shayneobrien / Generative Models
Programming Languages
Projects that are alternatives of or similar to Generative Models
Overview
PyTorch 0.4.1 | Python 3.6.5
Annotated implementations with comparative introductions for minimax, non-saturating, wasserstein, wasserstein gradient penalty, least squares, deep regret analytic, bounded equilibrium, relativistic, f-divergence, Fisher, and information generative adversarial networks (GANs), and standard, variational, and bounded information rate variational autoencoders (VAEs).
Paper links are supplied at the beginning of each file with a short summary of the paper. See src folder for files to run via terminal, or notebooks folder for Jupyter notebook visualizations via your local browser. The main file changes can be see in the train, train_D, and train_G of the Trainer class, although changes are not completely limited to only these two areas (e.g. Wasserstein GAN clamps weight in the train function, BEGAN gives multiple outputs from train_D, fGAN has a slight modification in viz_loss function to indicate method used in title).
All code in this repository operates in a generative, unsupervised manner on binary (black and white) MNIST. The architectures are compatible with a variety of datatypes (1D, 2D, square 3D images). Plotting functions work with binary/RGB images. If a GPU is detected, the models use it. Otherwise, they default to CPU. VAE Trainer classes contain methods to visualize latent space representations (see make_all function).
Usage
To initialize an environment:
python -m venv env
. env/bin/activate
pip install -r requirements.txt
For playing around in Jupyer notebooks:
jupyter notebook
To run from Terminal:
cd src
python bir_vae.py
New Models
One of the primary purposes of this repository is to make implementing deep generative model (i.e., GAN/VAE) variants as easy as possible. This is possible because, typically but not always (e.g. BIRVAE), the proposed modifications only apply to the way loss is computed for backpropagation. Thus, the core training class is structured in such a way that most new implementations should only require edits to the train_D and train_G functions of GAN Trainer classes, and the compute_batch function of VAE Trainer classes.
Suppose we have a non-saturating GAN and we wanted to implement a least-squares GAN. To do this, all we have to do is change two lines:
Original (NSGAN)
def train_D(self, images):
...
D_loss = -torch.mean(torch.log(DX_score + 1e-8) + torch.log(1 - DG_score + 1e-8))
return D_loss
def train_G(self, images):
...
G_loss = -torch.mean(torch.log(DG_score + 1e-8))
return G_loss
New (LSGAN)
def train_D(self, images):
...
D_loss = (0.50 * torch.mean((DX_score - 1.)**2)) + (0.50 * torch.mean((DG_score - 0.)**2))
return D_loss
def train_G(self, images):
...
G_loss = 0.50 * torch.mean((DG_score - 1.)**2)
return G_loss
Model Architecture
The architecture chosen in these implementations for both the generator (G) and discriminator (D) consists of a simple, two-layer feedforward network. While this will give sensible output for MNIST, in practice it is recommended to use deep convolutional architectures (i.e. DCGANs) to get nicer outputs. This can be done by editing the Generator and Discriminator classes for GANs, or the Encoder and Decoder classes for VAEs.
Visualization
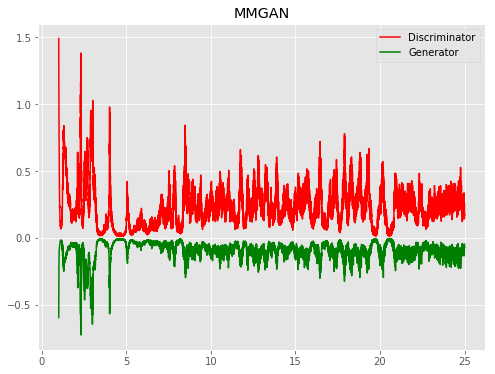
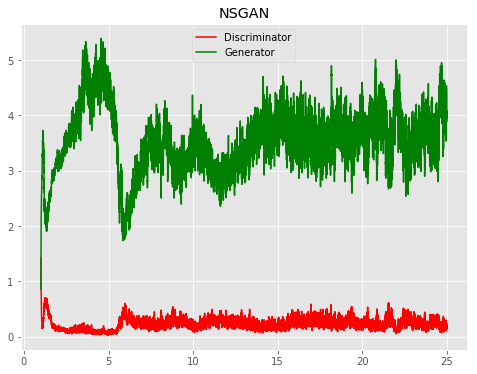
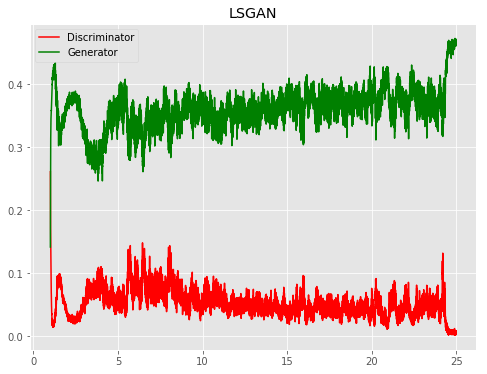
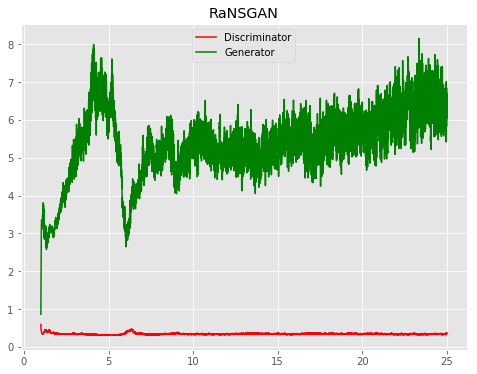
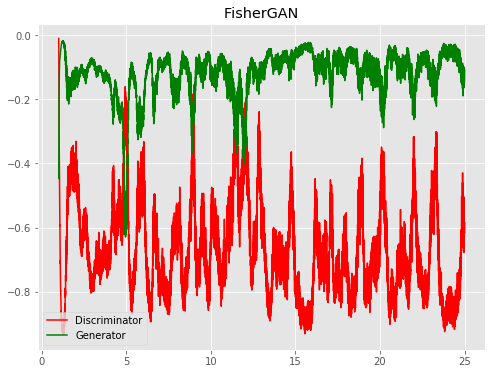
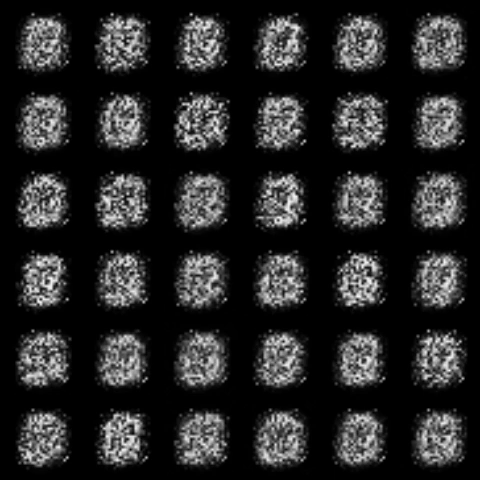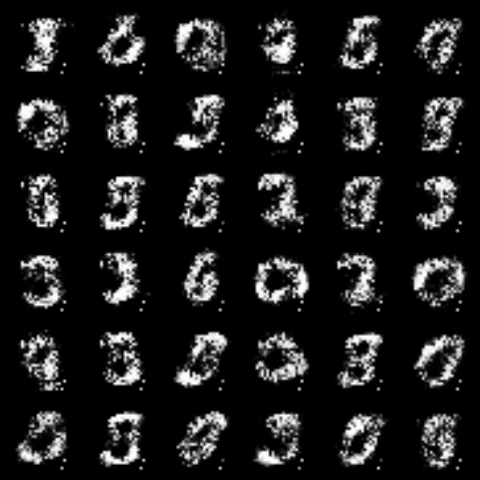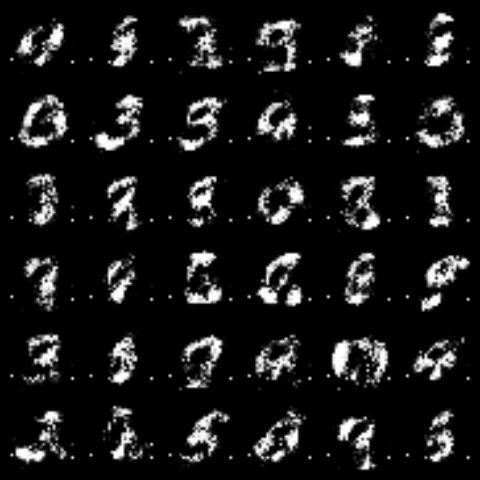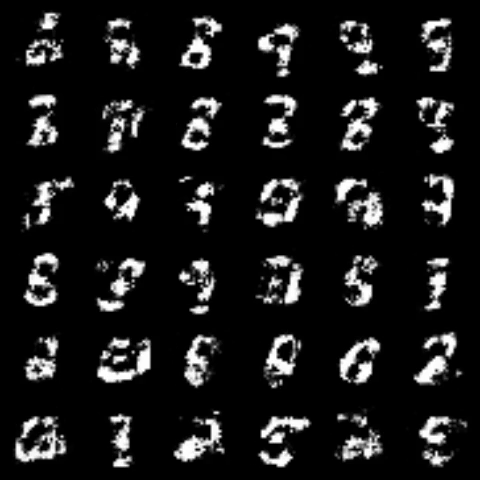
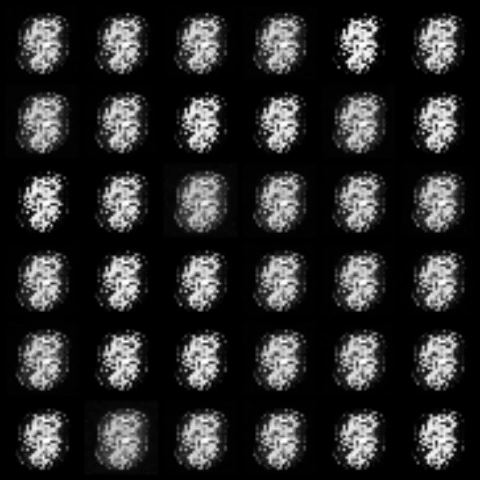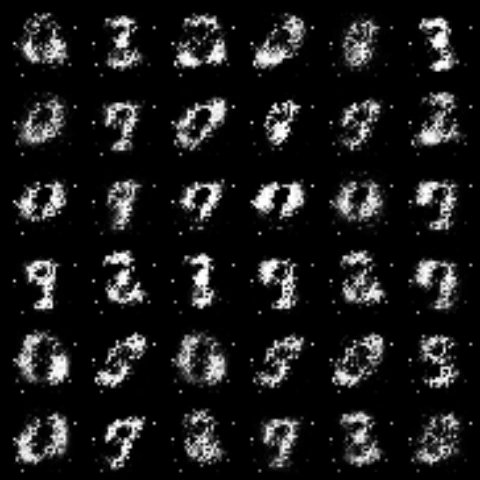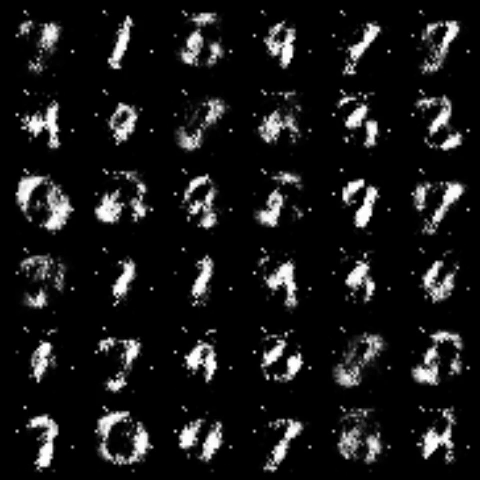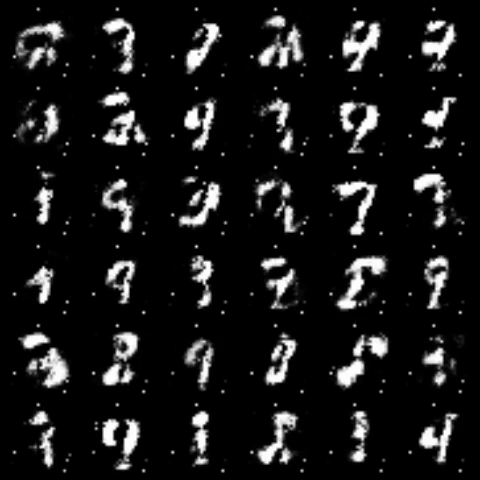
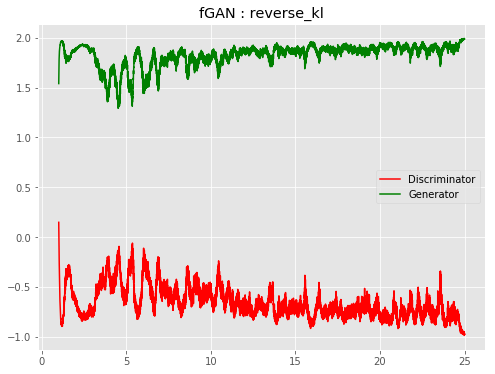
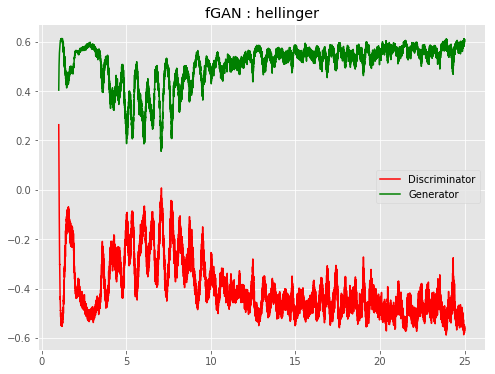
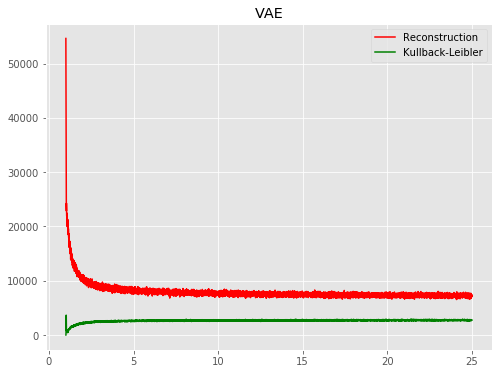
All models were trained for 25 epochs with hidden dimension 400, latent dimension 20. Other implementation specifics are as close to the respective original paper (linked) as possible.
| Model | Epoch 1 | Epoch 25 | Progress | Loss |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MMGAN |  |
 |
 |
 |
| NSGAN |  |
 |
 |
 |
| WGAN |  |
 |
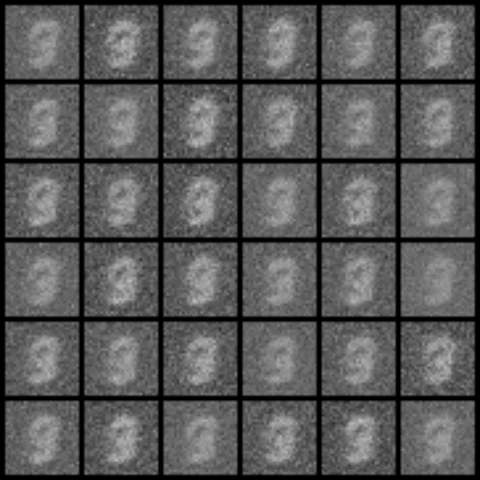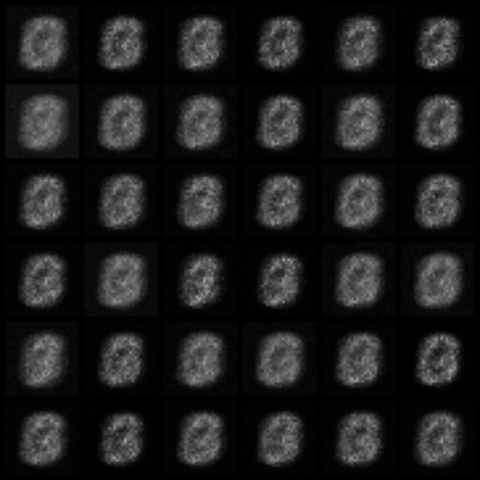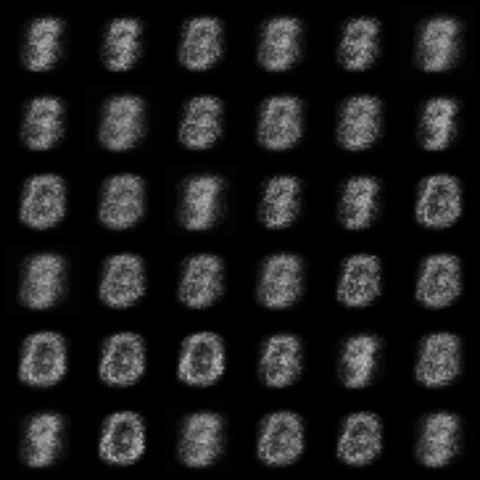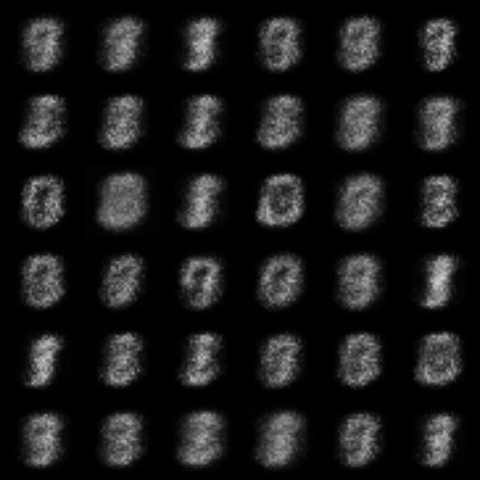 |
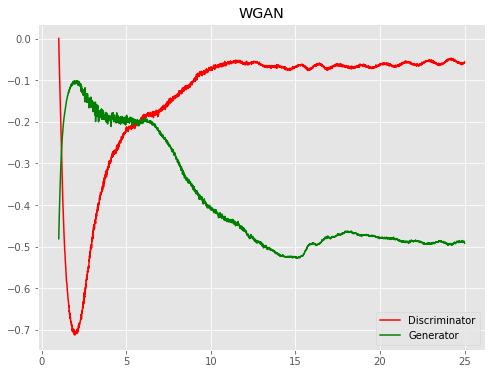 |
| WGPGAN | 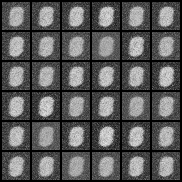 |
 |
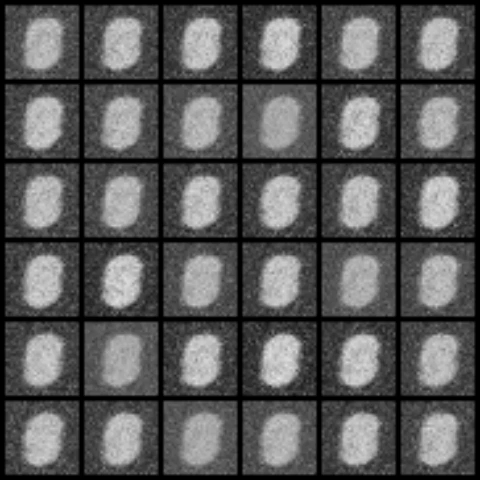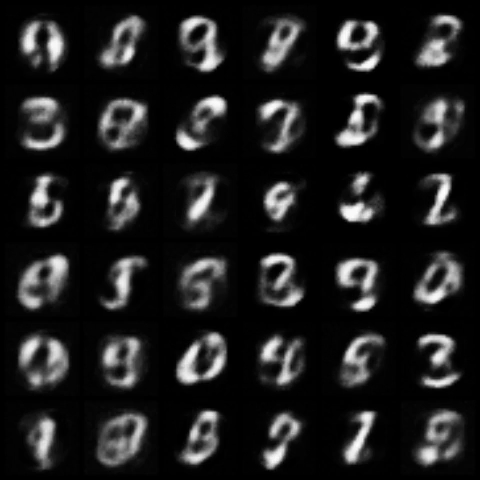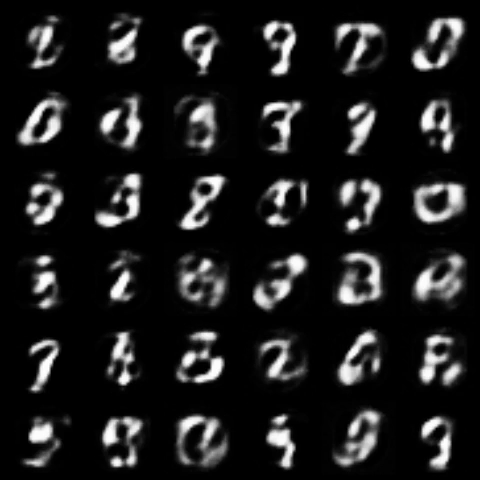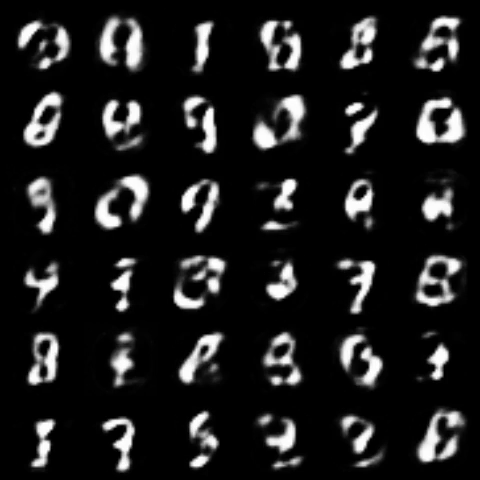 |
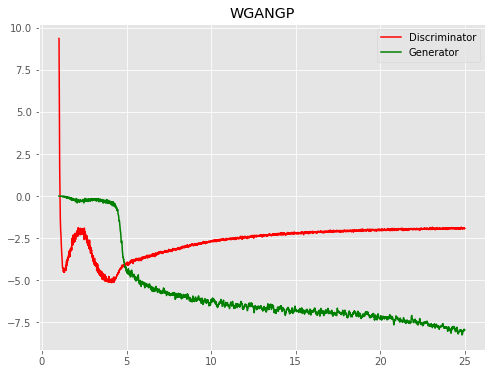 |
| DRAGAN |  |
 |
 |
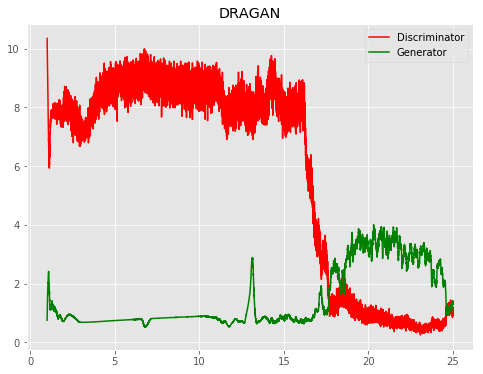 |
| BEGAN |  |
 |
 |
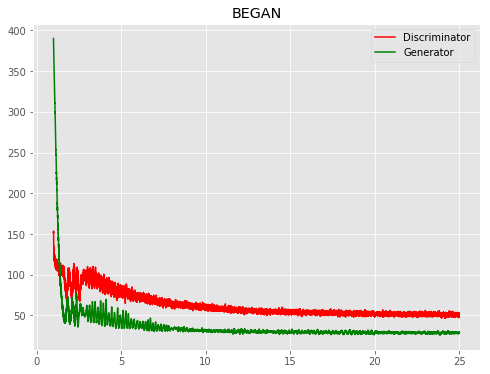 |
| LSGAN |  |
 |
 |
 |
| RaNSGAN |  |
 |
 |
 |
| FisherGAN |  |
 |
 |
 |
| InfoGAN | 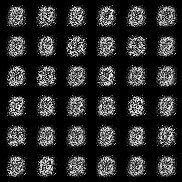 |
 |
 |
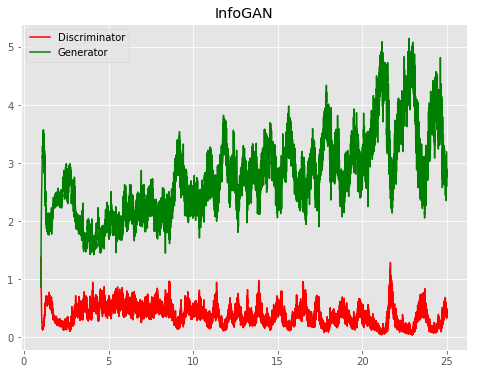 |
| f-TVGAN |  |
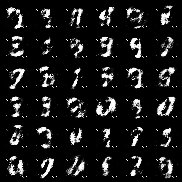 |
 |
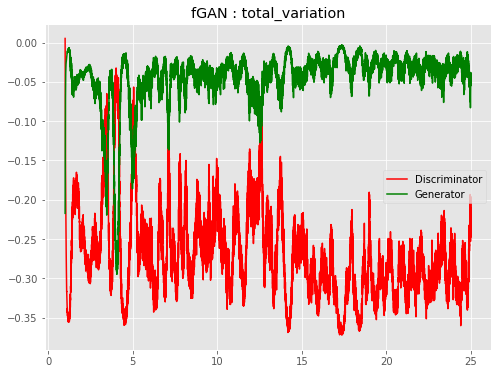 |
| f-PearsonGAN | 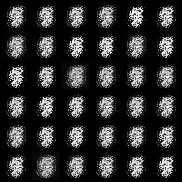 |
 |
 |
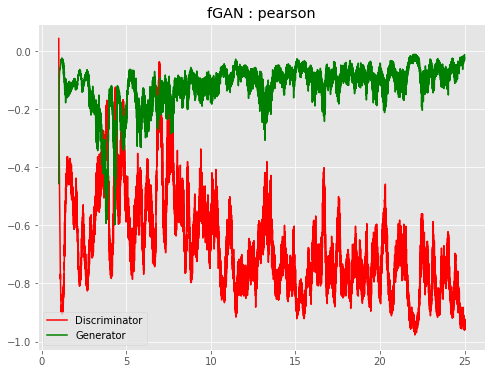 |
| f-JSGAN |  |
 |
 |
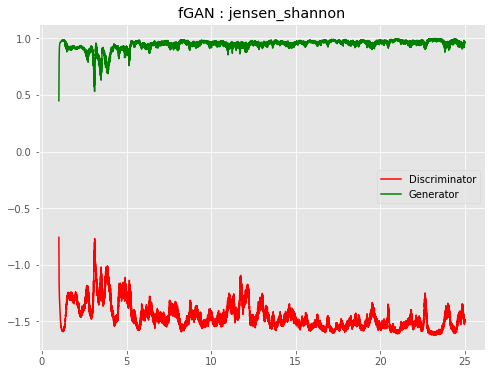 |
| f-ForwGAN |  |
 |
 |
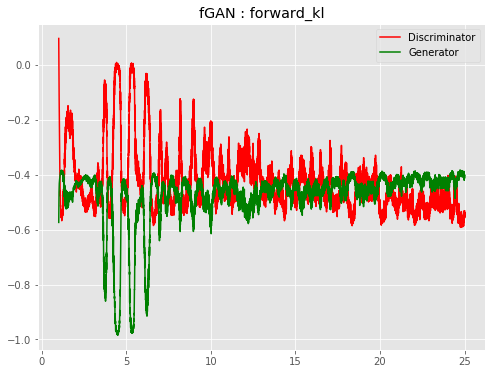 |
| f-RevGAN |  |
 |
 |
 |
| f-HellingerGAN |  |
 |
 |
 |
| VAE |  |
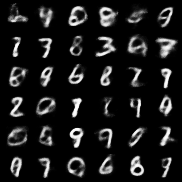 |
 |
 |
| BIRVAE |  |
 |
 |
 |
To Do
Models: CVAE, denoising VAE, adversarial autoencoder | Bayesian GAN, Self-attention GAN, Primal-Dual Wasserstein GAN
Architectures: Add DCGAN option
Datasets: Beyond MNIST
