hall-lab / Svtyper
Programming Languages
Projects that are alternatives of or similar to Svtyper
SVTyper
Bayesian genotyper for structural variants
Overview
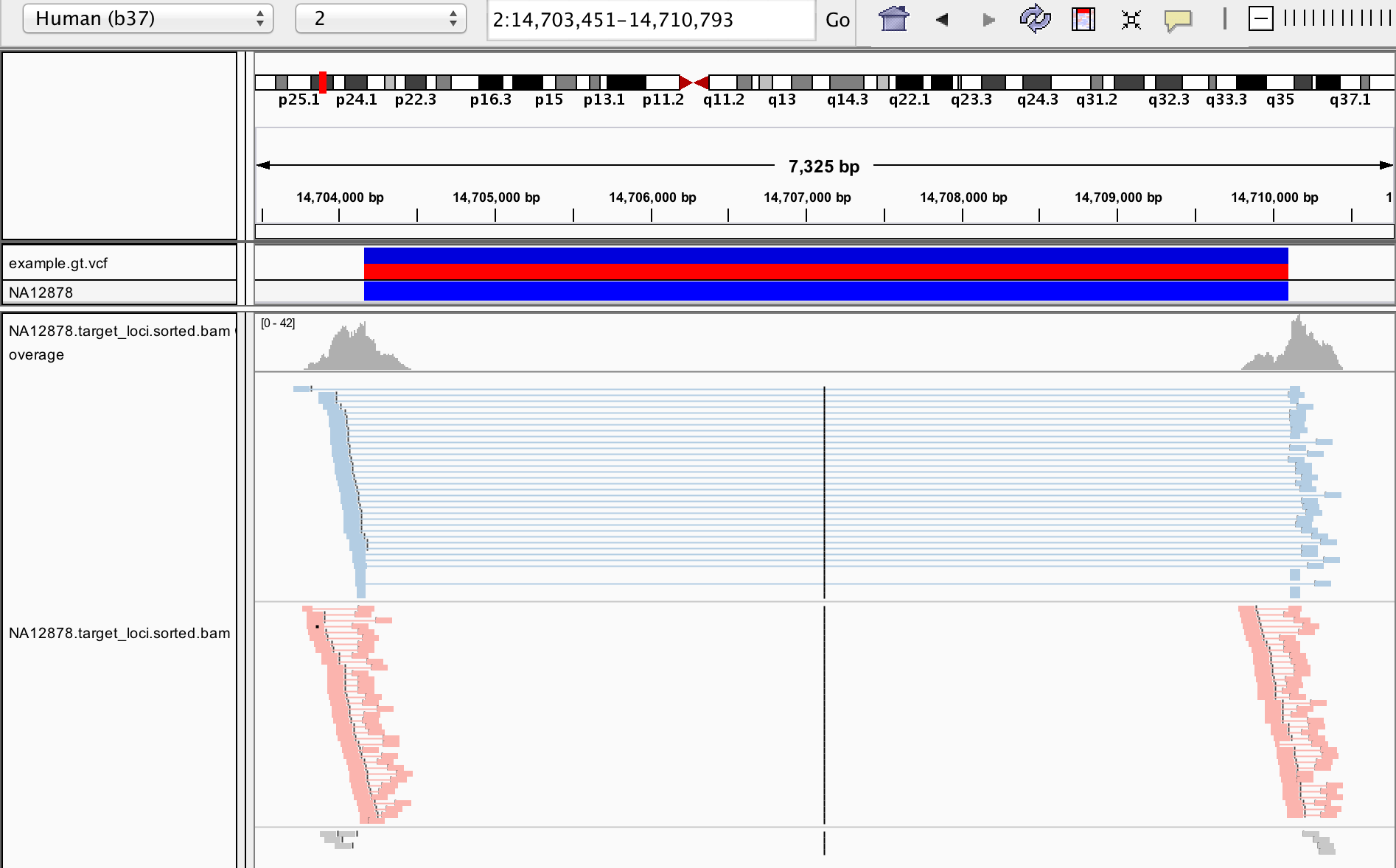
SVTyper performs breakpoint genotyping of structural variants (SVs) using whole genome sequencing data. Users must supply a VCF file of sites to genotype (which may be generated by LUMPY) as well as a BAM/CRAM file of Illumina paired-end reads aligned with BWA-MEM. SVTyper assesses discordant and concordant reads from paired-end and split-read alignments to infer genotypes at each site. Algorithm details and benchmarking are described in Chiang et al., 2015.
Installation
Requirements:
- Python 2.7.x
Install via pip
pip install git+https://github.com/hall-lab/svtyper.git
svtyper depends on pysam (version 0.15.0 or newer), numpy, and scipy; svtyper-sso additionally depends on cytoolz. If the dependencies aren't already available on your system, pip will attempt to download and install them.
svtyper vs svtyper-sso
svtyper is the original implementation of the genotyping algorithm, and works with multiple samples. svtyper-sso is an alternative implementation of svtyper that is optimized for genotyping a single sample. svtyper-sso is a parallelized implementation of svtyper that takes advantage of multiple CPU cores via the multiprocessing module. svtyper-sso can offer a 2x or more speedup (depending on how many CPU cores used) in genotyping a single sample. NOTE: svtyper-sso is not yet stable. There are minor logging differences between the two and svtyper-sso may exit with an error prematurely when processing CRAM files.
Example Usage
svtyper
As a Command Line Python Script
svtyper \
-i sv.vcf \
-B sample.bam \
-l sample.bam.json \
> sv.gt.vcf
As a Python Library
import svtyper.classic as svt
input_vcf = "/path/to/input.vcf"
input_bam = "/path/to/input.bam"
library_info = "/path/to/library_info.json"
output_vcf = "/path/to/output.vcf"
with open(input_vcf, "r") as inf, open(output_vcf, "w") as outf:
svt.sv_genotype(bam_string=input_bam,
vcf_in=inf,
vcf_out=outf,
min_aligned=20,
split_weight=1,
disc_weight=1,
num_samp=1000000,
lib_info_path=library_info,
debug=False,
alignment_outpath=None,
ref_fasta=None,
sum_quals=False,
max_reads=None)
# Results will be inside the /path/to/output.vcf file
svtyper-sso
As a Command Line Python Script
svtyper-sso \
--core 2 # number of cpu cores to use \
--batch_size 1000 # number of SVs to process in a single batch (default: 1000) \
--max_reads 1000 # skip genotyping if SV contains valid reads greater than this threshold (default: 1000) \
-i sv.vcf \
-B sample.bam \
-l sample.bam.json \
> sv.gt.vcf
As a Python Library
import svtyper.singlesample as sso
input_vcf = "/path/to/input.vcf"
input_bam = "/path/to/input.bam"
library_info = "/path/to/library_info.json"
output_vcf = "/path/to/output.vcf"
with open(input_vcf, "r") as inf, open(output_vcf, "w") as outf:
sso.sso_genotype(bam_string=input_bam,
vcf_in=inf,
vcf_out=outf,
min_aligned=20,
split_weight=1,
disc_weight=1,
num_samp=1000000,
lib_info_path=library_info,
debug=False,
alignment_outpath=None,
ref_fasta=None,
sum_quals=False,
max_reads=1000,
cores=2,
batch_size=1000)
# Results will be inside the /path/to/output.vcf file
Development
Requirements:
- Python 2.7 or newer
- GNU Make
- virtualenv (or conda for anaconda or miniconda users)
Setting Up a Development Environment
Using virtualenv
git clone https://github.com/hall-lab/svtyper.git
cd svtyper
virtualenv myvenv
source myvenv/bin/activate
pip install -e .
<add, edit, or delete code>
make test
# when you're finished with development
git push <remote-name> <branch>
deactivate
cd .. && rm -rf svtyper
Using conda
git clone https://github.com/hall-lab/svtyper.git
cd svtyper
conda create --channel bioconda --name mycenv pysam numpy scipy cytoolz # type 'y' when prompted with "proceed ([y]/n)?"
source activate mycenv
pip install -e .
<add, edit, or delete code>
make test
# when you're finished with development
git push <remote-name> <branch>
source deactivate
cd .. && rm -rf svtyper
conda remove --name mycenv --all
Troubleshooting
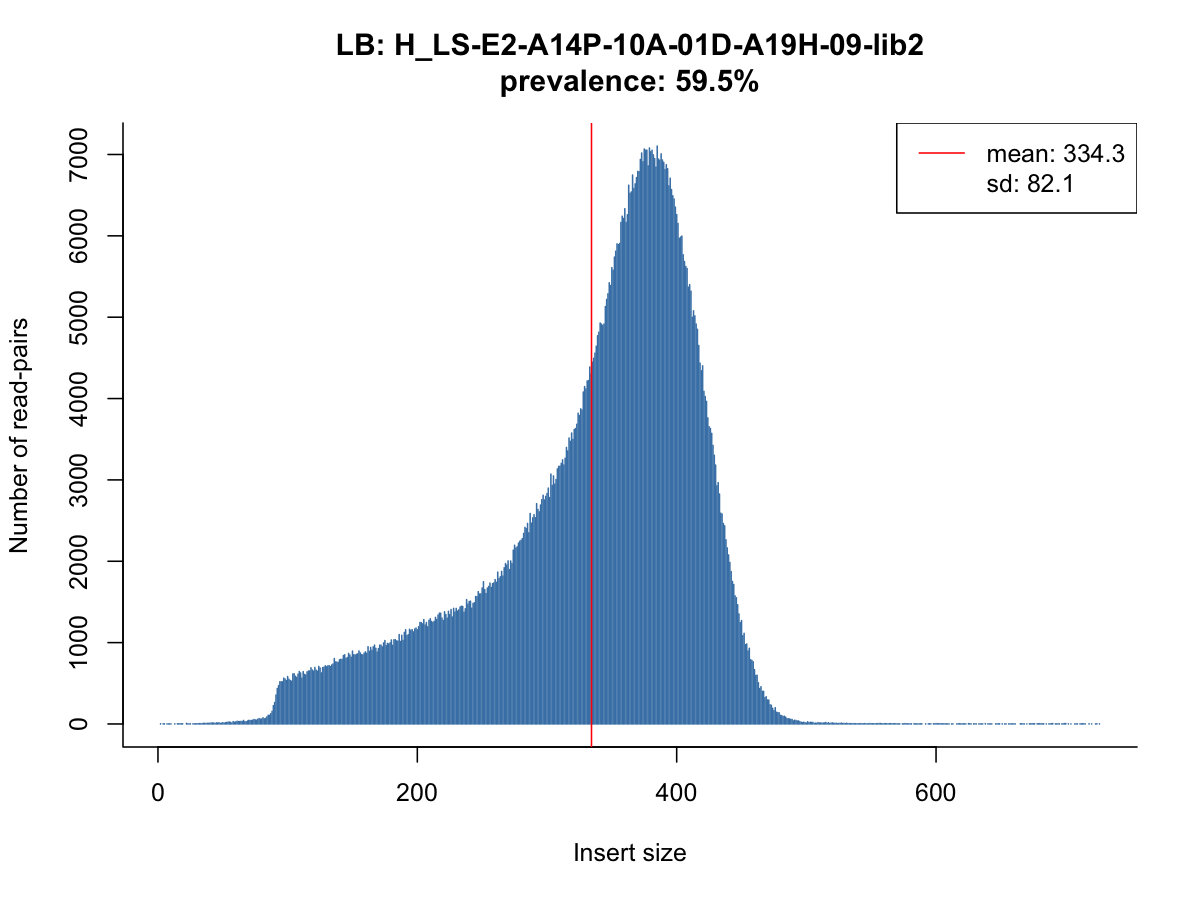
Many common issues are related to abnormal insert size distributions in the BAM file. SVTyper provides methods to assess and visualize the characteristics of sequencing libraries.
Running SVTyper with the -l flag creates a JSON file with essential metrics on a BAM file. SVTyper will sample the first N reads for the file (1 million by default) to parse the libraries, read groups, and insert size histograms. This can be done in the absence of a VCF file.
svtyper \
-B my.bam \
-l my.bam.json
The lib_stats.R script produces insert size histograms from the JSON file
scripts/lib_stats.R my.bam.json my.bam.json.pdf
Citation
C Chiang, R M Layer, G G Faust, M R Lindberg, D B Rose, E P Garrison, G T Marth, A R Quinlan, and I M Hall. SpeedSeq: ultra-fast personal genome analysis and interpretation. Nat Meth 12, 966–968 (2015). doi:10.1038/nmeth.3505.
http://www.nature.com/nmeth/journal/vaop/ncurrent/full/nmeth.3505.html