naturomics / Dlf
Programming Languages
Labels
Projects that are alternatives of or similar to Dlf
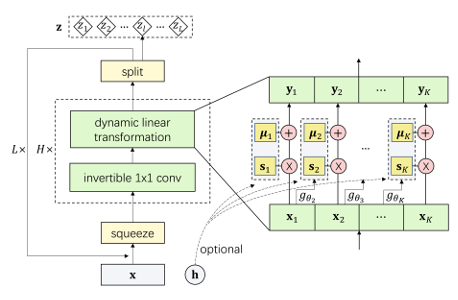
Dynamic Linear Flow (DLF)
Code for reproducing results in "Generative Model with Dynamic Linear Flow"
In our paper, we proposed Dynamic Linear Flow, a new family of exact likelihood-based methods. Our method benefits from the efficient computation of flow-based methods (RealNVP, Glow, etc.) and high density estimation performance of autoregressive methods (PixelCNN, PixelSNAIL etc.). DLF yields state-of-the-art performance in density estimation benchmarks and efficiently synthesizes high-resolution images. Additionally, DLF converges 10x faster than other flow-based models such as Glow. Read our paper for more details.
Requirements
- python3
- TensorFlow (tested with v1.12)
Setup
-
Install requirements
-
Clone this repo or click the Download ZIP button on upper right corner
git clone https://github.com/naturomics/DLF
cd DLF
- Download Datasets
All datasets are saved to folder data/{dataset_name} as default. If your datasets are saved at a different folder,
please specify it via --data_dir command line or change the default value in main.py file to point to the right folder.
- MNIST and CIFAR10 will be directly downloaded by the code.
- The preprocessed and downsampled
ImageNetdataset can be downloaded fromhttps://storage.googleapis.com/glow-demo/data/imagenet-oord-tfr.tar, 32x32 and 64x64 version included. Extract and move files to the corresponding folder (r05in the filename refers to resolution 2**5=32):
mkdir -p data/imagenet{32x32,64x64}/{train,validation}
tar -xf imagenet-oord-tfr.tar
mv mnt/host/imagenet-oord-tfr/train/*r05*.tfrecords data/imagenet32x32/train
mv mnt/host/imagenet-oord-tfr/validation/*r05*.tfrecords data/imagenet32x32/validation
mv mnt/host/imagenet-oord-tfr/train/*r06*.tfrecords data/imagenet64x64/train
mv mnt/host/imagenet-oord-tfr/validation/*r06*.tfrecords data/imagenet64x64/validation
- The preprocessed
CelebA 256x256is fromhttps://storage.googleapis.com/glow-demo/data/celeba-tfr.tar. Extract it to folderdata/celeba, for example:
wget https://storage.googleapis.com/glow-demo/data/celeba-tfr.tar
tar -xf celeba-tfr.tar
mv celeba-tfr data/celeba
If you are interested, see the scripts here to learn how these tfrecord files were generated.
Train the model
Outputs during training (train loss, validation loss, samples and model checkpoints) are saved to folder specified by --results_dir.
Using --num_gpus for multiple GPUs training. Run python main.py -h for more helps.
CIFAR 10 with K=2, non-inverse dynamic linear transformation
# unconditional
python main.py --results_dir results/cifar10_noCond --seed [0/1/2]
# class label conditional
python main.py --results_dir results/cifar10_addCond --conditioning --seed [0/1/2]
CIFAR 10 with K=2, inverse dynamic linear transformation
python main.py --results_dir results/cifar10_noCond_extraDep --decomposition 1 --seed [0/1/2]
CIFAR 10 with K=4 and 6, non-inverse dynamic linear transformation
python main.py --results_dir results/cifar10_noCond_4parts --num_parts 4 --width 308 --seed [0/1/2]
python main.py --results_dir results/cifar10_noCond_6parts --num_parts 6 --width 256 --seed [0/1/2]
ImageNet 32x32
python main.py --problem imagenet32x32 --results_dir results/imgnet32_noCond
ImageNet 64x64
python main.py --problem imagenet64x64 --results_dir results/imgnet64_noCond --num_levels 4 --width 384 --invconv_bias --batch_size 24
MNIST
# unconditional
python main.py --problem mnist --results_dir results/mnist_noCond --num_levels 2 --width 128 --batch_size 256
# class label conditional
python main.py --problem mnist --results_dir results/mnist_addCond --num_levels 2 --width 128 --conditioning --batch_size 256
CekebA-HQ 256x256
python main.py --problem celeba --results_dir results/celeba_noCond --num_levels 6 --width 128 --batch_size 4 --num_gpus 2 --l2_factor 0.1
Interpolation between images
Run the script demo.py to generate linearly interpolated samples between two real images:
# Specify --results_dir with results path of CelebA, e.g.
python demo.py --results_dir results/celeba_noCond
The outputs are saved to demo directory as default.
Pre-trained models
We will soon upload our trained models.
Train with your own dataset
We use tf.data API for data reading pipeline and we have written a script to standardize the code. To train with your own dataset,
all you need to do is writing the tfrecords maker and the corresponding parse function, and import it in file datasets/__init__.py.
See datasets/cifar10.py, datasets/mnist.py etc. for examples. When training, specify your dataset by --problem {dataset_name}
command line, where dataset_name is your script name. We will write a more detailed tutorial if needed.