FranxYao / Dgm_latent_bow
Programming Languages
Projects that are alternatives of or similar to Dgm latent bow
**Update**: On the Interpretability of Discrete Set Representations: A Bayesian Perspective
- The discussion about the identifiability and interpretability of the LBOW model in the unsupervised setting.
- Work in progress
The Latent Bag of Words Model
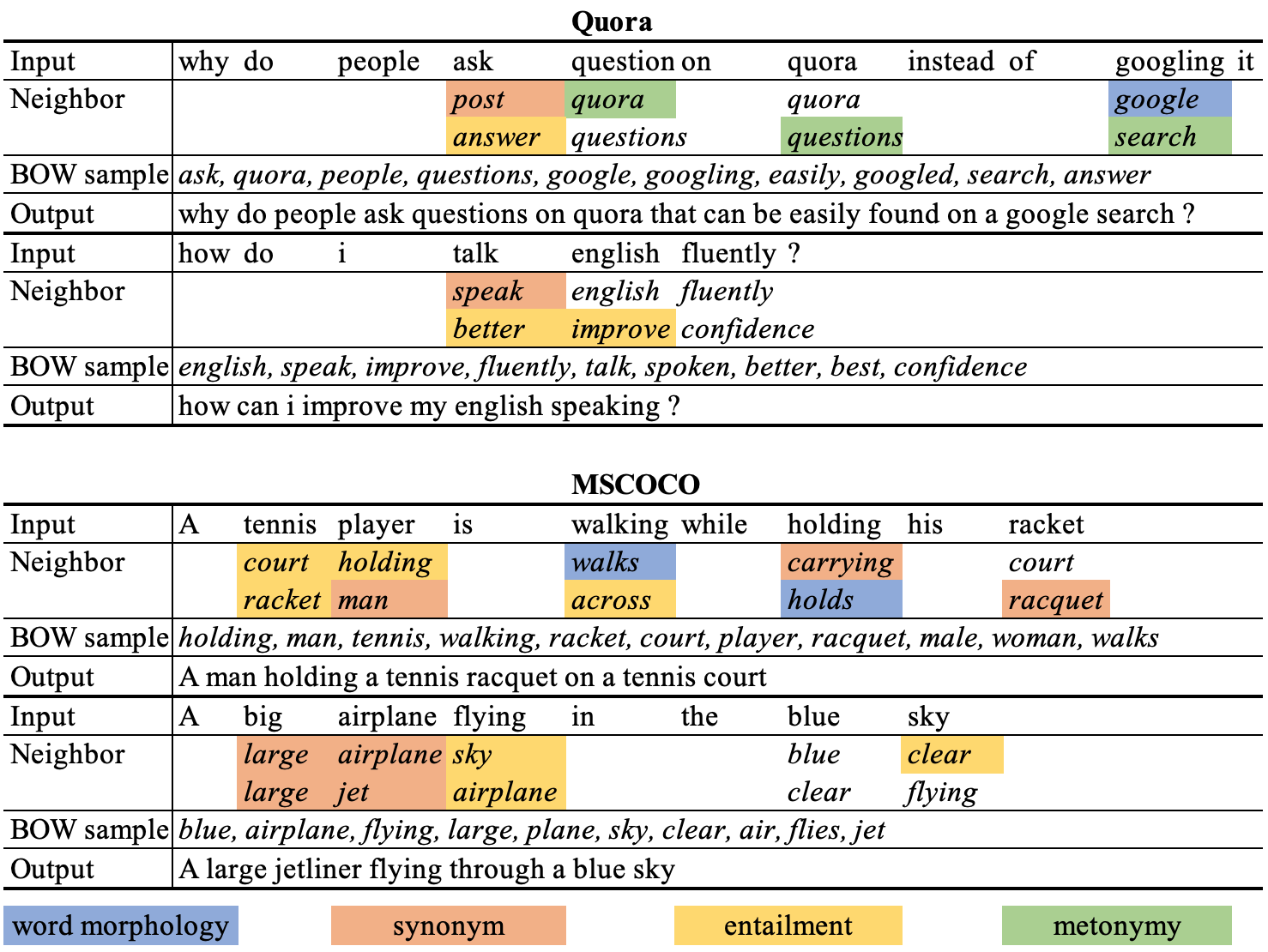
Implementation of Yao Fu, Yansong Feng and John Cunningham, Paraphrase Generation with Latent Bag of Words. NeurIPS 2019. paper
As is shown in the above example, given a source sentence, our model first infers the neighbor words of each source words, then sample a bag of words from the neighbors, then generate the paraphrase based on the sampled words
For more background about deep generative models for natural language processing, see the DGM4NLP journal list.
Reproduce
mkdir models
mkdir outputs
cd src
python3 main.py
# quicker start
python3 main.py --batch_size=5 --train_print_interval=10
# Monitor training:
loss: 9.1796 -- total loss
enc_loss: 3.1693 -- BOW NLL loss
dec_loss: 6.0103 -- Decoder loss
precision_confident: 0.4794 -- BOW precision on confident = most confident word neighbors
recall_confident: 0.1727 -- BOW recall on confident = most confident word neighbors
precision_topk: 0.1186 -- BOW percision on topk = tok predicted word neighbors
recall_topk: 0.2387 -- BOW recall on topk = tok predicted word neighbors
May need to install nltk stopwords first, just follow the prompt
Data
We use the MSCOCO(17) dataset and the Quora dataset. The Quora dataset is provided in the data/ folder. The MSCOCO dataset can be downloaded from its offical website
Code Structure
The core implementation is in the following files:
- config.py
- main.py
- controller.py
- latent_bow.py
Others
There are certain codes about testing the Wikibio dataset. These part of the code is not included in the paper, its just for tesing the data-to-text task. So the published part might be incomplete. If you do want to extend the model to data-to-text, feel free to contact me.
The rouge evaluation is from here: https://pypi.org/project/py-rouge/. There is also a google implementation recently: https://github.com/google-research/google-research/tree/master/rouge.
The main_test.py is not for testing the model, it is for debugging in the ipython terminal.
Embarrassingly, I cannot replicate the results in Pytorch ... I moved to Pytorch after this project and there are still many things to understand (as a many-year tfer). It seems that the pytorch LSTM does not support residual connections, which results in degraded performance when I changed the number of layers to be 2. If you happen to find a solution, or find something close, do contact me.