fajieyuan / Sigir2020_peterrec
Programming Languages
Projects that are alternatives of or similar to Sigir2020 peterrec
SIGIR2020_PeterRec
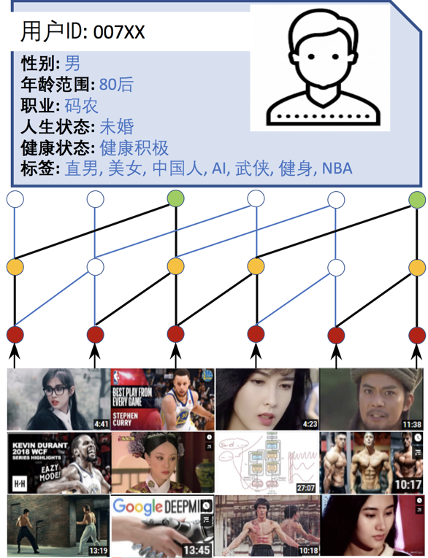
Parameter-Efficient Transfer from Sequential Behaviors for User Modeling and Recommendation
Chinese Introduction:
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/139048117
https://blog.csdn.net/abcdefg90876/article/details/109505669
Please cite our paper if you use our code or datasets in your publication.
@article{yuan2020parameter,
title={Parameter-Efficient Transfer from Sequential Behaviors for User Modeling and Recommendation},
author={Yuan, Fajie and He, Xiangnan and Karatzoglou, Alexandros and Zhang, Liguang},
journal={Proceedings of the 42nd international ACM SIGIR conference on Research and development in Information Retrieval},
year={2020}
}
If you want to use PeterRec in real production system. I strongly suggest: (1) understand our code released here ; (2)using TFRecord (tf.data.Dataset) and tf.estimator to replace feed_dict (slow), which is around 7~10 times faster; (3) contact [email protected] if you could not achieve expected results. (E.g., No personalization for new user recommendation, 99% there are bugs in your project!!)
PeterRec_cau_parallel.py: PeterRec with causal cnn and parallel insertion
PeterRec_cau_serial.py: PeterRec with causal cnn and serial insertion
PeterRec_cau_serial_lambdafm.py: PeterRec_cau_serial.py with lambdafm-based negative sampler and evaluate all items rather than sampling 100 items for evaluation.
PeterRec_noncau_parallel.py: PeterRec with noncausal cnn and parallel insertion
PeterRec_noncau_serial.py: PeterRec with causal cnn and serial insertion
NextitNet_TF_Pretrain.py: Petrained by NextItNet [0] (i.e., causal cnn)
GRec_TF_Pretrain.py: Petrained by the encoder of GRec [1] (i.e., noncausal cnn)
Demo Steps:
You can directly run our code:
First: python NextitNet_TF_Pretrain_topk.py (NextitNet_TF_Pretrain.py is slower than NextitNet_TF_Pretrain_topk.py due to the output of full softmax in the evaluation stage.)
After convergence (you can stop it once the pretrained model is saved!)
Second: python PeterRec_cau_serial.py (or PeterRec_cau_serial_lambdafm.py)
Note that you are ABLE to use two types of evaluation methods, sampled top-N as in our paper (i.e., PeterRec_cau_serial.py) or evaluating all items (i.e., PeterRec_cau_serial_lambdafm.py). Be careful, if you use PeterRec_cau_serial_lambdafm.py, which means you are optimizing top-N metrics, then you have to evaluate prediction accuracy among all items (as shown in this file), rather than sampled metrics --- since sampled metrics are more consistent with AUC rather than true top-N. But if you use BPR or CE loss with a random negative sampler, you should use sampled metrics since the two loss with the random sampler directly optimizes AUC, rather than top-N metrics. I refer you to a recent papaer "On Sampled Metrics for Item Recommendation" for more details. In short, sampled metrics = AUC, rather than true top-N. BPR optimizes AUC, while lambdafm optimizes true top-N metrics (e.g., [email protected], [email protected]). If you use the correct evaluation methods, all insights and conclusions in our paper hold well.
or
First: python GRec_TF_Pretrain_topk.py Second: python PeterRec_noncau_parallel.py
Running our paper:
Replacing the demo dataset with our public datasets (including both pretraining and finetuning):
You will reproduce the results reported in our paper using our papar settings, including learning rate, embedding size, dilations, batch size, etc. Note that the results reported in the paper are based on the same hyper-parameter settings for fair comparison and ablation tests. You may further finetune hyper-parameters to obtatin the best performance. For example, we use 0.001 as learning rate during finetuning, you may find 0.0001 performs better although all insights in the paper keep consistent. In addition, there are some other improvement places, such as the negative sampling used for funetuning. For simplicity, we implement a very basic one by uniformly sampling, you can use more advanced sampler such as LambdaFM (LambdaFM: Learning Optimal Ranking with Factorization Machines Using Lambda Surrogates), i.e., PeterRec_cau_serial_lambdafm.py. Similarly, our pretraining network (e.g., NextitNet_TF_Pretrain.py) also employs a basic sampling function in TF, you can also replace it with your own one if you are dealing with hundreds of millions of items in a very large-scale system.
DataSet (desensitized)Links
ColdRec2: https://drive.google.com/open?id=1OcvbBJN0jlPTEjE0lvcDfXRkzOjepMXH
ColdRec1: https://drive.google.com/open?id=1N7pMXLh8LkSYDX30-zId1pEMeNDmA7t6
Note that we have provided the original dataset used in the paper and several preprocessed datasets for an easy try. That is, for simplicity, we provide a source dataset along with a target dataset for each task, while in practice it is suggested to use one source dataset pretrained to serve all target tasks (make sure your source dataset covers all ID indices in the target task).
In fact, the ColdRec2 datasets has both clicking and liking actions, we have provided the following dataset, which can be used for future research by separating clicking and liking data.
DataSet (desensitized)Links
ColdRec2 (clicking and liking data is separated): https://drive.google.com/file/d/1imhHUsivh6oMEtEW-RwVc4OsDqn-xOaP/view?usp=sharing
recommendation settings (Be careful!)
it will be much slower if 'eval_iter' is smaller as it represents how often you perform evaluation. It may takes only 1 or 2 iterations to converge.
NextitNet_TF_Pretrain_topk.py
parser.add_argument('--eval_iter', type=int, default=10000,
help='Sample generator output evry x steps')
parser.add_argument('--save_para_every', type=int, default=10000,
help='save model parameters every')
parser.add_argument('--datapath', type=str, default='Data/Session/coldrec2_pre.csv',
help='data path')
model_para = {
'item_size': len(items),
'dilated_channels': 64, # in the paper we use 256, 64 is okay for our dataset
'dilations': [1,4,1,4,1,4,1,4,], # note 1 4 means 1 2 4 8
'kernel_size': 3,
'learning_rate':0.001,
'batch_size':32,# you can try 32, 64, 128, 256, etc.
'iterations':5, #you can just stop pretraining if performance does not change in the testing set. It may not need 5 iterations
'is_negsample':True #False denotes no negative sampling
}
PeterRec settings (E.g.,PeterRec_cau_serial.py/PeterRec_cau_serial_lambdafm):
parser.add_argument('--eval_iter', type=int, default=500,
help='Sample generator output evry x steps')
parser.add_argument('--save_para_every', type=int, default=500,
help='save model parameters every')
parser.add_argument('--datapath', type=str, default='Data/Session/coldrec2_fine.csv',
help='data path')
model_para = {
'item_size': len(items),
'target_item_size': len(targets),
'dilated_channels': 64,
'cardinality': 1, # 1 is ResNet, otherwise is ResNeXt (performs similarly, but slowly)
'dilations': [1,4,1,4,1,4,1,4,],
'kernel_size': 3,
'learning_rate':0.0001,
'batch_size':512, #you can not use batch_size=1 since in the following you use np.squeeze will reuduce one dimension
'iterations': 20, # note this is not the default setup, you should set it according to your own dataset by watching the performance in your testing set.
'has_positionalembedding': args.has_positionalembedding
}
Environments
- Tensorflow (version: 1.7.0)
- python 2.7
Related work:
[1]
@inproceedings{yuan2019simple,
title={A simple convolutional generative network for next item recommendation},
author={Yuan, Fajie and Karatzoglou, Alexandros and Arapakis, Ioannis and Jose, Joemon M and He, Xiangnan},
booktitle={Proceedings of the Twelfth ACM International Conference on Web Search and Data Mining},
pages={582--590},
year={2019}
}
[2]
@inproceedings{yuan2020future,
title={Future Data Helps Training: Modeling Future Contexts for Session-based Recommendation},
author={Yuan, Fajie and He, Xiangnan and Jiang, Haochuan and Guo, Guibing and Xiong, Jian and Xu, Zhezhao and Xiong, Yilin},
booktitle={Proceedings of The Web Conference 2020},
pages={303--313},
year={2020}
}
[3]
@article{sun2020generic,
title={A Generic Network Compression Framework for Sequential Recommender Systems},
author={Sun, Yang and Yuan, Fajie and Yang, Ming and Wei, Guoao and Zhao, Zhou and Liu, Duo},
journal={Proceedings of the Twelfth ACM International Conference on Web Search and Data Mining},
year={2020}
}
[4]
@article{yuan2020one,
title={One Person, One Model, One World: Learning Continual User Representation without Forgetting},
author={Yuan, Fajie and Zhang, Guoxiao and Karatzoglou, Alexandros and He, Xiangnan and Jose, Joemon and Kong, Beibei and Li, Yudong},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2009.13724},
year={2020}
}