Kyubyong / Word_prediction
Programming Languages
Word Prediction using Convolutional Neural Networks—can you do better than iPhone™ Keyboard?
In this project, we examine how well neural networks can predict the current or next word. Language modeling is one of the most important nlp tasks, and you can easily find deep learning approaches to it. Our contribution is threefold. First, we want to make a model that simulates a mobile environment, rather than having general modeling purposes. Therefore, instead of assessing perplexity, we try to save the keystrokes that the user need to type. To this end, we manually typed 64 English paragraphs with a iPhone 7 for comparison. It was super boring, but hopefully it will be useful for others. Next, we use CNNs instead of RNNs, which are more widely used in language modeling tasks. RNNs—even improved types such as LSTM or GRU—suffer from short term memory. Deep layers of CNNs are expected to overcome the limitation. Finally, we employ a character-to-word model here. Concretely, we predict the current or next word, seeing the preceding 50 characters. Because we need to make a prediction at every time step of typing, the word-to-word model dont't fit well. And the char-to-char model has limitations in that it depends on the autoregressive assumption. Our current belief is the character-to-word model is best for this task. Although our relatively simple model is still behind a few steps iPhone 7 Keyboard, we observed its potential.
Requirements
- numpy >= 1.11.1
- sugartensor >= 0.0.2.4
- lxml >= 3.6.4.
- nltk >= 3.2.1.
- regex
Background / Glossary / Metric
-
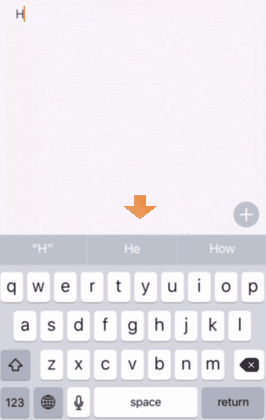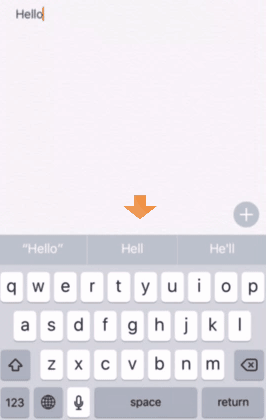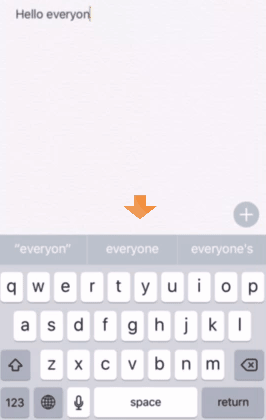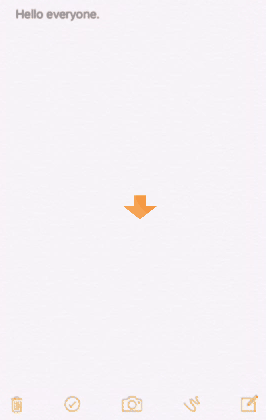
Most smartphone keyboards offer a word prediction option to save the user's typing. If you turn the option on, you can see suggested words on the top of the keyboard area. In iPhone, the leftmost one is verbatim, the middle one is appeared the top candidate.
-
Full Keystrokes (FK): the keystrokes when supposing that the user has deactivated the prediction option. In this exeriment, the number of FK is the same as the number of characters (including spaces).
-
Responsive Keystroke (RK): the keystrokes when supposing that so the user always choose it if their intended word is suggested. Especially, we take only the top candidate into consideration here.
-
Keystroke Savings Rate (KSR): the rate of savings by a predictive engine. It is simply calculated as follows.
- KSR = (FK - RK) / FK
Data
- For training and test, we build an English news corpus from wikinews dumps for the last 6 months.
Model Architecture / Hyper-parameters
- 20 * conv layer with kernel size=5, dimensions=300
- residual connection
Work Flow
- STEP 1. Download English wikinews dumps.
- STEP 2. Extract them and copy the xml files to
data/rawfolder. - STEP 3. Run
build_corpus.pyto build an English news corpus. - STEP 4. Run
prepro.pyto make vocabulary and training/test data. - STEP 5. Run
train.py. - STEP 6. Run
eval.pyto get the results for the test sentences. - STEP 7. We manually tested for the same test sentences with iPhone 7 keyboard.
if you want to use the pretrained model,
- Download the output files of STEP 3 and STEP 4, then extract them to
data/folder. - Download the pre-trained model files, then extract them to
asset/trainfolder. - Run
eval.py.
Updates
- In the fourth week of Feb., 2017, we refactored the source file for TensorFlow 1.0.
- In addition, we changed the last global-average pooling to inverse-weighted pooling. As a result, the #KSR improved from 0.39 to 0.42. Check this.
Results
The training took 4-5 2-3 days on my single GPU (gtx 1060). As can be seen below, our model is lower than iPhone in KSR by 8 5 percent points. Details are available in results.csv.
| #FK | #RK: Ours | #RK: iPhone 7 |
|--- |--- |--- |--- |--- |
| 40,787 | 24,727 (=0.39 ksr)
->23,753 (=0.42 ksr) | 21,535 (=0.47 ksr)|
Conclusions
- Unfortunately, our simple model failed to show better performance than the iPhone predictive engine.
- Keep in mind that in practice predictive engines make use of other information such as user history.
- There is still much room for improvement. Here are some ideas.
- You can refine the model architecture or hyperparameters.
- As always, bigger data is better.
- Can anybody implement a traditional n-gram model for comparison?
Cited By
- Zhe Zeng & Matthias Roetting, A Text Entry Interface using Smooth Pursuit Movements and Language Model, Proceeding ETRA '18 Proceedings of the 2018 ACM Symposium on Eye Tracking Research & Applications, 2018
