vlgiitr / Group Level Emotion Recognition
Projects that are alternatives of or similar to Group Level Emotion Recognition
Group-Level Emotion Recognition
This repository contains the code of our model submitted for the ICMI 2018 EmotiW Group-Level Emotion Recognition Challenge. The model was ranked 4th in the challenge.
Short Paper of our challenge submission can be found here. If you find our research work helpful, please consider citing:
@inproceedings{Gupta:2018:AMG:3242969.3264985,
author = {Gupta, Aarush and Agrawal, Dakshit and Chauhan, Hardik and Dolz, Jose and Pedersoli, Marco},
title = {An Attention Model for Group-Level Emotion Recognition},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 2018 on International Conference on Multimodal Interaction},
series = {ICMI `18},
year = {2018},
isbn = {978-1-4503-5692-3},
location = {Boulder, CO, USA},
pages = {611--615},
numpages = {5},
url = {http://doi.acm.org/10.1145/3242969.3264985},
doi = {10.1145/3242969.3264985},
acmid = {3264985},
publisher = {ACM},
address = {New York, NY, USA},
keywords = {attention mechanisms, convolutional neural networks, deep learning, group-level emotion recognition},
}
Contents
- Summary of the Model
- Setup Instructions and Dependencies
- Repository Overview
- Dataset Folder Overview
- Credits
- Guidelines for Contributors
- License
1. Summary of the Model
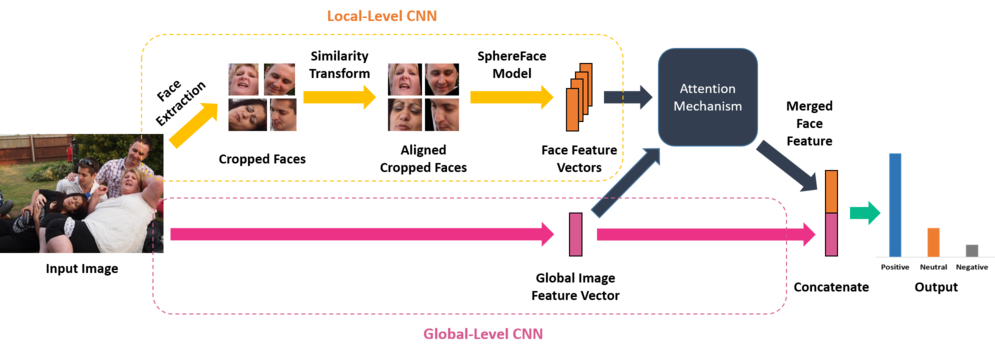
We propose an end-to-end model for jointly learning the scene and facial features of an image for group-level emotion recognition. An overview of the approach is presented in the following figure.
Our model is composed of two branches. The first branch is a global-level CNN that detects emotions on the basis of the image as a whole. The second is a local-level CNN that detects emotions on the basis of the faces present in the image. The content of each face is merged into a single representation by an attention mechanism. This single representation of the facial features is then concatenated with the image feature vector from the Global-Level CNN to build an end-to-end trainable model.
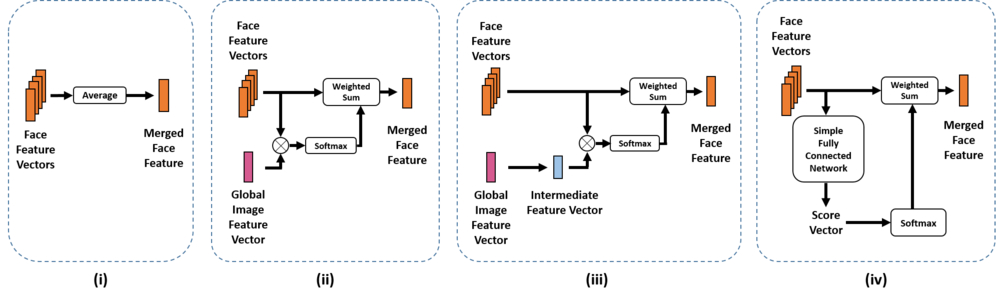
There are four different types of attention mechanisms that we use:
- Average Features
- Attention A: Global Image Feature Vector
- Attention B: Intermediate Feature Vector
- Attention C: Feature Score
The following figure gives an overview of the different attention mechanisms stated above.
More details of the model and our approach towards the challenge can be found in our short paper.
1.1. Corresponding Code for Models explained in Short Paper
| S. No. | Model in Paper | Code File in Repository |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Global_Simple | DenseNet161_emotiW |
| 2 | Global_EmotiC | Densenet_Emotiw_PretrainEmotiC_lr001 |
| 3 | Local | AlignedModel_EmotiW_lr01_Softmax |
| 4 | Local_FineTune | AlignedModelTrainerSoftmax_AlignedModel_EmotiW_lr01_Softmax |
| 5 | Local_FineTune_LSoftmax | AlignedModelTrainerLSoftmax_AlignedModel_EmotiW_lr001 |
| 6 | Average | PretrainedDenseNetAvgFaceFeatures_FineTune_2208_3_NoSoftmax |
| 7 | Attention_A | FaceAttention_AlignedModel_FullTrain_lr001_dropout_BN_SoftmaxLr01 |
| 8 | Attention_B | FaceAttention_AlignedModel_FullTrain_3para_lr001_dropout_BN_SoftmaxLr01 |
| 9 | Attention_B_EmotiC | FaceAttention_AlignedModel_FullTrain_3para_lr001_dropout_BN_SoftmaxLr01_EmotiC |
| 10 | Attention_C | FaceAttention_AlignedModel_FullTrain_4para_lr01_dropout_BN_SoftmaxLr01 |
| 11 | Attention_C_EmotiC | FaceAttention_AlignedModel_FullTrain_4para_lr001_dropout_BN_SoftmaxLr01_EmotiC |
For our best performing model, we use an ensemble of the 14 models defined in the repository.
2. Setup Instructions and Dependencies
You may setup the repository on your local machine by either downloading it or running the following line on cmd prompt.
git clone https://github.com/vlgiitr/Group-Level-Emotion-Recognition.git
Due to the large sizes of Dataset and TrainedModels, they have been stored on Google Drive. You may go to the Google Drive links given in the respective folders to download them.
The following dependencies are required by the repository:
- PyTorch v0.4
- TorchVision v0.2.1
- NumPy
- SciPy
- Scikit-Learn
- Matplotlib
- PIL
- Pickle
3. Repository Overview
The repository has the following directories and files:
-
Dataset: Contains various datasets used in the model.
-
Ensemble_Models: This contains code for the following:
- saving outputs of the models.
- evaluation of ensemble models using the saved outputs. Two kinds of ensembles are present:
- Weights of models in ensemble determined by handpicking.
- Weights of models in ensemble selected by SVM.
-
MTCNN: This contains iPython Notebooks for extracting individual face features and images using the MTCNN face detection model.
-
ModelOutputs: This contains
.npzfiles containing the outputs of all the models. -
Models_FullTrained: This contains the code for models trained on both the
trainandVALsubset ofemotiwdataset. -
Models_TrainDataset: This contains the code for models trained only on the
trainsubset ofemotiwdataset. -
TrainedModels: This contains pretrained checkpoints of the models used.
-
AlignedFaces_Extractor_Train.ipynbandAlignedFaces_Extractor_Test.ipynbcontains code to apply similarity transform to faces extracted from images using MTCNN model. -
Calculator_NumberOfFaces.ipynbcontains code to find the number of faces covering a certain percentage ofemotiwdataset. -
GlobalCNN_DenseNet161_EmotiC_lr001.pyis code for the Global DenseNet-161 model trained on the EmotiC dataset.
4. Dataset Folder Overview
The Dataset folder contains the following datasets:
-
AlignedCroppedImages: This contains
.jpgimage files of aligned faces corresponding to each image in theemotiwdataset.- It is generated from
CroppedFacesdataset usingAlignedFaces_Extractor_Train.ipynbandAlignedFaces_Extractor_Test.ipynb.
- It is generated from
-
CroppedFaces: This contains
.npzfiles for each image corresponding to theemotiwdataset.-
It is generated from
emotiwandFaceCoordinatesdataset usingFace_Cropper_TestDataset.ipynbandFace_Cropper_TrainValDataset.ipynb. -
Each
.npzfile contains the following:- a: This contains a list of the faces in the image in rgb array form
- b: This contains landmark coordinates for the corresponding faces.
-
-
emotic: This contains the EmotiC dataset used for pretraining the models.
- Images may be downloaded from here.
-
train_annotations.npzandval_annotations.npzcontain the following data:- image: list of image names in training subset or validation subset (corresponding to file).
-
folder: list of folder names corresponding to each image in
imagelist. - valence: list of valence scores corresponding to each image in 'image' list.
-
emotiw: This is the EmotiW 2018 Group-Level Emotion Recognition Dataset.
-
FaceCoordinates: This contains
.npzfiles for each image corresponding to theemotiwdataset.- It is generated from
emotiwdataset usingMTCNN/Face_Extractor_BB_Landmarks_Test.ipynbandMTCNN/Face_Extractor_BB_Landmarks_Train.ipynb. These files extract faces using MTCNN model. - Each
.npzfile contains the following:- a: This contains a list of bounding boxes coordinates of the faces present in an image.
- b: This contains landmark coordinates for the corresponding faces.
- It is generated from
-
FaceFeatures: This contains
.npzfiles for each image corresponding to theemotiwdataset.- It is generated from
emotidataset usingFace_Extractor_Feature_Test.pyandFace_Extractor_Feature_Train.ipynb. These files extract feature vector of faces in an image using MTCNN. - Each
.npzfile contains the following:- a: This contains a list of 256-dimensional facial features of faces in the corresponding image extracted from the last layer of MTCNN.
- It is generated from
-
Removed_EmotiW: This contains images removed from the
emotiwdataset as they were not detected properly by the MTCNN model. -
test_list: This contains a list of images from the
emotiwdataset to be used as EVAL dataset (as mentioned in paper). -
val_list: This contains a list of images from the
emotiwdataset to be used as VAL dataset (as mentioned in paper).
5. Credits
- The implementation of the MTCNN model has been adapted from this repository.
- The implementation of the SphereFace model (used in aligned models) has been adapted from this repository.
- We have used the EmotiW 2018 Group-Level Emotion Recognition Challenge dataset (given in
Dataset/emotiw), cited here:
@INPROCEEDINGS{7163151,
author={A. Dhall and J. Joshi and K. Sikka and R. Goecke and N. Sebe},
booktitle={2015 11th IEEE International Conference and Workshops on Automatic Face and Gesture Recognition (FG)},
title={The more the merrier: Analysing the affect of a group of people in images},
year={2015},
volume={1},
number={},
pages={1-8},
keywords={emotion recognition;learning (artificial intelligence);social networking (online);automatic affect analysis;emotion labelled database;mood display;multiple kernel learning based hybrid affect inference model;scene context based affect inference model;social media;Computational modeling;Context;Databases;Gold;Kernel;Mood;Videos},
doi={10.1109/FG.2015.7163151},
ISSN={},
month={May},}
6. Guidelines for Contributors
6.1. Reporting Bugs and Opening Issues
If you'd like to report a bug or open an issue then please:
Check if there is an existing issue. If there is then please add any more information that you have, or give it a 👍.
When submitting an issue please describe the issue as clearly as possible, including how to reproduce the bug. If you can include a screenshot of the issues, that would be helpful.
6.2. Pull Requests
Please first discuss the change you wish to make via an issue.
We don't have a set format for Pull Requests, but expect you to list changes, bugs generated and other relevant things in the PR message.
7. License
This repository is licensed under MIT license.