ilovepose / Darkpose
Projects that are alternatives of or similar to Darkpose
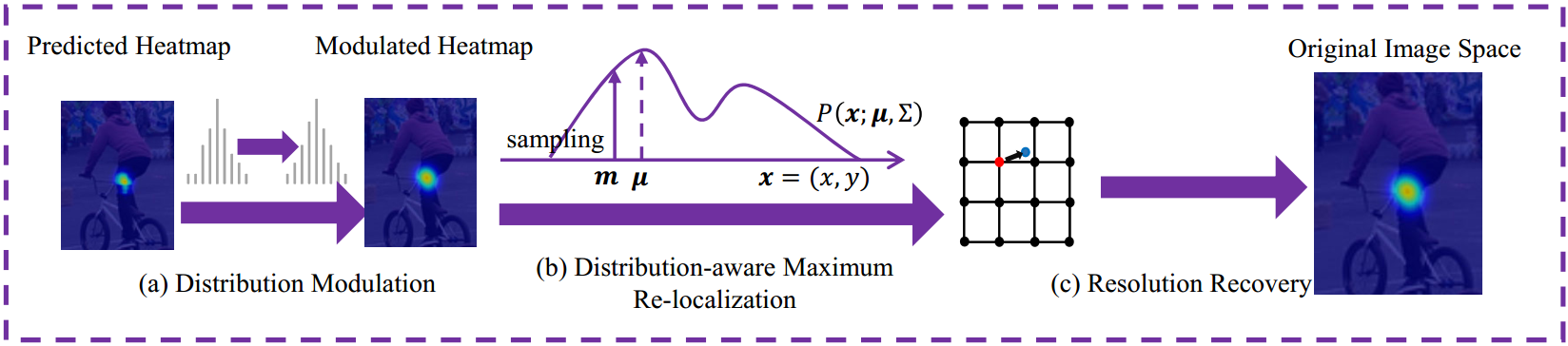
Distribution Aware Coordinate Representation for Human Pose Estimation
Serving as a model-agnostic plug-in, DARK significantly improves the performance of a variety of state-of-the-art human pose estimation models!
News
- [2019/10/14] DarkPose is now on ArXiv.
- [2019/10/15] Project page is created.
- [2019/10/27] DarkPose achieve 76.4 on the COCO test-challenge (2nd place entry of COCO Keypoints Challenge ICCV 2019)!
- [2020/02/24] DarkPose accepted by CVPR2020.
- [2020/06/17] Code is released.
- [2020/08/07] Pretrained models are provided.
Introduction
This work fills the gap by studying the coordinate representation with a particular focus on the heatmap. We formulate a novel Distribution-Aware coordinate Representation of Keypoint (DARK) method. Serving as a model-agnostic plug-in, DARK significantly improves the performance of a variety of state-of-the-art human pose estimation models!
Our CVPR2019 work Fast Human Pose Estimation can work seamlessly with DARK, which is available at Github
Main Results
Results on COCO val2017 with detector having human AP of 56.4 on COCO val2017 dataset
| Baseline | Input size | #Params | GFLOPs | AP | Ap .5 | AP .75 | AP (M) | AP (L) | AR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hourglass(4 Blocks) | 128×96 | 13.0M | 2.7 | 66.2 | 87.6 | 75.1 | 63.8 | 71.4 | 72.8 |
| Hourglass(4 Blocks) + DARK | 128×96 | 13.0M | 2.7 | 69.6 | 87.8 | 77.0 | 67.0 | 75.4 | 75.7 |
| Hourglass(8 Blocks) | 128×96 | 25.1M | 4.9 | 67.6 | 88.3 | 77.4 | 65.2 | 73.0 | 74.0 |
| Hourglass(8 Blocks) + DARK | 128×96 | 25.1M | 4.9 | 70.8 | 87.9 | 78.3 | 68.3 | 76.4 | 76.6 |
| SimpleBaseline-R50 | 128×96 | 34.0M | 2.3 | 59.3 | 85.5 | 67.4 | 57.8 | 63.8 | 66.6 |
| SimpleBaseline-R50 + DARK | 128×96 | 34.0M | 2.3 | 62.6 | 86.1 | 70.4 | 60.4 | 67.9 | 69.5 |
| SimpleBaseline-R101 | 128×96 | 53.0M | 3.1 | 58.8 | 85.3 | 66.1 | 57.3 | 63.4 | 66.1 |
| SimpleBaseline-R101 + DARK | 128×96 | 53.0M | 3.1 | 63.2 | 86.2 | 71.1 | 61.2 | 68.5 | 70.0 |
| SimpleBaseline-R152 | 128×96 | 68.6M | 3.9 | 60.7 | 86.0 | 69.6 | 59.0 | 65.4 | 68.0 |
| SimpleBaseline-R152 + DARK | 128×96 | 68.6M | 3.9 | 63.1 | 86.2 | 71.6 | 61.3 | 68.1 | 70.0 |
| HRNet-W32 | 128×96 | 28.5M | 1.8 | 66.9 | 88.7 | 76.3 | 64.6 | 72.3 | 73.7 |
| HRNet-W32 + DARK | 128×96 | 28.5M | 1.8 | 70.7 | 88.9 | 78.4 | 67.9 | 76.6 | 76.7 |
| HRNet-W48 | 128×96 | 63.6M | 3.6 | 68.0 | 88.9 | 77.4 | 65.7 | 73.7 | 74.7 |
| HRNet-W48 + DARK | 128×96 | 63.6M | 3.6 | 71.9 | 89.1 | 79.6 | 69.2 | 78.0 | 77.9 |
| HRNet-W32 | 256×192 | 28.5M | 7.1 | 74.4 | 90.5 | 81.9 | 70.8 | 81.0 | 79.8 |
| HRNet-W32 + DARK | 256×192 | 28.5M | 7.1 | 75.6 | 90.5 | 82.1 | 71.8 | 82.8 | 80.8 |
| HRNet-W32 | 384×288 | 28.5M | 16.0 | 75.8 | 90.6 | 82.5 | 72.0 | 82.7 | 80.9 |
| HRNet-W32 + DARK | 384×288 | 28.5M | 16.0 | 76.6 | 90.7 | 82.8 | 72.7 | 83.9 | 81.5 |
| HRNet-W48 | 384×288 | 63.6M | 32.9 | 76.3 | 90.8 | 82.9 | 72.3 | 83.4 | 81.2 |
| HRNet-W48 + DARK | 384×288 | 63.6M | 32.9 | 76.8 | 90.6 | 83.2 | 72.8 | 84.0 | 81.7 |
Note:
- Flip test is used.
- Person detector has person AP of 56.4 on COCO val2017 dataset.
- GFLOPs is for convolution and linear layers only.
Results on COCO test-dev2017 with detector having human AP of 60.9 on COCO test-dev2017 dataset
| Baseline | Input size | #Params | GFLOPs | AP | Ap.5 | AP.75 | AP(M) | AP(L) | AR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HRNet-W48 | 384x288 | 63.6M | 32.9 | 75.5 | 92.5 | 83.3 | 71.9 | 81.5 | 80.5 |
| HRNet-W48 + DARK | 384x288 | 63.6M | 32.9 | 76.2 | 92.5 | 83.6 | 72.5 | 82.4 | 81.1 |
| HRNet-W48* | 384x288 | 63.6M | 32.9 | 77.0 | 92.7 | 84.5 | 73.4 | 83.1 | 82.0 |
| HRNet-W48 + DARK* | 384x288 | 63.6M | 32.9 | 77.4 | 92.6 | 84.6 | 73.6 | 83.7 | 82.3 |
| HRNet-W48 + DARK*- | 384x288 | 63.6M | 32.9 | 78.2 | 93.5 | 85.5 | 74.4 | 84.2 | 83.5 |
| HRNet-W48 + DARK*-+ | 384x288 | 63.6M | 32.9 | 78.9 | 93.8 | 86.0 | 75.1 | 84.4 | 83.5 |
Note:
- Flip test is used.
- Person detector has person AP of 60.9 on COCO test-dev2017 dataset.
- GFLOPs is for convolution and linear layers only.
- * means using additional data from AI challenger for training.
- - means the detector ensemble with HTC and SNIPER.
- + means using model ensemble.
Results on MPII val
| PCKh | Baseline | Head | Shoulder | Elbow | Wrist | Hip | Knee | Ankle | Mean |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.5 | HRNet_w32 | 97.1 | 95.9 | 90.3 | 86.5 | 89.1 | 87.1 | 83.3 | 90.3 |
| 0.5 | HRNet_w32 + DARK | 97.2 | 95.9 | 91.2 | 86.7 | 89.7 | 86.7 | 84.0 | 90.6 |
| 0.1 | HRNet_w32 | 51.1 | 42.7 | 42.0 | 41.6 | 17.9 | 29.9 | 31.0 | 37.7 |
| 0.1 | HRNet_w32 + DARK | 55.2 | 47.8 | 47.4 | 45.2 | 20.1 | 33.4 | 35.4 | 42.0 |
Note:
- Flip test is used.
- Input size is 256x256
- GFLOPs is for convolution and linear layers only.
Quick start
1. Preparation
1.1 Prepare the dataset
For the MPII dataset, the original annotation files are in matlab format. We have converted them into json format, you also need to download them from OneDrive or GoogleDrive.
Extract them under {POSE_ROOT}/data, your directory tree should look like this:
${POSE_ROOT}/data/mpii
├── images
└── mpii_human_pose_v1_u12_1.mat
|—— annot
| |—— gt_valid.mat
└── |—— test.json
| |—— train.json
| |—— trainval.json
| |—— valid.json
└── images
|—— 000001163.jpg
|—— 000003072.jpg
For the COCO dataset, your directory tree should look like this:
${POSE_ROOT}/data/coco
├── annotations
├── images
│ ├── test2017
│ ├── train2017
│ └── val2017
└── person_detection_results
1.2 Download the pretrained models
Pretrained models are provided.
1.3 Prepare the environment
Setting the parameters in the file prepare_env.sh as follows:
# DATASET_ROOT=$HOME/datasets
# COCO_ROOT=${DATASET_ROOT}/MSCOCO
# MPII_ROOT=${DATASET_ROOT}/MPII
# MODELS_ROOT=${DATASET_ROOT}/models
Then execute:
bash prepare_env.sh
If you like, you can prepare the environment step by step
Citation
If you use our code or models in your research, please cite with:
@InProceedings{Zhang_2020_CVPR,
author = {Zhang, Feng and Zhu, Xiatian and Dai, Hanbin and Ye, Mao and Zhu, Ce},
title = {Distribution-Aware Coordinate Representation for Human Pose Estimation},
booktitle = {IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR)},
month = {June},
year = {2020}
}
Acknowledgement
Thanks for the open-source HRNet