Text Understanding with the Tsetlin Machine
This project contains the source code for a text categorization approach based on the recently introduced Tsetlin Machine. We have included the CUDA implementation, and will later also include the C source code. This is the code that we used to produce the empirical results in the paper "Using the Tsetlin Machine to Learn Human-Interpretable Rules for High-Accuracy Text Categorization with Medical Applications" (https://arxiv.org/abs/1809.04547). We have also included a script that preprocesses the IMDB Movie Review dataset for analysis by the Tsetlin Machine, plus an anonymized version of the clinically derived dataset described and referred to in Section III.A of the revised paper (soon to be published).
Background
Although deep learning in the form of convolutional neural networks (CNN), recurrent neural networks (RNNs), and Long Short Term Memory (LSTM) recently has provided a leap ahead in text categorization accuracy, this leap has come at the expense of interpretability and computational complexity.
The Tsetlin automaton developed by M.L. Tsetlin in the Soviet Union in the late 1950s represents a fundamental and versatile learning mechanism; arguably even more so than the artificial neuron. While the Tsetlin Machine is able to form complex non-linear patterns, the propositional formulae it composes have also turned out to be particularly suitable for human interpretation.
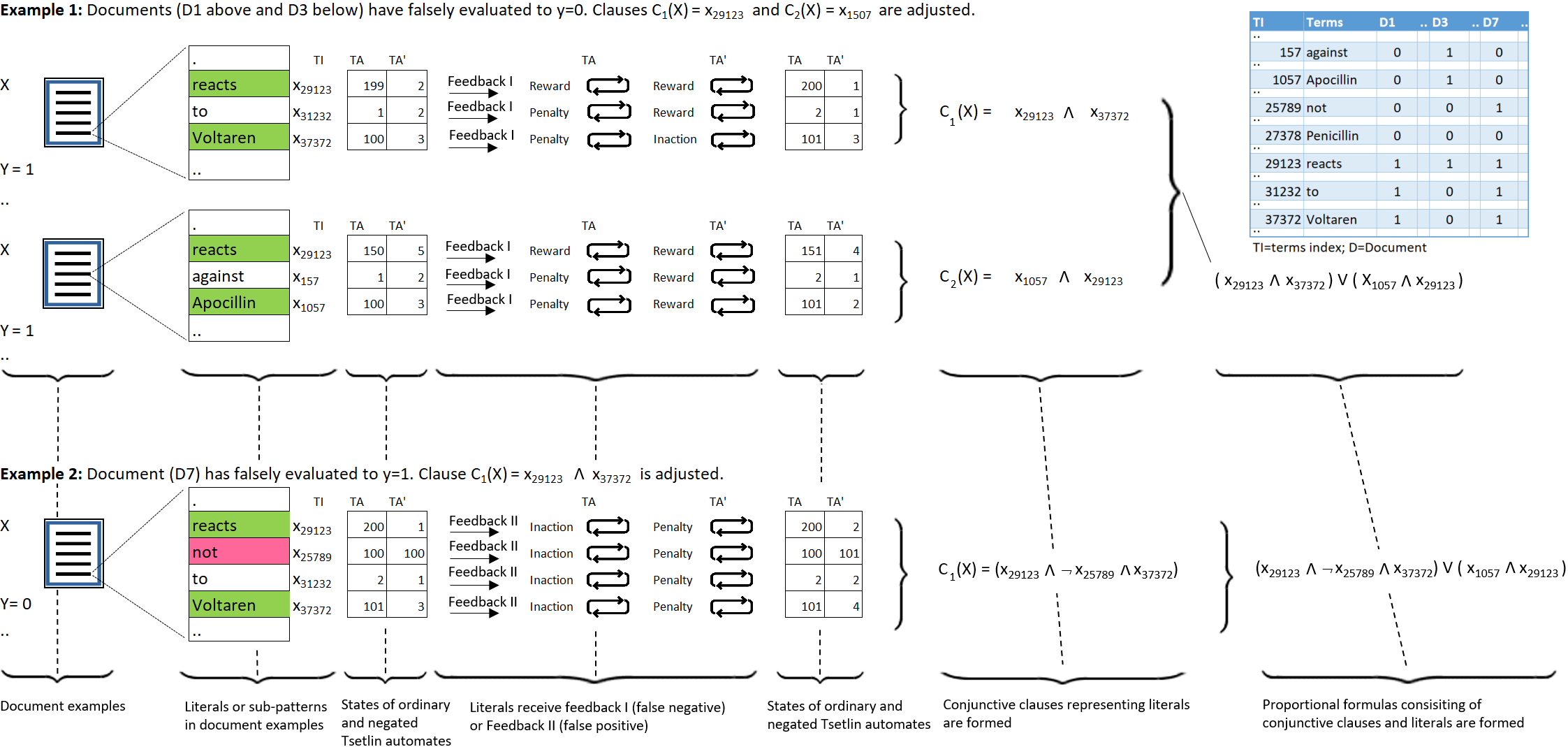
Briefly, the Tsetlin Machine represents the terms of a text as propositional variables. From these, categories are captured using simple propositional formulae, such as: if “rash” and “reaction” and “penicillin” then Allergy. The Tsetlin Machine learns these formulae from a labelled text, utilizing conjunctive clauses to represent the particular facets of each category. Indeed, even the absence of terms (negated features) can be used for categorization purposes. The figure below is from our text categorization paper and captures the essence of this process (the paper explains the details of the figure). It reflects a running example from the medical domain, where we use the Tsetlin Machine to detect patient allergies in Electronic Health Records.
The combination of computational simplicity, accuracy, and results that are highly interpretable, leaves the Tsetlin Machine worthy of further exploration in many text analysis directions.
For a general introduction to the Tsetlin Machine, we refer the reader to the original paper (https://arxiv.org/pdf/1804.01508.pdf). For the details on the text analysis approach, see https://arxiv.org/abs/1809.04547,
Also notice that research on the Tsetlin Machine for text understanding is an on-going project at the Centre for Artificial Intelligence Research CAIR at the University of Agder, Norway. More information will be added as the project advances.
Requirements
- Python 2.7.x https://www.python.org/downloads/
- Gcc http://gcc.gnu.org
- Numpy http://www.numpy.org/
- Cython http://cython.org/
- CUDA https://developer.nvidia.com/cuda
- NLTK http://www.nltk.org
- Scikit-learn http://scikit-learn.org
- Keras http://keras.io
- TensorFlow http://www.tensorflow.org
Instructions for use
- Edit the GPUConfig.cuh file (adjust the GRID_SIZE and BLOCK_SIZE parameters for optimal performance of your Nvidia card).
- Use the following command to compile the necessary C++ CUDA executable: nvcc -O3 TsetlinMachineIMDB.cu TsetlinMachine.cu TsetlinMachineKernels.cu -lcurand -o TsetlinMachineIMDB.out (don't worry about the compiler warnings produced)
- Produce the IMDB dataset by running the command: python produce_dataset.py
- Run the TsetlinMachine executable produced in step 2 to start categorization of the IMDB dataset: ./TsetlinMachineIMDB.out
- The results for each epoch are calculated as true positive, true negative, false positive, false negative, accuracy, recall, and precision (produced on screen and also saved to the file statistics.txt).
Important meta-parameters used for tuning the Tsetlin Machine
You may experiment with the Tsetlin Machine's hyperparameter settings by editing the TsetlinMachineConfig.cuh and the TsetlinMachineIMDB.cu files. Just remember to recompile after editing before you try a rerun!
The most important parameters of the Tsetlin Machine that we adjust are features, clauses, classes, epochs, s, threshold T, and states. Features describes the number of features in the dataset, and must be correct for the adequate number of Tsetlin automata to be initialized by the Tsetlin Machine. Clauses describes the number of clauses that the Tsetlin Machine will implement to solve the text learning problem, and roughly translates to the number of hidden nodes in a neural network layer. Epochs is similar to epochs typically used for artificial neural network training, and describes the number of cycles the Tsetlin Machine runs on the training dataset. T describes a value for the threshold function regulating how easily the available clauses are spent representing each specific sub-pattern, while s denotes precision and determines the granularity of the sub-patterns captured by the literals in the Tsetlin Machine. States describe the number of states for each Tsetlin automaton.
Further Work
- Optimize code base further.
- Leverage the Convolutional Tsetlin Machine to further increase accuracy performance.
Citation
Please cite the relevant Tsetlin Machine papers if you use the Tsetlin Machine in your work:
@article{berge2019,
author={Geir Thore {Berge} and Ole-Christoffer {Granmo} and Tor Oddbjørn {Tveit} and Morten {Goodwin} and Lei {Jiao} and Bernt Viggo {Matheussen}},
journal={IEEE Access},
title="{Using the Tsetlin Machine to Learn Human-Interpretable Rules for High-Accuracy Text Categorization with Medical Applications}",
volume={7},
pages={115134-115146},
year={2019},
doi={10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2935416},
ISSN={2169-3536}
}@article{granmo2018tsetlin,
author = {{Granmo}, Ole-Christoffer},
title = "{The Tsetlin Machine - A Game Theoretic Bandit Driven Approach to Optimal Pattern Recognition with Propositional Logic}",
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:1804.01508},
year={2018}
}Licence
Copyright (c) 2019 Geir Thore Berge and Ole-Christoffer Granmo
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all copies or substantial portions of the Software.
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM, OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE SOFTWARE.