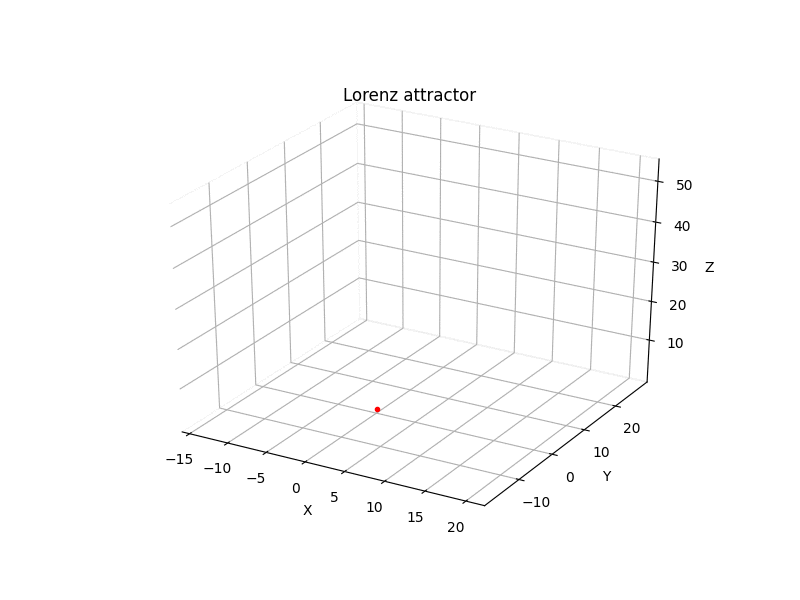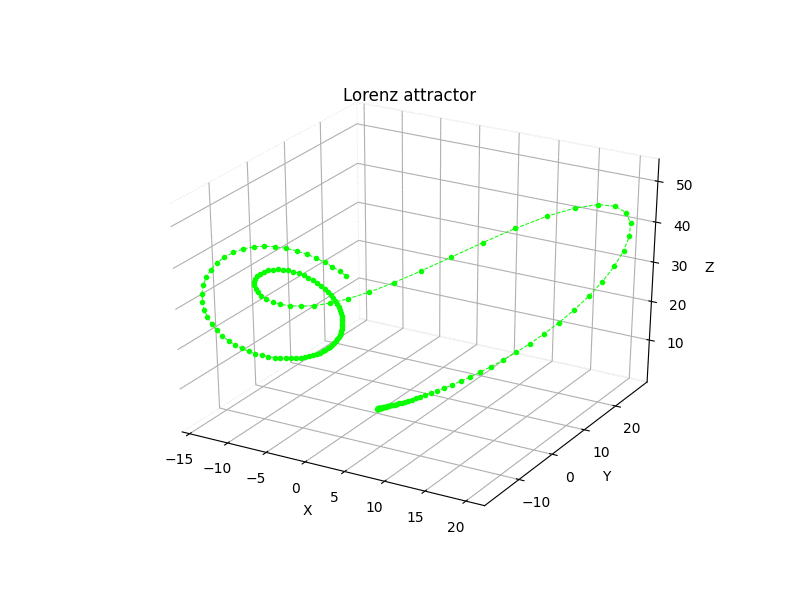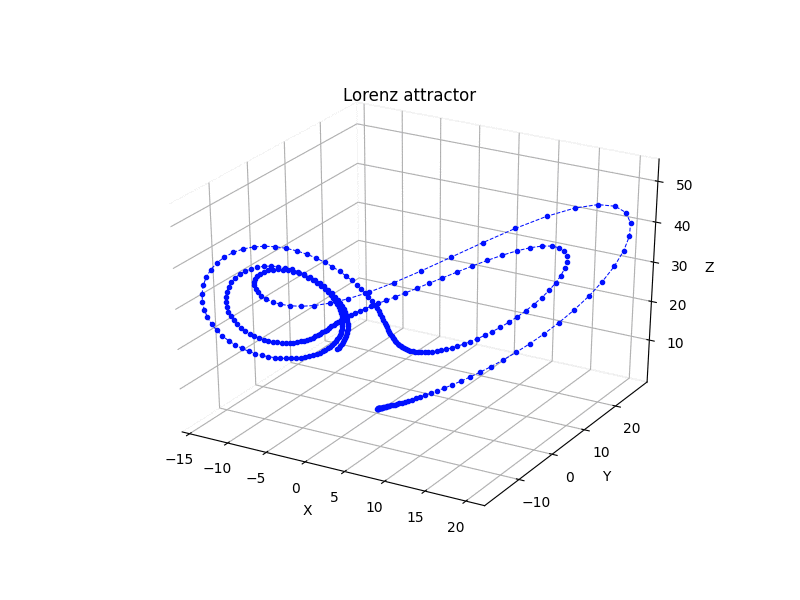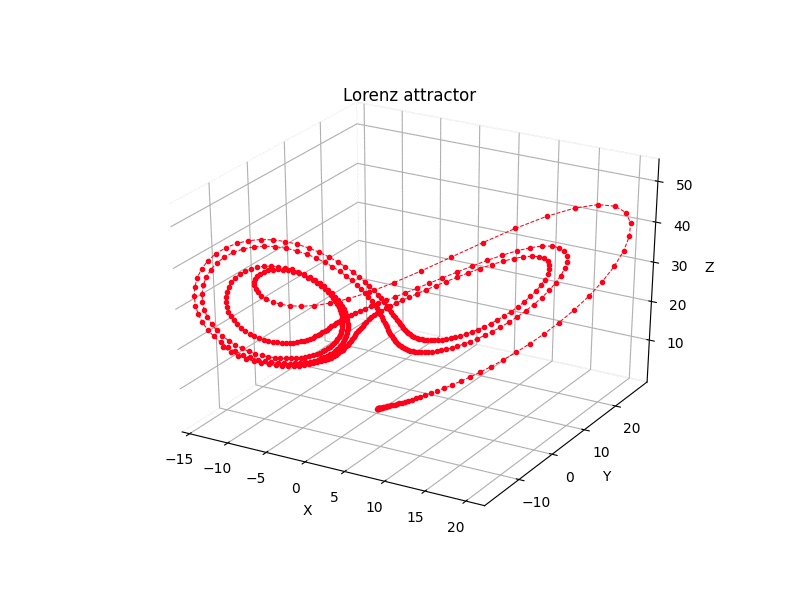
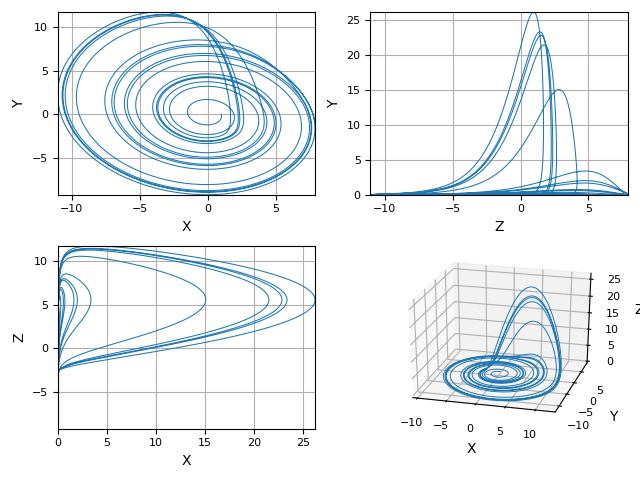
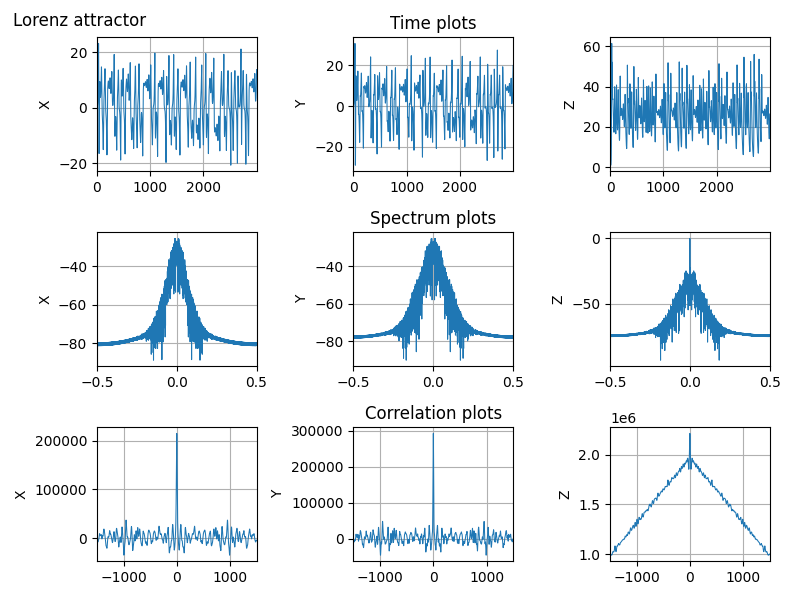
Python scripts for some 3rd-order chaotic systems (Lorenz attractor, Nose-Hoover oscillator, Rossler attractor, Riktake model, Duffing map etc.)
Chaotic attractors
Math model:
dx/dt = sigma * (y - x) dy/dt = rho * (x - z) - y dz/dt = x * y - beta * z
where sigma = 10, rho = 28 and beta = 8/3.
Main info
| Title | Analysis and modeling chaotic systems |
|---|---|
| Author | Alexander Kapitanov |
| Contact | <email_hidden> |
| Project lang | Python 3 |
| First Release | 30 May 2019 |
| License | GNU GPL 3.0. |
Chaotic system
Rossler attractor:
dx/dt = sigma * (y - x) dy/dt = rho * (x - z) - y dz/dt = x * y - beta * z
where a = 0.2, b = 0.2 and c = 5.7.
Spectrum and auto correlation
Source code
You can check the latest sources with the command:
$ git clone <chaospy.git> $ cd chaospy $ <install miniconda for your operation system> $ conda create -y -n venv python==3.9 $ conda activate venv $ pip install -r requirements.txt
Example run:
$ python run.py --show_plots --show_all lorenz
Dependencies
Project requires:
- Python (>= 3.9)
- NumPy (>= 1.19.0)
- SciPy (>= 1.5.1)
- Pandas (>= 1.1.0)
- Matplotlib (>= 3.2.2)
- Pytest (>= 5.4.3)
- Pre-commit (>= 2.6.0)
Chaotic models
- Lorenz
- Rossler
- Rikitake
- Duffing
- Nose Hoover
- Lotka Volterra
- Wang
- Chua
Help
usage: parser.py [-h] [-p POINTS] [-s STEP]
[--init_point INIT_POINT [INIT_POINT ...]] [--show_plots]
[--save_plots] [--add_2d_gif]
{lorenz,rossler,rikitake,chua,duffing,wang,nose-hoover,lotka-volterra}
...
Specify command line arguments for dynamic system.Calculate some math
parameters and plot some graphs of a given chaotic system.
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-p POINTS, --points POINTS
Number of points for dymanic system. Default: 1024.
-s STEP, --step STEP Step size for calculating the next coordinates of
chaotic system. Default: 100.
--init_point INIT_POINT [INIT_POINT ...]
Initial point as string of three floats: "X, Y, Z".
--show_plots Show plots of a model. Default: False.
--save_plots Save plots to PNG files. Default: False.
--add_2d_gif Add 2D coordinates to 3D model into GIF. Default:
False.
Chaotic models:
You can select one of the chaotic models:
{lorenz,rossler,rikitake,chua,duffing,wang,nose-hoover,lotka-volterra}
lorenz Lorenz chaotic model
rossler Rossler chaotic model
rikitake Rikitake chaotic model
chua Chua chaotic model
duffing Duffing chaotic model
wang Wang chaotic model
nose-hoover Nose-hoover chaotic model
lotka-volterra Lotka-volterra chaotic model
Chaotic attractors are used as subparse command. Example:
Lorenz attractor
usage: parser.py lorenz [-h] [--sigma SIGMA] [--beta BETA] [--rho RHO] optional arguments: -h, --help show this help message and exit Lorenz model arguments: --sigma SIGMA Lorenz system parameter. Default: 10 --beta BETA Lorenz system parameter. Default: 2.6666666666666665 --rho RHO Lorenz system parameter. Default: 28
Chua circuit
usage: parser.py chua [-h] [--alpha ALPHA] [--beta BETA] [--mu0 MU0]
[--mu1 MU1]
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
Chua model arguments:
--alpha ALPHA Chua system parameter. Default: 0.1
--beta BETA Chua system parameter. Default: 28
--mu0 MU0 Chua system parameter. Default: -1.143
--mu1 MU1 Chua system parameter. Default: -0.714