taesungp / Contrastive Unpaired Translation
Programming Languages
Labels
Projects that are alternatives of or similar to Contrastive Unpaired Translation
Contrastive Unpaired Translation (CUT)
video (1m) | video (10m) | website | paper

We provide our PyTorch implementation of unpaired image-to-image translation based on patchwise contrastive learning and adversarial learning. No hand-crafted loss and inverse network is used. Compared to CycleGAN, our model training is faster and less memory-intensive. In addition, our method can be extended to single image training, where each “domain” is only a single image.
Contrastive Learning for Unpaired Image-to-Image Translation
Taesung Park, Alexei A. Efros, Richard Zhang, Jun-Yan Zhu
UC Berkeley and Adobe Research
In ECCV 2020
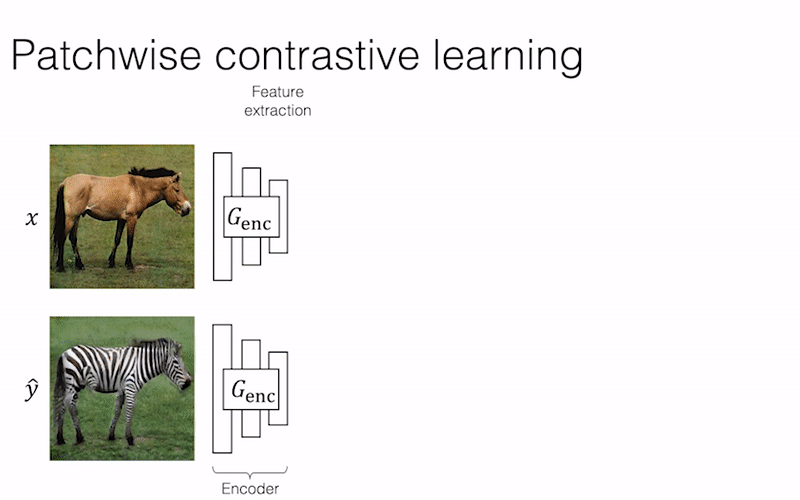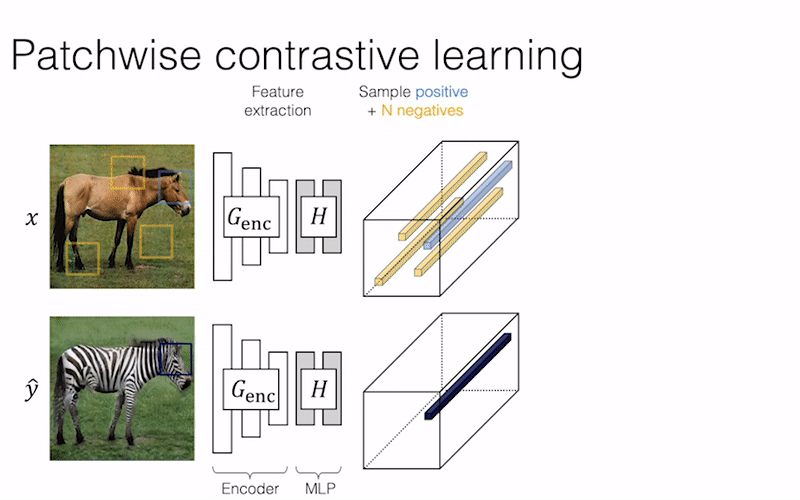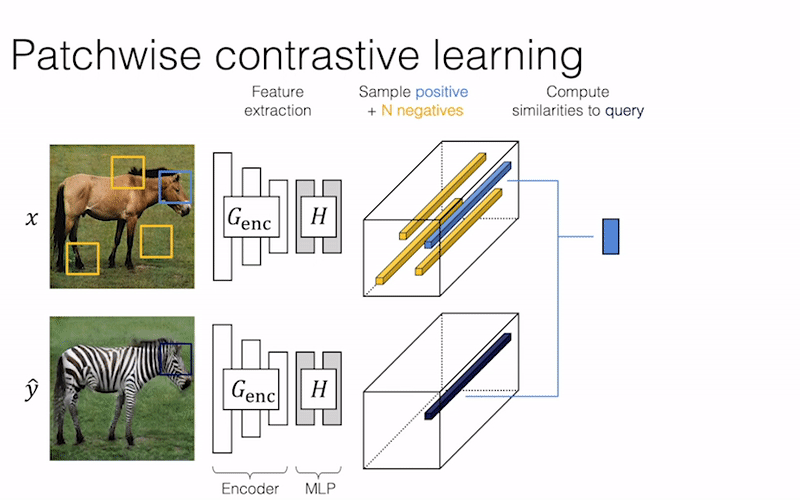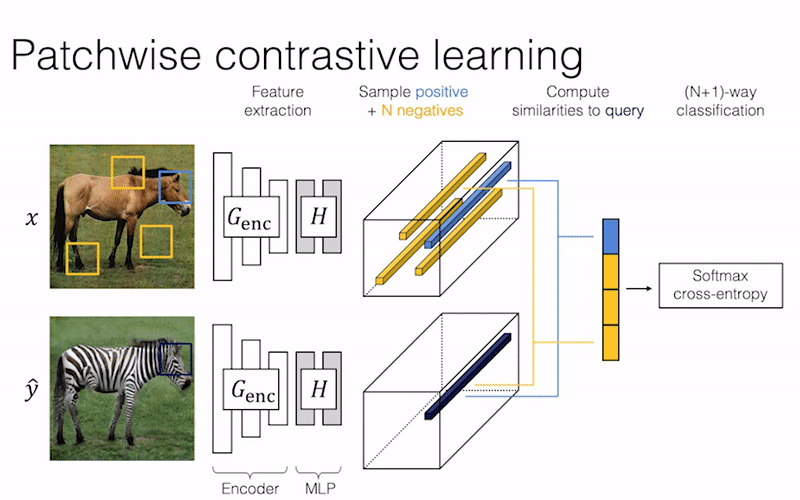
Pseudo code
import torch
cross_entropy_loss = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
# Input: f_q (BxCxS) and sampled features from H(G_enc(x))
# Input: f_k (BxCxS) are sampled features from H(G_enc(G(x))
# Input: tau is the temperature used in PatchNCE loss.
# Output: PatchNCE loss
def PatchNCELoss(f_q, f_k, tau=0.07):
# batch size, channel size, and number of sample locations
B, C, S = f_q.shape
# calculate v * v+: BxSx1
l_pos = (f_k * f_q).sum(dim=1)[:, :, None]
# calculate v * v-: BxSxS
l_neg = torch.bmm(f_q.transpose(1, 2), f_k)
# The diagonal entries are not negatives. Remove them.
identity_matrix = torch.eye(S)[None, :, :]
l_neg.masked_fill_(identity_matrix, -float('inf'))
# calculate logits: (B)x(S)x(S+1)
logits = torch.cat((l_pos, l_neg), dim=2) / tau
# return PatchNCE loss
predictions = logits.flatten(0, 1)
targets = torch.zeros(B * S, dtype=torch.long)
return cross_entropy_loss(predictions, targets)
Example Results
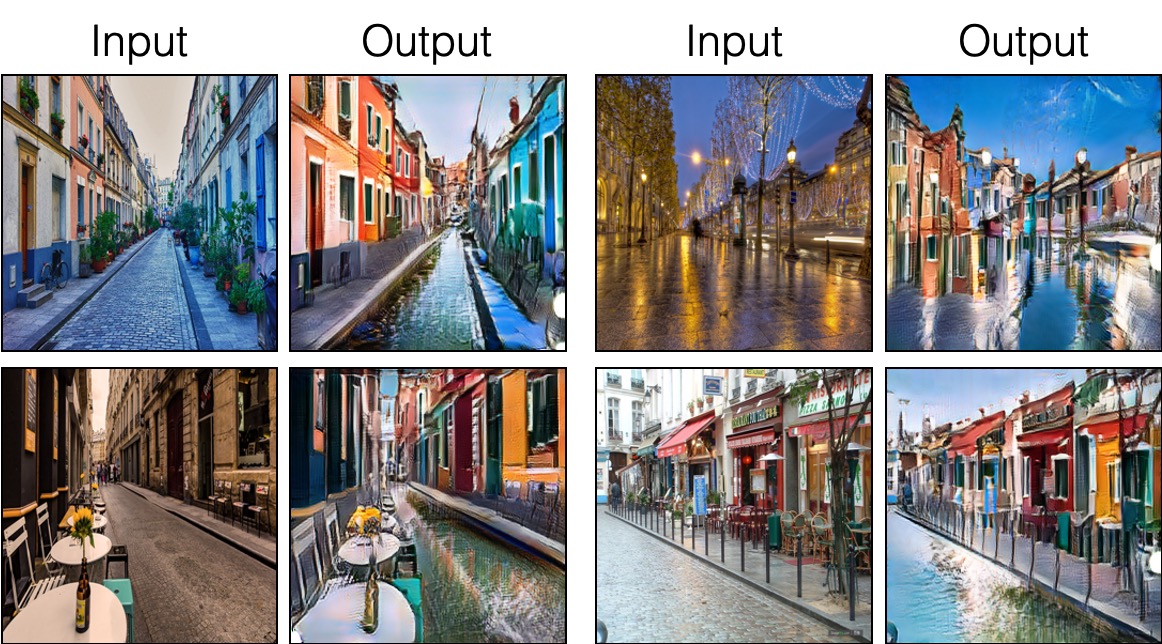
Unpaired Image-to-Image Translation

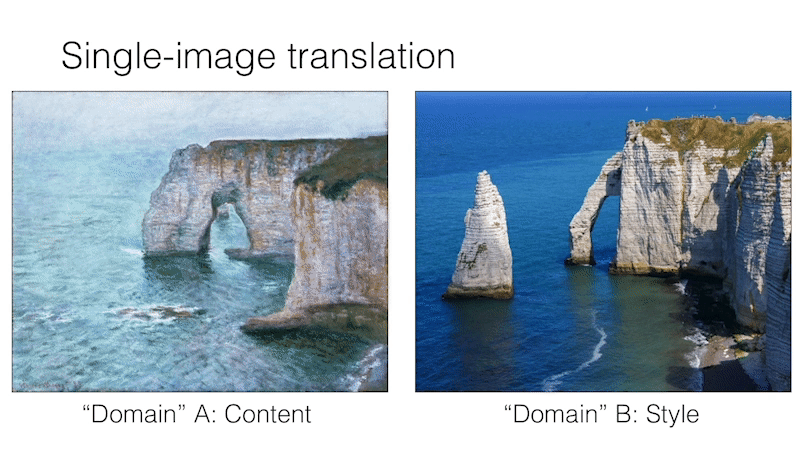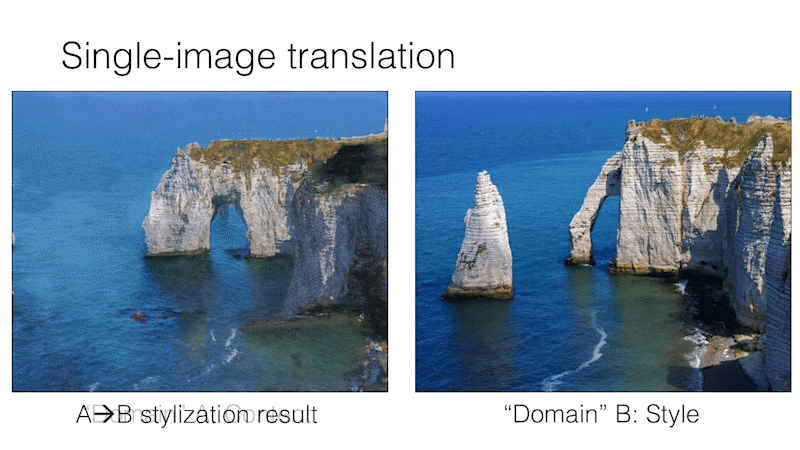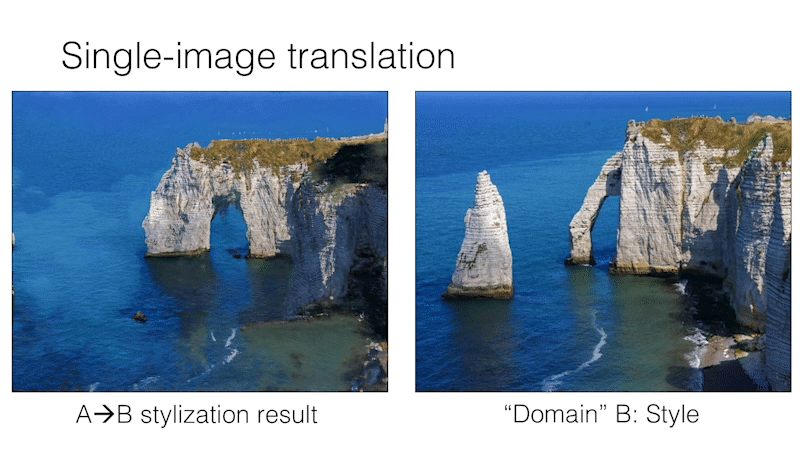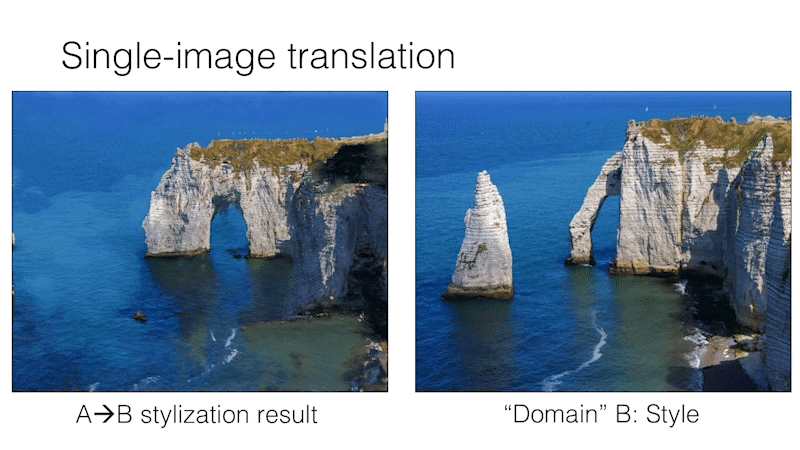
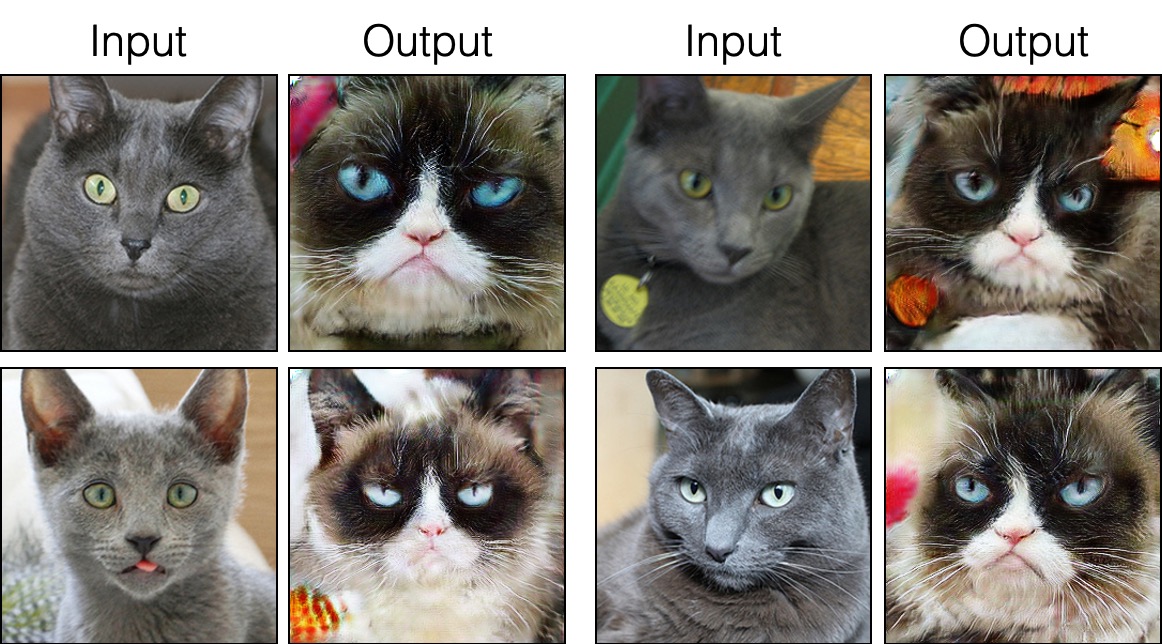
Single Image Unpaired Translation
Russian Blue Cat to Grumpy Cat
Parisian Street to Burano's painted houses

Prerequisites
- Linux or macOS
- Python 3
- CPU or NVIDIA GPU + CUDA CuDNN
Update log
9/12/2020: Added single-image translation.
Getting started
- Clone this repo:
git clone https://github.com/taesungp/contrastive-unpaired-translation CUT
cd CUT
-
Install PyTorch 1.1 and other dependencies (e.g., torchvision, visdom, dominate, gputil).
For pip users, please type the command
pip install -r requirements.txt.For Conda users, you can create a new Conda environment using
conda env create -f environment.yml.
CUT and FastCUT Training and Test
- Download the
grumpifycatdataset (Fig 8 of the paper. Russian Blue -> Grumpy Cats)
bash ./datasets/download_cut_dataset.sh grumpifycat
The dataset is downloaded and unzipped at ./datasets/grumpifycat/.
-
To view training results and loss plots, run
python -m visdom.serverand click the URL http://localhost:8097. -
Train the CUT model:
python train.py --dataroot ./datasets/grumpifycat --name grumpycat_CUT --CUT_mode CUT
Or train the FastCUT model
python train.py --dataroot ./datasets/grumpifycat --name grumpycat_FastCUT --CUT_mode FastCUT
The checkpoints will be stored at ./checkpoints/grumpycat_*/web.
- Test the CUT model:
python test.py --dataroot ./datasets/grumpifycat --name grumpycat_CUT --CUT_mode CUT --phase train
The test results will be saved to a html file here: ./results/grumpifycat/latest_train/index.html.
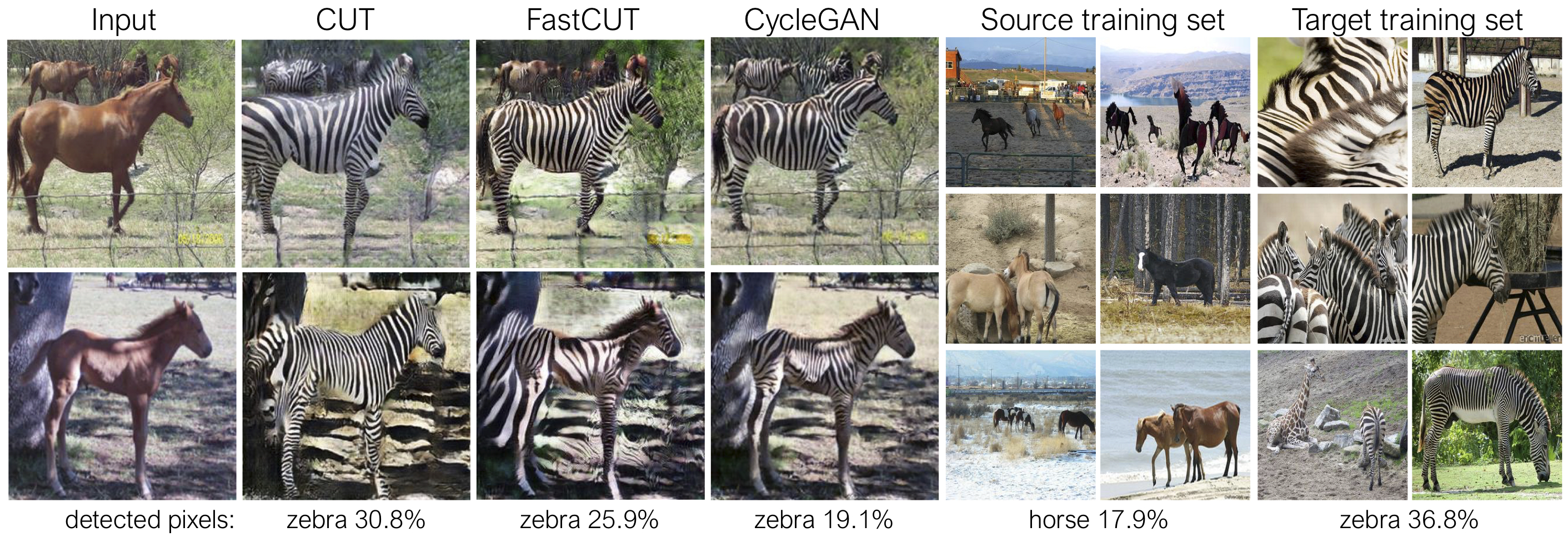
CUT, FastCUT, and CycleGAN
CUT is trained with the identity preservation loss and with lambda_NCE=1, while FastCUT is trained without the identity loss but with higher lambda_NCE=10.0. Compared to CycleGAN, CUT learns to perform more powerful distribution matching, while FastCUT is designed as a lighter (half the GPU memory, can fit a larger image), and faster (twice faster to train) alternative to CycleGAN. Please refer to the paper for more details.
In the above figure, we measure the percentage of pixels belonging to the horse/zebra bodies, using a pre-trained semantic segmentation model. We find a distribution mismatch between sizes of horses and zebras images -- zebras usually appear larger (36.8% vs. 17.9%). Our full method CUT has the flexibility to enlarge the horses, as a means of better matching of the training statistics than CycleGAN. FastCUT behaves more conservatively like CycleGAN.
Training using our launcher scripts
Please see experiments/grumpifycat_launcher.py that generates the above command line arguments. The launcher scripts are useful for configuring rather complicated command-line arguments of training and testing.
Using the launcher, the command below generates the training command of CUT and FastCUT.
python -m experiments grumpifycat train 0 # CUT
python -m experiments grumpifycat train 1 # FastCUT
To test using the launcher,
python -m experiments grumpifycat test 0 # CUT
python -m experiments grumpifycat test 1 # FastCUT
Possible commands are run, run_test, launch, close, and so on. Please see experiments/__main__.py for all commands. Launcher is easy and quick to define and use. For example, the grumpifycat launcher is defined in a few lines:
from .tmux_launcher import Options, TmuxLauncher
class Launcher(TmuxLauncher):
def common_options(self):
return [
Options( # Command 0
dataroot="./datasets/grumpifycat",
name="grumpifycat_CUT",
CUT_mode="CUT"
),
Options( # Command 1
dataroot="./datasets/grumpifycat",
name="grumpifycat_FastCUT",
CUT_mode="FastCUT",
)
]
def commands(self):
return ["python train.py " + str(opt) for opt in self.common_options()]
def test_commands(self):
# Russian Blue -> Grumpy Cats dataset does not have test split.
# Therefore, let's set the test split to be the "train" set.
return ["python test.py " + str(opt.set(phase='train')) for opt in self.common_options()]
Apply a pre-trained CUT model and evaluate
The tutorial for using pretrained models will be released soon.
SinCUT Single Image Unpaired Training
To train SinCUT (single-image translation, shown in Fig 9, 13 and 14 of the paper), you need to
- set the
--modeloption as--model sincut, which invokes the configuration and codes at./models/sincut_model.py, and - specify the dataset directory of one image in each domain, such as the example dataset included in this repo at
./datasets/single_image_monet_etretat/.
For example, to train a model for the Etretat cliff (first image of Figure 13), please use the following command.
python train.py --model sincut --name singleimage_monet_etretat --dataroot ./datasets/single_image_monet_etretat
or by using the experiment launcher script,
python -m experiments singleimage run 0
For single-image translation, we adopt network architectural components of StyleGAN2, as well as the pixel identity preservation loss used in DTN and CycleGAN. In particular, we adopted the code of rosinality, which exists at models/stylegan_networks.py.
The training takes several hours. To generate the final image using the checkpoint,
python test.py --model sincut --name singleimage_monet_etretat --dataroot ./datasets/single_image_monet_etretat
or simply
python -m experiments singleimage run_test 0
Datasets
Download CUT/CycleGAN/pix2pix datasets and learn how to create your own datasets.
Citation
If you use this code for your research, please cite our paper.
@inproceedings{park2020cut,
title={Contrastive Learning for Unpaired Image-to-Image Translation},
author={Taesung Park and Alexei A. Efros and Richard Zhang and Jun-Yan Zhu},
booktitle={European Conference on Computer Vision},
year={2020}
}
If you use the original pix2pix and CycleGAN model included in this repo, please cite the following papers
@inproceedings{CycleGAN2017,
title={Unpaired Image-to-Image Translation using Cycle-Consistent Adversarial Networks},
author={Zhu, Jun-Yan and Park, Taesung and Isola, Phillip and Efros, Alexei A},
booktitle={IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV)},
year={2017}
}
@inproceedings{isola2017image,
title={Image-to-Image Translation with Conditional Adversarial Networks},
author={Isola, Phillip and Zhu, Jun-Yan and Zhou, Tinghui and Efros, Alexei A},
booktitle={IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR)},
year={2017}
}
Acknowledgments
We thank Allan Jabri and Phillip Isola for helpful discussion and feedback. Our code is developed based on pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix. We also thank pytorch-fid for FID computation, drn for mIoU computation, and stylegan2-pytorch for the PyTorch implementation of StyleGAN2 used in our single-image translation setting.