Device Tree Kubernetes Node Labeller
This tool provides a custom Kubernetes controller for automatically labelling nodes with devicetree properties.
It is inspired by and re-uses much of the Kubernetes controller plumbing from the amdgpu-node-labeller.
Use Cases
k8s-dt-node-labeller was developed in order to facilitate targeted deployments into hybrid (e.g. armhf, arm64)
Kubernetes clusters, as well as for targeting heterogeneous accelerators in Edge deployments - specifically those that
show up as platform devices (FPGAs, embedded GPUs, etc.) as opposed to those that are dynamically discoverable at
run-time via bus enumeration (e.g. USB, PCI). The latter cases are handled by the official node-feature-discovery
(NFD) labeller, which can be used in conjunction with k8s-dt-node-labeller for more comprehensive node labelling.
Overview
k8s-dt-node-labeller is primarily concerned with top-level system characteristics, and therefore limits itself to
walking through the top-level devicetree node looking for compatible properties to expose as Kubernetes node labels.
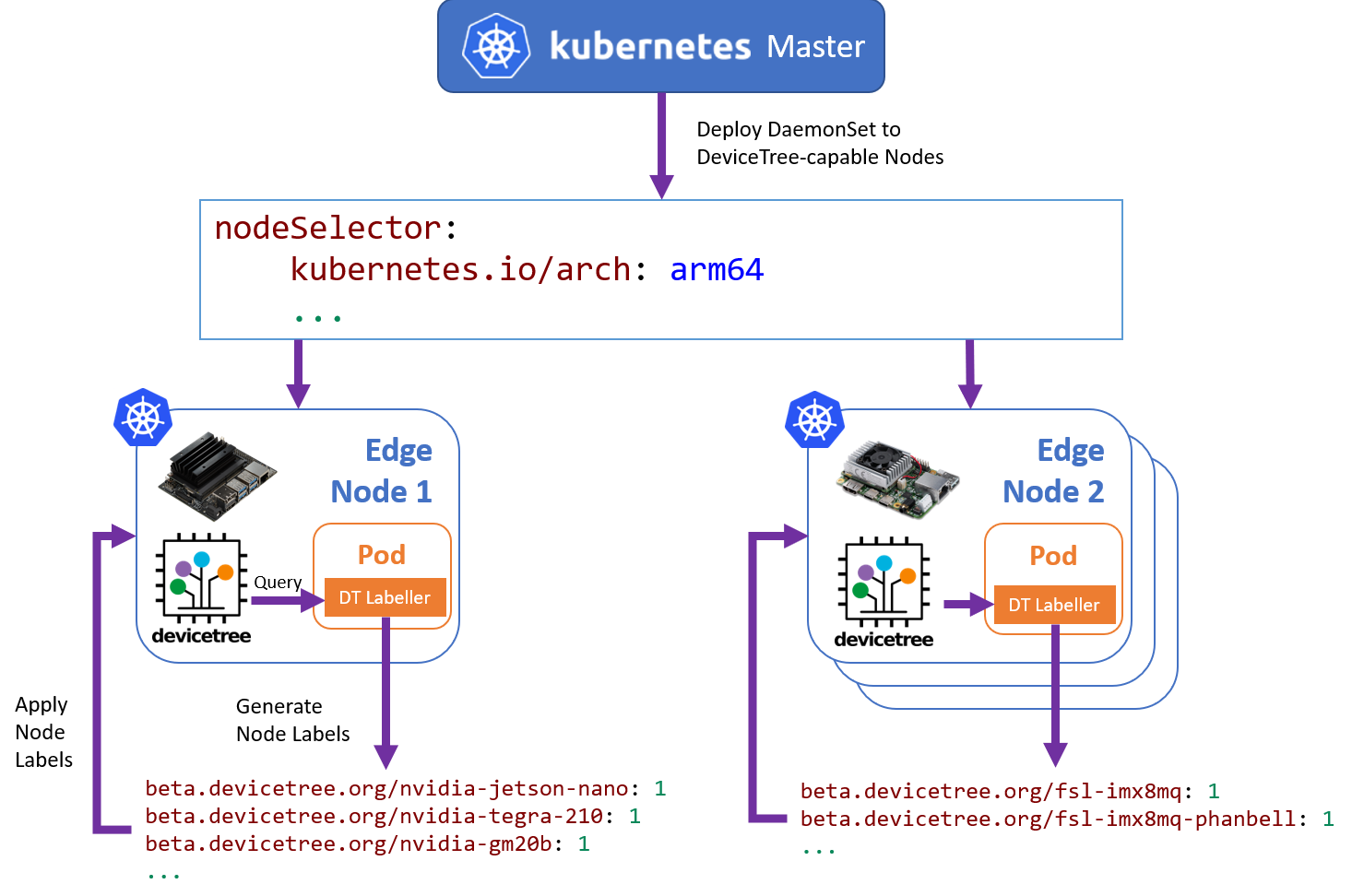
As k8s-dt-node-labeller requires access to the target node's devicetree instance, the labeller must be run directly
on the target node that is to be labelled. An overview of the general labelling flow (in the context of a Kubernetes
DaemonSet) is provided below:
It is expected that the node labeller is run when the node is registered with the cluster, such that pods relying on specific labels are able to be scheduled and placed appropriately.
Labelling is possible in a number of different ways:
- Running Node-Local via the CLI App
- Running Node-Local via Docker
- Deploying as a Kubernetes DaemonSet directly
- Deploying as part of a combined Kubernetes NFD DaemonSet
Regardless of the method of deployment, the labels will be generated and applied to the local node.
Limitations
k8s-dt-node-labeller only generates labels from properties at the top-level of the devicetree and those specifically
defined by the user by design. It does not recurse down the tree, nor does it make any attempt to enumerate busses that
are better served by bus-specific device detection logic. While the labeller can attest to the existence of a node in
the devicetree, it offers no device-specific information or control - all of which would need to be implemented
through a device-specific device plugin.
Installation
If planning to use the CLI App directly, this can be compiled and installed as other Go projects:
$ go get github.com/adaptant-labs/k8s-dt-node-labeller
For Docker containers and Kubernetes deployment instructions, see below.
Usage
General usage is as follows:
$ k8s-dt-node-labeller --help
devicetree Node Labeller for Kubernetes
Usage: k8s-dt-node-labeller [flags] [-n devicetree nodes...]
-d Display detected devicetree nodes
-f Write detected features to NFD features file
-kubeconfig string
Paths to a kubeconfig. Only required if out-of-cluster.
-n string
Additional devicetree node names
A dry-run is possible by specifying the -d flag:
$ k8s-dt-node-labeller -d
Discovered the following devicetree properties:
beta.devicetree.org/nvidia-jetson-nano: 1
beta.devicetree.org/nvidia-tegra210: 1
By default, compatible strings from the top-level / node are discovered and converted to node labels. Additional
node specifications are possible via the -n flag, as below:
$ k8s-dt-node-labeller -d -n gpu pwm-fan
Discovered the following devicetree properties:
beta.devicetree.org/nvidia-jetson-nano: 1
beta.devicetree.org/nvidia-tegra210: 1
beta.devicetree.org/nvidia-tegra210-gm20b: 1
beta.devicetree.org/nvidia-gm20b: 1
beta.devicetree.org/pwm-fan: 1
In the case of Docker or Kubernetes Deployment, note that these arguments can also be passed on to the container directly.
Running Node-Local via the CLI App
In order to submit the labels to the cluster, ensure a valid kubeconfig can be found (e.g. by setting the KUBECONFIG
environment variable, or through specifying the location with the -kubeconfig parameter) and execute the node
labeller as-is:
$ k8s-dt-node-labeller
{"level":"info","ts":1585701002.694782,"logger":"k8s-dt-node-labeller.entrypoint","msg":"setting up manager"}
{"level":"info","ts":1585701003.1179338,"logger":"controller-runtime.metrics","msg":"metrics server is starting to listen","addr":":8080"}
{"level":"info","ts":1585701003.118381,"logger":"k8s-dt-node-labeller.entrypoint","msg":"Setting up controller"}
{"level":"info","ts":1585701003.1185818,"logger":"k8s-dt-node-labeller.entrypoint","msg":"starting manager"}
{"level":"info","ts":1585701003.1190712,"logger":"controller-runtime.manager","msg":"starting metrics server","path":"/metrics"}
{"level":"info","ts":1585701003.1193638,"logger":"controller-runtime.controller","msg":"Starting EventSource","controller":"k8s-dt-node-labeller","source":"kind source: /, Kind="}
{"level":"info","ts":1585701003.2218263,"logger":"controller-runtime.controller","msg":"Starting Controller","controller":"k8s-dt-node-labeller"}
{"level":"info","ts":1585701003.222448,"logger":"controller-runtime.controller","msg":"Starting workers","controller":"k8s-dt-node-labeller","worker count":1}
...
Running Node-Local via Docker
Multi-arch Docker images are available on Docker Hub at adaptant/k8s-dt-node-labeller. These may be run as-is
in-cluster, or out of cluster with an appropriate KUBECONFIG passed through.
Note that as the labeller requires access to the host's /sys/firmware directory, this must either be passed through
explicitly, or the container run in privileged mode:
$ docker run --privileged adaptant/k8s-dt-node-labeller
...
Deploying as a Kubernetes DaemonSet
An example deployment configuration for a DaemonSet is provided in k8s-dt-labeller-ds.yaml, which can be directly
applied to the running cluster:
$ kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/adaptant-labs/k8s-dt-node-labeller/k8s-dt-labeller-ds.yaml
This will create a special dt-labeller service account, cluster role, and binding with the permission to list and
reconcile nodes. Note that as the labeller requires access to an unmasked /sys/firmware, it must also be run in a
privileged securityContext.
Deploying with NFD
When used together with NFD k8s-dt-node-labeller runs in one-shot mode as an init container, providing a static list
of discovered features and labels to pass off to NFD, for use with its local feature discovery.
$ kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/adaptant-labs/k8s-dt-node-labeller/k8s-dt-labeller-nfd.yaml
In this configuration, the nfd-master, nfd-worker, and k8s-dt-node-labeller are all deployed in the same Pod in
order to facilitate node-local labelling. While the k8s-dt-node-labeller requires access to an unmasked
/sys/firmware, and must, therefore, run in a privileged securityContext, the NFD application containers are able to
run without elevated permissions.
Verifying Labelling
After the labeller has run, the node labels can be viewed from kubectl:
$ kubectl describe node jetson-nano
Name: jetson-nano
Roles: <none>
Labels: beta.devicetree.org/nvidia-jetson-nano=1
beta.devicetree.org/nvidia-tegra210=1
beta.kubernetes.io/arch=arm64
beta.kubernetes.io/instance-type=k3s
beta.kubernetes.io/os=linux
k3s.io/hostname=jetson-nano
k3s.io/internal-ip=192.168.xxx.xxx
kubernetes.io/arch=arm64
kubernetes.io/hostname=jetson-nano
kubernetes.io/os=linux
node.kubernetes.io/instance-type=k3s
...
Features and bugs
Please file feature requests and bugs in the issue tracker.
Acknowledgements
This project has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under grant agreement No 825480 (SODALITE).
License
k8s-dt-node-labeller is licensed under the terms of the Apache 2.0 license, the full
version of which can be found in the LICENSE file included in the distribution.