CAP 中文
CAP is a library based on .Net standard, which is a solution to deal with distributed transactions, has the function of EventBus, it is lightweight, easy to use, and efficient.
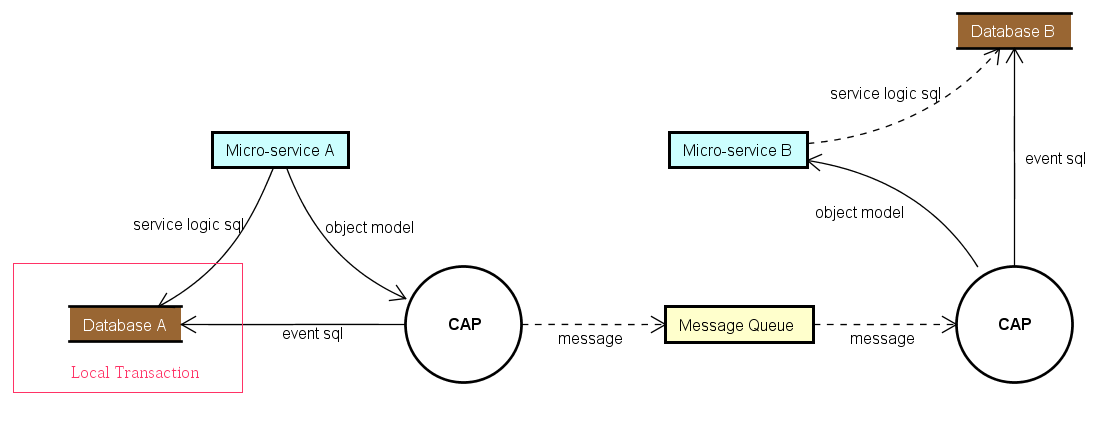
In the process of building an SOA or MicroService system, we usually need to use the event to integrate each service. In the process, simple use of message queue does not guarantee reliability. CAP adopts local message table program integrated with the current database to solve exceptions that may occur in the process of the distributed system calling each other. It can ensure that the event messages are not lost in any case.
You can also use CAP as an EventBus. CAP provides a simpler way to implement event publishing and subscriptions. You do not need to inherit or implement any interface during subscription and sending process.
Architecture overview
CAP implements the Outbox Pattern described in the eShop ebook.
Getting Started
NuGet
CAP can be installed in your project with the following command.
PM> Install-Package DotNetCore.CAP
CAP supports RabbitMQ, Kafka, AzureService, AmazonSQS as message queue, following packages are available to install:
PM> Install-Package DotNetCore.CAP.Kafka
PM> Install-Package DotNetCore.CAP.RabbitMQ
PM> Install-Package DotNetCore.CAP.AzureServiceBus
PM> Install-Package DotNetCore.CAP.AmazonSQS
CAP supports SqlServer, MySql, PostgreSql,MongoDB as event log storage.
// select a database provider you are using, event log table will integrate into.
PM> Install-Package DotNetCore.CAP.SqlServer
PM> Install-Package DotNetCore.CAP.MySql
PM> Install-Package DotNetCore.CAP.PostgreSql
PM> Install-Package DotNetCore.CAP.MongoDB //need MongoDB 4.0+ cluster
Configuration
First, you need to configure CAP in your Startup.cs:
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
//......
services.AddDbContext<AppDbContext>(); //Options, If you are using EF as the ORM
services.AddSingleton<IMongoClient>(new MongoClient("")); //Options, If you are using MongoDB
services.AddCap(x =>
{
// If you are using EF, you need to add the configuration:
x.UseEntityFramework<AppDbContext>(); //Options, Notice: You don't need to config x.UseSqlServer(""") again! CAP can autodiscovery.
// If you are using ADO.NET, choose to add configuration you needed:
x.UseSqlServer("Your ConnectionStrings");
x.UseMySql("Your ConnectionStrings");
x.UsePostgreSql("Your ConnectionStrings");
// If you are using MongoDB, you need to add the configuration:
x.UseMongoDB("Your ConnectionStrings"); //MongoDB 4.0+ cluster
// CAP support RabbitMQ,Kafka,AzureService as the MQ, choose to add configuration you needed:
x.UseRabbitMQ("ConnectionString");
x.UseKafka("ConnectionString");
x.UseAzureServiceBus("ConnectionString");
x.UseAmazonSQS();
});
}
Publish
Inject ICapPublisher in your Controller, then use the ICapPublisher to send messages
public class PublishController : Controller
{
private readonly ICapPublisher _capBus;
public PublishController(ICapPublisher capPublisher)
{
_capBus = capPublisher;
}
[Route("~/adonet/transaction")]
public IActionResult AdonetWithTransaction()
{
using (var connection = new MySqlConnection(ConnectionString))
{
using (var transaction = connection.BeginTransaction(_capBus, autoCommit: true))
{
//your business logic code
_capBus.Publish("xxx.services.show.time", DateTime.Now);
}
}
return Ok();
}
[Route("~/ef/transaction")]
public IActionResult EntityFrameworkWithTransaction([FromServices]AppDbContext dbContext)
{
using (var trans = dbContext.Database.BeginTransaction(_capBus, autoCommit: true))
{
//your business logic code
_capBus.Publish("xxx.services.show.time", DateTime.Now);
}
return Ok();
}
}
Subscribe
In Controller Action
Add the Attribute [CapSubscribe()] on Action to subscribe to messages:
public class PublishController : Controller
{
[CapSubscribe("xxx.services.show.time")]
public void CheckReceivedMessage(DateTime datetime)
{
Console.WriteLine(datetime);
}
}
In Business Logic Service
If your subscription method is not in the Controller, then your subscribe class needs to implement ICapSubscribe interface:
namespace BusinessCode.Service
{
public interface ISubscriberService
{
void CheckReceivedMessage(DateTime datetime);
}
public class SubscriberService: ISubscriberService, ICapSubscribe
{
[CapSubscribe("xxx.services.show.time")]
public void CheckReceivedMessage(DateTime datetime)
{
}
}
}
Then register your class that implements ISubscriberService in Startup.cs
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
//Note: The injection of services needs before of `services.AddCap()`
services.AddTransient<ISubscriberService,SubscriberService>();
services.AddCap(x=>
{
//...
});
}Use partials for topic subscriptions
To group topic subscriptions on class level you're able to define a subscription on a method as a partial. Subscriptions on the message queue will then be a combination of the topic defined on the class and the topic defined on the method. In the following example the Create(..) function will be invoked when receiving a message on customers.create
[CapSubscribe("customers")]
public class CustomersSubscriberService : ICapSubscribe
{
[CapSubscribe("create", isPartial: true)]
public void Create(Customer customer)
{
}
}Subscribe Group
The concept of a subscription group is similar to that of a consumer group in Kafka. it is the same as the broadcast mode in the message queue, which is used to process the same message between multiple different microservice instances.
When CAP startups, it will use the current assembly name as the default group name, if multiple same group subscribers subscribe to the same topic name, there is only one subscriber that can receive the message. Conversely, if subscribers are in different groups, they will all receive messages.
In the same application, you can specify Group property to keep subscriptions in different subscribe groups:
[CapSubscribe("xxx.services.show.time", Group = "group1" )]
public void ShowTime1(DateTime datetime)
{
}
[CapSubscribe("xxx.services.show.time", Group = "group2")]
public void ShowTime2(DateTime datetime)
{
}
ShowTime1 and ShowTime2 will be called one after another because all received messages are processed linear.
You can change that behaviour increasing ConsumerThreadCount.
BTW, You can specify the default group name in the configuration:
services.AddCap(x =>
{
x.DefaultGroup = "default-group-name";
});
Dashboard
CAP also provides dashboard pages, you can easily view messages that were sent and received. In addition, you can also view the message status in real time in the dashboard. Use the following command to install the Dashboard in your project.
PM> Install-Package DotNetCore.CAP.Dashboard
In the distributed environment, the dashboard built-in integrates Consul as a node discovery, while the realization of the gateway agent function, you can also easily view the node or other node data, It's like you are visiting local resources.
services.AddCap(x =>
{
//...
// Register Dashboard
x.UseDashboard();
// Register to Consul
x.UseDiscovery(d =>
{
d.DiscoveryServerHostName = "localhost";
d.DiscoveryServerPort = 8500;
d.CurrentNodeHostName = "localhost";
d.CurrentNodePort = 5800;
d.NodeId = 1;
d.NodeName = "CAP No.1 Node";
});
});The default dashboard address is :http://localhost:xxx/cap, you can configure relative path /cap with x.UseDashboard(opt =>{ opt.MatchPath="/mycap"; }).
Contribute
One of the easiest ways to contribute is to participate in discussions and discuss issues. You can also contribute by submitting pull requests with code changes.