Tortoise ORM

Introduction
Tortoise ORM is an easy-to-use asyncio ORM (Object Relational Mapper) inspired by Django.
Tortoise ORM was built with relations in mind and admiration for the excellent and popular Django ORM. It's engraved in its design that you are working not with just tables, you work with relational data.
You can find the docs at Documentation
Note
Tortoise ORM is a young project and breaking changes are to be expected. We keep a Changelog and it will have possible breakage clearly documented.
Tortoise ORM is supported on CPython >= 3.7 for SQLite, MySQL and PostgreSQL.
Why was Tortoise ORM built?
Python has many existing and mature ORMs, unfortunately they are designed with an opposing paradigm of how I/O gets processed.
asyncio is relatively new technology that has a very different concurrency model, and the largest change is regarding how I/O is handled.
However, Tortoise ORM is not the first attempt of building an asyncio ORM. While there are many cases of developers attempting to map synchronous Python ORMs to the async world, initial attempts did not have a clean API.
Hence we started Tortoise ORM.
Tortoise ORM is designed to be functional, yet familiar, to ease the migration of developers wishing to switch to asyncio.
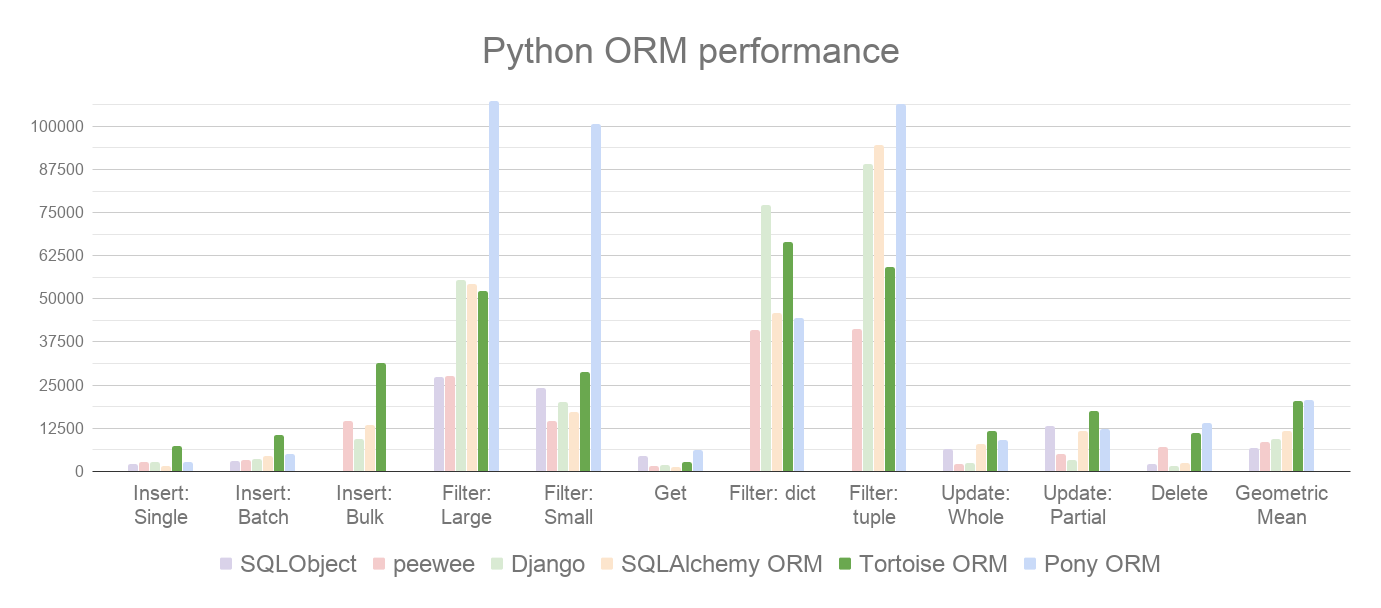
It also performs well when compared to other Python ORMs. In our benchmarks, where we measure different read and write operations (rows/sec, more is better), it's trading places with Pony ORM:
How is an ORM useful?
When you build an application or service that uses a relational database, there is a point where you can't get away with just using parameterized queries or even query builder. You just keep repeating yourself, writing slightly different code for each entity. Code has no idea about relations between data, so you end up concatenating your data almost manually. It is also easy to make mistakes in how you access your database, which can be exploited by SQL-injection attacks. Your data rules are also distributed, increasing the complexity of managing your data, and even worse, could lead to those rules being applied inconsistently.
An ORM (Object Relational Mapper) is designed to address these issues, by centralising your data model and data rules, ensuring that your data is managed safely (providing immunity to SQL-injection) and keeping track of relationships so you don't have to.
Getting Started
Installation
First you have to install Tortoise ORM like this:
pip install tortoise-ormYou can also install with your db driver (aiosqlite is builtin):
pip install tortoise-orm[asyncpg]Or for MySQL:
pip install tortoise-orm[aiomysql]Or another asyncio MySQL driver asyncmy:
pip install tortoise-orm[asyncmy]Quick Tutorial
The primary entity of tortoise is tortoise.models.Model.
You can start writing models like this:
from tortoise.models import Model
from tortoise import fields
class Tournament(Model):
id = fields.IntField(pk=True)
name = fields.TextField()
def __str__(self):
return self.name
class Event(Model):
id = fields.IntField(pk=True)
name = fields.TextField()
tournament = fields.ForeignKeyField('models.Tournament', related_name='events')
participants = fields.ManyToManyField('models.Team', related_name='events', through='event_team')
def __str__(self):
return self.name
class Team(Model):
id = fields.IntField(pk=True)
name = fields.TextField()
def __str__(self):
return self.nameAfter you defined all your models, tortoise needs you to init them, in order to create backward relations between models and match your db client with the appropriate models.
You can do it like this:
from tortoise import Tortoise
async def init():
# Here we connect to a SQLite DB file.
# also specify the app name of "models"
# which contain models from "app.models"
await Tortoise.init(
db_url='sqlite://db.sqlite3',
modules={'models': ['app.models']}
)
# Generate the schema
await Tortoise.generate_schemas()Here we create a connection to an SQLite database in the local directory called db.sqlite3. Then we discover and initialise the models.
Tortoise ORM currently supports the following databases:
- SQLite (requires
aiosqlite) - PostgreSQL (requires
asyncpg) - MySQL (requires
aiomysql)
generate_schema generates the schema on an empty database. Tortoise generates schemas in safe mode by default which
includes the IF NOT EXISTS clause, so you may include it in your main code.
After that you can start using your models:
# Create instance by save
tournament = Tournament(name='New Tournament')
await tournament.save()
# Or by .create()
await Event.create(name='Without participants', tournament=tournament)
event = await Event.create(name='Test', tournament=tournament)
participants = []
for i in range(2):
team = await Team.create(name='Team {}'.format(i + 1))
participants.append(team)
# M2M Relationship management is quite straightforward
# (also look for methods .remove(...) and .clear())
await event.participants.add(*participants)
# You can query a related entity with async for
async for team in event.participants:
pass
# After making a related query you can iterate with regular for,
# which can be extremely convenient when using it with other packages,
# for example some kind of serializers with nested support
for team in event.participants:
pass
# Or you can make a preemptive call to fetch related objects
selected_events = await Event.filter(
participants=participants[0].id
).prefetch_related('participants', 'tournament')
# Tortoise supports variable depth of prefetching related entities
# This will fetch all events for Team and in those events tournaments will be prefetched
await Team.all().prefetch_related('events__tournament')
# You can filter and order by related models too
await Tournament.filter(
events__name__in=['Test', 'Prod']
).order_by('-events__participants__name').distinct()Migration
Tortoise ORM uses Aerich as its database migration tool, see more detail at its docs.
Contributing
Please have a look at the Contribution Guide.
License
This project is licensed under the Apache License - see the LICENSE.txt file for details.
