soumyadip007 / Data Structure And Algorithm Using Python
Licence: apache-2.0
In computer science, a data structure is a data organization, management, and storage format that enables efficient access and modification. More precisely, a data structure is a collection of data values, the relationships among them, and the functions or operations that can be applied to the data. (Using Python 3)
Stars: ✭ 141
Labels
Projects that are alternatives of or similar to Data Structure And Algorithm Using Python
Nbconvert Examples
Examples that illustrate how nbconvert can be used
Stars: ✭ 139 (-1.42%)
Mutual labels: jupyter-notebook
Recotour
A tour through recommendation algorithms in python [IN PROGRESS]
Stars: ✭ 140 (-0.71%)
Mutual labels: jupyter-notebook
Voc2coco
How to create custom COCO data set for object detection
Stars: ✭ 140 (-0.71%)
Mutual labels: jupyter-notebook
Imageprocessing
MicaSense RedEdge and Altum image processing tutorials
Stars: ✭ 139 (-1.42%)
Mutual labels: jupyter-notebook
Popmusicmaker
Pop Music Maker built on HMM and Random Forest-like structure. Inspired by the desire to build my own model can serve as alternative to LSTMs / deep learning in generating pop music. Website is currently down due to costs incurred.
Stars: ✭ 140 (-0.71%)
Mutual labels: jupyter-notebook
Python For Algorithms Data Structures And Interviews
Files for Udemy Course on Algorithms and Data Structures
Stars: ✭ 1,917 (+1259.57%)
Mutual labels: jupyter-notebook
Categoricalencodingbenchmark
Benchmarking different approaches for categorical encoding for tabular data
Stars: ✭ 140 (-0.71%)
Mutual labels: jupyter-notebook
Interactive Corporate Report
ICR - Automated and Intelligent Company Report Built in Python (by @firmai)
Stars: ✭ 139 (-1.42%)
Mutual labels: jupyter-notebook
Dash eth
This project is trying to fetch real time balance & orderbook of ETH and visualise using dash
Stars: ✭ 140 (-0.71%)
Mutual labels: jupyter-notebook
Intro To Tensorflow
This is an introduction to tensorflow
Stars: ✭ 139 (-1.42%)
Mutual labels: jupyter-notebook
Interactive machine learning
IPython widgets, interactive plots, interactive machine learning
Stars: ✭ 140 (-0.71%)
Mutual labels: jupyter-notebook
Practical Machine Learning With Python
Master the essential skills needed to recognize and solve complex real-world problems with Machine Learning and Deep Learning by leveraging the highly popular Python Machine Learning Eco-system.
Stars: ✭ 1,868 (+1224.82%)
Mutual labels: jupyter-notebook
Data-Strcture-Algorithm-using-Python
Topics:
- Queues
- Stacks
- Doubly Linked Lists
- Singly Linked Lists
- Binary Search Trees
- Tree Traversal
- Sortings
- Searchings
- Dynamic Programming
- Heap
- Graph
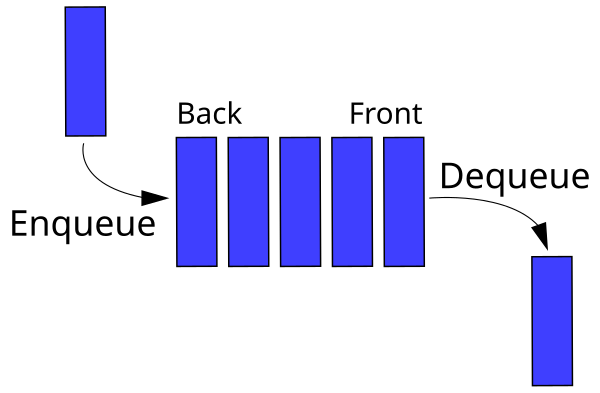
Queues
- Should have the methods:
enqueue,dequeue, andlen.-
enqueueshould add an item to the back of the queue. -
dequeueshould remove and return an item from the front of the queue. -
lenreturns the number of items in the queue.
-
Doubly Linked Lists
- The
ListNodeclass, which represents a single node in the doubly-linked list, has already been implemented for you. Inspect this code and try to understand what it is doing to the best of your ability. - The
DoublyLinkedListclass itself should have the methods:add_to_head,add_to_tail,remove_from_head,remove_from_tail,move_to_front,move_to_end,delete, andget_max.-
add_to_headreplaces the head of the list with a new value that is passed in. -
add_to_tailreplaces the tail of the list with a new value that is passed in. -
remove_from_headremoves the head node and returns the value stored in it. -
remove_from_tailremoves the tail node and returns the value stored in it. -
move_to_fronttakes a reference to a node in the list and moves it to the front of the list, shifting all other list nodes down. -
move_to_endtakes a reference to a node in the list and moves it to the end of the list, shifting all other list nodes up. -
deletetakes a reference to a node in the list and removes it from the list. The deleted node'spreviousandnextpointers should point to each afterwards. -
get_maxreturns the maximum value in the list.
-
- The
headproperty is a reference to the first node and thetailproperty is a reference to the last node.
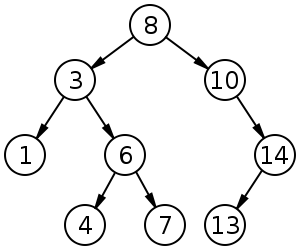
Binary Search Trees
- Should have the methods
insert,contains,get_max.-
insertadds the input value to the binary search tree, adhering to the rules of the ordering of elements in a binary search tree. -
containssearches the binary search tree for the input value, returning a boolean indicating whether the value exists in the tree or not. -
get_maxreturns the maximum value in the binary search tree. -
for_eachperforms a traversal of every node in the tree, executing the passed-in callback function on each tree node value. There is a myriad of ways to perform tree traversal; in this case any of them should work.
-
Heaps
- Should have the methods
insert,delete,get_max,_bubble_up, and_sift_down.-
insertadds the input value into the heap; this method should ensure that the inserted value is in the correct spot in the heap -
deleteremoves and returns the 'topmost' value from the heap; this method needs to ensure that the heap property is maintained after the topmost element has been removed. -
get_maxreturns the maximum value in the heap in constant time. -
get_sizereturns the number of elements stored in the heap. -
_bubble_upmoves the element at the specified index "up" the heap by swapping it with its parent if the parent's value is less than the value at the specified index. -
_sift_downgrabs the indices of this element's children and determines which child has a larger value. If the larger child's value is larger than the parent's value, the child element is swapped with the parent.
-
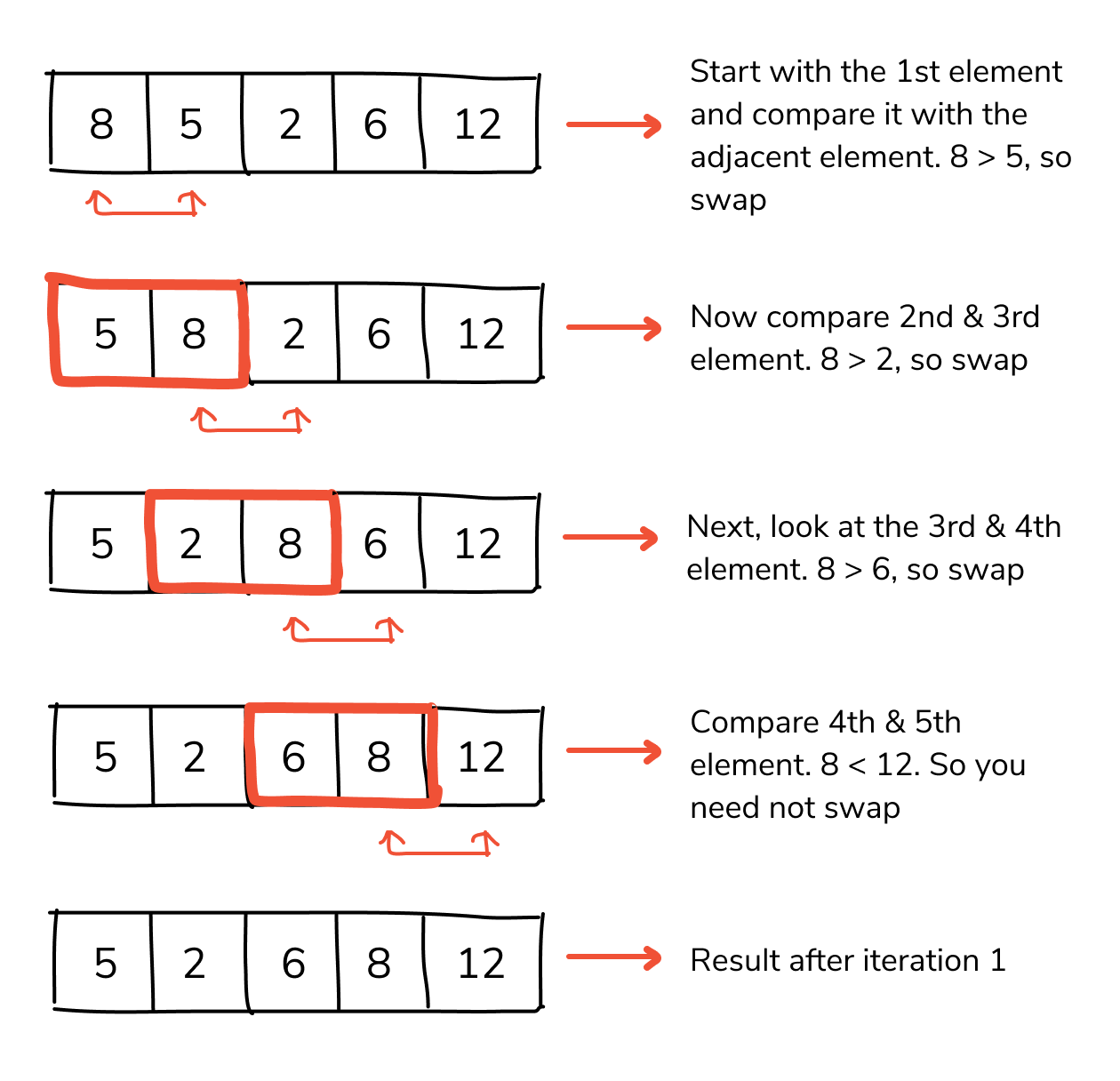
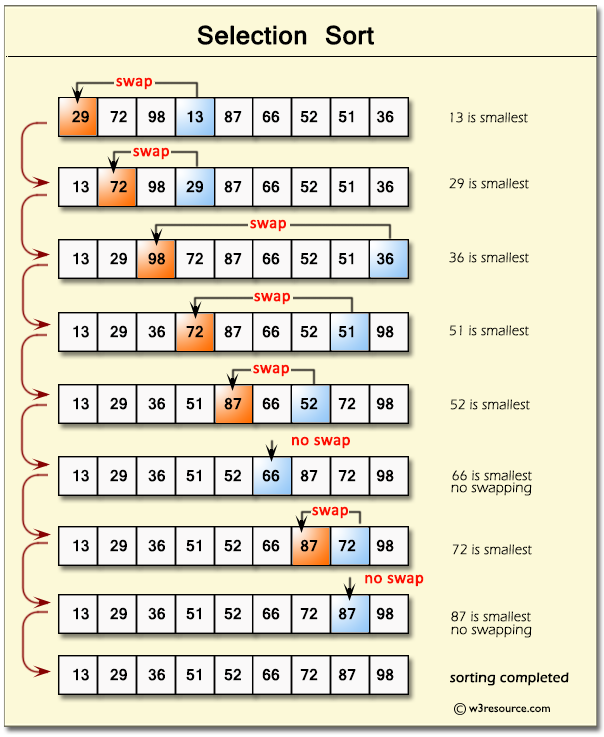
Sorting
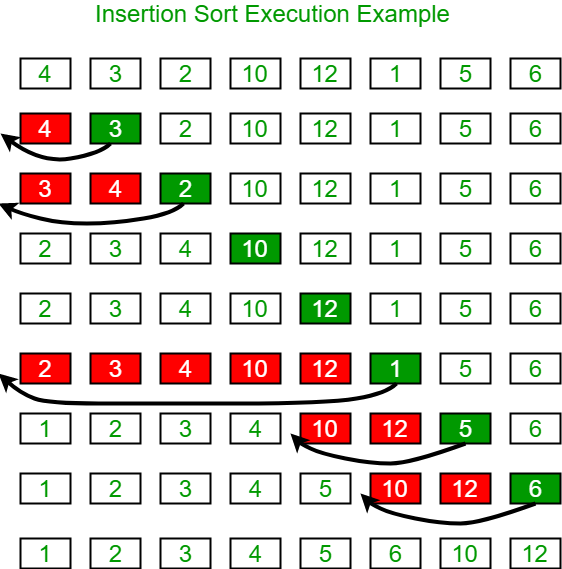
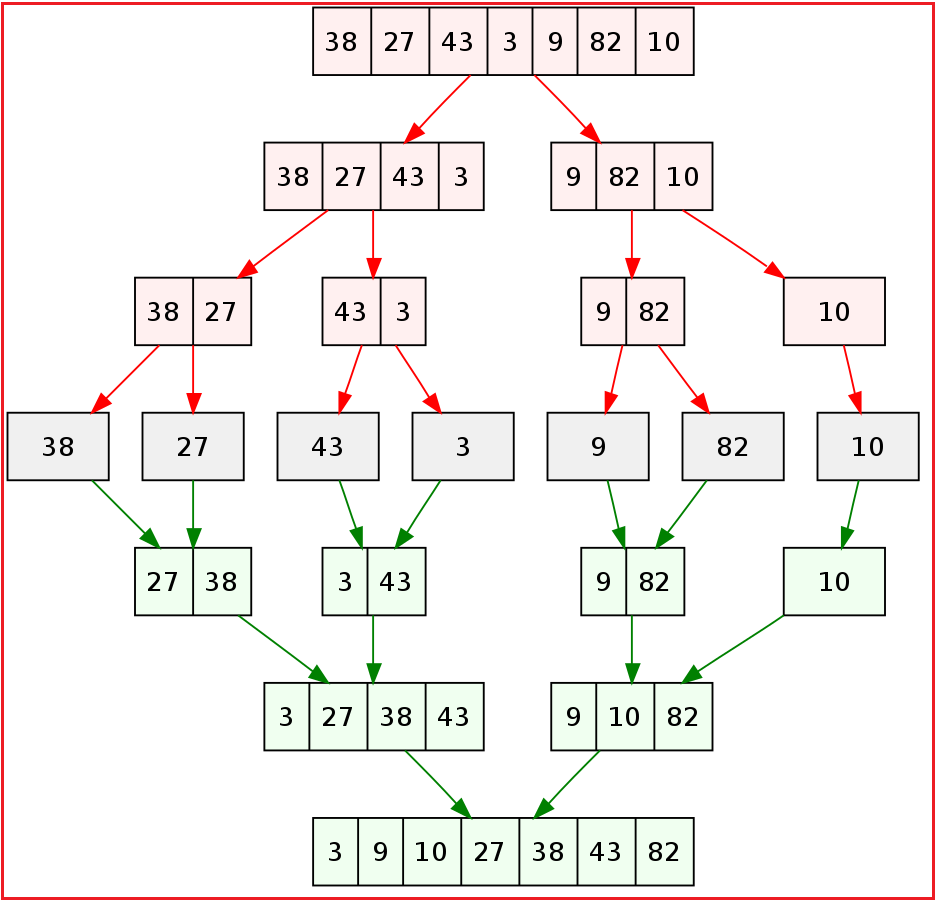
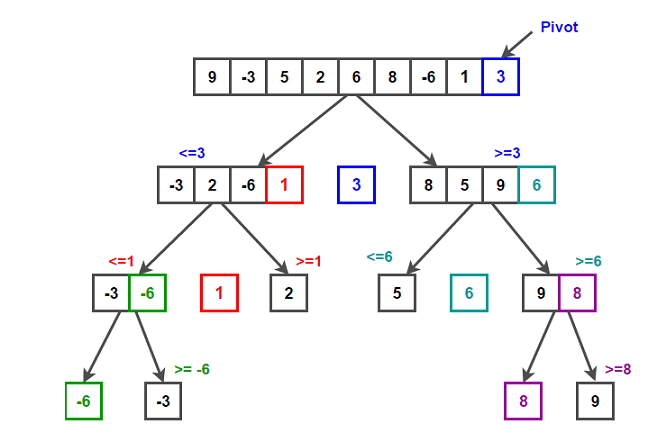
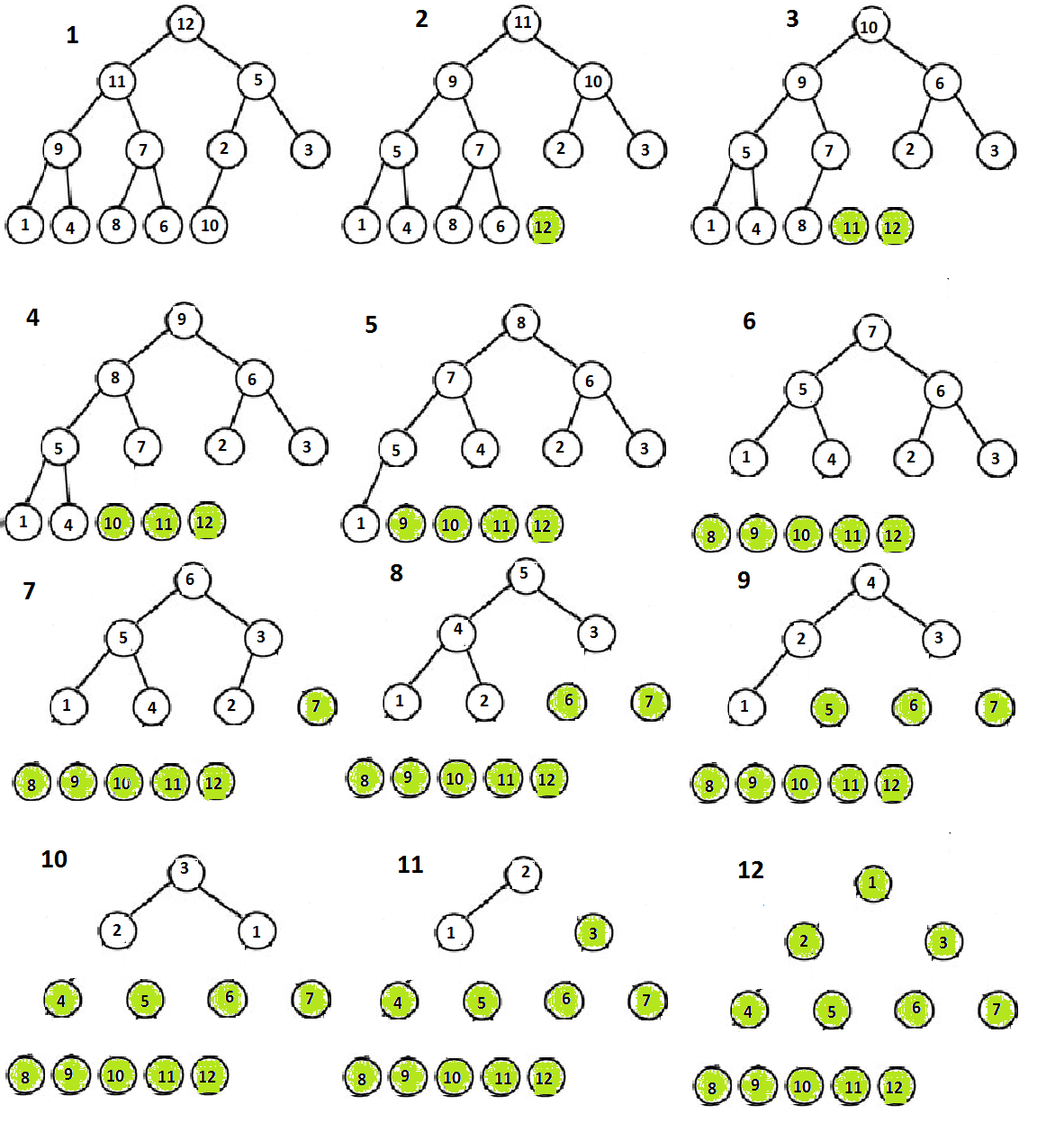
Note that the project description data, including the texts, logos, images, and/or trademarks,
for each open source project belongs to its rightful owner.
If you wish to add or remove any projects, please contact us at [email protected].