seahorn / Sea Dsa
Projects that are alternatives of or similar to Sea Dsa
SeaDsa: A Points-to Analysis for Verification of Low-level C/C++
SeaDsa is a context-, field-, and array-sensitive unification-based
points-to analysis for LLVM bitcode inspired
by DSA.
SeaDsa is an order of magnitude more scalable and precise than Dsa
and a previous implementation of SeaDsa thanks to improved handling
of context sensitivity, addition of partial flow-sensitivity, and type-awareness.
Although SeaDsa can analyze arbitrary LLVM bitcode, it has been
tailored for use in program verification of C/C++ programs. It can be
used as a stand-alone tool or together with
the SeaHorn
verification framework and its analyses.
Requirements
SeaDsa is written in C++ and uses the Boost library. The main requirements
are:
- C++ compiler supporting c++11
- Boost >= 1.55
- LLVM 5.0
To run tests, install the following packages:
sudo pip install lit OutputChecksudo easy_install networkxsudo apt-get install libgraphviz-devsudo easy_install pygraphviz
Project Structure
- The main Points-To Graph data structures,
Graph,Cell, andNode, are defined ininclude/Graph.hhandsrc/Graph.cc. - The Local analysis is in
include/Local.hhandsrc/DsaLocal.cc. - The Bottom-Up analysis is in
include/BottomUp.hhandsrc/DsaBottomUp.cc. - The Top-Down analysis is in
include/TopDown.hhandsrc/DsaTopDown.cc. - The interprocedural node cloner is in
include/Cloner.hhandsrc/Clonner.cc. - Type handling code is in
include/FieldType.hh,include/TypeUtils.hh,src/FieldType.cc, andsrc/TypeUtils.cc. - The allocator function discovery is in
include/AllocWrapInfo.hhandsrc/AllocWrapInfo.cc.
Compilation and Usage
Program Verification benchmarks
Instructions on running program verification benchmarks, together with recipes for building real-world projects and our results, can be found in tea-dsa-extras.
Integration in other C++ projects (for users)
SeaDsa contains two directories: include and src. Since SeaDsa
analyzes LLVM bitcode, LLVM header files and libraries must be
accessible when building with SeaDsa.
If your project uses cmake then you just need to add in your
project's CMakeLists.txt:
include_directories(sea_dsa/include)
add_subdirectory(sea_dsa)
Standalone (for developers)
If you already installed llvm-5.0 on your machine:
mkdir build && cd build
cmake -DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=run -DLLVM_DIR=__here_llvm-5.0__/share/llvm/cmake ..
cmake --build . --target install
Otherwise:
mkdir build && cd build
cmake -DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=run ..
cmake --build . --target install
To run tests:
cmake --build . --target test-sea-dsa
Visualizing Memory Graphs and Complete Call Graphs
Consider a C program called tests/c/simple.c:
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef struct S {
int** x;
int** y;
} S;
int g;
int main(int argc, char** argv){
S s1, s2;
int* p1 = (int*) malloc(sizeof(int));
int* q1 = (int*) malloc(sizeof(int));
s1.x = &p1;
s1.y = &q1;
*(s1.x) = &g;
return 0;
}
-
Generate bitcode:
clang -O0 -c -emit-llvm -S tests/c/simple.c -o simple.ll
The option -O0 is used to disable clang optimizations. In general,
it is a good idea to enable clang optimizations. However, for trivial
examples like simple.c, clang simplifies too much so nothing useful
would be observed. The options -c -emit-llvm -S generate bitcode in
human-readable format.
-
Run
sea-dsaon the bitcode and print memory graphs to dot format:seadsa -sea-dsa=butd-cs -sea-dsa-type-aware -sea-dsa-dot simple.ll
The options -sea-dsa=butd-cs -sea-dsa-type-aware enable the analysis
implemented in our FMCAD'19 paper (see References). This command will
generate a FUN.mem.dot file for each function FUN in the bitcode
program. In our case, the only function is main and thus, there is
one file named main.mem.dot. The file is generated in the current
directory. If you want to store the .dot files in a different
directory DIR then add the option -sea-dsa-dot-outdir=DIR
-
Visualize
main.mem.dotby transforming it to apdffile:dot -Tpdf main.mem.dot -o main.mem.pdf open main.mem.pdf // replace with you favorite pdf viewer
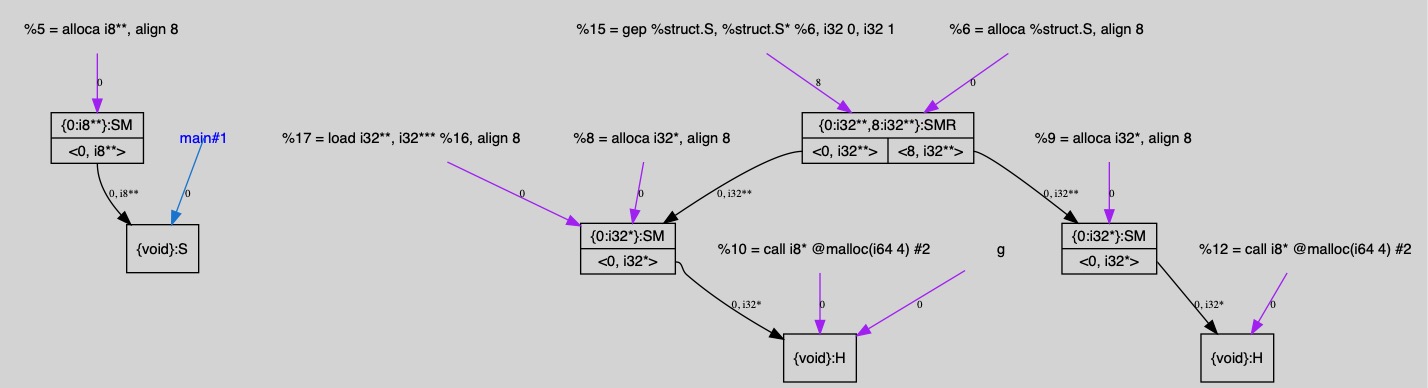
In our memory model, a pointer is represented by a cell which is a pair of a memory object and offset. Memory objects are represented as nodes in the memory graph. Edges are between cells.
Each node field represents a cell (i.e., an offset in the node). For
instance, the node fields <0,i32**> and <8,i32**> pointed by %6
and %15, respectively are two different cells from the same memory
object. The field <8,i32**> represents the cell at offset 8 in the
corresponding memory object and its type is i32**. Since edges are
between cells, they are labeled with a number that represents the
offset in the destination node. Blue edges connect formal parameters
of the function with a cell. Purple edges connect LLVM pointer
variables with cells. Nodes can have markers such as S (stack
allocated memory), H (heap allocate memory), M (modified memory),
R (read memory), E (externally allocated memory), etc. If a node
is red then it means that the analysis lost field sensitivity for that
node. The label {void} is used to denote that the node has been
allocated but it has not been used by the program.
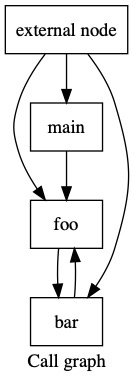
sea-dsa can also resolve indirect calls. An indirect call is a
call where the callee is not known statically. sea-dsa identifies
all possible callees of an indirect call and generates a LLVM call
graph as output.
Consider this example in tests/c/complete_callgraph_5.c:
struct class_t;
typedef int (*FN_PTR)(struct class_t *, int);
typedef struct class_t {
FN_PTR m_foo;
FN_PTR m_bar;
} class_t;
int foo(class_t *self, int x)
{
if (x > 10) {
return self->m_bar(self, x + 1);
} else
return x;
}
int bar (class_t *self, int y) {
if (y < 100) {
return y + self->m_foo(self, 10);
} else
return y - 5;
}
int main(void) {
class_t obj;
obj.m_foo = &foo;
obj.m_bar = &bar;
int res;
res = obj.m_foo(&obj, 42);
return 0;
}
Type the commands:
clang -c -emit-llvm -S tests/c/complete_callgraph_5.c -o ex.ll
sea-dsa --sea-dsa-callgraph-dot ex.ll
It generates a .dot file called callgraph.dot in the current
directory. Again, the .dot file can be converted to a .pdf file
and opened with the commands:
dot -Tpdf callgraph.dot -o callgraph.pdf
open callgraph.pdf
sea-dsa can also print some statistics about the call graph
resolution process (note that you need to call clang with -g to
print file,line, and column information):
sea-dsa --sea-dsa-callgraph-stats ex.ll
=== Sea-Dsa CallGraph Statistics ===
** Total number of indirect calls 0
** Total number of resolved indirect calls 3
%16 = call i32 %12(%struct.class_t* %13, i32 %15) at tests/c/complete_callgraph_5.c:14:12
RESOLVED
Callees:
i32 bar(%struct.class_t*,i32)
%15 = call i32 %13(%struct.class_t* %14, i32 10) at tests/c/complete_callgraph_5.c:23:16
RESOLVED
Callees:
i32 foo(%struct.class_t*,i32)
%11 = call i32 %10(%struct.class_t* %2, i32 42) at tests/c/complete_callgraph_5.c:36:9
RESOLVED
Callees:
i32 foo(%struct.class_t*,i32)
Dealing with C/C++ library and external calls
The pointer semantics of external calls can be defined by writing a
wrapper that calls any of these functions defined in
sea_dsa/sea_dsa.h:
extern void sea_dsa_alias(const void *p, ...);extern void sea_dsa_collapse(const void *p);extern void sea_dsa_mk_seq(const void *p, unsigned sz);
sea_dsa_alias unifies all argument's cells, sea_dsa_collapse tells
sea-dsa to collapse (i.e., loss of field-sensitivity) the cell
pointed by p, and sea_dsa_mk_seq tells sea-dsa to mark as
sequence the node pointed by p with size sz.
For instance, consider an external call foo defined as follows:
extern void* foo(const void*p1, void *p2, void *p3);
Suppose that the returned pointer should be unified to p2 but not to
p1. In addition, we would like to collapse the cell corresponding to
p3. Then, we can replace the above prototype of foo with the
following definition:
#include "sea_dsa/sea_dsa.h"
void* foo(const void*p1, void *p2, void*p3) {
void* r = sea_dsa_new();
sea_dsa_alias(r,p2);
sea_dsa_collapse(p3);
return r;
}