ropensci / Osmplotr
Programming Languages
Projects that are alternatives of or similar to Osmplotr
R package to produce visually impressive customisable images of
OpenStreetMap (OSM) data downloaded internally from the overpass
api. The above map was produced directly from
osmplotr with no further modification. This README briefly
demonstrates the following functionality:
4. Highlighting Selected Areas
6. Highlighting Areas Bounded by Named Highways
1. Quick Introduction
But first the easy steps to map making:
-
Specify the bounding box for the desired region
bbox <- get_bbox (c(-0.15, 51.5, -0.10, 51.52))
-
Download the desired data—in this case, all building perimeters.
dat_B <- extract_osm_objects (key = 'building', bbox = bbox)
-
Initiate an
osm_basemapwith desired background (bg) colourmap <- osm_basemap (bbox = bbox, bg = 'gray20')
-
Overlay objects on plot in the desired colour.
map <- add_osm_objects (map, dat_B, col = 'gray40')
-
Print the map to graphics device of choice
print_osm_map (map)
2. Installation
First install the package
install.packages ('osmplotr')
or the development version
devtools::install_github ('ropensci/osmplotr')
And then load it in the usual way
library (osmplotr)
3. A Simple Map
Simple maps can be made by overlaying different kinds of OSM data in different colours:
dat_H <- extract_osm_objects (key = 'highway', bbox = bbox)
dat_P <- extract_osm_objects (key = 'park', bbox = bbox)
dat_G <- extract_osm_objects (key = 'landuse', value = 'grass', bbox = bbox)
map <- osm_basemap (bbox = bbox, bg = 'gray20')
map <- add_osm_objects (map, dat_B, col = 'gray40')
map <- add_osm_objects (map, dat_H, col = 'gray80')
map <- add_osm_objects (map, dat_P, col = 'darkseagreen')
map <- add_osm_objects (map, dat_G, col = 'darkseagreen1')
print_osm_map (map)
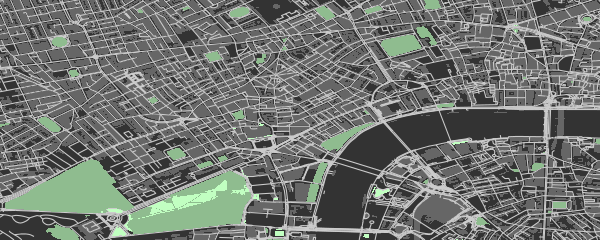
4. Highlighting Selected Areas
osmplotr is primarily intended as a data visualisation tool,
particularly through enabling selected regions to be highlighted.
Regions can be defined according to simple point boundaries:
pts <- sp::SpatialPoints (cbind (c (-0.115, -0.13, -0.13, -0.115),
c (51.505, 51.505, 51.515, 51.515)))
OSM objects within the defined regions can then be highlighted with
different colour schemes. cols defines colours for each group (with
only one here), while bg defines the colour of the remaining,
background area.
map <- osm_basemap (bbox = bbox, bg = 'gray20')
map <- add_osm_groups (map, dat_B, groups = pts, cols = 'orange', bg = 'gray40')
map <- add_osm_objects (map, london$dat_P, col = 'darkseagreen1')
map <- add_osm_groups (map, london$dat_P, groups = pts, cols = 'darkseagreen1',
bg = 'darkseagreen', boundary = 0)
print_osm_map (map)
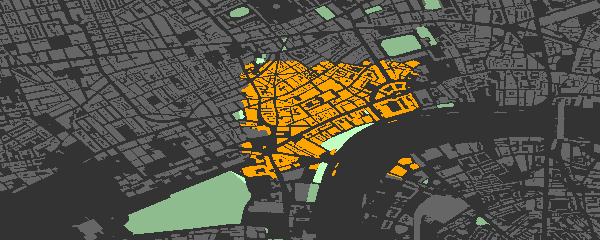
Note the border = 0 argument on the last call divides the park
polygons precisely along the border. The same map highlighted in
dark-on-light:
map <- osm_basemap (bbox = bbox, bg = 'gray95')
map <- add_osm_groups (map, dat_B, groups = pts, cols = 'gray40', bg = 'gray85')
map <- add_osm_groups (map, dat_H, groups = pts, cols = 'gray20', bg = 'gray70')
print_osm_map (map)
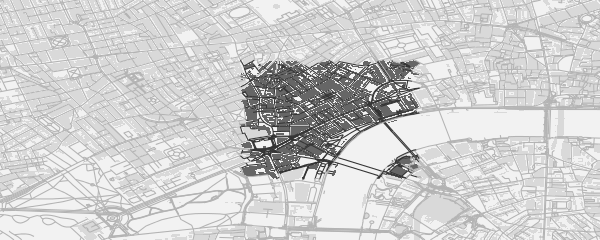
5. Highlighting Clusters
add_osm_groups also enables plotting an entire region as a group of
spatially distinct clusters of defined colours. Groups can be defined by
simple spatial points denoting their centres:
set.seed (2)
ngroups <- 12
x <- bbox [1, 1] + runif (ngroups) * diff (bbox [1, ])
y <- bbox [2, 1] + runif (ngroups) * diff (bbox [2, ])
groups <- cbind (x, y)
groups <- apply (groups, 1, function (i)
sp::SpatialPoints (matrix (i, nrow = 1, ncol = 2)))
Calling add_osm_groups with no bg argument forces all points lying
outside those defined groups to be allocated to the nearest groups, and
thus produces an inclusive grouping extending across an entire region.
map <- osm_basemap (bbox = bbox, bg = 'gray20')
map <- add_osm_groups (map, dat_B, groups = groups,
cols = rainbow (length (groups)), border_width = 2)
print_osm_map (map)
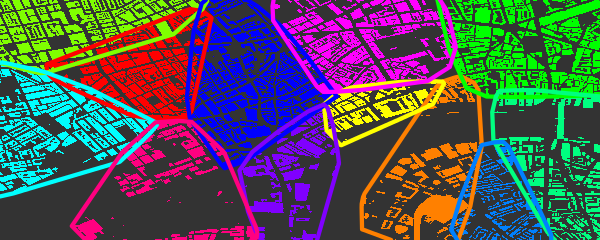
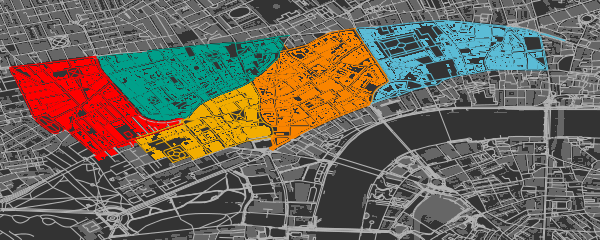
6. Highlighting Areas Bounded by Named Highways
An alternative way of defining highlighted groups is by naming the highways encircling desired regions.
# These highways extend beyond the previous, smaller bbox
bbox_big <- get_bbox (c(-0.15, 51.5, -0.10, 51.52))
highways <- c ('Davies.St', 'Berkeley.Sq', 'Berkeley.St', 'Piccadilly',
'Regent.St', 'Oxford.St')
highways1 <- connect_highways (highways = highways, bbox = bbox_big)
highways <- c ('Regent.St', 'Oxford.St', 'Shaftesbury')
highways2 <- connect_highways (highways = highways, bbox = bbox_big)
highways <- c ('Piccadilly', 'Shaftesbury.Ave', 'Charing.Cross.R',
'Saint.Martin', 'Trafalgar.Sq', 'Cockspur.St',
'Pall.Mall', 'St.James')
highways3 <- connect_highways (highways = highways, bbox = bbox_big)
highways <- c ('Charing.Cross', 'Duncannon.St', 'Strand', 'Aldwych',
'Kingsway', 'High.Holborn', 'Shaftesbury.Ave')
highways4 <- connect_highways (highways = highways, bbox = bbox_big)
highways <- c ('Kingsway', 'Holborn', 'Farringdon.St', 'Strand',
'Fleet.St', 'Aldwych')
highways5 <- connect_highways (highways = highways, bbox = bbox_big)
groups <- list (highways1, highways2, highways3, highways4, highways5)
And then passing these lists of groups returned by connect_highways to
add_osm_groups, this time with some Wes Anderson flair.
map <- osm_basemap (bbox = bbox, bg = 'gray20')
library (wesanderson)
cols <- wes_palette ('Darjeeling', 5)
map <- add_osm_groups (map, dat_B, groups = groups, boundary = 1,
cols = cols, bg = 'gray40', colmat = FALSE)
map <- add_osm_groups (map, dat_H, groups = groups, boundary = 0,
cols = cols, bg = 'gray70', colmat = FALSE)
print_osm_map (map)
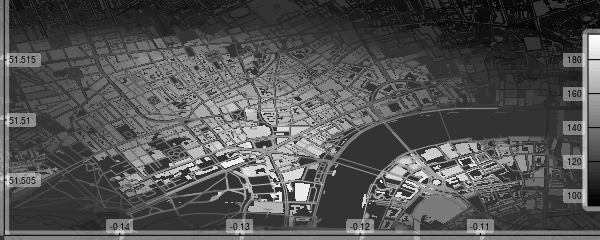
7. Data Surfaces
Finally, osmplotr contains a function add_osm_surface that spatially
interpolates a given set of spatial data points and colours OSM objects
according to a specified colour gradient. This is illustrated here with
the volcano data projected onto the bbox.
x <- seq (bbox [1, 1], bbox [1, 2], length.out = dim (volcano)[1])
y <- seq (bbox [2, 1], bbox [2, 2], length.out = dim (volcano)[2])
xy <- cbind (rep (x, dim (volcano) [2]), rep (y, each = dim (volcano) [1]))
z <- as.numeric (volcano)
dat <- data.frame (x = xy [, 1], y = xy [, 2], z = z)
map <- osm_basemap (bbox = bbox, bg = 'gray20')
cols <- gray (0:50 / 50)
map <- add_osm_surface (map, dat_B, dat = dat, cols = cols)
# Darken cols by ~20%
map <- add_osm_surface (map, dat_H, dat = dat,
cols = adjust_colours (cols, -0.2))
map <- add_colourbar (map, cols = cols, zlims = range (volcano))
map <- add_axes (map)
print_osm_map (map)
8. Gallery
Got a nice osmplotr map? Please contribute in one of the following
ways:
-
Fork repo, add link to
README.md/.Rmd, and send pull request; or -
Open issue with details; or
-
Send email to address in
DESCRIPTION.
See package vignettes (basic
maps and
data
maps) for
a lot more detail and further capabilities of osmplotr. Please note
that this project is released with a Contributor Code of
Conduct. By participating in this project you agree
to abide by its terms.


