radixdb
RadixDB is a key-value static (read-only) database that provides fast lookups and "longest matching" operation.
Overview
This library provides a C99 implementation of the PATRICIA Trie for NUL terminated strings. Each node store a bit position and two children. The position is the next bit location in which two members differ. For a given set of elements there is an unique tree that satisfies the given conditions, so the structure does not need complex balancing algorithms. The depth tree is bounded by the length of the longest element, rather than the number of elements (as with an unbalanced tree). This implementation does not use external nodes, so data is found, while traversing the tree, at a node where the parent node has a bit position which is equal or greater than the node bit position.
The implementation uses 3 control words of 32-bit each (bit position then left and right children), followed by the key length and the value length in bytes also in 32-bit words, then the key and the value. With this configuration the overhead of each key-value pair added to the tree is 20 bytes (5 words of 32-bits).
It provides the following:
- O(k) operations. In some cases, this can be faster than a hash table.
- Optimized largest prefix match operation.
This implementation does not support deletion, as it was conceived for usage in large read-only databases.
Build
$ make
This will generate six binary files: radixdbmk, radixdbget, radixdbmatch,
radixdbdump, radixdbstats and radixdb2dot.
The radixdbmk program
In order to generate a radixdb file, do:
$ ./radixdbmk < f > f.radixdb
A record is encoded for radixdbmk as +klen,dlen:key->data followed by a
newline. Here klen is the number of bytes in key and dlen is the number
of bytes in data. The end of data is indicated by an extra newline. For
example:
+3,5:one->Hello
+3,7:two->Goodbye
Keys and data do not have to fit into memory, but radixdbmk needs at least 20
bytes of memory per record. A database cannot exceed 4 gigabytes.
f is portable across machines.
The radixdbget program
$ ./radixdbget f.radixdb k
radixdbget searches for a record with key k in a constant database
f.radixdb. The constant database must be readable.
Normally radixdbget prints the data with key k and exits 0. If there is no
record with the key k, radixdbget exits 2.
If radixdbget encounters a read error, write error, or database format error,
it complains and exits 1.
The radixdbmatch program
$ ./radixdbmatch f.radixdb k
radixdbmatch searches for the longest prefix available in the constant
database f.radixdb matching k, in the format +klen,dlen:key->data.
Say f.radixdb has the following:
+4,1:roma->1
+7,1:romanus->2
Then, the following are true:
$ ./radixdbmatch f.radixdb romae
+4,1:roma->1
$ ./radixdbmatch f.radixdb romanuseos
+7,1:romanus->2
The radixdbdump program
$ ./radixdbdump f.radixdb
radixdbdump reverses the operation performed by radixdbmk. The order of
the database records is preserved.
The radixdbstats program
$ ./radixdbstats f.radixdb
radixdbstats shows useful statistics about the database records contained in
the constant database f.radixdb. Example:
number of records: 11
key min/avg/max length: 2/4/4
val min/avg/max length: 8/9/9
max depth: 4
max bit depth: 30
The key and value lengths are given in bytes, whereas the max bit depth is given in bits. In the example above, the created trie can reach any leaf by checking a max of 4 bits, up to the 30th bit of the input key.
The radixdb2dot program
$ ./radixdb2dot f.radixdb | dot -Tpng -of.png
radixdb2dot dumps the database in a format recognized by the Graphviz dot
tool. This tool has informational/academic/toy purposes, and does not perform
well on very long databases.
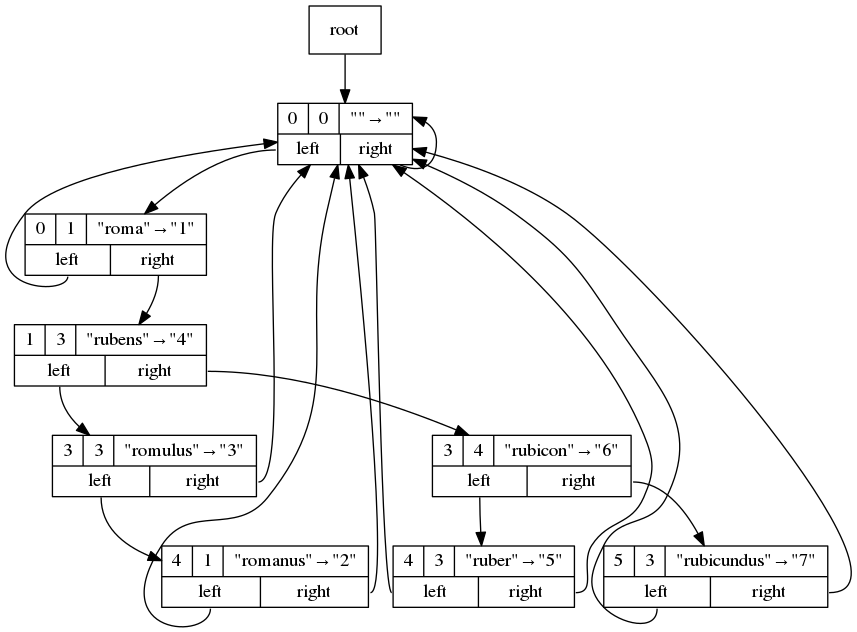
Here's a toy example:
On each record, you will find:
- First line:
- 1st field: bit position, byte index
- 2nd field: bit position, bit index
- 3rd field: key -> value
- Second line:
- Left and right pointers
Note the format above is not how the code has been implemented internally, but
a way to ease the visualization. Particularly, the 1st and 2nd field
represented in each record are stored as a single 32-bit integer
(byte index * 8 + bit index).
Have fun!