LikeTheSalad / Android String Reference
Programming Languages
Labels
Projects that are alternatives of or similar to Android String Reference
Android String XML Reference
Table of Contents
What is it
Android String XML Reference is a Gradle plugin which resolves placeholders of XML strings referenced into other XML strings at buildtime. You won't have to write any Java or Kotlin code into your project to make it work and you will still be able to access to the 'resolved' strings the same way as with any other manually added string to your XML files.
In other words, if you're looking to do something like this:
Input:
<resources>
<string name="app_name">My App Name</string>
<string name="template_welcome_message">Welcome to ${app_name}</string>
</resources>
Output:
<!-- Auto generated -->
<resources>
<string name="welcome_message">Welcome to My App Name</string>
</resources>
Without having to write any Java or Kotlin code, then this plugin might help you.
How to use
1.- Templates
All you have to do is to define string templates inside your XML string files,
the file to add these templates to can be any file inside your values folders,
not necessarily the "strings.xml" file but any other within the same directory will
work too.
In order to create a template all you need to do is to set its name with the
template_ prefix. So for example, if you want your final "resolved" string name
to be "my_message", then its template name will be like so:
<string name="template_my_message">
Your templates will contain references to other strings in the form
of "placeholders", the placeholder format is ${another_string_name} where
"another_string_name" will be the name of any other string you have in your project.
Following our example above for our "template_my_message" template, let's say that we have another string in our project named "app_name" (which content is "My app name") and we want to place it inside our "template_my_message" template, we can do it like so:
<string name="template_my_message">Welcome to ${app_name}</string>
A template can contain from zero to any amount of placeholders. Any string within your values folder (even other templates) can be referenced inside a placeholder. And that's it, we've defined a template with a placeholder inside. Meaning that when we run the plugin, we'll get as a result the following "resolved" string:
<!-- Auto generated -->
<string name="my_message">Welcome to My app name</string>
Notice that for the final "resolved" string name, the template_ prefix has been removed.
2.- Running it
By default, the task that resolves the string templates will run during
your app's build process, unless you want to change this and rather
running it manually, which is explained below under Running it manually.
Since it runs by default during your project's build, then there's many ways of running it, some of those could be:
- By pressing on the "play" button of Android Studio:

- Or, by pressing on the "make" button on Android Studio:

- Or, if you prefer command line, then you can run it by calling the build command:
./gradlew buildor the assemble command:./gradlew assembleor by calling the specific task to resolve the strings which has the following format:./gradlew resolve[BUILD_VARIANT]Placeholdersmore info on this command below under "Running it manually".
2.1- How to know if it worked?
After the task has run, now you will be able to access to the "resolved" strings,
which are the previously defined "templates" but without the template_ prefix.
So following our previous example of our template "template_my_message", we now
will be able to access to the new auto-generated resolved string: my_message, the
same way as with any other string, e.g. This way for Java and Kotlin: R.string.my_message and this way for XML layouts: @string/my_message.
2.2- Where do resolved strings go to?
By default the resolved strings go into your app's build folder, specifically under the build/generated/resolved path. That's where this plugin places them into when it is run. The build folder is usually ignored for a VCS repository, so the resolved strings won't go into your repo unless you want to change it by applying the following configuration into your app's build.gradle file:
// Optional:
stringXmlReference {
keepResolvedFiles = true // By default it is false.
// If false: Resolved strings will go into the 'app/build' dir (which is a hidden dir for your VCS).
// If true: Resolved string will go into the 'app/src' dir.
}
The following cases are supported:
- Regular base strings.
- Multi-language strings.
- Flavor specific strings.
- Flavor specific with multi-language strings.
Both values and templates can be overridden for a different language and also for a different flavor. So if for example you have templates in your project which contain the app name placeholder (e.g. ${app_name}) then if you need to create a flavor with a different app name value, you just have to override the 'app_name' string inside the flavor's 'values' folder and that's it, now for this flavor you'll get all of the old strings but with the new app_name.
Same for languages, based on the example above, if you need to translate your 'my_message' string to spanish for example, you just have to override the template 'template_my_message' inside the 'values-es' folder and you'll get the translated 'my_message' string in the 'resolved.xml' file inside the 'values-es' folder.
3- Configurable options
This plugin has a default configuration that will work just fine for most projects, but if you think there are some aspects of it that you need to change based on the requirements and/or limitations on your project, you might find useful the following configuration params that are available for it.
3.1- Available configuration parameters
-
resolveOnBuild (Boolean, default is
true, added in version 1.0.0). When true, this plugin will automatically resolve your app's templates (only if it's needed to) during your app's build process. When false this plugin won't run automatically during your app's build process and instead you'd have to run it manually by calling the proper Gradle commands depending on the build variant you'd want to resolve the strings for. More info on this below under "Running it manually". -
keepResolvedFiles (Boolean, default is
false, added in version 1.1.0). When false, it will send all of the resolved strings to your app's build directory. Otherwise, when true, it will send all of the resolved strings to your app's src dir, meaning that you will see them in your working directory. -
useDependenciesRes (Boolean, default is
false, added in version 1.2.0). When false, it will only take your app's string resources into account for resolving your string's placeholders. When true, it will take both your app's strings as well as your app's dependencies strings for doing the resolving process. It will take all strings from your dependencies, even templates (if any) which will be resolved too.
3.2- How to change a configuration parameter?
In order to set any of the configuration parameters available, you'll have to add to your app's build.gradle file
the block stringXmlReference, and inside it you can add all of the params you'd want to change and make them
equal to the values you'd like to set for them.
Here's an example of how to change the params
// App's build.gradle file
android {
//...
}
// Example of how to change some config flags
stringXmlReference {
keepResolvedFiles = true // Its default value is false.
useDependenciesRes = true // Its default value is false.
}
Use case examples
Here's a couple of examples for some of the use cases supported by this plugin
1.- Simple use case
Within our app/main/res/values folder, we have the following file:
<!--strings.xml-->
<resources>
<string name="app_name">Test</string>
<string name="template_welcome_message">Welcome to ${app_name}</string>
</resources>
After building our project we get:
<!--Auto generated-->
<resources>
<string name="welcome_message">Welcome to Test</string>
</resources>
2.- Multi files use case
Within our app/main/res/values folder, we have the following files:
<!--strings.xml-->
<resources>
<string name="app_name">Test</string>
<string name="template_welcome_message">Welcome to ${app_name}</string>
<string name="template_app_version_name">The version for ${app_name} is ${my_version}</string>
</resources>
<!--my_configs.xml-->
<resources>
<string name="my_version">1.0.0</string>
</resources>
After building our project we get:
<resources>
<string name="app_version_name">The version for Test is 1.0.0</string>
<string name="welcome_message">Welcome to Test</string>
</resources>
So no matter which file contains a template or a value used in a template, as long as it's within your app's values folders, then the plugin will find it.
3.- Multi languages use case
Within our app/main/res/values folder, we have the following file:
<!--strings.xml-->
<resources>
<string name="app_name">Test</string>
<string name="template_welcome_message">Welcome to ${app_name}</string>
</resources>
Then, Within our app/main/res/values-es folder, we have the following file:
<!--any_file.xml-->
<resources>
<string name="template_welcome_message">Bienvenido a ${app_name}</string>
</resources>
After building our project, what we get for our default values folder is:
<!--Auto generated-->
<resources>
<string name="welcome_message">Welcome to Test</string>
</resources>
And then what we get for our spanish values-es folder is:
<!--Auto generated-->
<resources>
<string name="welcome_message">Bienvenido a Test</string>
</resources>
4.- Flavors use case
Let's say we've defined a flavor in our project, named demo, then:
Within our app/main/res/values folder, we have the following files:
<!--strings.xml-->
<resources>
<string name="app_name">Test</string>
<string name="template_welcome_message">Welcome to ${app_name}</string>
<string name="template_app_version_name">The version for ${app_name} is ${my_version}</string>
</resources>
<!--my_configs.xml-->
<resources>
<string name="my_version">1.0.0</string>
</resources>
And for our app/demo/res/values folder we add the following file:
<!--any_file.xml-->
<resources>
<string name="app_name">Demo app</string>
</resources>
After building the demo variant of our project, we'll get for such variant:
<!--Auto generated-->
<resources>
<string name="app_version_name">The version for Demo app is 1.0.0</string>
<string name="welcome_message">Welcome to Demo app</string>
</resources>
So we see that the app_name value has been overridden by the demo's app_name, this doesn't only happen for values but also for templates, we can also override templates within our demo's resources.
Those were some of the use cases that you can achieve using this plugin, there's more of them such as overriding flavor's multi languages from the base values folder and also working with multi-dimension flavors. You can play around with it, it all should work the way you'd expect it to work.
Adding it to your project
Note: If you're migrating from version
1.0.0the only change is that now theresolved.xmlfiles go by default to theapp/buildfolder to keep them hidden from your working dir and the VCS, if you still want to keep these files then you can configure this behavior as explained above inWhere do resolved strings go to?.
We're going to need to modify two build.gradle files in our project in order to make
this plugin work, those are:
-
Root's
build.gradle -
App's
build.gradle
1.- Where to find the build.gradle files
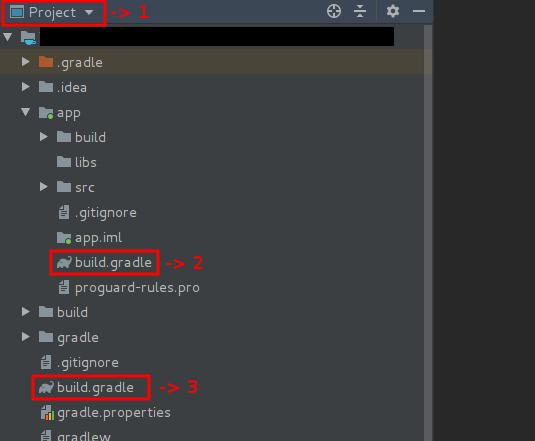
To get a better idea of where you can find these files, take a look at this Android Studio screenshot below:
- The number 1 selection is to make sure that you've selected the "Project"
view in order to see the
build.gradlefiles as shown on this image. - The number 2 selection represents your App's build.gradle file.
- The number 3 selection represents your Root's build.gradle file.
2.- What to add to the build.gradle files
2.1- Changes to your Root's build.gradle file
First, in your Root's build.gradle file, you'll need to add this
line into your buildscript dependencies block:
classpath "com.likethesalad.android:string-reference:1.2.1"
Example:
// Root's build.gradle file
buildscript {
repositories {
jcenter()
//or
mavenCentral()
}
dependencies {
//...
classpath "com.likethesalad.android:string-reference:1.2.1"
// NOTE: Do not place your application dependencies here; they belong
// in the individual module build.gradle files
}
}
Please note that you must also add (if not there already) either
jcenter()ormavenCentral()to your buildscript's repositories block as shown above.
2.2- Changes to your App's build.gradle file
In your App's build.gradle file you have to add the following line below the apply plugin: 'com.android.application'
one:
apply plugin: 'placeholder-resolver'
Example:
// App's build.gradle file
apply plugin: 'com.android.application'
apply plugin: 'placeholder-resolver'
android {
//...
}
2.3- Sync your project
After your changes to the build.gradle files are done, you should see the above message in Android Studio that has a "Sync Now" button. You have to click on that button for the changes to take effect. After the sync is done, you'll be ready to go! you can start adding your string templates to your app's resources.
Running it manually
If you want to avoid running the templates resolver task
automatically during the build process of your project and rather running it manually, then
you can turn it off by adding the following into your App's build.gradle file, where you've added this plugin to:
// Optional
stringXmlReference {
resolveOnBuild = false // By default it is true.
// If true: The templates resolver task will run automatically during your project's build.
// If false: The templates resolver task won't run automatically, you'll have to run it by explicitly calling
// it as explained below.
}
And that's it, now you'll have to make sure to trigger the task
manually whenever you need your resolved strings to get
updated by running: resolve[BUILD_VARIANT]Placeholders depending
on your build configuration. For example, to run it for the debug variant,
you'll have to run: resolveDebugPlaceholders, or if you have flavors
setup in your application, e.g. say you have 'demo' as a flavor defined,
then you can run resolveDemoDebugPlaceholders to generate the strings
for the demo flavor on the debug variant and so on.
License
MIT License
Copyright (c) 2019 LikeTheSalad.
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal
in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all
copies or substantial portions of the Software.
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE
SOFTWARE.