vkosuri / Courseramachinelearning
Programming Languages
Labels
Projects that are alternatives of or similar to Courseramachinelearning
Machine Learning By Prof. Andrew Ng 🌟🌟🌟🌟⭐️
This page continas all my coursera machine learning courses and resources 📖 by Prof. Andrew Ng 👨
Table of Contents
- Breif Intro
- Video lectures Index
- Programming Exercise Tutorials
- Programming Exercise Test Cases
- Useful Resources
- Schedule
- Extra Information
- Online E-Books
- Aditional Information
Breif Intro
The most of the course talking about hypothesis function and minimising cost funtions
Hypothesis
A hypothesis is a certain function that we believe (or hope) is similar to the true function, the target function that we want to model. In context of email spam classification, it would be the rule we came up with that allows us to separate spam from non-spam emails.
Cost Function
The cost function or Sum of Squeared Errors(SSE) is a measure of how far away our hypothesis is from the optimal hypothesis. The closer our hypothesis matches the training examples, the smaller the value of the cost function. Theoretically, we would like J(θ)=0
Gradient Descent
Gradient descent is an iterative minimization method. The gradient of the error function always shows in the direction of the steepest ascent of the error function. Thus, we can start with a random weight vector and subsequently follow the negative gradient (using a learning rate alpha)
Differnce between cost function and gradient descent functions
| Cost Function | Gradient Descent |
|---|---|
|
|
Bias and Variance
When we discuss prediction models, prediction errors can be decomposed into two main subcomponents we care about: error due to "bias" and error due to "variance". There is a tradeoff between a model's ability to minimize bias and variance. Understanding these two types of error can help us diagnose model results and avoid the mistake of over- or under-fitting.
Source: http://scott.fortmann-roe.com/docs/BiasVariance.html
Hypotheis and Cost Function Table
| Algorithem | Hypothesis Function | Cost Function | Gradient Descent |
|---|---|---|---|
| Linear Regression | 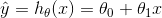 |
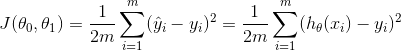 |
|
| Linear Regression with Multiple variables | 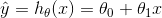 |
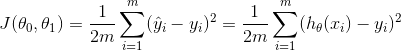 |
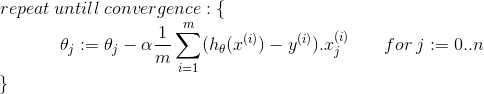 |
| Logistic Regression | 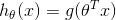 |
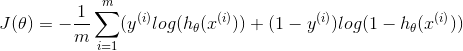 |
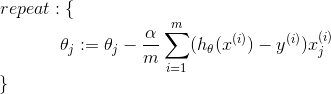 |
| Logistic Regression with Multiple Variable | 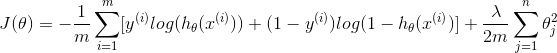 |
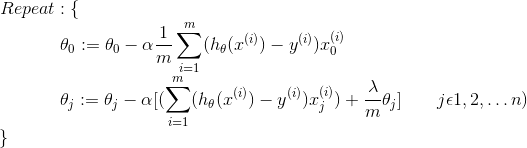 |
|
| Nural Networks | 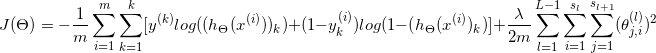 |
Regression with Pictures
Video lectures Index
https://class.coursera.org/ml/lecture/preview
Programming Exercise Tutorials
https://www.coursera.org/learn/machine-learning/discussions/all/threads/m0ZdvjSrEeWddiIAC9pDDA
Programming Exercise Test Cases
https://www.coursera.org/learn/machine-learning/discussions/all/threads/0SxufTSrEeWPACIACw4G5w
Useful Resources
https://www.coursera.org/learn/machine-learning/resources/NrY2G
Schedule:
Week 1 - Due 07/16/17:
- Welcome - pdf - ppt
- Linear regression with one variable - pdf - ppt
- Linear Algebra review (Optional) - pdf - ppt
- Lecture Notes
- Errata
Week 2 - Due 07/23/17:
- Linear regression with multiple variables - pdf - ppt
- Octave tutorial pdf
- Programming Exercise 1: Linear Regression - pdf - Problem - Solution
- Lecture Notes
- Errata
- Program Exercise Notes
Week 3 - Due 07/30/17:
- Logistic regression - pdf - ppt
- Regularization - pdf - ppt
- Programming Exercise 2: Logistic Regression - pdf - Problem - Solution
- Lecture Notes
- Errata
- Program Exercise Notes
Week 4 - Due 08/06/17:
- Neural Networks: Representation - pdf - ppt
- Programming Exercise 3: Multi-class Classification and Neural Networks - pdf - Problem - Solution
- Lecture Notes
- Errata
- Program Exercise Notes
Week 5 - Due 08/13/17:
- Neural Networks: Learning - pdf - ppt
- Programming Exercise 4: Neural Networks Learning - pdf - Problem - Solution
- Lecture Notes
- Errata
- Program Exercise Notes
Week 6 - Due 08/20/17:
- Advice for applying machine learning - pdf - ppt
- Machine learning system design - pdf - ppt
- Programming Exercise 5: Regularized Linear Regression and Bias v.s. Variance - pdf - Problem - Solution
- Lecture Notes
- Errata
- Program Exercise Notes
Week 7 - Due 08/27/17:
- Support vector machines - pdf - ppt
- Programming Exercise 6: Support Vector Machines - pdf - Problem - Solution
- Lecture Notes
- Errata
- Program Exercise Notes
Week 8 - Due 09/03/17:
- Clustering - pdf - ppt
- Dimensionality reduction - pdf - ppt
- Programming Exercise 7: K-means Clustering and Principal Component Analysis - pdf - Problems - Solution
- Lecture Notes
- Errata
- Program Exercise Notes
Week 9 - Due 09/10/17:
- Anomaly Detection - pdf - ppt
- Recommender Systems - pdf - ppt
- Programming Exercise 8: Anomaly Detection and Recommender Systems - pdf - Problems - Solution
- Lecture Notes
- Errata
- Program Exercise Notes
Week 10 - Due 09/17/17:
- Large scale machine learning - pdf - ppt
- Lecture Notes
Week 11 - Due 09/24/17:
Extra Information
- Linear Algebra Review and Reference Zico Kolter
- CS229 Lecture notes
- CS229 Problems
- Financial time series forecasting with machine learning techniques
- Octave Examples
Online E Books
- Introduction to Machine Learning by Nils J. Nilsson
- Introduction to Machine Learning by Alex Smola and S.V.N. Vishwanathan
- Introduction to Data Science by Jeffrey Stanton
- Bayesian Reasoning and Machine Learning by David Barber
- Understanding Machine Learning, © 2014 by Shai Shalev-Shwartz and Shai Ben-David
- Elements of Statistical Learning, by Hastie, Tibshirani, and Friedman
- Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning, by Christopher M. Bishop
Aditional Information
💥 Course Status 👇
Links
Statistics Models
- HMM - Hidden Markov Model
- CRFs - Conditional Random Fields
- LSI - Latent Semantic Indexing
- MRF - Markov Random Fields