odedshimon / Bruteshark
Projects that are alternatives of or similar to Bruteshark
About
BruteShark is a Network Forensic Analysis Tool (NFAT) that performs deep processing and inspection of network traffic (mainly PCAP files, but it also capable of directly live capturing from a network interface). It includes: password extracting, building a network map, reconstruct TCP sessions, extract hashes of encrypted passwords and even convert them to a Hashcat format in order to perform an offline Brute Force attack.
The main goal of the project is to provide solution to security researchers and network administrators with the task of network traffic analysis while they try to identify weaknesses that can be used by a potential attacker to gain access to critical points on the network.
Two BruteShark versions are available, A GUI based application (Windows) and a Command Line Interface tool (Windows and Linux).
The various projects in the solution can also be used independently as infrastructure for analyzing network traffic on Linux or Windows machines. For further details see the Architecture section.
The project was developed in my spare time to address two main passions of mine: software architecture and analyzing network data.
I love to get feedbacks from BruteShark users, your opinion is important to me! Feel free to contact me on [email protected] or create new issue.
Please ⭐️ this repository if this project helped you!
What it can do
- Extracting and encoding usernames and passwords (HTTP, FTP, Telnet, IMAP, SMTP...)
- Extract authentication hashes and crack them using Hashcat (Kerberos, NTLM, CRAM-MD5, HTTP-Digest...)
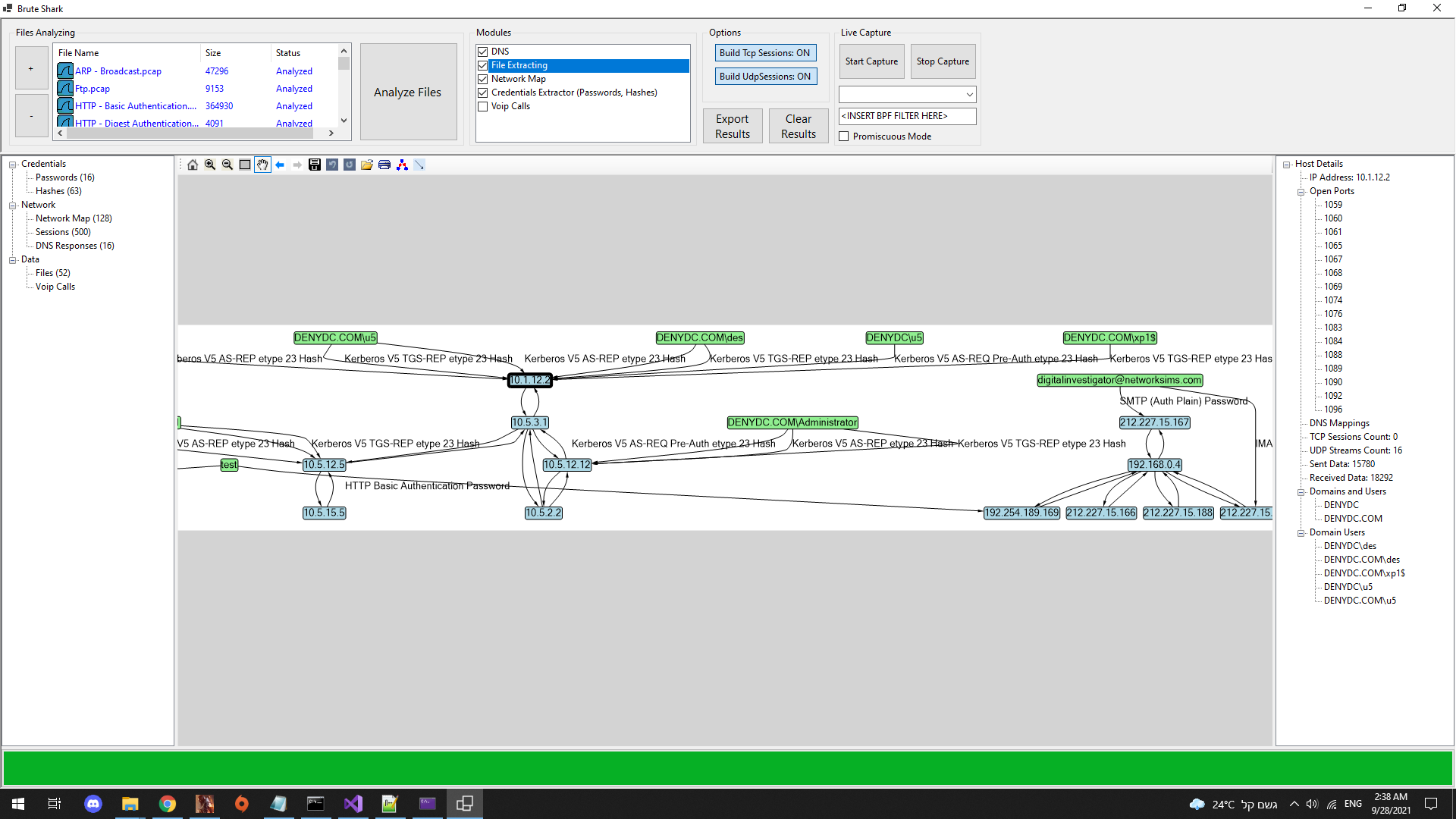
- Build visual network diagram (Network nodes & users)
- Extract DNS queries
- Reconstruct all TCP & UDP Sessions
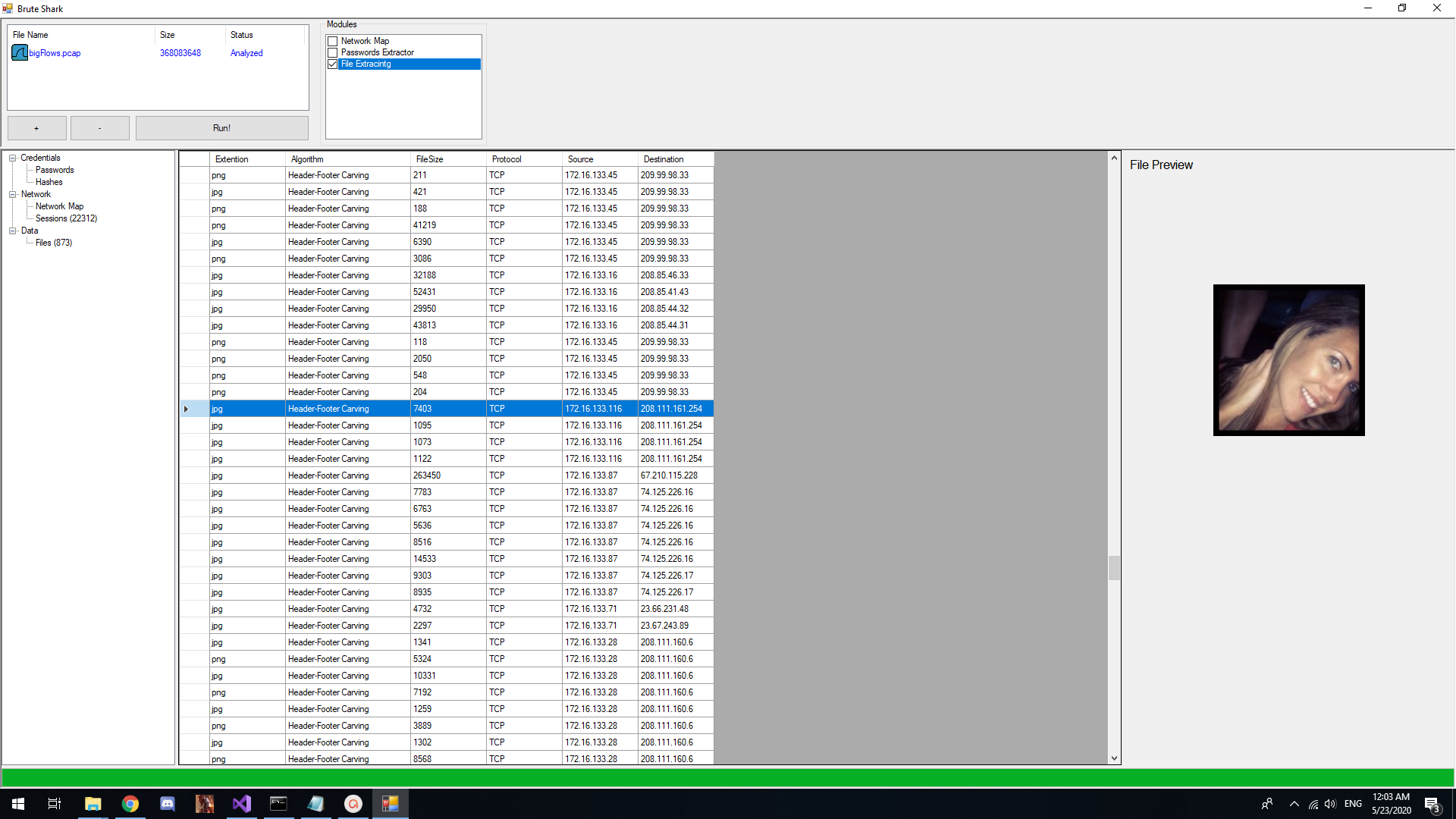
- File Carving
Download
Windows
- Prerequisites:
- WinPcap / Npcap driver (Wireshark installs one of this by default)
- .NET Core SDK
- Download Windows Installer (64 Bit).
Linux
- Prerequisites: libpcap driver
- Download BruteSharkCli and just run it:
# Create a symbolyc link between libpcap.so and the actual libpcap file (e.g. libpcap.so.0.8) # That needed due to a known issue in SharpPcap (https://github.com/chmorgan/sharppcap/issues/167) find /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu -type f | grep libpcap | head -1 | xargs -i sudo ln -s {} /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libpcap.so wget https://github.com/odedshimon/BruteShark/releases/latest/download/BruteSharkCli ./BruteSharkCli
Examples
Videos
How do i crack (by mistake!) Windows 10 user NTLM password
Run Brute Shark CLI on Ubuntu with Mono
Hashes Extracting
Building a Network Diagram
File Carving
Password Extracting
Reconstruct all TCP Sessions
Brute Shark CLI
Usage
In general, it is recommended to use the example PCAP files folder, load, run and explore the results.
Modules
BruteShark is a modular tool, designed for expansion.
Credentials Module
This module is responsible for extracting and encoding usernames and passwords as well as authentication hashes. In fact this module is responsible for updating two display tables, passwords table and hashes table. While usernames and passwords are straight forward to use, hashes most often used in more complex attacks like pass-the-hash or by brute-forcing them to get the password. BruteShark is integrated with Hashcat so all the hashes extracted can be converted to a Hashcat input file. | Protocol | Hash Type | Hascat Mode (-m) | |-----------------|------------------|------------------| | HTTP | HTTP-Digest | 11400 | | SMTP\IMAP | CRAM-MD5 | 16400 | | NTLM (e.g. SMB) | NTLMv1 | 5500 | | NTLM (e.g. SMB) | NTLMv2 | 5600 | | Kerberos | AS-REQ etype 23 | 7500 | | Kerberos | TGS-REP etype 23 | 13100 | | Kerberos | AS-REP etype 23 | 18200 |
Network Map Module
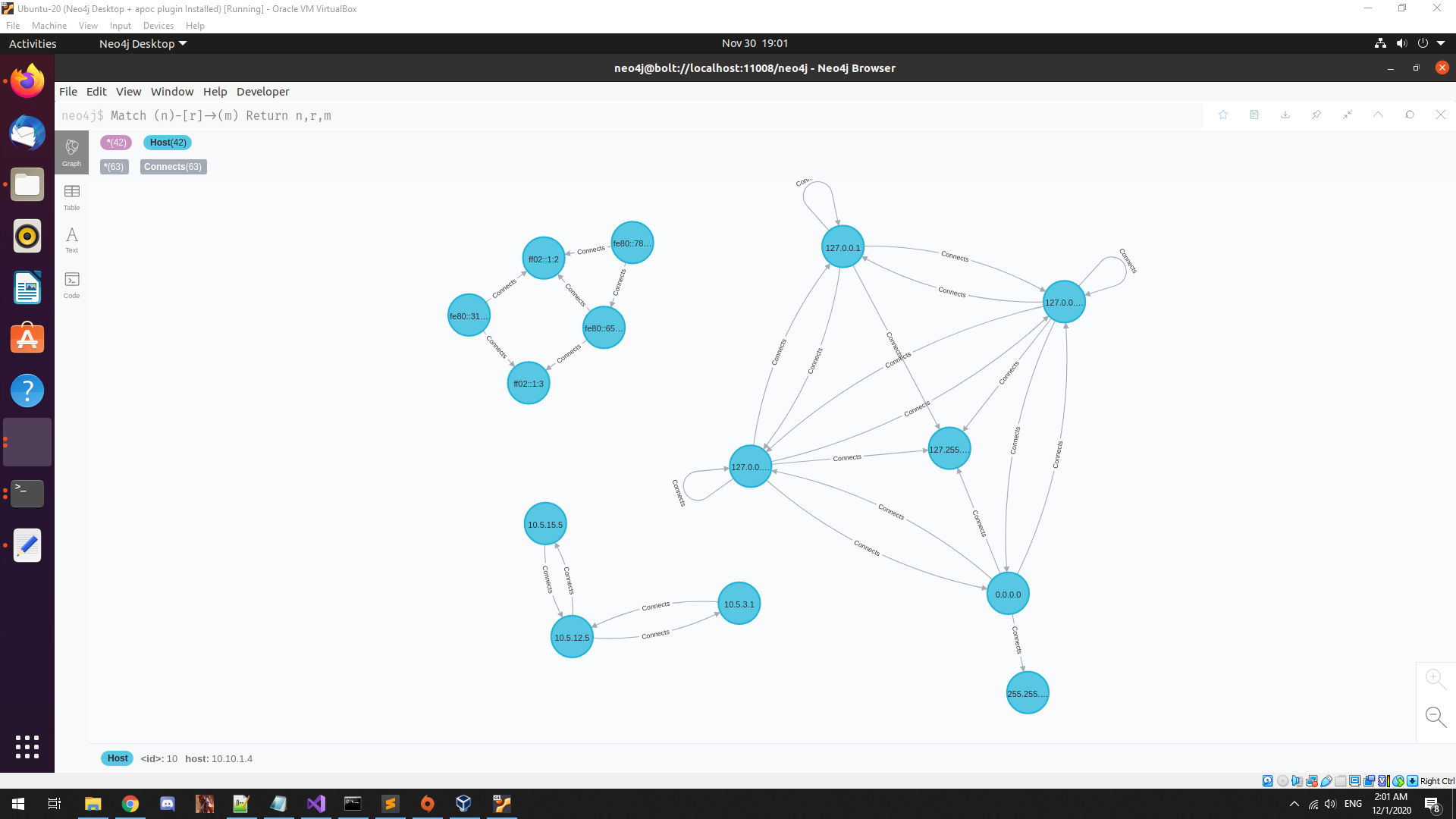
This module is responsible for building the network map by identifying components in the network and the connections between them. The network map can be exported to JSON format for analysis with external tools such as Neo4j.
Files Extracting Module
This module tries to extract files from UDP / TCP sessions (Therefore, note that in order for this module to be effective, the "Build TCP Sessions" / "Build UDP Sessions" should be turn on). Currently this module supports classic forensics techniques of file carving by "Header-Footer" algorithm which is effective for files with known file header and footer like JPG, PNG, PDF.
BruteSharkDesktop
The GUI is pretty self-explanatory, just load the wanted files, configure the wanted modules and press the run button.
BruteSharkCli
BruteSharkCli has two modes: single command and shell mode. The single command mode works by geting all the relevant parameters for the processing and then printing the results to stdout or files. The shell mode allows to perform each step individually.
Single Command Mode
Print the help menu:
C:\Users\King\Desktop\BruteSharkCli>BruteSharkCli --help
BruteSharkCli 1.0.0.0
Copyright c 2018
-d, --input-dir The input directory containing the files to be processed.
-i, --input The files to be processed seperated by comma
-m, --modules The modules to be separterd by comma: Credentials, FileExtracting, NetworkMap
-o, --output Output direcorty for the results files.
--help Display this help screen.
-p, --promiscious Configures whether to start live capture on normal or promiscious mode (sometimes needs super
user privileges to to do so),use along with -l for live catpure.
-l, --live-capture Caputre and process packets live from a network interface.
-f, --filter add a capture bpf filter to the live traffic processing.
--help Display this help screen.
--version Display version information.
Get credentials from all files in a directory (passwords and hashes will be printed to stdout):
C:\Users\King\Desktop\BruteSharkCli>BruteSharkCli -m Credentials -d "C:\Users\King\Desktop\Pcap Files"
[+] Started analyzing 5 files
File : Ftp.pcap Processing Started
Found: Network Credential: 192.168.0.114=>192.168.0.193(FTP) => csanders:echo
File : Ftp.pcap Processing Finished
File : HTTP - Basic Authentication.pcap Processing Started
Found: Network Credential: 192.168.0.4=>192.254.189.169(HTTP Basic Authentication) => test:fail
Found: Network Credential: 192.168.0.4=>192.254.189.169(HTTP Basic Authentication) => test:fail2
Found: Network Credential: 192.168.0.4=>192.254.189.169(HTTP Basic Authentication) => test:fail3
Found: Network Credential: 192.168.0.4=>192.254.189.169(HTTP Basic Authentication) => test:test
File : HTTP - Basic Authentication.pcap Processing Finished
File : IMAP - Authenticate CRAM-MD5.cap Processing Started
Found: Hash: 10.0.2.101=>10.0.1.102:10.0.1.102(IMAP) CRAM-MD5 => aGVtbWluZ3dheSAyOWYyMGI2NjkzNDdhYTA4MTc0OTA2NWQ5MDNhNDllNA==
File : IMAP - Authenticate CRAM-MD5.cap Processing Finished
File : SMB - NTLMSSP (smb3 aes 128 ccm).pcap Processing Started
Found: Hash: 10.160.64.139=>10.160.65.202:10.160.65.202(NTLMSSP) NTLMv2 => 39dbdbeb1bdd29b07a5d20c8f82f2cb701010000000000008a8ce7a9f4ced201e7969a04872c16890000000002000800530055005300450001000c0057005300320030003100360004000e0073007500730065002e006400650003001c005700530032003000310036002e0073007500730065002e006400650005000e0073007500730065002e0064006500070008008a8ce7a9f4ced20100000000
File : SMB - NTLMSSP (smb3 aes 128 ccm).pcap Processing Finished
File : SMTP - Auth Login.pcap Processing Started
Found: Network Credential: 10.10.1.4=>74.53.140.153(SMTP (Auth Login)) => [email protected]:[email protected]
File : SMTP - Auth Login.pcap Processing Finished
[X] Bruteshark finished processing
Get credentials from all files in a directory and also export extracted hashes (if found) to a Hashcat input files.
BruteSharkCli -m Credentials -d C:\Users\King\Desktop\Pcap_Examples -o C:\Users\King\Desktop\Results
Run multiple modules on all files in a directory and also export all the results.
BruteSharkCli -m Credentials,NetworkMap,FileExtracting -d C:\Users\King\Desktop\Pcap_Examples -o C:\Users\King\Desktop\Results
Sniff an interface named Wi-Fi, run multiple modules and also export all the results to a directory (the results will be exported only when stoping the sniffer by hitting CTRL + C).
BruteSharkCli -l Wi-Fi -m Credentials,NetworkMap,FileExtracting,DNS -o C:\Users\King\Desktop\Test Export
Architecture
All BruteShark projects are implemented using .Net Core and .Net Standard for modern and cross platform support.
The solution is designed with three layer architecture, including a one or more projects at each layer - DAL, BLL and PL.
The separation between layers is created by the fact that each project refers only its own objects.
PcapProcessor (DAL)
As the Data Access Layer, this project is responsible for reading raw PCAP files using appropriate drivers (WinPcap, libpcap) and the amazing wrapper library SharpPcap by Chris Morgan. Can analyze a list of files at once, and provides additional features like reconstruction of all TCP Sessions (using the awesome project TcpRecon).
PcapAnalyzer (BLL)
The Business Logic Layer, responsible for analyzing network information (packet, TCP Session etc.), implements a pluggable mechanism. Each plugin is basically a class that implements the interface IModule. All plugins are loaded using reflection:
private void _initilyzeModulesList()
{
// Create an instance for any available modules by looking for every class that
// implements IModule.
this._modules = AppDomain.CurrentDomain.GetAssemblies()
.SelectMany(s => s.GetTypes())
.Where(p => typeof(IModule).IsAssignableFrom(p) && !p.IsInterface)
.Select(t => (IModule)Activator.CreateInstance(t))
.ToList();
// Register to each module event.
foreach(var m in _modules)
{
m.ParsedItemDetected += (s, e) => this.ParsedItemDetected(s, e);
}
}
BruteSharkDesktop (PL)
Desktop application for Windows based on WinForms. Uses a cross-cutting project by the meaning it referrers both the DAL and BLL layers. This is done by composing each of the layers, register to their events, when event is triggered, cast the event object to the next layer equivalent object, and send it to next layer.
public MainForm()
{
InitializeComponent();
_files = new HashSet<string>();
// Create the DAL and BLL objects.
_processor = new PcapProcessor.Processor();
_analyzer = new PcapAnalyzer.Analyzer();
_processor.BuildTcpSessions = true;
// Create the user controls.
_networkMapUserControl = new NetworkMapUserControl();
_networkMapUserControl.Dock = DockStyle.Fill;
_sessionsExplorerUserControl = new SessionsExplorerUserControl();
_sessionsExplorerUserControl.Dock = DockStyle.Fill;
_hashesUserControl = new HashesUserControl();
_hashesUserControl.Dock = DockStyle.Fill;
_passwordsUserControl = new GenericTableUserControl();
_passwordsUserControl.Dock = DockStyle.Fill;
// Contract the events.
_processor.TcpPacketArived += (s, e) => _analyzer.Analyze(Casting.CastProcessorTcpPacketToAnalyzerTcpPacket(e.Packet));
_processor.TcpSessionArived += (s, e) => _analyzer.Analyze(Casting.CastProcessorTcpSessionToAnalyzerTcpSession(e.TcpSession));
_processor.FileProcessingStarted += (s, e) => SwitchToMainThreadContext(() => OnFileProcessStart(s, e));
_processor.FileProcessingEnded += (s, e) => SwitchToMainThreadContext(() => OnFileProcessEnd(s, e));
_processor.ProcessingPrecentsChanged += (s, e) => SwitchToMainThreadContext(() => OnProcessingPrecentsChanged(s, e));
_analyzer.ParsedItemDetected += (s, e) => SwitchToMainThreadContext(() => OnParsedItemDetected(s, e));
_processor.TcpSessionArived += (s, e) => SwitchToMainThreadContext(() => OnSessionArived(Casting.CastProcessorTcpSessionToBruteSharkDesktopTcpSession(e.TcpSession)));
_processor.ProcessingFinished += (s, e) => SwitchToMainThreadContext(() => OnProcessingFinished(s, e));
InitilizeFilesIconsList();
this.modulesTreeView.ExpandAll();
}
Contributing
First off, thanks for taking the time to contribute! BruteShark welcomes contributions from everyone.
When contributing to this repository, please first discuss the change you wish to make via issue or an email before making a change.
How Can You Contribute?
- Implemening new features from BruteShark Issues, look for "good first isuue" and "help wanted" labels.
- Uploading example PCAP files, especially files, with interesting content.
- Proposing new features by Creating an Issue.
- Reporting a bug by Creating an Issue.
- Discussing the current state of the code.
- Creating videos and example tutorials of using BruteShark.