
logdir="./logdir",
valid_loader="valid",
valid_metric="loss",
minimize_valid_metric=True,
verbose=True,
)CV - MNIST model distillation
import os
import torch
from torch import nn, optim
from torch.nn import functional as F
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
from catalyst import dl
from catalyst.contrib import MNIST
# [!] teacher model should be already pretrained
teacher = nn.Sequential(nn.Flatten(), nn.Linear(28 * 28, 10))
student = nn.Sequential(nn.Flatten(), nn.Linear(28 * 28, 10))
criterion = {"cls": nn.CrossEntropyLoss(), "kl": nn.KLDivLoss(reduction="batchmean")}
optimizer = optim.Adam(student.parameters(), lr=0.02)
train_data = MNIST(os.getcwd(), train=True)
valid_data = MNIST(os.getcwd(), train=False)
loaders = {
"train": DataLoader(train_data, batch_size=32),
"valid": DataLoader(valid_data, batch_size=32),
}
class DistilRunner(dl.Runner):
def handle_batch(self, batch):
x, y = batch
self.model["teacher"].eval() # let's manually set teacher model to eval mode
with torch.no_grad():
t_logits = self.model["teacher"](x)
s_logits = self.model["student"](x)
self.batch = {
"t_logits": t_logits, "s_logits": s_logits, "targets": y,
"s_logprobs": F.log_softmax(s_logits, dim=-1), "t_probs": F.softmax(t_logits, dim=-1)
}
runner = DistilRunner()
callbacks = [
dl.AccuracyCallback(input_key="t_logits", target_key="targets", num_classes=2, prefix="teacher_"),
dl.AccuracyCallback(input_key="s_logits", target_key="targets", num_classes=2, prefix="student_"),
dl.CriterionCallback(input_key="s_logits", target_key="targets", metric_key="cls_loss", criterion_key="cls"),
dl.CriterionCallback(input_key="s_logprobs", target_key="t_probs", metric_key="kl_div_loss", criterion_key="kl"),
dl.MetricAggregationCallback(metric_key="loss", metrics=["kl_div_loss", "cls_loss"], mode="mean"),
dl.OptimizerCallback(metric_key="loss", model_key="student"),
dl.CheckpointCallback(logdir="./logs", loader_key="valid", metric_key="loss", minimize=True, save_n_best=3),
]
# model training
runner.train(
model={"teacher": teacher, "student": student},
criterion=criterion,
optimizer=optimizer,
loaders=loaders,
num_epochs=1,
logdir="./logs",
verbose=True,
callbacks=callbacks,
)CV - MNIST metric learning
import os
from torch.optim import Adam
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
from catalyst import dl
from catalyst.data import BatchBalanceClassSampler
from catalyst.contrib import data, datasets, models, nn
# 1. train and valid loaders
train_dataset = datasets.MnistMLDataset(root=os.getcwd())
sampler = BatchBalanceClassSampler(
labels=train_dataset.get_labels(), num_classes=5, num_samples=10, num_batches=10
)
train_loader = DataLoader(dataset=train_dataset, batch_sampler=sampler)
valid_dataset = datasets.MnistQGDataset(root=os.getcwd(), gallery_fraq=0.2)
valid_loader = DataLoader(dataset=valid_dataset, batch_size=1024)
# 2. model and optimizer
model = models.MnistSimpleNet(out_features=16)
optimizer = Adam(model.parameters(), lr=0.001)
# 3. criterion with triplets sampling
sampler_inbatch = data.HardTripletsSampler(norm_required=False)
criterion = nn.TripletMarginLossWithSampler(margin=0.5, sampler_inbatch=sampler_inbatch)
# 4. training with catalyst Runner
class CustomRunner(dl.SupervisedRunner):
def handle_batch(self, batch) -> None:
if self.is_train_loader:
images, targets = batch["features"].float(), batch["targets"].long()
features = self.model(images)
self.batch = {"embeddings": features, "targets": targets,}
else:
images, targets, is_query = \
batch["features"].float(), batch["targets"].long(), batch["is_query"].bool()
features = self.model(images)
self.batch = {"embeddings": features, "targets": targets, "is_query": is_query}
callbacks = [
dl.ControlFlowCallback(
dl.CriterionCallback(input_key="embeddings", target_key="targets", metric_key="loss"),
loaders="train",
),
dl.ControlFlowCallback(
dl.CMCScoreCallback(
embeddings_key="embeddings",
labels_key="targets",
is_query_key="is_query",
topk_args=[1],
),
loaders="valid",
),
dl.PeriodicLoaderCallback(
valid_loader_key="valid", valid_metric_key="cmc01", minimize=False, valid=2
),
]
runner = CustomRunner(input_key="features", output_key="embeddings")
runner.train(
model=model,
criterion=criterion,
optimizer=optimizer,
callbacks=callbacks,
loaders={"train": train_loader, "valid": valid_loader},
verbose=False,
logdir="./logs",
valid_loader="valid",
valid_metric="cmc01",
minimize_valid_metric=False,
num_epochs=10,
)CV - MNIST GAN
import os
import torch
from torch import nn
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
from catalyst import dl
from catalyst.contrib import Flatten, GlobalMaxPool2d, Lambda, MNIST
latent_dim = 128
generator = nn.Sequential(
# We want to generate 128 coefficients to reshape into a 7x7x128 map
nn.Linear(128, 128 * 7 * 7),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, inplace=True),
Lambda(lambda x: x.view(x.size(0), 128, 7, 7)),
nn.ConvTranspose2d(128, 128, (4, 4), stride=(2, 2), padding=1),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, inplace=True),
nn.ConvTranspose2d(128, 128, (4, 4), stride=(2, 2), padding=1),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(128, 1, (7, 7), padding=3),
nn.Sigmoid(),
)
discriminator = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(1, 64, (3, 3), stride=(2, 2), padding=1),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(64, 128, (3, 3), stride=(2, 2), padding=1),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, inplace=True),
GlobalMaxPool2d(),
Flatten(),
nn.Linear(128, 1),
)
model = {"generator": generator, "discriminator": discriminator}
criterion = {"generator": nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss(), "discriminator": nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss()}
optimizer = {
"generator": torch.optim.Adam(generator.parameters(), lr=0.0003, betas=(0.5, 0.999)),
"discriminator": torch.optim.Adam(discriminator.parameters(), lr=0.0003, betas=(0.5, 0.999)),
}
train_data = MNIST(os.getcwd(), train=False)
loaders = {"train": DataLoader(train_data, batch_size=32)}
class CustomRunner(dl.Runner):
def predict_batch(self, batch):
batch_size = 1
# Sample random points in the latent space
random_latent_vectors = torch.randn(batch_size, latent_dim).to(self.device)
# Decode them to fake images
generated_images = self.model["generator"](random_latent_vectors).detach()
return generated_images
def handle_batch(self, batch):
real_images, _ = batch
batch_size = real_images.shape[0]
# Sample random points in the latent space
random_latent_vectors = torch.randn(batch_size, latent_dim).to(self.device)
# Decode them to fake images
generated_images = self.model["generator"](random_latent_vectors).detach()
# Combine them with real images
combined_images = torch.cat([generated_images, real_images])
# Assemble labels discriminating real from fake images
labels = \
torch.cat([torch.ones((batch_size, 1)), torch.zeros((batch_size, 1))]).to(self.device)
# Add random noise to the labels - important trick!
labels += 0.05 * torch.rand(labels.shape).to(self.device)
# Discriminator forward
combined_predictions = self.model["discriminator"](combined_images)
# Sample random points in the latent space
random_latent_vectors = torch.randn(batch_size, latent_dim).to(self.device)
# Assemble labels that say "all real images"
misleading_labels = torch.zeros((batch_size, 1)).to(self.device)
# Generator forward
generated_images = self.model["generator"](random_latent_vectors)
generated_predictions = self.model["discriminator"](generated_images)
self.batch = {
"combined_predictions": combined_predictions,
"labels": labels,
"generated_predictions": generated_predictions,
"misleading_labels": misleading_labels,
}
runner = CustomRunner()
runner.train(
model=model,
criterion=criterion,
optimizer=optimizer,
loaders=loaders,
callbacks=[
dl.CriterionCallback(
input_key="combined_predictions",
target_key="labels",
metric_key="loss_discriminator",
criterion_key="discriminator",
),
dl.CriterionCallback(
input_key="generated_predictions",
target_key="misleading_labels",
metric_key="loss_generator",
criterion_key="generator",
),
dl.OptimizerCallback(
model_key="generator",
optimizer_key="generator",
metric_key="loss_generator"
),
dl.OptimizerCallback(
model_key="discriminator",
optimizer_key="discriminator",
metric_key="loss_discriminator"
),
],
valid_loader="train",
valid_metric="loss_generator",
minimize_valid_metric=True,
num_epochs=20,
verbose=True,
logdir="./logs_gan",
)
# visualization (matplotlib required):
# import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# %matplotlib inline
# plt.imshow(runner.predict_batch(None)[0, 0].cpu().numpy())CV - MNIST VAE
import os
import torch
from torch import nn, optim
from torch.nn import functional as F
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
from catalyst import dl, metrics
from catalyst.contrib import MNIST
LOG_SCALE_MAX = 2
LOG_SCALE_MIN = -10
def normal_sample(loc, log_scale):
scale = torch.exp(0.5 * log_scale)
return loc + scale * torch.randn_like(scale)
class VAE(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_features, hid_features):
super().__init__()
self.hid_features = hid_features
self.encoder = nn.Linear(in_features, hid_features * 2)
self.decoder = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(hid_features, in_features), nn.Sigmoid())
def forward(self, x, deterministic=False):
z = self.encoder(x)
bs, z_dim = z.shape
loc, log_scale = z[:, : z_dim // 2], z[:, z_dim // 2 :]
log_scale = torch.clamp(log_scale, LOG_SCALE_MIN, LOG_SCALE_MAX)
z_ = loc if deterministic else normal_sample(loc, log_scale)
z_ = z_.view(bs, -1)
x_ = self.decoder(z_)
return x_, loc, log_scale
class CustomRunner(dl.IRunner):
def __init__(self, logdir, device):
super().__init__()
self._logdir = logdir
self._device = device
def get_engine(self):
return dl.DeviceEngine(self._device)
def get_loggers(self):
return {
"console": dl.ConsoleLogger(),
"csv": dl.CSVLogger(logdir=self._logdir),
"tensorboard": dl.TensorboardLogger(logdir=self._logdir),
}
@property
def stages(self):
return ["train"]
def get_stage_len(self, stage: str) -> int:
return 3
def get_loaders(self, stage: str):
train_data = MNIST(os.getcwd(), train=True)
valid_data = MNIST(os.getcwd(), train=False)
loaders = {
"train": DataLoader(train_data, batch_size=32),
"valid": DataLoader(valid_data, batch_size=32),
}
return loaders
def get_model(self, stage: str):
model = self.model if self.model is not None else VAE(28 * 28, 64)
return model
def get_optimizer(self, stage: str, model):
return optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=0.02)
def get_callbacks(self, stage: str):
return {
"optimizer": dl.OptimizerCallback(metric_key="loss"),
"checkpoint": dl.CheckpointCallback(
self._logdir, loader_key="valid", metric_key="loss", minimize=True
),
}
def on_loader_start(self, runner):
super().on_loader_start(runner)
self.meters = {
key: metrics.AdditiveMetric(compute_on_call=False)
for key in ["loss_ae", "loss_kld", "loss"]
}
def handle_batch(self, batch):
x, _ = batch
x = x.view(x.size(0), -1)
x_, loc, log_scale = self.model(x, deterministic=not self.is_train_loader)
loss_ae = F.mse_loss(x_, x)
loss_kld = (-0.5 * torch.sum(1 + log_scale - loc.pow(2) - log_scale.exp(), dim=1)).mean()
loss = loss_ae + loss_kld * 0.01
self.batch_metrics = {"loss_ae": loss_ae, "loss_kld": loss_kld, "loss": loss}
for key in ["loss_ae", "loss_kld", "loss"]:
self.meters[key].update(self.batch_metrics[key].item(), self.batch_size)
def on_loader_end(self, runner):
for key in ["loss_ae", "loss_kld", "loss"]:
self.loader_metrics[key] = self.meters[key].compute()[0]
super().on_loader_end(runner)
def predict_batch(self, batch):
random_latent_vectors = torch.randn(1, self.model.hid_features).to(self.device)
generated_images = self.model.decoder(random_latent_vectors).detach()
return generated_images
runner = CustomRunner("./logs", "cpu")
runner.run()
# visualization (matplotlib required):
# import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# %matplotlib inline
# plt.imshow(runner.predict_batch(None)[0].cpu().numpy().reshape(28, 28))CV - MNIST multistage finetuning
import os
from torch import nn, optim
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
from catalyst import dl, utils
from catalyst.contrib import MNIST
class CustomRunner(dl.IRunner):
def __init__(self, logdir, device):
super().__init__()
self._logdir = logdir
self._device = device
def get_engine(self):
return dl.DeviceEngine(self._device)
def get_loggers(self):
return {
"console": dl.ConsoleLogger(),
"csv": dl.CSVLogger(logdir=self._logdir),
"tensorboard": dl.TensorboardLogger(logdir=self._logdir),
}
@property
def stages(self):
return ["train_freezed", "train_unfreezed"]
def get_stage_len(self, stage: str) -> int:
return 3
def get_loaders(self, stage: str):
train_data = MNIST(os.getcwd(), train=True)
valid_data = MNIST(os.getcwd(), train=False)
loaders = {
"train": DataLoader(train_data, batch_size=32),
"valid": DataLoader(valid_data, batch_size=32),
}
return loaders
def get_model(self, stage: str):
model = (
self.model
if self.model is not None
else nn.Sequential(nn.Flatten(), nn.Linear(784, 128), nn.ReLU(), nn.Linear(128, 10))
)
if stage == "train_freezed":
# freeze layer
utils.set_requires_grad(model[1], False)
else:
utils.set_requires_grad(model, True)
return model
def get_criterion(self, stage: str):
return nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
def get_optimizer(self, stage: str, model):
if stage == "train_freezed":
return optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=1e-3)
else:
return optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=1e-1)
def get_scheduler(self, stage: str, optimizer):
return None
def get_callbacks(self, stage: str):
return {
"criterion": dl.CriterionCallback(
metric_key="loss", input_key="logits", target_key="targets"
),
"optimizer": dl.OptimizerCallback(metric_key="loss"),
# "scheduler": dl.SchedulerCallback(loader_key="valid", metric_key="loss"),
# "accuracy": dl.AccuracyCallback(
# input_key="logits", target_key="targets", topk_args=(1, 3, 5)
# ),
# "classification": dl.PrecisionRecallF1SupportCallback(
# input_key="logits", target_key="targets", num_classes=10
# ),
# "confusion_matrix": dl.ConfusionMatrixCallback(
# input_key="logits", target_key="targets", num_classes=10
# ),
"checkpoint": dl.CheckpointCallback(
self._logdir, loader_key="valid", metric_key="loss", minimize=True, save_n_best=3
),
}
def handle_batch(self, batch):
x, y = batch
logits = self.model(x)
self.batch = {
"features": x,
"targets": y,
"logits": logits,
}
runner = CustomRunner("./logs", "cpu")
runner.run()CV - MNIST multistage finetuning (distributed)
import os
from torch import nn, optim
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
from catalyst import dl, utils
from catalyst.contrib import MNIST
class CustomRunner(dl.IRunner):
def __init__(self, logdir):
super().__init__()
self._logdir = logdir
def get_engine(self):
return dl.DistributedDataParallelEngine()
def get_loggers(self):
return {
"console": dl.ConsoleLogger(),
"csv": dl.CSVLogger(logdir=self._logdir),
"tensorboard": dl.TensorboardLogger(logdir=self._logdir),
}
@property
def stages(self):
return ["train_freezed", "train_unfreezed"]
def get_stage_len(self, stage: str) -> int:
return 3
def get_loaders(self, stage: str):
train_data = MNIST(os.getcwd(), train=True)
valid_data = MNIST(os.getcwd(), train=False)
loaders = {
"train": DataLoader(train_data, batch_size=32),
"valid": DataLoader(valid_data, batch_size=32),
}
return loaders
def get_model(self, stage: str):
model = nn.Sequential(nn.Flatten(), nn.Linear(784, 128), nn.ReLU(), nn.Linear(128, 10))
if stage == "train_freezed": # freeze layer
utils.set_requires_grad(model[1], False)
else:
utils.set_requires_grad(model, True)
return model
def get_criterion(self, stage: str):
return nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
def get_optimizer(self, stage: str, model):
if stage == "train_freezed":
return optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=1e-3)
else:
return optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=1e-1)
def get_callbacks(self, stage: str):
return {
"criterion": dl.CriterionCallback(
metric_key="loss", input_key="logits", target_key="targets"
),
"optimizer": dl.OptimizerCallback(metric_key="loss"),
"accuracy": dl.AccuracyCallback(
input_key="logits", target_key="targets", topk_args=(1, 3, 5)
),
"classification": dl.PrecisionRecallF1SupportCallback(
input_key="logits", target_key="targets", num_classes=10
),
# catalyst[ml] required ``pip install catalyst[ml]``
# "confusion_matrix": dl.ConfusionMatrixCallback(
# input_key="logits", target_key="targets", num_classes=10
# ),
"checkpoint": dl.CheckpointCallback(
self._logdir,
loader_key="valid",
metric_key="loss",
minimize=True,
save_n_best=3,
# here is the main trick:
load_on_stage_start={
"model": "best",
"global_epoch_step": "last",
"global_batch_step": "last",
"global_sample_step": "last",
},
),
"verbose": dl.TqdmCallback(),
}
def handle_batch(self, batch):
x, y = batch
logits = self.model(x)
self.batch = {
"features": x,
"targets": y,
"logits": logits,
}
if __name__ == "__main__":
runner = CustomRunner("./logs")
runner.run()AutoML - hyperparameters optimization with Optuna
import os
import optuna
import torch
from torch import nn
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
from catalyst import dl
from catalyst.contrib import MNIST
def objective(trial):
lr = trial.suggest_loguniform("lr", 1e-3, 1e-1)
num_hidden = int(trial.suggest_loguniform("num_hidden", 32, 128))
train_data = MNIST(os.getcwd(), train=True)
valid_data = MNIST(os.getcwd(), train=False)
loaders = {
"train": DataLoader(train_data, batch_size=32),
"valid": DataLoader(valid_data, batch_size=32),
}
model = nn.Sequential(
nn.Flatten(), nn.Linear(784, num_hidden), nn.ReLU(), nn.Linear(num_hidden, 10)
)
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=lr)
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
runner = dl.SupervisedRunner(input_key="features", output_key="logits", target_key="targets")
runner.train(
model=model,
criterion=criterion,
optimizer=optimizer,
loaders=loaders,
callbacks={
"accuracy": dl.AccuracyCallback(
input_key="logits", target_key="targets", num_classes=10
),
# catalyst[optuna] required ``pip install catalyst[optuna]``
"optuna": dl.OptunaPruningCallback(
loader_key="valid", metric_key="accuracy01", minimize=False, trial=trial
),
},
num_epochs=3,
)
score = trial.best_score
return score
study = optuna.create_study(
direction="maximize",
pruner=optuna.pruners.MedianPruner(
n_startup_trials=1, n_warmup_steps=0, interval_steps=1
),
)
study.optimize(objective, n_trials=3, timeout=300)
print(study.best_value, study.best_params)Config API - minimal example
import torch
from torch.utils.data import TensorDataset
from catalyst import dl
NUM_SAMPLES, NUM_FEATURES, NUM_CLASSES = int(1e4), int(1e1), 4
LOGDIR = "./logs"
class CustomConfigRunner(dl.SupervisedConfigRunner):
def get_datasets(self, stage: str):
# sample data
X = torch.rand(NUM_SAMPLES, NUM_FEATURES)
y = (torch.rand(NUM_SAMPLES,) * NUM_CLASSES).to(torch.int64)
# pytorch dataset
dataset = TensorDataset(X, y)
datasets = {"train": dataset, "valid": dataset}
return datasets
runner = CustomConfigRunner(
input_key="features",
output_key="logits",
target_key="targets",
loss_key="loss",
config={
"args": {
"logdir": LOGDIR,
"valid_loader": "valid",
"valid_metric": "accuracy01",
"minimize_valid_metric": False,
"verbose": False,
},
"model": {
"_target_": "Linear",
"in_features": NUM_FEATURES,
"out_features": NUM_CLASSES,
},
"engine": {"_target_": "DeviceEngine"},
"loggers": {
"console": {"_target_": "ConsoleLogger"},
"csv": {"_target_": "CSVLogger", "logdir": LOGDIR},
"tensorboard": {"_target_": "TensorboardLogger", "logdir": LOGDIR},
},
"stages": {
"stage1": {
"num_epochs": 10,
"criterion": {"_target_": "CrossEntropyLoss"},
"optimizer": {"_target_": "Adam", "lr": 1e-3},
"scheduler": {"_target_": "MultiStepLR", "milestones": [2]},
"loaders": {"batch_size": 32, "num_workers": 1},
"callbacks": {
"accuracy": {
"_target_": "AccuracyCallback",
"input_key": "logits",
"target_key": "targets",
"num_classes": NUM_CLASSES,
},
"classification": {
"_target_": "PrecisionRecallF1SupportCallback",
"input_key": "logits",
"target_key": "targets",
"num_classes": NUM_CLASSES,
},
"criterion": {
"_target_": "CriterionCallback",
"input_key": "logits",
"target_key": "targets",
"metric_key": "loss",
},
"optimizer": {"_target_": "OptimizerCallback", "metric_key": "loss"},
"scheduler": {"_target_": "SchedulerCallback"},
"checkpointer": {
"_target_": "CheckpointCallback",
"logdir": LOGDIR,
"loader_key": "valid",
"metric_key": "accuracy01",
"minimize": False,
"save_n_best": 3,
},
},
},
},
},
)
runner.run()Blog Posts
Talks
Community
Accelerated with Catalyst
Research Papers
- Hierarchical Attention for Sentiment Classification with Visualization
- Pediatric Bone Age Assessment
- Implementation of the paper "Tell Me Where to Look: Guided Attention Inference Network"
- Implementation of the paper "Filter Response Normalization Layer: Eliminating Batch Dependence in the Training of Deep Neural Networks"
- Implementation of the paper "Utterance-level Aggregation For Speaker Recognition In The Wild"
- Implementation of the paper "Looking to Listen at the Cocktail Party: A Speaker-Independent Audio-Visual Model for Speech Separation"
- Implementation of the paper "ESRGAN: Enhanced Super-Resolution Generative Adversarial Networks"
Blog Posts
Competitions
- Kaggle Quick, Draw! Doodle Recognition Challenge - 11th place
- Catalyst.RL - NeurIPS 2018: AI for Prosthetics Challenge – 3rd place
- Kaggle Google Landmark 2019 - 30th place
- iMet Collection 2019 - FGVC6 - 24th place
- ID R&D Anti-spoofing Challenge - 14th place
- NeurIPS 2019: Recursion Cellular Image Classification - 4th place
- MICCAI 2019: Automatic Structure Segmentation for Radiotherapy Planning Challenge 2019
- 3rd place solution for
Task 3: Organ-at-risk segmentation from chest CT scans - and 4th place solution for
Task 4: Gross Target Volume segmentation of lung cancer
- 3rd place solution for
- Kaggle Seversteal steel detection - 5th place
- RSNA Intracranial Hemorrhage Detection - 5th place
- APTOS 2019 Blindness Detection – 7th place
- Catalyst.RL - NeurIPS 2019: Learn to Move - Walk Around – 2nd place
- xView2 Damage Assessment Challenge - 3rd place
Toolkits
- Catalyst.RL – A Distributed Framework for Reproducible RL Research by Scitator
- Catalyst.Classification - Comprehensive classification pipeline with Pseudo-Labeling by Bagxi and Pdanilov
- Catalyst.Segmentation - Segmentation pipelines - binary, semantic and instance, by Bagxi
- Catalyst.Detection - Anchor-free detection pipeline by Avi2011class and TezRomacH
- Catalyst.GAN - Reproducible GANs pipelines by Asmekal
- Catalyst.Neuro - Brain image analysis project, in collaboration with TReNDS Center
- MLComp – Distributed DAG framework for machine learning with UI by Lightforever
- Pytorch toolbelt - PyTorch extensions for fast R&D prototyping and Kaggle farming by BloodAxe
- Helper functions - An assorted collection of helper functions by Ternaus
- BERT Distillation with Catalyst by elephantmipt
Other
- CamVid Segmentation Example - Example of semantic segmentation for CamVid dataset
- Notebook API tutorial for segmentation in Understanding Clouds from Satellite Images Competition
- Catalyst.RL - NeurIPS 2019: Learn to Move - Walk Around – starter kit
- Catalyst.RL - NeurIPS 2019: Animal-AI Olympics - starter kit
- Inria Segmentation Example - An example of training segmentation model for Inria Sattelite Segmentation Challenge
- iglovikov_segmentation - Semantic segmentation pipeline using Catalyst
- Logging Catalyst Runs to Comet - An example of how to log metrics, hyperparameters and more from Catalyst runs to Comet
See other projects at the GitHub dependency graph.
If your project implements a paper, a notable use-case/tutorial, or a Kaggle competition solution, or if your code simply presents interesting results and uses Catalyst, we would be happy to add your project to the list above! Do not hesitate to send us a PR with a brief description of the project similar to the above.
Contribution Guide
We appreciate all contributions. If you are planning to contribute back bug-fixes, there is no need to run that by us; just send a PR. If you plan to contribute new features, new utility functions, or extensions, please open an issue first and discuss it with us.
- Please see the Contribution Guide for more information.
- By participating in this project, you agree to abide by its Code of Conduct.
User Feedback
We've created [email protected] as an additional channel for user feedback.
- If you like the project and want to thank us, this is the right place.
- If you would like to start a collaboration between your team and Catalyst team to improve Deep Learning R&D, you are always welcome.
- If you don't like Github Issues and prefer email, feel free to email us.
- Finally, if you do not like something, please, share it with us, and we can see how to improve it.
We appreciate any type of feedback. Thank you!
Acknowledgments
Since the beginning of the Сatalyst development, a lot of people have influenced it in a lot of different ways.
Catalyst.Team
- Dmytro Doroshenko (ditwoo)
- Eugene Kachan (bagxi)
- Nikita Balagansky (elephantmipt)
- Sergey Kolesnikov (scitator)
Catalyst.Contributors
- Aleksey Grinchuk (alexgrinch)
- Aleksey Shabanov (AlekseySh)
- Alex Gaziev (gazay)
- Andrey Zharkov (asmekal)
- Artem Zolkin (arquestro)
- David Kuryakin (dkuryakin)
- Evgeny Semyonov (lightforever)
- Eugene Khvedchenya (bloodaxe)
- Ivan Stepanenko
- Julia Shenshina (julia-shenshina)
- Nguyen Xuan Bac (ngxbac)
- Roman Tezikov (TezRomacH)
- Valentin Khrulkov (khrulkovv)
- Vladimir Iglovikov (ternaus)
- Vsevolod Poletaev (hexfaker)
- Yury Kashnitsky (yorko)
Trusted by
- Awecom
- Researchers at the Center for Translational Research in Neuroimaging and Data Science (TReNDS)
- Deep Learning School
- Researchers at Emory University
- Evil Martians
- Researchers at the Georgia Institute of Technology
- Researchers at Georgia State University
- Helios
- HPCD Lab
- iFarm
- Kinoplan
- Researchers at the Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology
- Neuromation
- Poteha Labs
- Provectus
- Researchers at the Skolkovo Institute of Science and Technology
- SoftConstruct
- Researchers at Tinkoff
- Researchers at Yandex.Research
Citation
Please use this bibtex if you want to cite this repository in your publications:
@misc{catalyst,
author = {Kolesnikov, Sergey},
title = {Catalyst - Accelerated deep learning R&D},
year = {2018},
publisher = {GitHub},
journal = {GitHub repository},
howpublished = {\url{https://github.com/catalyst-team/catalyst}},
}