stojanovic / Alexa Skill Kit
Programming Languages
Projects that are alternatives of or similar to Alexa Skill Kit
Alexa Skill Kit
Library for effortless Alexa Skill development with AWS Lambda.
| 🚀 Installation | 🤔 How it works | 🤖 Usage | 📕 API reference | 🤘 How to contribute | ⚖️ License |
|---|
Installation
Alexa Skill Kit is available as a Node.js module on NPM. To install it, run the following command in an existing Node.js project:
npm install alexa-skill-kit --save
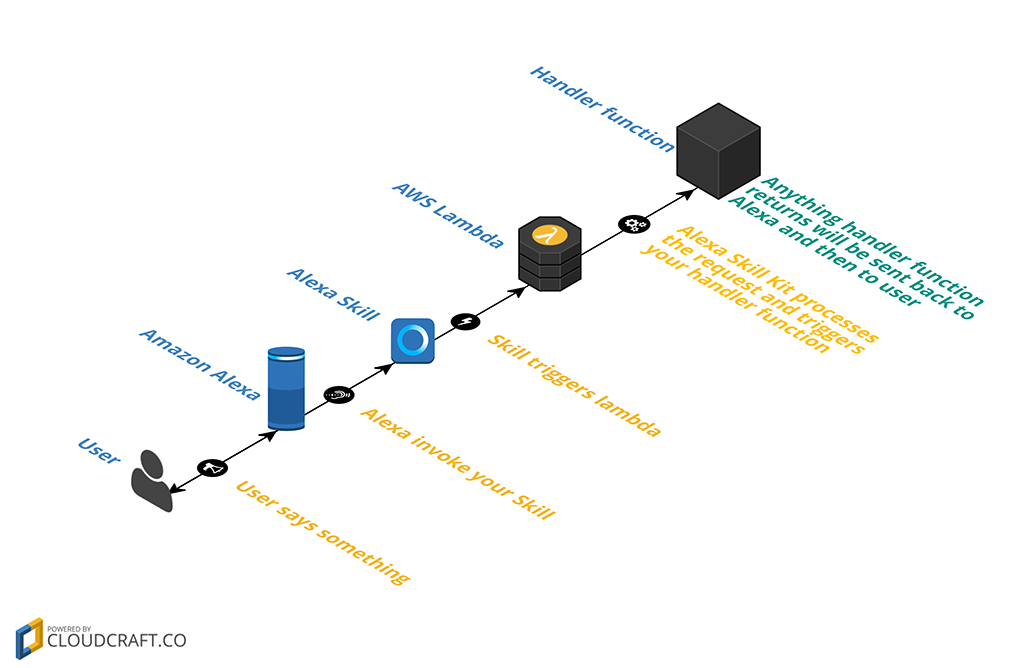
How it works
Usage
Alexa Skill Kit is a library that simplifies the development of Alexa Skills with Node.js and AWS Lambda. It doesn't require any specific deploy style, it can work with manually created Lambda functions, deployment via Claudia.js, etc.
Since I recommend Claudia.js because of it's simplicity all the following examples will use it. You can get it from NPM here: npmjs.com/package/claudia.
After installing the Alexa Skill Kit from NPM, require it in your code:
const alexaSkillKit = require('alexa-skill-kit')
or with import* syntax:
import alexaSkillKit from 'alexa-skill-kit'
* import syntax is not supported in Node.js, you need to use additional library like Babel to make it work.
After requiring it, you simply need to pass event and context from Lambda function, beside event and function, you need to pass a handler function as the last param.
For Example:
const alexaSkillKit = require('alexa-skill-kit')
exports.handler = function(event, context) {
alexaSkillKit(event, context, parsedMessage => {
// Do something
})
}
How to reply
Alexa Skill Kit simplifies replying to Alexa requests. There's a few things you can do:
| 📝 Replying with a simple text | 🛠 Replying with an object | 💄 More complex replies | ⏳ Async replies | | ----- | ----- | ----- | ----- | ----- |
Keep on reading and all of them will be explained bellow.
Replying with a simple text
If you want Alexa to reply with a simple text you simply need to return the text in a handler function. Alexa Skill Kit will wrap the text in a valid object.
For example:
const alexaSkillKit = require('alexa-skill-kit')
exports.handler = function(event, context) {
alexaSkillKit(event, context, parsedMessage => {
return 'Hello'
})
}
An example above will reply to Alexa with the following object:
{
"version": "1.0",
"response": {
"shouldEndSession": true,
"outputSpeech": {
"type": "PlainText",
"text": "Hello"
}
}
}
As you can see, session will be closed by default. To keep the session opened or to answer with more complex request you can send an object instead of the text.
Replying with an object
If you want to keep the session opened or you want to return something more than a simple output speech you can send an object and Alexa Skill Kit will not modify it.
For example:
const alexaSkillKit = require('alexa-skill-kit')
exports.handler = function(event, context) {
alexaSkillKit(event, context, parsedMessage => {
return {
version: '1.0',
response: {
shouldEndSession: false,
outputSpeech: {
type: 'PlainText',
text: 'Hello'
},
card: {
type: 'Simple',
title: 'Simple Card',
content: 'An example for a simple card reply'
}
}
}
})
}
More complex replies
Building objects manually is hard and boring. I recommend using Alexa Message Builder module to simplify building more complex replies.
Alexa Message Builder is available on NPM, and you can add it to your project with following command:
npm install alexa-message-builder --save
After that simply require it with Alexa Skill Kit like this:
const alexaSkillKit = require('alexa-skill-kit')
const AlexaMessageBuilder = require('alexa-message-builder')
exports.handler = function(event, context) {
alexaSkillKit(event, context, parsedMessage => {
return new AlexaMessageBuilder()
.addText('Hello')
.addSimpleCard('Simple Card', 'An example for a simple card reply')
.keepSession()
.get()
})
}
An example above is the same as the example from "Replying with an object" section.
Why Alexa Message Builder is not the part of Alexa Skill Kit?
Well, without a real reason, Alexa Message Builder was developed before Alexa Skill Kit, and they are separate modules in case anyone needs just one of them without the other.
Async replies
Alexa Skill Kit uses promises to handle async replies. To be able to reply asynchronously simply return the promise and resolve it with a text or an object and Alexa Skill Kit will apply the same rules as above.
For example:
const alexaSkillKit = require('alexa-skill-kit')
exports.handler = function(event, context) {
alexaSkillKit(event, context, parsedMessage => {
return fetchSomethingFromTheServer()
.then(result => doSomethingWithTheResult(result))
.then(processedResult => {
return `Here's an info from the server: ${processedResult}`
})
})
}
Alexa Skill Kit will answer with the text:
`Here's an info from the server: ${processedResult}`
API reference
Alexa Skill Kit (function) receives following attributes:
- Event (
object, required) — an unmodified object received from Amazon Alexa. If your Lambda function receives an object that is not valid Amazon Alexa request it will not parse it and your handler function will never be called. - Context (
object, required) — a context object received on AWS Lambda, it is recommended not to modify it, but Alexa Skill Kit will usecontext.succeedandcontext.failfunctions only, so you can pass a custom object that contains those two functions from and original context object. - Handler (
function, required) — a function that receives parsed event and returns a reply that will be passed to Amazon Alexa.
Handler function is a function that receives parsed event and can return string, object or a promise that will return string or object when it is resolved.
In case you don't want Alexa to reply simply return null or don't return at all.
Parsed object is an object that contains following properties:
- type (string) - type of the request, it can be 'LaunchRequest', 'IntentRequest', 'SessionEndedRequest', or one of the 'AudioPlayer' or 'PlaybackController' requests
- request (object) - full request object from Alexa request
- intent: (object, can be null) - intent object from Alexa request, if the request does not contain intent, this property will be
null - session: (object, can be null) - session object from Alexa request, if session doesn't exists in the request, this property will be
null - sessionAttributes: (object) - an object with session attributes from Alexa request, if they does not exist, this property will be an empty object (
{}) - user: (object) - user object from Alexa request, Alexa Skill Kit will try to load user from the context, then from the session and finally, it'll set an empty object if user info is not found
- originalRequest: (object) - full Alexa request, as received from AWS Lambda and as described in an official documentation.
Contribute
Folder structure
The main body of code is in the lib directory.
The tests are in the spec directory, and should follow the structure of the corresponding source files. All executable test file names should end with -spec, so they will be automatically picked up by npm test. Any additional project files, helper classes etc that must not be directly executed by the test runner should not end with -spec. You can use the spec/helpers directory to store Jasmine helpers, that will be loaded before any test is executed.
Running tests
We use Jasmine for unit and integration tests. Unless there is a very compelling reason to use something different, please continue using Jasmine for tests. The existing tests are in the spec folder. Here are some useful command shortcuts:
Run all the tests:
npm test
Run only some tests:
npm test -- filter=prefix
Get detailed hierarchical test name reporting:
npm test -- full
We use ESLint for syntax consistency, and the linting rules are included in this repository. Running npm test will check the linting rules as well. Please make sure your code has no linting errors before submitting a pull request.
License
MIT - See LICENSE