ShawnyXiao / Springboot Mybatis
Programming Languages
Projects that are alternatives of or similar to Springboot Mybatis
SpringBoot-MyBatis
最近由于实训,发现很多同学都在开发 Java 后台,因此少不了重复繁杂的配置工作,这个框架就是为了减少这些不必要的工作。它集成了 Spring Boot 和 MyBatis(后期我又集成了 Spring Security OAuth 以支持 OAuth 2.0),并实现了一个类似“书籍管理”的模块(支持 RESTful API)以供参考,框架简单易懂。完全可以根据自己的需要,修改这个框架,以实现自己想实现的功能。
向导
启动
注意:你需要确保你的系统上已安装了 Git 和 Maven(也就是在命令行窗口中键入 git 或 mvn 后,能有非错误性的提示),否则接下来的步骤将无法进行。
首先,你应该要将这个代码库克隆到你的磁盘上,并进入此目录。启动命令行窗口,键入:
git clone https://github.com/ShawnyXiao/SpringBoot-MyBatis.git
cd SpringBoot-MyBatis
然后,启动应用(初次启动的话,这个过程会需要稍微久一点的时间)。在命令行窗口中键入:
mvn spring-boot:run
此时,你可以尝试发出一个 HTTP 请求。例如,利用浏览器向你的 Web 应用发出一个 HTTP GET 请求,在地址栏键入:
http://localhost:8080/books/1
你将会看到,你的 Web 应用通过 JSON 字符串来做出响应:
{
"id": 1,
"name": "社会研究方法教程",
"author": "袁方",
"price": 68,
"topic": "社会学",
"publishDate": 1425139200000,
"bookStoreId": 1
}
技术
- Spring Boot
- MyBatis
- Spring Security OAuth
- MySQL or HSQLDB (a in-memory database)
- Maven
- Commons Logging
- Java 8 Lambda Expressions
- Lombok
- Apache Commons Lang
- Apache Commons Collection4
细节
这个项目其实有点像一个 Demo 项目。我没有将 Spring Boot、MyBatis 和其他框架提供的功能再封装一层(虽然可以这样做),以提供更加应用级的接口。这是因为我觉得这些框架已经提供了很好的封装度和灵活度,完全只需要“掌控”他们,再“利用”他们,你就能实现你想要的。既然是一个 Demo 项目,所以对于初学者,还是有必要讲解一下其中的“门道”。对于我个人来说,这一个部分就有点像在回忆:“我当时怎么做的,为什么这样做”。(顺序有点乱,请根据需要阅读)
文件目录
`-- src
|-- main
| |-- java
| | `-- com
| | `-- shawn
| | |-- constant
| | |-- model
| | | |-- dto
| | | `-- entity
| | |-- monitor
| | |-- repository
| | | `-- mybatis
| | |-- service
| | | `-- impl
| | |-- security
| | |-- util
| | `-- web
| | |-- controller
| | |-- excetpion
| | `-- filter
| `-- resources
| |-- com
| | `-- shawn
| | `-- repository
| | `-- mybatis
| `-- db
| `-- hsqldb
`-- test
`-- ...(& so on)
-
src/main/java/com/shawn/constant: 该目录放置了各种常量类 -
src/main/java/com/shawn/model: 该目录放置了各种模型类,其子目录 dto 放置了 DTO(Data Trasfer Object)类,其另一子目录 entity 放置了实体类 -
src/main/java/com/shawn/monitor: 该目录放置了各种监测类 -
src/main/java/com/shawn/repository: 该目录放置了数据库增删改查的接口,其子目录 impl 放置了这些接口的实现类 -
src/main/java/com/shawn/service: 该目录下放置服务(一个服务对应于一些业务逻辑的集合)的接口,其子目录 impl 放置了这些接口的实现类 -
src/main/java/com/shawn/security: 该目录放置了 Spring Security OAuth 的相关配置 -
src/main/java/com/shawn/util: 该目录放置了各种工具类 -
src/main/java/com/shawn/web: 该目录放置了和网络层相关的一切,包括控制器、异常处理、过滤器等等 -
src/main/resources/com/shawn/repository/mybatis: 该目录放置了 MyBatis 的映射器 XML 文件 -
src/main/resources/db: 该目录放置了有关内存数据库的脚本,其子目录 hsqldb 放置了 HSQL 的数据库脚本
架构
为了节约时间就不谈架构的重要性了,那我们先把关注点放在 Web 应用的职责上(Web 应用应该做些什么):
- 它应该能够处理用户的输入,并且返回正确的相应给用户
- 它应该拥有一套异常处理机制,来应对错误发生的时候
- 它应该拥有一个事务管理策略
- 它应该能够对用户进行认证和授权
- 它应该要实现业务逻辑,为用户提供服务
- 它应该要能操纵数据库和其他资源
- ……
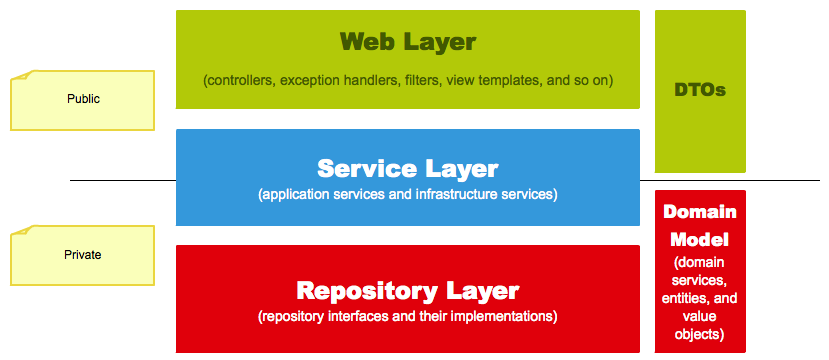
那么,怎样才能,既实现这些职责,又达到低耦合高内聚(提供一定的封装度和灵活度)的要求?三层架构可以支持这一切,它的概览如下图所示:
- Web层:Web 应用的最顶层。它负责处理用户输入以及返回正确的相应给用户;处理其他层抛出的异常并向用户反映错误的发生;对用户进行认证,拒绝未认证的用户访问。
- Service层:Web 应用的中间层。它应该组织业务逻辑,为 Web 层提供服务;使得所有服务都是事务性的(要么完成,要么什么都没做);负责用户的授权。
- Repository层:Web 应用的最底层。它负责操纵数据库,以实现对数据库的增删改查。
那么,这三层的组件要如何交互呢?最佳实践是:上层组件使用下层组件,使用模型(Model)作为交互媒介。模型包括两种:数据传输对象(DTO)和领域模型(Domain Model)。
- DTO: 一种用户可见的数据容器。它用来传输用户可见的数据,屏蔽了 Web 应用的内部实现。
- Domain Model: 具有领域特征的数据容器。一般来说,它对应于数据库中的表,它代表了 Web 应用的内部实现,应该对用户透明。
Lombok
一直以来,都觉得 POJO 类里面的 get、set 方法使得代码显得非常臃肿,不像 C# 里从语言层面支持了 get 访问器和 set 访问器。那么在 Java 中有没有类似可以消除这样冗余代码的技巧呢?答案就是 Lombok。Lombok 提供了简单的注解的形式来帮助我们简化消除一些必须有但显得很臃肿的 Java 代码。举个例子:
不使用 Lombok:
public class BookStore {
private long id;
private String name;
private String address;
public BookStore() {
}
public long getId() {
return id;
}
public BookStore setId(long id) {
this.id = id;
return this;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public BookStore setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
return this;
}
public String getAddress() {
return address;
}
public BookStore setAddress(String address) {
this.address = address;
return this;
}
}
使用 Lombok:
import lombok.Getter;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Setter;
import lombok.experimental.Accessors;
@Accessors(chain = true)
@NoArgsConstructor
@Getter
@Setter
public class BookStore {
private long id;
private String name;
private String address;
}
在本项目中使用的 Lombok 注解有:
@Accessors@NoArgsConstructor@Getter@Setter@ToString@CommonsLog
日志记录
曾经,我一直使用控制台输出(也就是 System.out.println)来让我的程序告诉我它在编译期和运行期做了些什么。这样的确是简单,但是往往伴随着显著的劣势。举两个例子:
- 在开发环境中,我想看到调试的信息,但在生产环境中,我并不想看到任何调试信息
- 我想将所有信息输出到一个文件,以便我有空了就打开这个文件,看下哪里出错了
上面的两个例子足以显示使用控制台输出是无法满足我们的需求的,那么怎样做才是最佳实践呢?答案就是使用日志框架。日志框架为我们提供了日志开关、日志级别配置、日志格式配置等等,带来了适度的灵活性和封装性。引用前面说过的一句话:只需要“掌控”他们,再“利用”他们,你就能实现你想要的。
本项目使用了 Spring Boot 默认提供的 Commons Logging。对于一切想要记录日志的类,只需要在它的头上使用 Lombok 提供的注解 @CommonsLog,便能使用日志记录功能了。举个例子:
@CommonsLog
public class XxxClass {
public void XxxMethod() {
log.info("This is an info log.");
log.error("This is an error log.");
}
}
这段代码会产生怎样的效果呢?效果如下:
2017-01-01 13:35:52.698 INFO 13184 --- [nio-8080-exec-1] com.shawn.xxx.XxxClass : This is an info log.
2017-01-01 13:35:52.738 ERROR 13184 --- [nio-8080-exec-1] com.shawn.xxx.XxxClass : This is an error log.
本项目对日志记录的有效配置全部位于 src/main/resources/application.properties 下,包括日志级别的配置、输出到日志文件的配置等等,如下:
...
### Logging ###
# Log levels (TRACE, DEBUG, INFO, WARN, ERROR, FATAL, OFF)
logging.level.root=INFO
logging.level.org.springframework=INFO
logging.level.org.springframework.web=INFO
logging.level.org.mybatis=INFO
logging.level.com.shawn=DEBUG
# File output
project.name=SpringBoot-Mybatis
logging.file=/${project.name}/logs/SpringBoot-Mybatis.log
...
记录日志只是有效地利用日志的第一步,更重要的是如何对程序运行时产生的日志进行处理和分析。这样的处理和分析的能力对于实际系统的维护尤其重要。典型的场景包括:
- 当日志中包含满足特定条件的记录时,触发相应的通知机制,比如邮件或短信通知
- 在程序运行出现错误时,快速定位潜在的问题源
性能监控
大概5个月之前,我参与的一个项目中存在了一个严重的性能问题,但是在开发和测试过程中并没有人发现这个问题,而是系统上线后,客户发现并提出,导致这个性能问题造成了严重的后果。因此,非常有必要对开发、测试以及上线的系统进行性能监控,及时做出补救措施,以造成不必要的后果。
那么,我们到底应该监控什么呢,或者说性能到底是什么呢?对于 Web 应用来说,性能就是 Web 系统采取某个动作(动作也就是 Web 系统对每个请求所执行的操作的集合)所消耗的时间。了解到我们应该监控 Web 系统的每个动作,那么更进一步,怎么才能监控每个动作呢?本项目采用的是 Spring AOP 技术。三个步骤如下:
- 使用
@Aspect注解声明一个切面(Aspect)。如下:
@Aspect
public class XxxAspect {
}
- 在切面中声明一个切入点(Pointcut),切入点声明包含两个部分:一个包含名字和任意参数的签名;一个切入点表达式,该表达式决定了我们关注哪个方法的执行。如下:
@Pointcut("execution(* xxxMethod(..))") // 切入点表达式
private void monitorXxxMethod() {} // 切入点签名
- 在切面中声明通知(Advice)。举一个声明环绕通知的例子:
@Around("monitorXxxMethod") // 使用了第二点中申明的切入点
public Object doSomething(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable {
// 在方法执行前,做某些操作
Object retVal = pjp.proceed();
// 在方法执行后,做某些操作
return retVal;
}
根据上述三个步骤,在本项目中,性能监测代码是这样的:
@CommonsLog
@Aspect
@Component
public class PerformanceMonitor {
/**
* A join point is in the controller layer if the method is
* modified by public and defined in a type in the
* com.shawn.service package or any sub-package under that
* and modified by public.
*/
@Pointcut("execution(public * com.shawn.web.controller..*(..))")
private void controllerLayer() {
}
/**
* Monitor the elapsed time of method on controller layer, in
* order to detect performance problems as soon as possible.
* If elapsed time > 1 s, log it as an error. Otherwise, log it
* as an info.
*/
@Around("controllerLayer()")
public Object monitorElapsedTime(ProceedingJoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint) throws Throwable {
// Timing the method in controller layer
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
stopWatch.start();
Object result = proceedingJoinPoint.proceed();
stopWatch.stop();
// Log the elapsed time
double elapsedTime = stopWatch.getTime() / 1000;
Signature signature = proceedingJoinPoint.getSignature();
String infoString = "[" + signature.toShortString() + "][Elapsed time: " + elapsedTime + " s]";
if (elapsedTime > 1) {
log.error(infoString + "[Note that it's time consuming!]");
} else {
log.info(infoString);
}
// Return the result
return result;
}
}
因此,系统每执行一个动作(也就是,每响应一个请求所执行的操作),在日志上都会记录下它所消耗的时间,若超过1秒,则会以 error 级别记录日志。如下:
2017-01-03 22:58:19.431 ERROR 6384 --- [nio-8080-exec-9] com.shawn.monitor.PerformanceMonitor : [BookController.postBook(..)][Elapsed time: 1.457 s][Note that it's time consuming!]
2017-01-03 22:58:47.875 INFO 6384 --- [io-8080-exec-10] com.shawn.monitor.PerformanceMonitor : [BookController.getBooks(..)][Elapsed time: 0.656 s]
2017-01-03 22:59:16.356 INFO 6384 --- [nio-8080-exec-1] com.shawn.monitor.PerformanceMonitor : [BookController.putBook(..)][Elapsed time: 0.618 s]
2017-01-03 22:59:51.259 INFO 6384 --- [nio-8080-exec-3] com.shawn.monitor.PerformanceMonitor : [BookController.deleteBook(..)][Elapsed time: 0.016 s]
OAuth 2.0
为了使服务器的资源受到保护,也就是只让信任的客户端访问受保护的资源,本项目选择 Spring Security OAuth 来集成 OAuth 2.0 来保护我们服务器的资源。
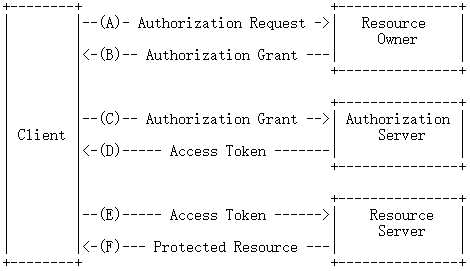
只有了解了 OAuth 2.0 的运行流程,我们才能正确的使用它。所以,首先,我们先来了解一下 OAuth 2.0 的运行流程。它的运行流程如下图,摘自 RFC 6749。
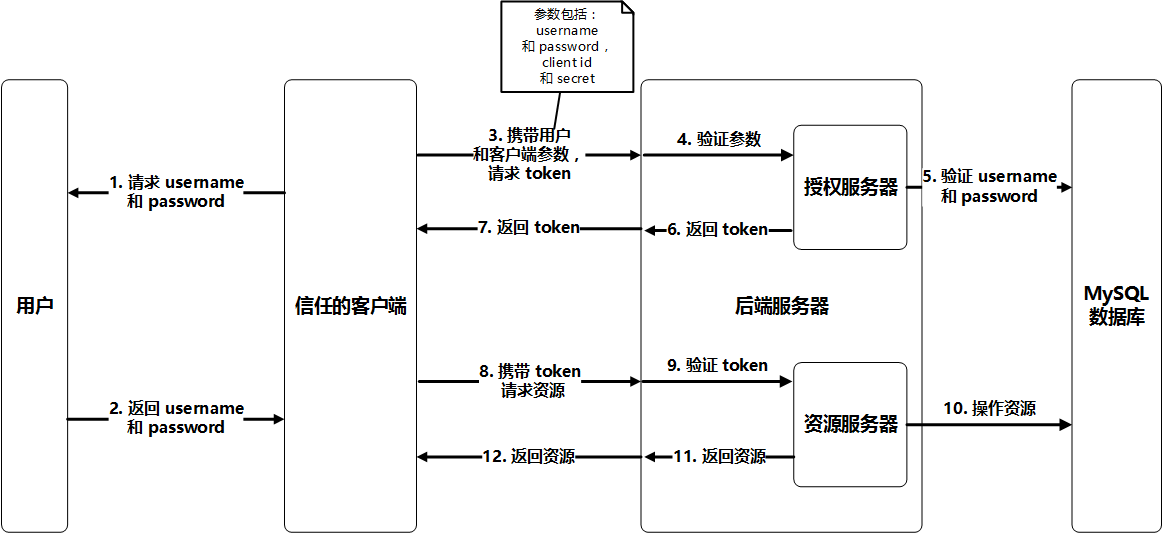
OAuth 2.0 有4种授权方式,分别是:授权码模式(authorization code),简化模式(implicit),密码模式(resource owner password credentials)和客户端模式(client credentials),本项目只采用密码模式。因此,基于上述流程以及密码授权模式,本项目做出了相应的定制,如下图:
既然清楚了运行流程,那么接下来要进行的是对 Spring Security OAuth 的配置,涉及到这些的类有:
-
com.shawn.model.dto.CustomUserDetails: 该类是一个模型类,实现了UserDetails接口。它主要负责传送用户的认证信息,包括:用户名, 密码, 该用户所拥有的权限等等 -
com.shawn.security.AuthorizationServerConfiguration: 该类是一个配置类,继承了AuthorizationServerConfigurerAdapter。它主要负责授权服务器的配置,包括:信任的客户端信息的管理、请求令牌的 URL 的配置、 令牌的管理、如何认证用户的配置、对于请求令牌的 URL 的安全约束的配置等等 -
com.shawn.security.ResourceServerConfiguration: 该类是一个配置类,继承了ResourceServerConfigurerAdapter。他主要负责资源服务器的配置,包括:对于请求资源的 URL 的安全约束的配置等等 -
com.shawn.security.WebSecurityConfiguration: 该类是一个配置类,继承了GlobalAuthenticationConfigurerAdapter。它主要负责有关认证的配置,包括:用户的认证信息的获取等等 -
com.shawn.service.UserService: 该类是一个服务类的接口,继承了UserDetailsService接口 -
com.shawn.service.impl.UserServiceImpl: 该类是UserService接口的实现类
有了这些配置,我们实现的效果是:
- 获取 book 资源(查)的请求一律不需要认证
- 对 book 资源进行修改的请求(增删改)需要认证
- 对 user 资源的所有请求(增删改查)都需要认证
使用途径
首先,我们尝试访问不需要认证的资源:
curl http://localhost:8080/books/1
正如我们所期待的,服务器返回了 ID 为 1 的 book 资源给客户端,如下:
{
"id": 1,
"name": "社会研究方法教程",
"author": "袁方",
"price": 68.0,
"topic": "社会学",
"publishDate": 1425139200000,
"bookStoreId": 1
}
接下来,我们尝试不带认证信息的访问需要认证的资源(尝试删除 ID 为 1 的 book):
curl http://localhost:8080/books/1 -X DELETE
我们收到如下的 JSON 字符串响应,告诉我们需要认证了才能访问这个资源:
{
"error": "unauthorized",
"error_description": "Full authentication is required to access this resource"
}
为了访问受保护的资源,我们需要先向授权服务器请求访问令牌(access token):
curl http://localhost:8080/oauth/token -X POST -u client:fucksecurity -d "grant_type=password&username=shawn&password=fucksecurity"
授权服务器验证了我们的客户端和用户信息,验证成功后将我们需要的令牌(token)信息作为响应传回:
{
"access_token": "ca741611-a30e-4504-b84e-fdf9cec0da9a",
"token_type": "bearer",
"refresh_token": "1a1fb46e-8ab4-4a3b-84c4-e70892eaa570",
"expires_in": 43199,
"scope": "read write"
}
接下来,我们可以使用上个请求返回的 access_token,操作受保护的资源:
curl http://localhost:8080/books/1 -X DELETE -H "Authorization: Bearer ca741611-a30e-4504-b84e-fdf9cec0da9a"
响应成功返回,为了验证 ID 为 1 的 book 确实被删除,我们尝试获取 ID 为 1 的 book 信息:
curl http://localhost:8080/books/1
响应的 HTTP 状态码为 404,并传回了以下 JSON 字符串,这说明 ID 为 1 的 book 确实已经被删除:
{
"code": 1003,
"message": "Book with id 1 is not found."
}
最后,随着时间(在本项目中是 43199 秒)的消逝,access_token 会过期。可以使用曾经请求访问令牌时返回的 refresh_token 来获取一个新的 access_token:
curl http://localhost:8080/oauth/token -X POST -u client:fucksecurity -d "grant_type=refresh_token&refresh_token=1a1fb46e-8ab4-4a3b-84c4-e70892eaa570"
Lambda 表达式
为了使代码可读性更强、更简洁,本项目大量的使用了 Lambda 表达式。为了体现 Lambda 表达式的优势,我们来看一下对比:
不使用 Lambda 表达式:
Runnable r = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run(){
System.out.println("I just want to tell you why to use lambda expressions.");
}
};
使用 Lambda 表达式:
Runnable r = () -> System.out.println("I just want to tell you why to use lambda expressions.");
所以接下来,我们一起来了解一下 Lambda 表达式语法和适用场景。
Lambda 表达式的语法
一个 Lambda 表达式包含以下几个组成部分:
-
一个逗号分隔,小括号包围的形参集合。你可以忽略参数的数据类型;如果只有一个参数,你还可以忽略小括号。
合法的例子:(int a, int b) (a, b) (int a) a ()不合法的例子:
(String a, b) (a, String b) int a -
一个箭头符号。
唯一合法的例子:->不合法的例子:
- > --> -< <- -
一个主体。要么是一个表达式,要么是一个由大括号包围语句块。如果 Lambda 表达式实现的是一个 void 方法,而且只有一条语句,那么可以忽略大括号。
合法的例子:a == b {return a == b;} {result = (a == b); return result;} System.out.println("Hello, world!")不合法的例子:
a == b; {return a == b}
现在讲上面3个部分组合起来,实现完整的 Lambda 表达式。例如:
(a, b) -> a == b
(int a, int b) -> {result = (a == b); return result;}
a -> {System.out.println(a);}
() -> System.out.println("Hello, world!")
哪类情况适合使用 Lambda 表达式
-
如果你想对某些变量做一些处理,而你又想降这些处理封装起来,那么你应该使用 Lambda 表达式。举个例子:当你想对一个集合的每一个元素做过滤处理的时候,你就应该使用 Lambda 表达式了。(下面的例子涉及一些 Stream API,这里只需要关注
filter()方法)double average = cars.stream() .filter(c -> c.isBMW() && c.isRed) .mapToDoule(c -> c.getSpeed()) .averge() .getAsDouble(); -
如果你只想要一个简单的函数式接口的实例(只想要实现函数式接口中的唯一的抽象方法),那么你应该使用 Lambda 表达式。举个例子:
button.setOnAction( event -> System.out.println("Hello World!") );
在本项目中,第一类情况大量的出现。例如,com.shawn.web.controller.BookController 中的一段代码:
...
@GetMapping("/{bookId}")
public ResponseEntity<?> getBookById(@PathVariable Long bookId) {
return bookService
.getBookById(bookId)
.map(ResponseEntity::ok)
.orElseThrow(() -> new ResourceNotFoundException()
.setResourceName(ResourceNameConstant.BOOK)
.setId(bookId));
}
...
未完待续……
引用
- Understanding Spring Web Application Architecture: The Classic Way
- MyBatis
- mybatis – MyBatis 3 | Mapper XML Files
- Mybatis关联查询一对一和一对多的实现 - 林炳文Evankaka的专栏 - 博客频道 - CSDN.NET
- Mybatis 鉴别器 - jordandandan的专栏 - 博客频道 - CSDN.NET
- Exception Handling in Spring MVC
- Spring Boot中Web应用的统一异常处理 | 程序猿DD
- java - Spring Boot REST service exception handling - Stack Overflow
- Getting Started · Managing Transactions
- HTTP Tutorial
- ResponseEntity (Spring Framework 4.3.4.RELEASE API)
- ServletUriComponentsBuilder (Spring Framework 4.3.4.RELEASE API)
- Optional (Java Platform SE 8 )
- Java 8 Optional类深度解析 - ImportNew
- Spring REST: Exception handling on a @Controller level
- Spring REST: Exception handling on a @ControllerAdvice level
- Spring REST: Exception handling on a @ControllerAdvice level
- Spring MVC中文翻译文档
- 22. Web MVC framework
- Spring Boot Reference Guide
- MIME 参考手册
- MIME - Wikipedia
- 多用途互联网邮件扩展 - 维基百科,自由的百科全书
- MIME协议分析 - 彭令鹏(bripengandre)的专栏 - 博客频道 - CSDN.NET
- Difference between CR LF, LF and CR line break types? - Stack Overflow
- Newline - Wikipedia
- http HEAD vs GET performance - Stack Overflow
- HTTP 缓存 | Web | Google Developers
- http - How to control web page caching, across all browsers? - Stack Overflow
- The BalusC Code: Webapplication performance tips and tricks
- Yahoo前端优化十四条军规 - 51CTO.COM
- Best Practices for Speeding Up Your Web Site - Yahoo Developer Network
- HTTP | MDN
- 解決問題的第一步: Authentication vs. Authorization
- Repositories | GitHub Developer Guide
- RESTful API 设计最佳实践 - 文章 - 伯乐在线
- Best Practices for Designing a Pragmatic RESTful API | Vinay Sahni
- POST /eff/you/this/is/the/right/url - RESTful API Design
- 418: I'm a teapot, and other bad API responses - RESTful API Design
- Error Handling: RESTful API Design Part III
- 11. Aspect Oriented Programming with Spring
- Chapter 6. 使用Spring进行面向切面编程(AOP)
- AOP with Spring Framework
- StopWatch (Apache Commons Lang 3.4 API)
- Java 日志管理最佳实践
- rest - RESTful Authentication - Stack Overflow
- 理解OAuth 2.0 - 阮一峰的网络日志
- RESTful authentication using Spring Security on Spring Boot, and jQuery as a web client – Codes And Notes
- Secure Spring REST API using OAuth2 - WebSystique
- royclarkson/spring-rest-service-oauth: A simple OAuth protected REST service built with Spring Boot and Spring Security OAuth
- Introduction | Spring Security 参考手册
- Tutorial · Building REST services with Spring
- 了解OAuth2.0
- Spring Security:结合 Spring-OAuth,支持 Mysql 数据库(基于SpringBoot) · Issue #59 · pzxwhc/MineKnowContainer
- Spring Security OAuth
- spring-security-oauth/tests/annotation/multi at master · spring-projects/spring-security-oauth
- Lambda Expressions (The Java™ Tutorials > Learning the Java Language > Classes and Objects)
- Java SE 8: Lambda Quick Start
- 如何选择开源许可证? - 阮一峰的网络日志