imatge-upc / Retrieval 2017 Cam
Programming Languages
Labels
Projects that are alternatives of or similar to Retrieval 2017 Cam
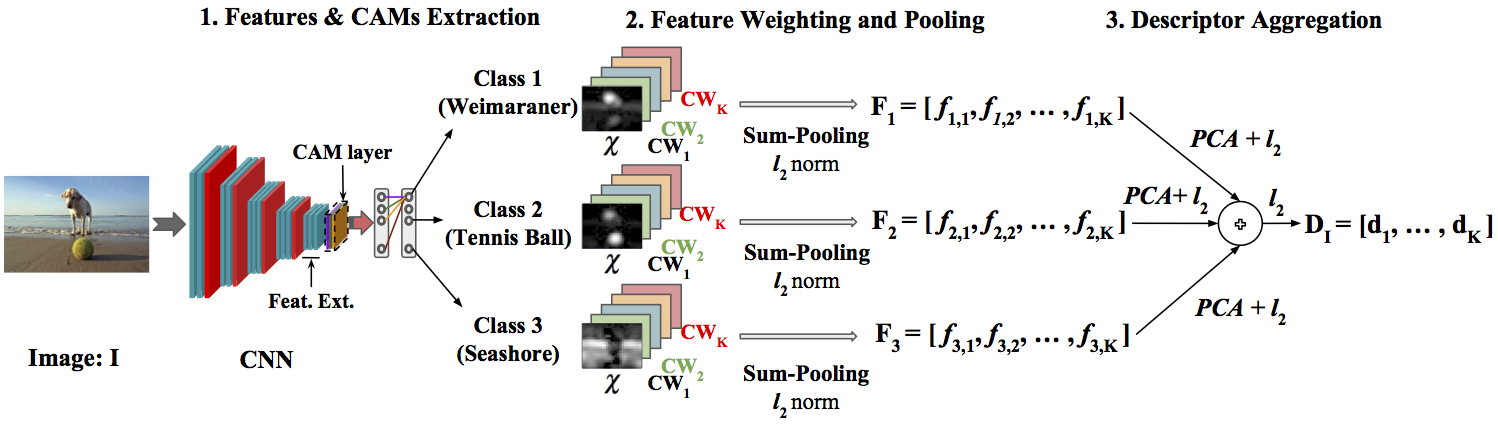
Class-Weighted Convolutional Features for Image Retrieval
28th British Machine Vision Conference (BMVC 2017)
 |
 |
 |
|---|---|---|
| Albert Jimenez | Xavier Giro-i-Nieto | Jose M.Alvarez |
A joint collaboration between:
 |
 |
|---|---|
| UPC Image Processing Group | Data61 |
Abstract
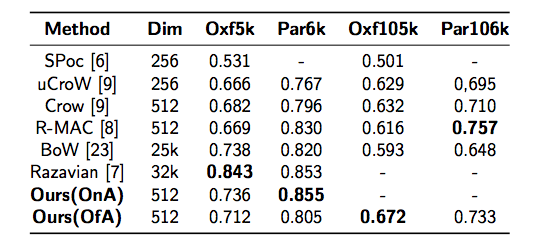
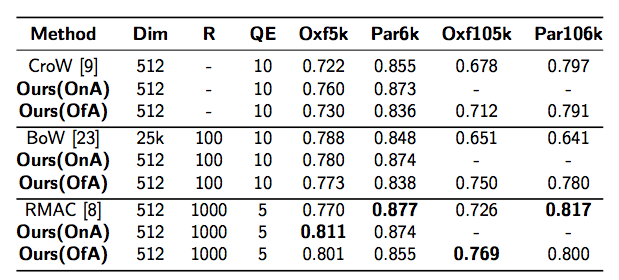
Image retrieval in realistic scenarios targets large dynamic datasets of unlabeled images. In these cases, training or fine-tuning a model every time new images are added to the database is neither efficient nor scalable. Convolutional neural networks trained for image classification over large datasets have been proven effective feature extractors for image retrieval. The most successful approaches are based on encoding the activations of convolutional layers, as they convey the image spatial information. In this paper, we go beyond this spatial information and propose a local-aware encoding of convolutional features based on semantic information predicted in the target image. To this end, we obtain the most discriminative regions of an image using Class Activation Maps (CAMs). CAMs are based on the knowledge contained in the network and therefore, our approach, has the additional advantage of not requiring external information. In addition, we use CAMs to generate object proposals during an unsupervised re-ranking stage after a first fast search. Our experiments on two public available datasets for instance retrieval, Oxford5k and Paris6k, demonstrate the competitiveness of our approach outperforming the current state-of-the-art when using off-the-shelf models trained on ImageNet.
Publication
A preprint of this paper is available on arXiv and in the BMVC 2017 proceedings.
Please cite with the following Bibtex code:
@InProceedings{Jimenez_2017_BMVC,
author = {Jimenez, Albert and Alvarez, Jose M., and Giro-i-Nieto, Xavier},
title = {Class-Weighted Convolutional Features for Visual Instance Search},
booktitle = {28th British Machine Vision Conference (BMVC)},
month = {September},
year = {2017}
}
You may also want to refer to our publication with the more human-friendly Chicago style:
Albert Jimenez, Jose M. Alvarez, and Xavier Giro-i-Nieto. "Class-Weighted Convolutional Features for Visual Instance Search." In Proceedings of the 28th British Machine Vision Conference (BMVC). 2017.
Slides
<iframe src="//www.slideshare.net/slideshow/embed_code/key/3dG0uuBHScqPTa" width="595" height="485" frameborder="0" marginwidth="0" marginheight="0" scrolling="no" style="border:1px solid #CCC; border-width:1px; margin-bottom:5px; max-width: 100%;" allowfullscreen> </iframe>Results
Comparison with State of the Art
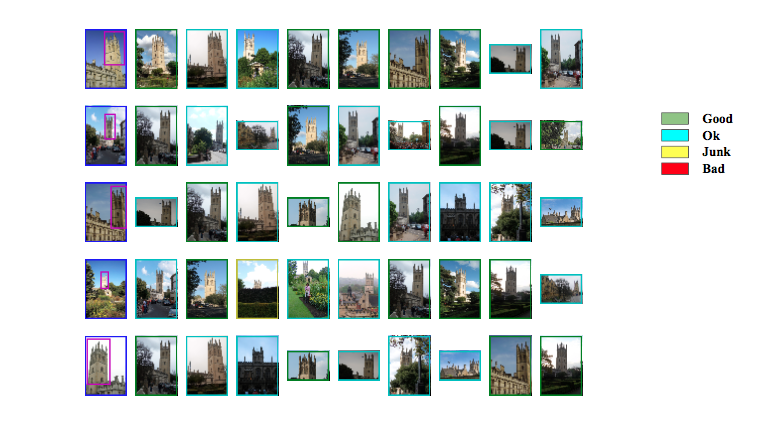
Qualitative Results
Code Usage
In this repository we provide the code used in our experiments. VGG-16 CAM experiments where carried out using Keras running over Theano. DenseNet and ResNet experiments were carried out using PyTorch.
In the next Section we explain how to run the code in Keras+Theano. To run the experiments using PyTorch, the requirements are the same plus having installed Pytorch and the torchvision package.
Prerequisites
Was done previous to Keras 2.0 but should work with that version as well.
Python packages necessary specified in requirements.txt run:
pip install -r requirements.txt
Our Experiments have been carried out in these datasets:
-
Oxford Buildings (and Oxford 105k).
-
Paris Buildings (and Paris 106k).
Here we provide the weigths of the model (paste them in models folder):
How to run the code?
First thing to do (important!) is setting the path of your images and model weights. We provide lists (also modify path! - Find and Replace) that divide images in vertical and horizontal for faster processing. At the beggining of each script there are some parameters that can be tuned like image preprocessing. I have added a parser for arguments, at the beginning of each script it is shown an example of how to run them.
Feature Extraction
Both scripts extract Class-Weighted Vectors. The first one is used for the original datasets. The second for the distractors. You tune the preprocessing parameters of the images as well as the number of Class-Weighted Vectors extracted. In "Online Aggregation" the order of the stored vectors is the imagenet class order, while in "Offline Aggregation" the order of the vector is from class more probable to less probable (predicted by the network).
- A_Oxf_Par_Feat_CAMs_Extraction.py
- A_Dist_Feat_CAMs_Extraction.py
A_Oxf_Par_Feat_CAMs_Extraction.py -d <dataset> -a <agreggation>
Aggregation, Ranking and Evaluation
In both scripts you can choose the dataset you want to evaluate and if use query expansion or re-ranking. The first one is for offline aggregation. The second one performs aggregation at the moment of testing.
- B_Offline_Eval.py
- B_Online_Aggregation_Eval.py
B_Online_Aggregation_Eval.py -d <dataset> --nc_q <nclasses_query> --pca <n_classes_pca> --qe <n_query_exp> --re <n_re_ranking> --nc_re <n_classes_re_ranking>
Aknowledgements
We would like to specially thank Albert Gil and Josep Pujal from our technical support team at the Image Processing Group at UPC.
 |
 |
|---|---|
| Albert Gil | Josep Pujal |
Contact
If you have any general doubt about our work or code which may be of interest for other researchers, please use the mailto:[email protected].