microsoft / Cocosnet
Programming Languages
Projects that are alternatives of or similar to Cocosnet
Cross-domain Correspondence Learning for Exemplar-based Image Translation (CVPR 2020 oral, official Pytorch implementation)
Project page | Paper | Video
Pan Zhang, Bo Zhang, Dong Chen, Lu Yuan, and Fang Wen.
Abstract
We present a general framework for exemplar-based image translation, which synthesizes a photo-realistic image from the input in a distinct domain (e.g., semantic segmentation mask, or edge map, or pose keypoints), given an exemplar image. The output has the style (e.g., color, texture) in consistency with the semantically corresponding objects in the exemplar. We propose to jointly learn the cross domain correspondence and the image translation, where both tasks facilitate each other and thus can be learned with weak supervision. The images from distinct domains are first aligned to an intermediate domain where dense correspondence is established. Then, the network synthesizes images based on the appearance of semantically corresponding patches in the exemplar. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach in several image translation tasks. Our method is superior to state-of-the-art methods in terms of image quality significantly, with the image style faithful to the exemplar with semantic consistency. Moreover, we show the utility of our method for several applications
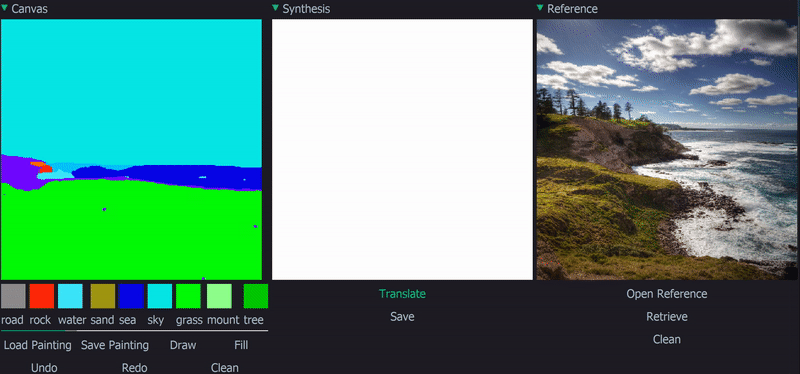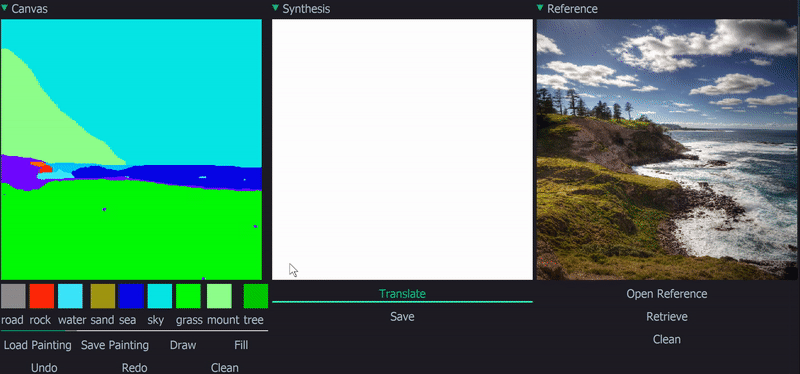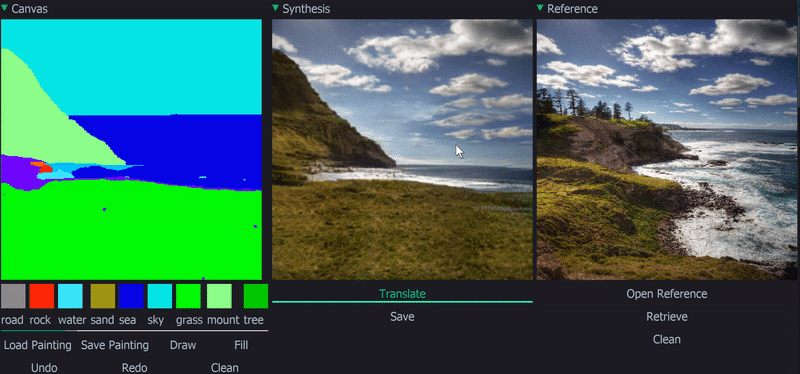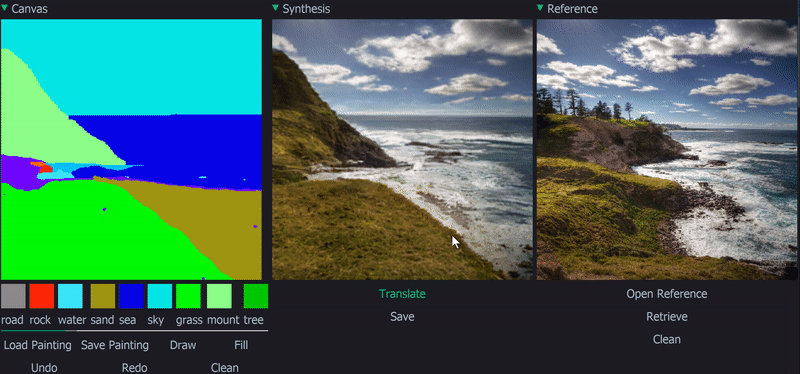
Demo
Installation
Clone the Synchronized-BatchNorm-PyTorch repository.
cd models/networks/
git clone https://github.com/vacancy/Synchronized-BatchNorm-PyTorch
cp -rf Synchronized-BatchNorm-PyTorch/sync_batchnorm .
cd ../../
Install dependencies:
pip install -r requirements.txt
Inference Using Pretrained Model
1) ADE20k (mask-to-image)
Download the pretrained model from here and save them in checkpoints/ade20k. Then run the command
python test.py --name ade20k --dataset_mode ade20k --dataroot ./imgs/ade20k --gpu_ids 0 --nThreads 0 --batchSize 6 --use_attention --maskmix --warp_mask_losstype direct --PONO --PONO_C
The results are saved in output/test/ade20k. If you don't want to use mask of exemplar image when testing, you can download model from here, save them in checkpoints/ade20k, and run
python test.py --name ade20k --dataset_mode ade20k --dataroot ./imgs/ade20k --gpu_ids 0 --nThreads 0 --batchSize 6 --use_attention --maskmix --noise_for_mask --warp_mask_losstype direct --PONO --PONO_C --which_epoch 90
2) Celebahq (mask-to-face)
Download the pretrained model from here, save them in checkpoints/celebahq, then run the command:
python test.py --name celebahq --dataset_mode celebahq --dataroot ./imgs/celebahq --gpu_ids 0 --nThreads 0 --batchSize 4 --use_attention --maskmix --warp_mask_losstype direct --PONO --PONO_C --warp_bilinear --adaptor_kernel 4
, then the results will be saved in output/test/celebahq.
3) Celebahq (edge-to-face)
Download the pretrained model from here, save them in checkpoints/celebahqedge, then run
python test.py --name celebahqedge --dataset_mode celebahqedge --dataroot ./imgs/celebahqedge --gpu_ids 0 --nThreads 0 --batchSize 4 --use_attention --maskmix --PONO --PONO_C --warp_bilinear --adaptor_kernel 4
the results will be stored in output/test/celebahqedge.
4) DeepFashion (pose-to-image)
Download the pretrained model from here, save them in checkpoints/deepfashion, then run the following command:
python test.py --name deepfashion --dataset_mode deepfashion --dataroot ./imgs/DeepFashion --gpu_ids 0 --nThreads 0 --batchSize 4 --use_attention --PONO --PONO_C --warp_bilinear --no_flip --warp_patch --video_like --adaptor_kernel 4
and the results are saved in output/test/deepfashion.
Training
Pretrained VGG model Download from here, move it to models/. This model is used to calculate training loss.
1) ADE20k (mask-to-image)
-
Dataset Download ADE20k, move
ADEChallengeData2016/annotations/ADE_train_*.pngtoADEChallengeData2016/images/training/,ADEChallengeData2016/annotations/ADE_val_*.pngto `ADEChallengeData2016/images/validation/ -
Retrieval_pairs We use image retrieval to find exemplars for exemplar-based training. Download
ade20k_ref.txtandade20k_ref_test.txtfrom here, save or replace them indata/ -
Run the command, note
dataset_pathis your ade20k root, e.g.,/data/Dataset/ADEChallengeData2016/images. We use 8 32GB Tesla V100 GPUs for training. You can setbatchSizeto 16, 8 or 4 with fewer GPUs and changegpu_ids.python train.py --name ade20k --dataset_mode ade20k --dataroot dataset_path --niter 100 --niter_decay 100 --use_attention --maskmix --warp_mask_losstype direct --weight_mask 100.0 --PONO --PONO_C --batchSize 32 --vgg_normal_correct --gpu_ids 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7
-
If you don't want to use mask of the exemplar image when testing, you can run
python train.py --name ade20k --dataset_mode ade20k --dataroot dataset_path --niter 100 --niter_decay 100 --use_attention --maskmix --noise_for_mask --mask_epoch 150 --warp_mask_losstype direct --weight_mask 100.0 --PONO --PONO_C --vgg_normal_correct --batchSize 32 --gpu_ids 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7
2) Celebahq (mask-to-face)
-
Dataset Download Celebahq, we combine the parsing mask except glasses. You can download and unzip annotations, then move folder
all_parts_except_glasses/toCelebAMask-HQ/CelebAMask-HQ-mask-anno/ -
Retrieval_pairs We use image retrieval to find exemplars for examplar-based training. Download
celebahq_ref.txtandcelebahq_ref_test.txtfrom here, save or replace them indata/ -
Train_Val split We randomly split images to train set and validation set. Download
train.txtandval.txtfrom here, save them inCelebAMask-HQ/ - Run the command, note
dataset_pathis your celebahq root, e.g./data/Dataset/CelebAMask-HQ. In our experiment we use 8 32GB Tesla V100 GPUs for training. You can setbatchSizeto 16, 8 or 4 with fewer GPUs and changegpu_ids.python train.py --name celebahq --dataset_mode celebahq --dataroot dataset_path --niter 30 --niter_decay 30 --which_perceptual 4_2 --weight_perceptual 0.001 --use_attention --maskmix --warp_mask_losstype direct --weight_mask 100.0 --PONO --PONO_C --vgg_normal_correct --fm_ratio 1.0 --warp_bilinear --warp_cycle_w 0.1 --batchSize 32 --gpu_ids 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7
3) Celebahq (edge-to-face)
- Dataset Download the dataset
- Retrieval_pairs same as Celebahq (Mask-to-face)
- Train_Val split same as Celebahq (Mask-to-face)
- Run the following command. Note that
dataset_pathis your celebahq root, e.g./data/Dataset/CelebAMask-HQ. We use 8 32GB Tesla V100 GPUs to train the network. You can setbatchSizeto 16, 8 or 4 with fewer GPUs and changegpu_ids.python train.py --name celebahqedge --dataset_mode celebahqedge --dataroot dataset_path --niter 30 --niter_decay 30 --which_perceptual 4_2 --weight_perceptual 0.001 --use_attention --maskmix --PONO --PONO_C --vgg_normal_correct --fm_ratio 1.0 --warp_bilinear --warp_cycle_w 1 --batchSize 32 --gpu_ids 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7
4) DeepFashion (pose-to-image)
-
Dataset Download DeepFashion, we use OpenPose to estimate pose of DeepFashion. Download and unzip openpose results, then move folder
pose/toDeepFashion/ -
Retrieval_pairs Download
deepfashion_ref.txt,deepfashion_ref_test.txtanddeepfashion_self_pair.txtfrom here, save or replace them indata/ -
Train_Val split Download
train.txtandval.txtfrom here, save them inDeepFashion/ - Run the following command. Note that
dataset_pathis your DeepFashion dataset root, e.g./data/Dataset/DeepFashion. We use 8 32GB Tesla V100 GPUs to train the network. You can setbatchSizeto 16, 8 or 4 with fewer GPUs and changegpu_ids.python train.py --name deepfashion --dataset_mode deepfashion --dataroot dataset_path --niter 50 --niter_decay 50 --which_perceptual 4_2 --weight_perceptual 0.001 --use_attention --real_reference_probability 0.0 --PONO --PONO_C --vgg_normal_correct --fm_ratio 1.0 --warp_bilinear --warp_self_w 100 --no_flip --warp_patch --video_like --batchSize 32 --gpu_ids 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7
Citation
If you use this code for your research, please cite our papers.
@inproceedings{zhang2020cross,
title={Cross-domain Correspondence Learning for Exemplar-based Image Translation},
author={Zhang, Pan and Zhang, Bo and Chen, Dong and Yuan, Lu and Wen, Fang},
booktitle={Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition},
pages={5143--5153},
year={2020}
}
Acknowledgments
This code borrows heavily from SPADE. We also thank Jiayuan Mao for his Synchronized Batch Normalization code.