gridap / Gridap.jl
Programming Languages
Projects that are alternatives of or similar to Gridap.jl
| Documentation |
|---|
 
|
| Build Status |
|
|
| Community |
| Citation |
What
Gridap provides a set of tools for the grid-based approximation of partial differential equations (PDEs) written in the Julia programming language. The library currently supports linear and nonlinear PDE systems for scalar and vector fields, single and multi-field problems, conforming and nonconforming finite element (FE) discretizations, on structured and unstructured meshes of simplices and n-cubes. Gridap is extensible and modular. One can implement new FE spaces, new reference elements, use external mesh generators, linear solvers, post-processing tools, etc. See, e.g., the list of available Gridap plugins.
Gridap has a very expressive API allowing to solve complex PDEs with very few lines of code. The user can write the underlying weak form with a syntax almost 1:1 to the mathematical notation, and Gridap generates an efficient FE assembly loop automatically by leveraging the Julia JIT compiler. For instance, the weak form for an interior penalty DG method for the Poisson equation can be specified simply as:
a(u,v) =
∫( ∇(v)⋅∇(u) )*dΩ +
∫( (γ/h)*v*u - v*(n_Γ⋅∇(u)) - (n_Γ⋅∇(v))*u )*dΓ +
∫(
(γ/h)*jump(v*n_Λ)⋅jump(u*n_Λ) -
jump(v*n_Λ)⋅mean(∇(u)) -
mean(∇(v))⋅jump(u*n_Λ)
)*dΛ
l(v) =
∫( v*f )*dΩ +
∫( (γ/h)*v*u - (n_Γ⋅∇(v))*u )*dΓ
See the complete code here. As an example for multi-field PDEs, this is how the weak form for the Stokes equation with Neumann boundary conditions can be specified:
a((u,p),(v,q)) =
∫( ∇(v)⊙∇(u) - (∇⋅v)*p + q*(∇⋅u) )*dΩ
l((v,q)) =
∫( v⋅f + q*g )*dΩ +
∫( v⋅(n_Γ⋅∇u) - (n_Γ⋅v)*p )*dΓ
See the complete code here.
Documentation
- STABLE — Documentation for the most recently tagged version of Gridap.jl.
- DEVEL — Documentation for the in-development version of Gridap.
Tutorials
A hands-on user-guide to the library is available as a set of tutorials. They are available as Jupyter notebooks and html pages.
Installation
Gridap is a registered package in the official Julia package registry. Thus, the installation of Gridap is straight forward using the Julia's package manager. Open the Julia REPL, type ] to enter package mode, and install as follows
pkg> add Gridap
Plugins
- GridapGmsh Generate a FE mesh with GMSH and use it in Gridap.
- GridapMakie Makie plotting recipies for Gridap.
- GridapPardiso Use the Intel Pardiso MKL direct sparse solver in Gridap.
- GridapEmbedded Embedded finite elements in Julia.
- GridapODEs Gridap support for time-dependent PDEs.
- GridapDistributed Distributed-memory extension of Gridap.
Examples
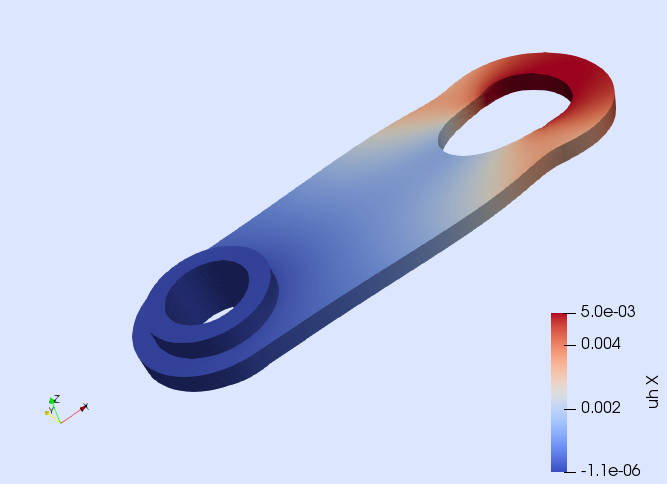
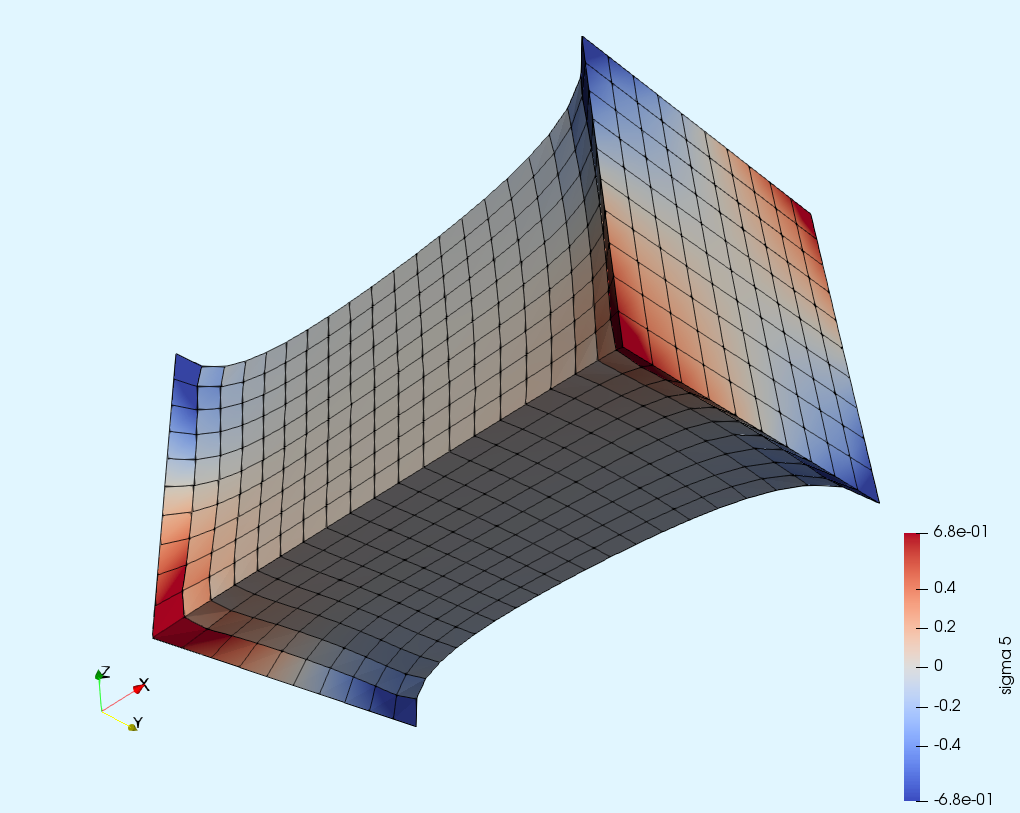
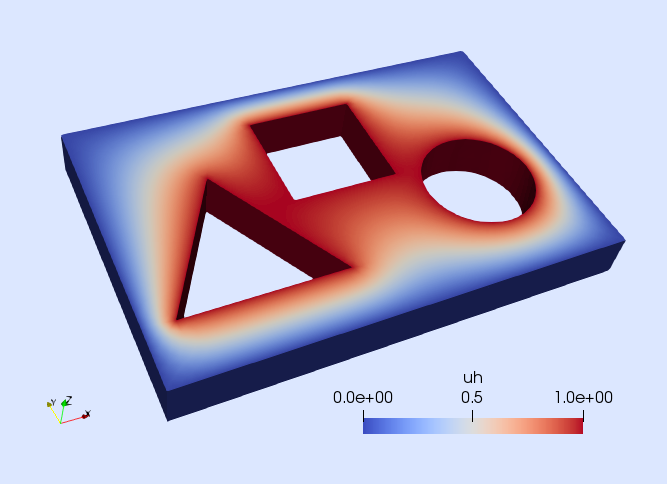
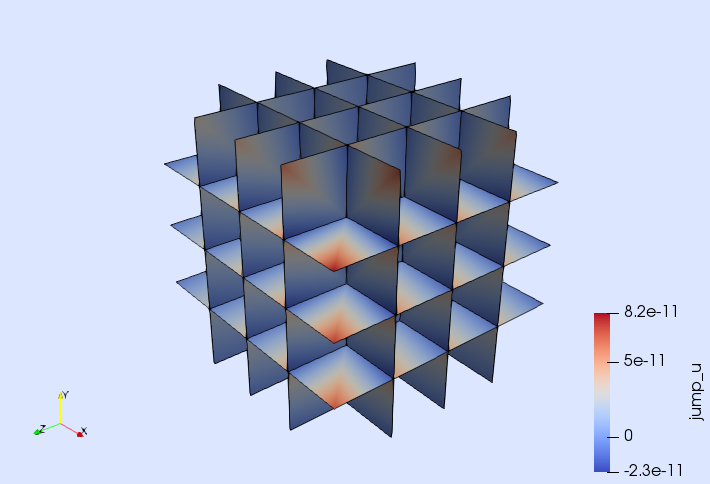
These are some popular PDEs solved with the Gridap library. Examples taken from the Gridap Tutorials.
 |
 |
 |
 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Poisson equation | Linear elasticity | Hyper-elasticity | p-Laplacian |
 |
 |
 |
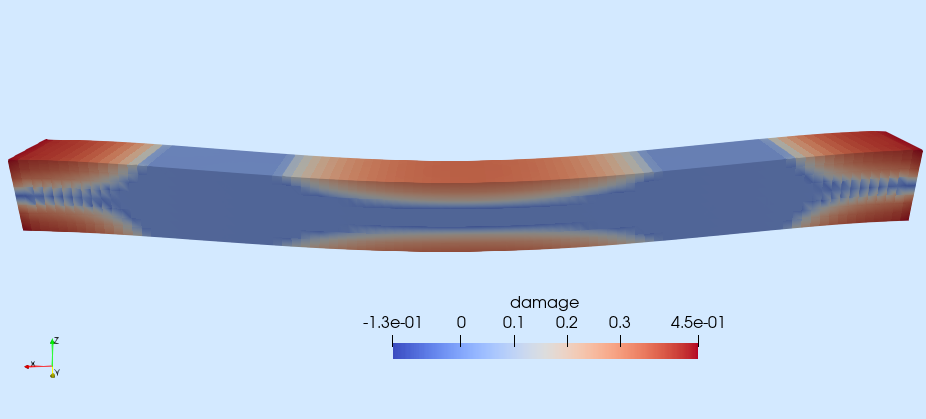 |
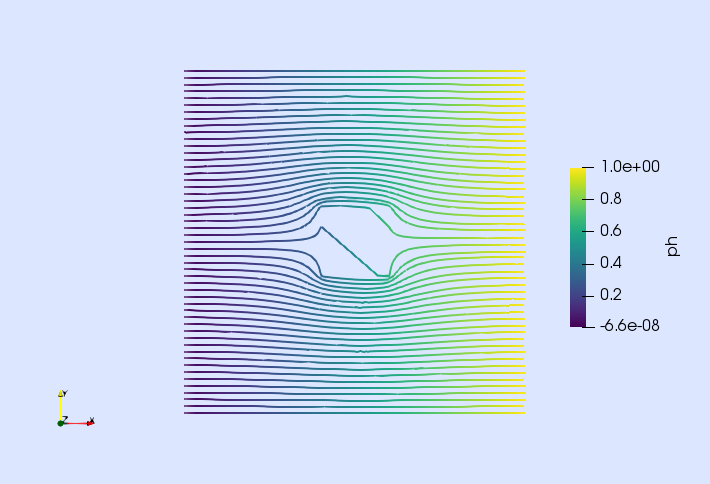
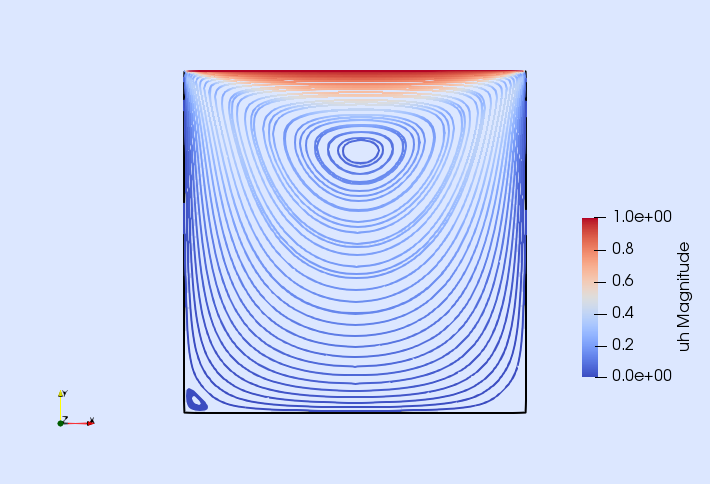
| Poisson eq. with DG | Darcy eq. with RT | Incompressible Navier-Stokes | Isotropic damage |
Gridap community
Join to our gitter chat to ask questions and interact with the Gridap community.
Contributing to Gridap
Gridap is a collaborative project open to contributions. If you want to contribute, please take into account:
- Before opening a PR with a significant contribution, contact the project administrators, e.g., by writing a message in our gitter chat or by opening an issue describing what you are willing to implement. Wait for feed-back.
- Carefully read and follow the instructions in the CONTRIBUTING.md file.
- Carefully read and follow the instructions in the CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md file.
- Open a PR with your contribution.
Want to help? We have a number of issues waiting for help. You can start contributing to the Gridap project by solving some of those issues.
How to cite Gridap
In order to give credit to the Gridap contributors, we simply ask you to cite the refence below in any publication in which you have made use of Gridap packages:
@article{Badia2020,
doi = {10.21105/joss.02520},
url = {https://doi.org/10.21105/joss.02520},
year = {2020},
publisher = {The Open Journal},
volume = {5},
number = {52},
pages = {2520},
author = {Santiago Badia and Francesc Verdugo},
title = {Gridap: An extensible Finite Element toolbox in Julia},
journal = {Journal of Open Source Software}
}
Contact
Please, contact the project administrators, Santiago Badia and Francesc Verdugo, for further questions about licenses and terms of use.

