TayfunCesur / Githubprojectbrowser
Programming Languages
Labels
Projects that are alternatives of or similar to Githubprojectbrowser
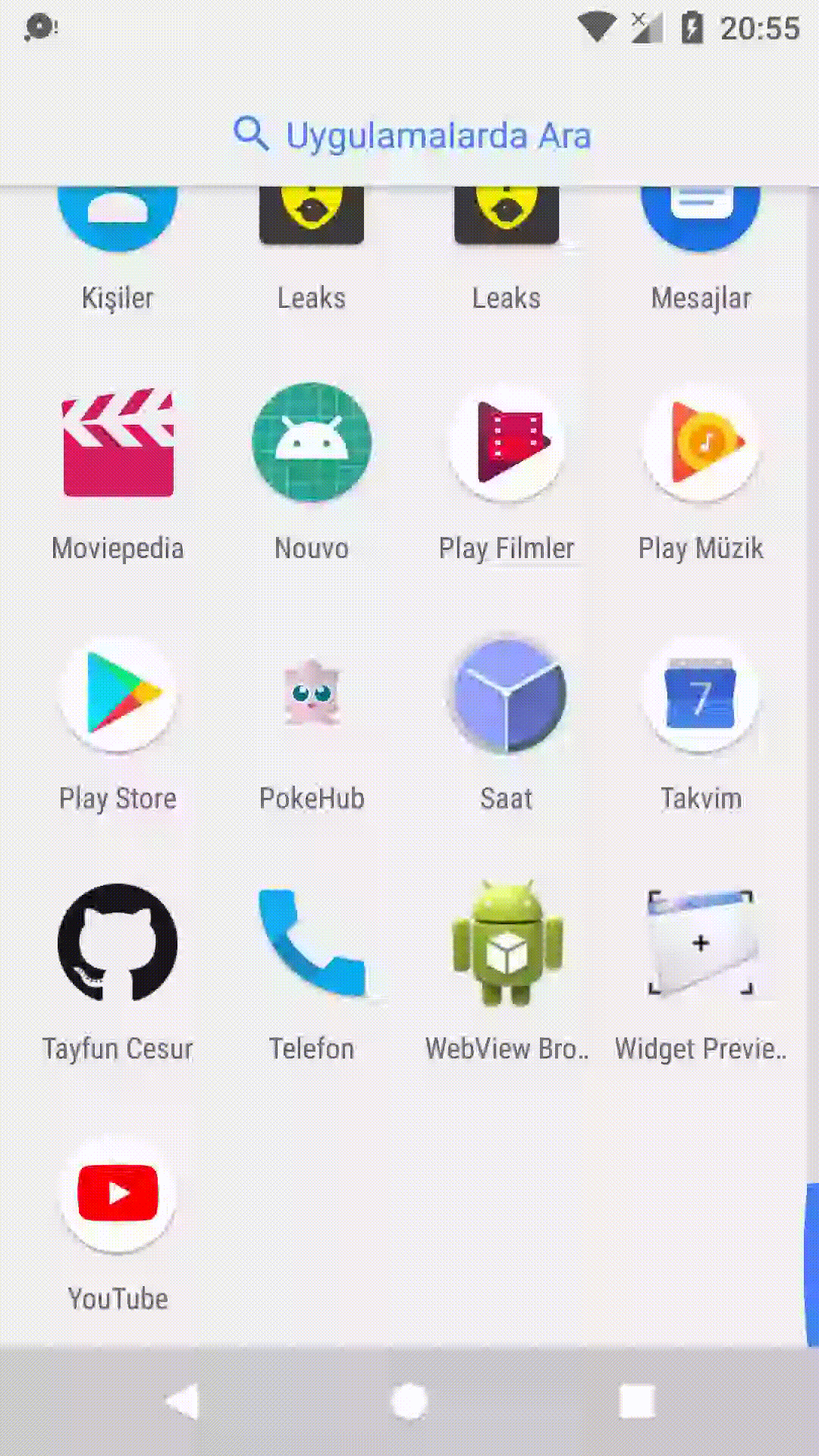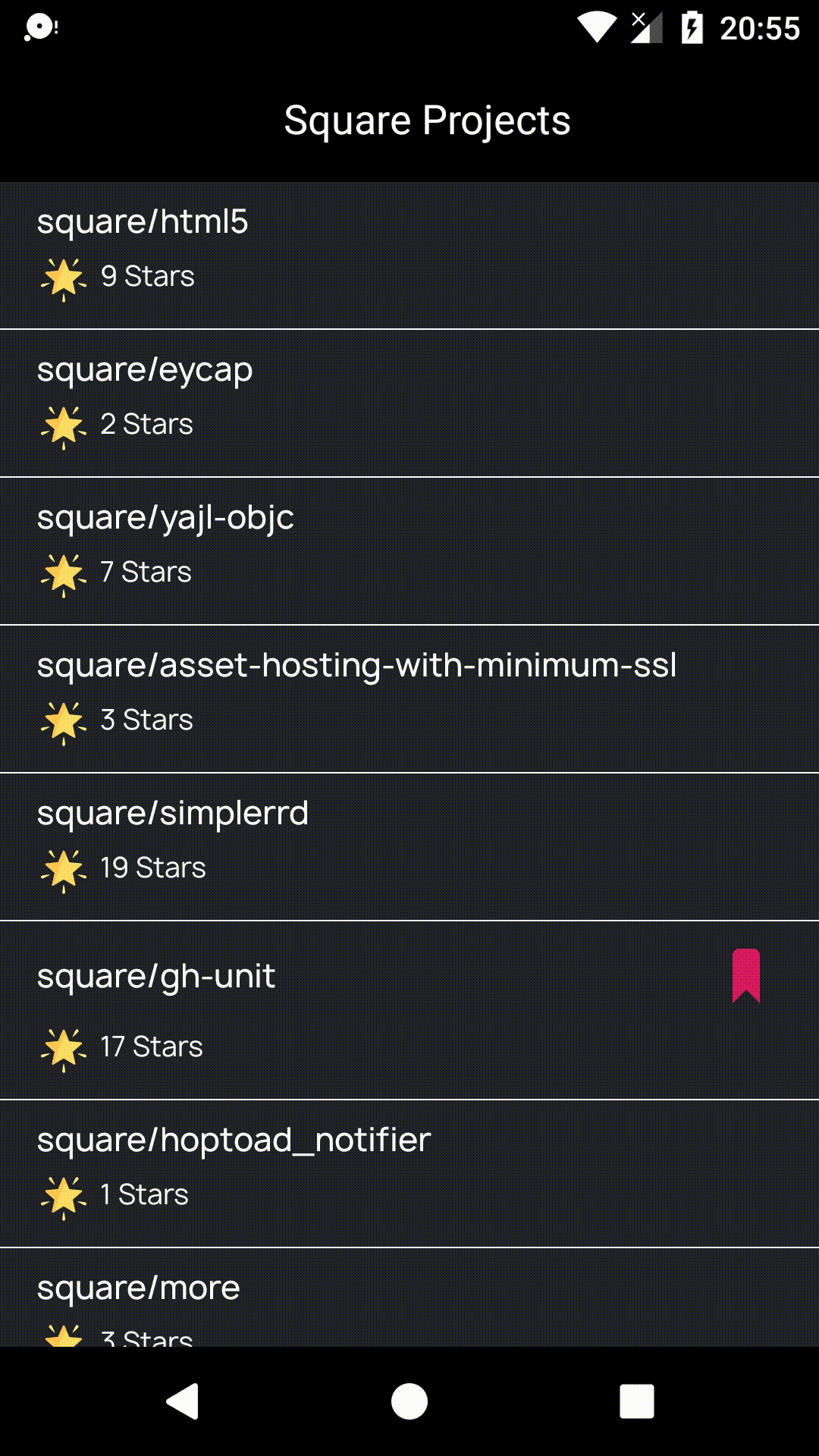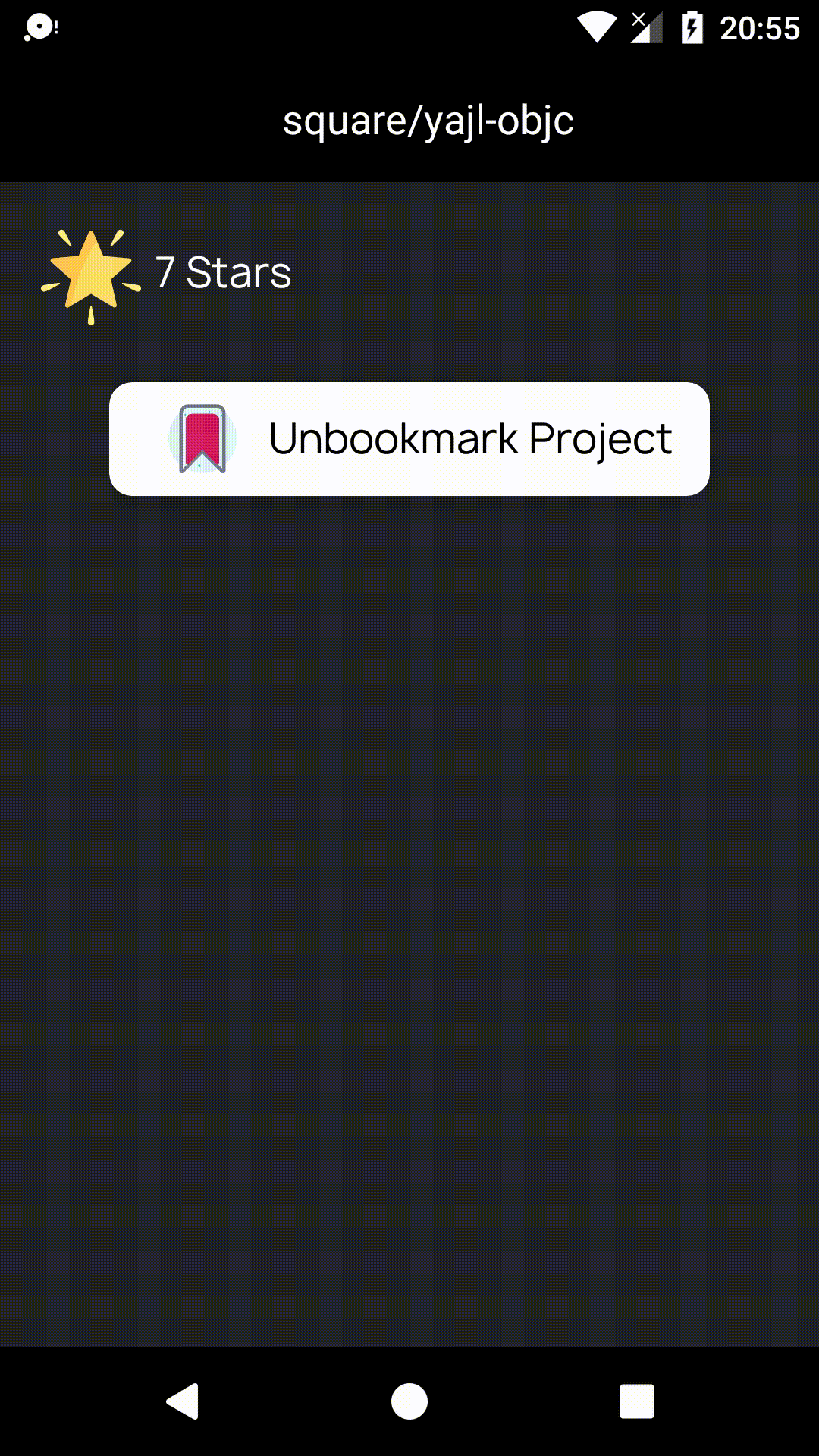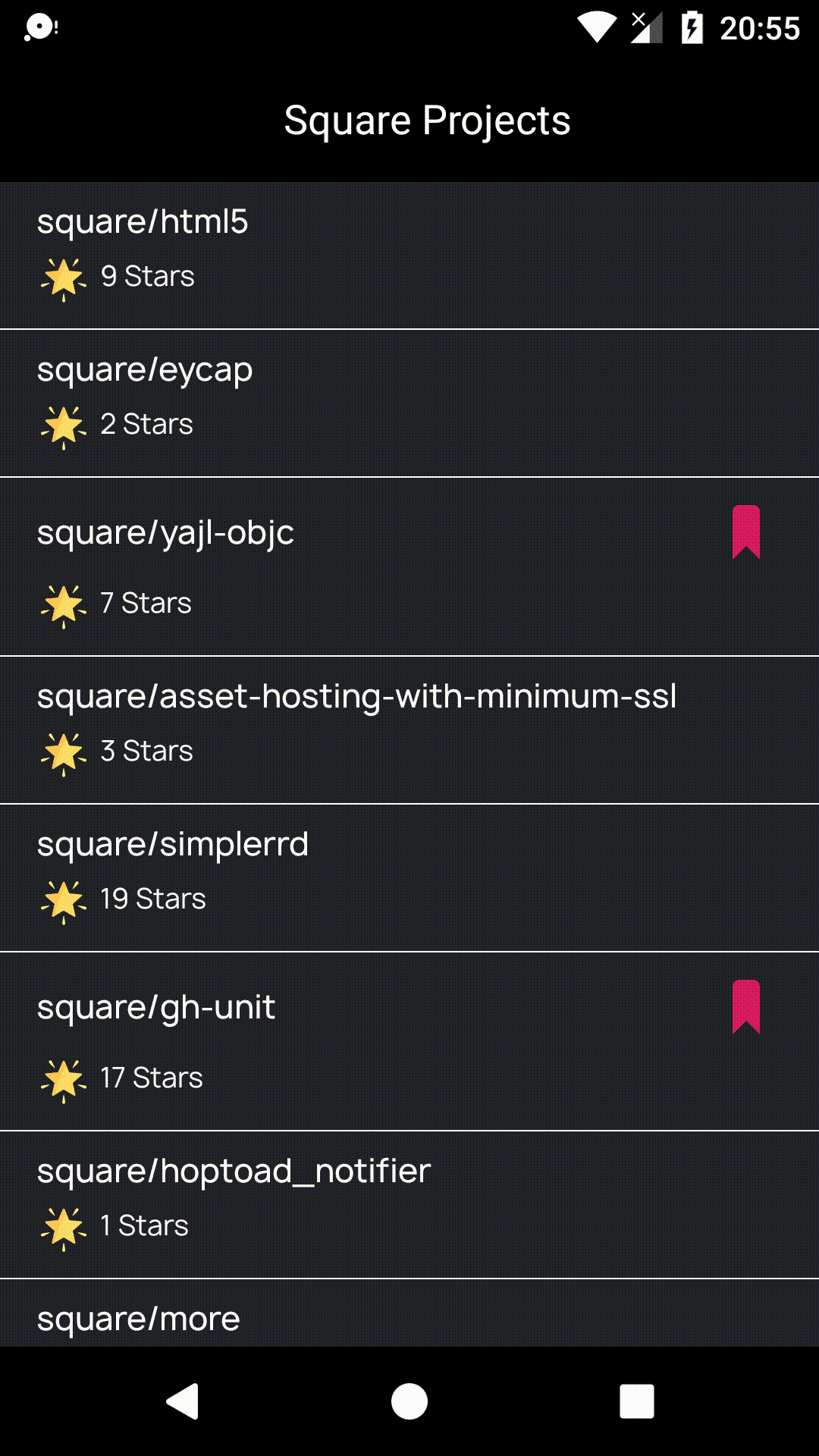
Github Project Browser
This is a sample Android Project that is based on Uncle Bob's Clean Architecture .It contains six different layers but the count of layers may change with respect to your project, you may have more or less layers. All of them have own mission but none of them interests with the others. That is the main idea actually. I will not explain the Clean Architecture because this is already well documented. I will just explain how I implemented. Here is the preview of project for just motivation before diving
Layers
When you do an action in your application, the flow will be like below respectively
- UI Layer is the layer that displays your data. You may use multi UI layer in your project. (For instance you have already an app that runs in phones and if you want to expand your targets for new platforms such as watches or TVs. There is no problem for you anymore.)
- Presentation Layer is the layer like a gateway between your UI and Business. You can use any design pattern in here(MVP,MVVM,MVI etc.) (MVVM is used in this project)
- Domain Layer, is the core layer that represents the use cases of project. You can think this layer as a middleman.
-
Data Layer, is the layer that determines where the data will come from.
It has two sublayers.
- Remote Layer is the layer that fetches the data from network. (Retrofit2 is used in this project)
- Cache Layer is the layer that is responsible for getting data from sqlite (Room is used in this project)
UI Layer
As I mentioned above, this is the layer that displays your data. It may use your presenters or your ViewModels. (ViewModels are used in this projects.) This layer works as usual way. I mean, observes your livedatas and displays the user.
Presentation
This is the layer that is the easiest one in my opinion. It's mission is so simple. It has ViewModels that are just executing your command like below.( For instance, getProjects)
fun getProjects() {
remoteProjectsLiveData.postValue(Resource.Loading())
getProjects.execute(ProjectsSubscriber())//Here, the flow navigates through the domain layer
}
The ViewModel's main functions are so simple like above.
Domain
This is the core layer. You should determine your projects use cases. For instance, in this project, I needed four use cases. These are, (in my ProjectsRepository interface)
- getProjects(): Observable<List>
- getBookmarkedProjects(): Observable<List>
- bookmarkProject(projectId: String): Completable
- unbookmarkProject(projectId: String)
But of course that depends on your projects needs. And you can imagine this interface like a bridge that navigates your flow to the data layer. So if you want to display projects, your class (GetProjects) calls the getProjects() function of the ProjectsRepository and then the flow navigates through the data layer because data layer implements your bridge.
Data
The core class of Data layer is ProjectsDataRepository class in this project because that class implements your use cases and takes care of them.
class ProjectsDataRepository @Inject constructor(
private val mapper: ProjectMapper,
private val dataStore: ProjectsDataStoreFactory
) : ProjectsRepository { // This is the interface that represents your use cases
// You defined it in the Domain Layer
override fun getProjects(): Observable<List<Project>> {
return dataStore.getRemoteDataStore().getProjects().map {
it.map {
mapper.mapFromEntity(it)
}
}
}
}
You can think this layer responsible for getting and serving data through the Domain layer but it doesn't care about where or how the data comes. It just a navigator that navigates your flow through the Remote or Cache. In this project, Data layer navigates the flow if getProjects() calls, because projects must be fetched from network, but if the other use cases are intended for example bookmarkProject or getBookmarkedProjects, these data must be fetched from local storage.So data layer navigates your flow though the cache layer.
Remote Layer
This layer is also easy layer because it has only one responsibility. It just making a network request via Retrofit2 It has only one class that is called by ProjectsRemoteImpl
Cache Layer
This layer is responsible for managing the local storage, getting and serving data through the Data Layer. It uses Room which is an awesome library. It just calls the DAO functions.
Keynotes & Bonuses
Mapper
This project have many mapper classes. This was my decision actually not a requirement but this is good way because for this, each layer can work with different model and anyone don't depends on some other model. I have mapper interface like below,(For example CacheMapper, because I can cache some additional data like creationDate etc which doesn't concerns the other layers.)
interface CacheMapper<I, O> { //Like I: Input, O:Output
fun mapFromCache(cache: I): O
fun mapToCache(dataToCache: O): I
}
Dependencies
Many of these layers above uses same dependencies like RX, JavaxAnnotation, or mockito for testing. So it would be really good to manage them all in one file. For this reason, this project uses the dependencies.gradle file and it applies in main build.gradle file
apply from: 'dependencies.gradle'
Bonus 1: Tests
This project contains all its units and UI tests and I strongly recommmend you to have a look cache layer unit tests because there are Room and local storage tests.
Bonus 2: ReactiveNetwork
You can learn the implementation of the ReactiveNetwork and how to broadcast the network connection with Rx from this project. It is really useful because there is a behaviour changes between API levels.
Core Libraries
Summary
To use Clean Architecture or not, this is not requirement actually this is up to you and your project. But if you want to seperate your concerns for example testing, maintaining. I found it really useful.
Thanks
This project is based on Joe Birch's Github Trending If you have any questions, hit me on Twitter
Licence
Copyright 2019 Tayfun CESUR
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
limitations under the License.