maxint-rd / Tm16xx
Projects that are alternatives of or similar to Tm16xx
TM16xx
Arduino TM16xx library for LED & KEY and LED Matrix modules based on TM1638, TM1637, TM1640 and similar chips. Simply use print() on 7-segment displays and use Adafruit GFX on matrix displays.
TM16xx LEDs and Buttons library
This Arduino library facilitates driving LED displays using TM16xx LED driver chips. The TM16xx chip family allows driving 7-segment LED displays or LED matrices. Next to built-in high-frequency LED multiplexing, they offer control of LED brightness. Most TM16xx chips also support reading key-scan data for button presses. Using this library you can simply use print() on a 7-segment display or use Adafruit GFX on a LED matrix. Currently this library supports the TM1620, TM1628, TM1630, TM1637, TM1638, TM1640, TM1650 and TM1668 chips. Note that there are similar chips made by other manufacturers that may be compatible with the Titan Micro chips. For instance: the HBS640 by WINRISE is compatible with the TM1640.
Made by Maxint R&D. See https://github.com/maxint-rd/
Initial version was based on the TM1638 library by Ricardo Batista. Further inspiration from the TM1637 library by Avishay, the Max72xxPanel library by Mark Ruys and the OneButton library by Matthias Hertel.
Table of contents
- TM16xx chip features
- Library structure
- Basic usage
- TM16xxDisplay class
- TM16xxMatrix class
- TM16xxMatrixGFX class
- TM16xxButtons class
- New in this library
- Features & limitations
- More information
TM16xx chip features
| Type | segments x digits | buttons | interface |
|---|---|---|---|
| TM1620 | 8 x 6 - 10 x 4 | n/a | DIN/CLK/STB |
| TM1628 | 10 x 7 - 13 x 4 | 10 x 2 multi | DIO/CLK/STB |
| TM1630 | 7 x 5 - 8 x 4 | 7 x 1 multi | DIO/CLK/STB |
| TM1637 | 8 x 6 (common anode) | 8 x 2 single | DIO/CLK |
| TM1638 | 10 x 8 | 8 x 3 multi | DIO/CLK/STB |
| TM1640 | 8 x 16 | n/a | DIN/CLK |
| TM1650 | 8 x 4 | 7 x 4 single | DIO/CLK (SDA/SCL) |
| TM1668 | 10 x 7 - 13 x 4 | 10 x 2 multi | DIO/CLK/STB |
See the documents folder for datasheets containing more information about these chips and their pinouts.
Library structure
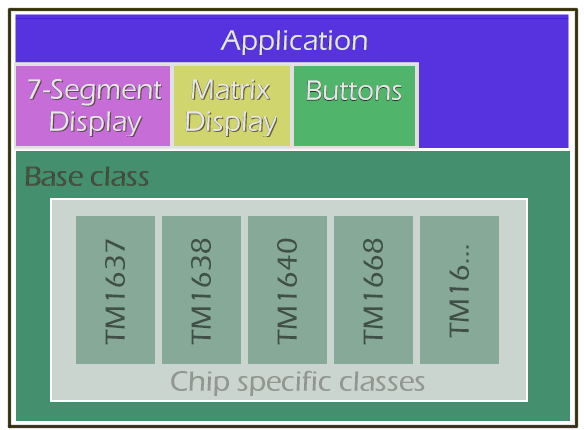
This library has a layered structure to simplify the support of multiple TM16xx chips. By using a base class that provides a uniform API, your application doesn't need chip specific code. Likewise, the library can offer common functionality in display specific classes that support multiple chips.
The figure below illustrates that concept:
Basic usage
To use this library you need to include the class that matches the chip on your module and instantiate the object:
#include <TM1638.h>
TM1638 module(8, 9, 7); // DIO=8, CLK=9, STB=7
In the setup() function you can set the intensity of the display, but that's not mandatory:
void setup() {
module.setupDisplay(true, 2); // on=true, intensity-2 (range 0-7)
module.setDisplayToString("HALO"); // display simple text
}
In the loop() function you can use basic display methods provided by the base class:
void loop() {
int nTime = ((millis() / 1000) / 60) * 100 + (millis() / 1000) % 60; // convert time to minutes+seconds as integer
module.setDisplayToDecNumber(nTime, _BV(4)); // display milliseconds with dot on digit 4
}
For the easy to use print() method and more advance display methods you can use the TM16xxDisplay class.
The TM16xx chip makes it easy to see if a button is pressed. To check if a button was pressed you can use the getButtons() method:
uint32_t dwButtons=module.getButtons();
Serial.println(dwButtons, HEX);
Please note that while you don't need to write any code for debouncing, the button state may be reset when you display something. For advanced detection of button clicks, double clicks and long presses you can use the TM16xxButtons class.
TM16xxDisplay class
The TM16xxDisplay class adds some bytes to the memory footprint, but it provides the familiar easy to use print() and println() functions. Next to that it also provides some more advanced display methods. To use that class on top of the base class, all you need to do is instantiate it, refering to the chip specific class:
TM1638 module(8, 9, 7); // DIO=8, CLK=9, STB=7
TM16xxDisplay display(&module, 8); // TM16xx object, 8 digits
Simple print example using the TM16xxDisplay class:
#include <TM1638.h>
#include <TM16xxDisplay.h>
TM1638 module(8, 9, 7); // DIO=8, CLK=9, STB=7
TM16xxDisplay display(&module, 8); // TM16xx object, 8 digits
void setup() {
display.println(F("HELLO !"));
}
int nCount=0;
void loop() {
delay(1000);
display.print("Count:");
display.println(nCount++);
}
See TM16xxDisplay.h for the provided methods.
TM16xxMatrix class
The TM16xxMatrix class provides basic methods for using a single LED-matrix module. For more advanced graphics use the TM16xxMatrixGFX class. To use the TM16xxMatrix class on top of the base class, all you need to do is instantiate it, refering to the chip specific class:
TM1640 module(9, 10); // DIN=9, CLK=10
#define MATRIX_NUMCOLUMNS 16
#define MATRIX_NUMROWS 8
TM16xxMatrix matrix(&module, MATRIX_NUMCOLUMNS, MATRIX_NUMROWS); // TM16xx object, columns, rows
Note that the TM1640 has sufficient outputs to drive two 8x8 matrices.
These methods can be used to set the pixels of the matrix:
matrix.setAll(true); // set all pixels on
matrix.setPixel(5,6, true); // set one pixel on
matrix.setPixel(3,2, false); // set another pixel off
See TM16xxMatrix.h for the provided methods.
TM16xxMatrixGFX class
The TM16xxMatrixGFX class implements the popular Adafruit GFX interface to drive one or more TM16xx based LED-matrix modules. To use the TM16xxMatrixGFX class you first need to include the proper header files:
#include <Adafruit_GFX.h>
#include <TM1640.h>
#include <TM16xxMatrixGFX.h>
Then you can instantiate the TM16xxMatrixGFX class, refering to the chip specific class:
TM1640 module(13, 14); // For ESP8266/WeMos D1-mini: DIN=D7/13/MOSI, CLK=D5/14/SCK
#define MATRIX_NUMCOLUMNS 8
#define MATRIX_NUMROWS 8
TM16xxMatrixGFX matrix(&module, MATRIX_NUMCOLUMNS, MATRIX_NUMROWS); // TM16xx object, columns, rows
Note that the TM1640 has sufficient outputs to drive two 8x8 matrices. The WeMOS D1 Mini Matrix LED Shield also uses the TM1640, but has only one 8x8 matrix.
These methods can be used to draw on the matrix:
matrix.setIntensity(1); // Use a value between 0 and 7 for brightness
matrix.fillScreen(LOW); // Clear the matrix
matrix.drawPixel(1, 4, HIGH); // set one pixel in the memory bitmap on
matrix.write(); // Send the memory bitmap to the display
In addition all the Adafruit GFX methods can be used, e.g.:
matrix.drawChar(0, 0, 'A', HIGH, LOW, 1);
matrix.drawLine(0, matrix. height(), matrix.width(), 0, HIGH);
matrix.drawRect(0, 0, 6, 6, HIGH);
Multiple identical modules can be combined to form a large matrix. The data line can be shared to reduce the number of pins:
TM1640 module(D7, D5); // For ESP8266/WeMos D1-mini: DIN=D7/13/MOSI, CLK=D5/14/SCK
TM1640 module2(D7, D6); // For ESP8266/WeMos D1-mini: shared DIN=D7/13/MOSI, different CLK
TM16xx * modules[]={&module,&module2}; // put modules in an array
TM16xxMatrixGFX matrix(modules, MODULE_SIZECOLUMNS, MODULE_SIZEROWS, 2, 1); // modules, size of each module, size combined
See Adafruit GFX documentation and TM16xxMatrixGFX.h for the provided methods. See the library examples for more information.
TM16xxButtons class
The TM16xxButtons class enlarges the footprint a bit, but based on the popular OneButton library library, it adds more advanced methods to use buttons. Next to simply polling the state of each button, you can define callback functions that will be called when a button is released, clicked, double-clicked or long pressed. To use this class on top of the base class, all you need to do is include the proper headers and instantiate the buttons object, refering to the chip specific class, for example:
#include <TM1638.h>
#include <TM16xxButtons.h>
TM1638 module(8, 9, 7); // DIO=8, CLK=9, STB=7
TM16xxButtons buttons(&module); // TM16xx object
Then you define the functions you want to use to handle the button events:
void fnClick(byte nButton)
{ // byte nButton is the button-number (first button is number 0)
Serial.print(F("Button "));
Serial.print(nButton);
Serial.println(F(" click."));
}
In setup() you need to attach the callback function:
void setup()
{
.
.
buttons.attachClick(fnClick);
}
(BTW. Besides a click function, you can also attach a function to handle release, doubleclick and longpress events).
In loop() you need to call the tick() function that detects all state changes and calls the callback functions as needed:
void loop()
{
buttons.tick();
.
.
// do your other things
}
To implement a shift key, you can use the isPressed() function. See TM16xxButtons.h for the provided methods and the Button clicks example for more information.
New in this library
Added library functionality:
- Revised library structure to simplify support of other TM16xx chips.
- Basic functionality in base class for a uniform API.
- Support for TM1637. Note: TM1637 does not support simultaneous button presses. (Method derived from TM1637 library but using pins in standard output mode when writing).
- Support for TM1668. Note: TM1668 can be used in 10x7 - 13x4 display modes. Datasheet partly translated.
- Support for TM1650. Note: TM1650 can be used in 8x4 or 7x4 display mode. Datasheet fully translated.
- Reduced required RAM memory by using PROGMEM fonts.
- Support for ATtiny44A and ESP8266 in addition to regular Arduinos.
- Separate classes for LED matrix and advanced LED display support.
- Simple display of text and numbers on 7-segment displays using familiar print() and println() methods.
- Support for the Adafruit GFX graphics library for advanced graphics on a LED matrix.
- Full support for QYF-TM1638 module (8 digit common anode LED display and 4x4 keypad)
- Support for TM1638 in Anode Mode (10 digit common anode LED 8 segment display) [TM1638Anode.h]
- Support for combining multiple modules into one large Adafruit GFX matrix.
- Support for scanning all possible keys (K1, K2 and K3 lines) on TM1638.
- Support for release, click, doubleclick and long press button detection using callback functions.
- Added library examples.
- Support for TM1620 (thanks @eddwhite)
- Support for TM1630 (thanks @tokuhira)
- Support for TM1628. Note: TM1628 can be used in 10x7 - 13x4 display modes.
Functionality in original library by Ricardo Batista:
- Support for the TM1638 and TM1640, including common anode TM1638 module;
- Helper methods for displaying numbers in decimal, hexadecimal and binary;
- Support for multiple chained TM1638 and for TM1638 in inverted position;
- Support for dimming the display and LEDs and for writing text;
- Reading simultaneous button presses on TM1638;
Features & limitations
- The current version of this library supports ESP8266/ESP32, Atmel ATmega (e.g. ATmega328 and ATmega168) and Atmel ATtiny MCUs. Due to the required memory, the smallest ATtiny MCU supported is the ATtiny44. Please let me know if you've successfully used this library with other MCUs.
- The TM16xx chips offer no support for daisychaining multiple chips, but when separate Clk or Latch lines are used the Din line can be shared for combined displays.
- The library doesn't support combining multiple 7-segment modules into one display, but it is possible to define multiple display objects for multiple different modules. See the TM1638_TM1637ex_two_modules example.
- The TM16xxMatrixGFX class does support combining multiple LED Matrix module into one large matrix. Please note that the TM1640 supports up to 16 digits or an 8x16 LED matrix.
- The QYF-TM1638 module (TM138 with common anode display) is fully supported. Please note that while multiple buttons can be pressed, pressing more than two buttons can give faulty results due to the lack of short-out preventing diodes on the module.
- The popular TM1638 LED & KEY module comes in a number of varieties. My version has some odd button wiring sequence: S1=KS1, S5=KS2, S2=KS3, S6=KS4, S3=KS5, S7=KS6, S4=KS7, S8=KS8
- The TM1668 class has experimental support for using RGB LEDs on Grids 5-7. Some information about the wiring can be found in the example code. Most likely future versions will have a specific class for using RGB LEDs. The TM1680 has 8x24 outputs which sounds ideal for creating a 8x8 RGB matrix. Unfortunately these chips don't support individual LED brightness, only intensity of the whole display.
- The TM1650 datasheet mentions SDA and SCL pins. The used protocol resembles I2C, but lacks addressing. For that reason this library doesn't use the I2C Wire library, but (slow) bitbanging using digitalWrite.
- The WeMOS D1 mini Matrix LED Shield and the TM1640 Mini LED Matrix 8x16 by Maxint R&D have R1 on the right-top. Call setMirror(true) to reverse the x-mirrorring.
- When using TM16xxButtons, the amount of memory used can become too large. To preserve RAM memory on smaller MCUs such as the ATtiny44A, the number of buttons is limited to 8 on the ATtiny MCUs. This can be changed by setting the maximum in the TM16xxButtons.h header file:
#define TM16XX_BUTTONS_MAXBUTTONS 8 // Note: changing this define requires recompilation of the library
- An alternative RAM preserving implementation using dynamic memory allocation is optional, but not suitable for small MCUs as using malloc/free will increase the required FLASH program space by over 600 bytes. Modify the TM16XX_OPT_BUTTONS_... defines in the header file at your own risk.
More information
Examples
See the library examples for more information on how to use this library. See also the original examples by Ricardo Batista. Most will still work or only require minor changes.
Links
- Manufacturer: Titan Micro Electronics - LED driver datasheets
- Original TM1638/TM1640 library: https://github.com/rjbatista/tm1638-library
- TM1637 library used for reference: https://github.com/avishorp/TM1637
- A TM1637 library optimized for speed and size: https://github.com/Erriez/ErriezTM1637
- TM1650 library that uses the Wire interface: https://github.com/mozgy/Mozz_TM1650
- MAX7219 LED Matrix library: https://github.com/markruys/arduino-Max72xxPanel
- OneButton multi-state buttons: https://github.com/mathertel/OneButton
- Adafruit GFX library: https://github.com/adafruit/Adafruit-GFX-Library
- Adafruit GFX documentation: https://learn.adafruit.com/adafruit-gfx-graphics-library
- Matrix transposition used in TM1638QYF: https://www.chessprogramming.org/Flipping_Mirroring_and_Rotating#Anti-Diagonal
Disclaimer
- All code on this GitHub account, including this library is provided to you on an as-is basis without guarantees and with all liability dismissed. It may be used at your own risk. Unfortunately I have no means to provide support.