Boostport / Kubernetes Vault
Programming Languages
Labels
Projects that are alternatives of or similar to Kubernetes Vault
No Longer Being Maintained.
The integration between Vault and Kubernetes has been greatly improved over the last few years and Kubernetes-Vault is no longer required for deployments using recent versions of Vault and Kubernetes.
To use Vault with Kubernetes directly, you can use the Kubernetes Auth Method and the Vault Agent as a side-car to retrieve and renew secrets from Vault.
Kubernetes Vault Integration
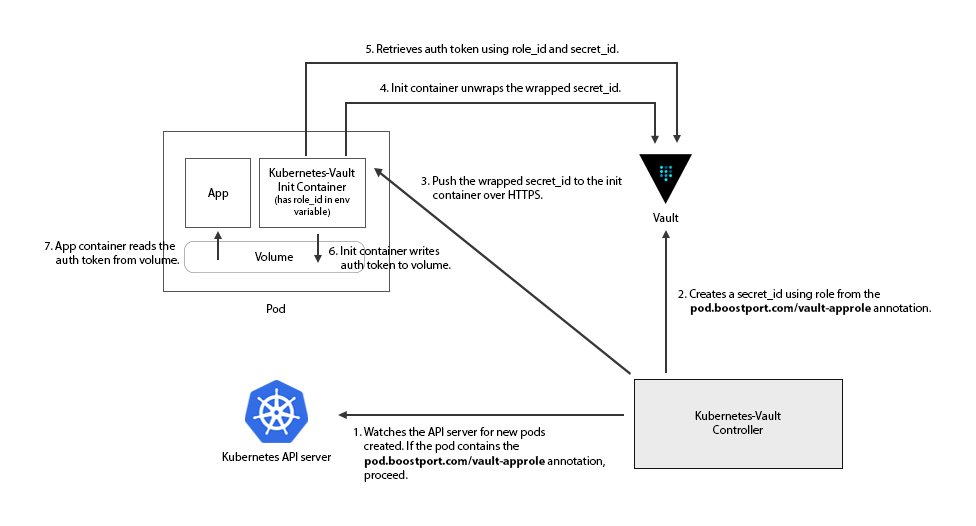
The Kubernetes-Vault project allows pods to automatically receive a Vault token using Vault's AppRole auth backend.
Highlights
- Secure by default. The Kubernetes-Vault controller does not allow using root tokens to authenticate against Vault.
- Prometheus metrics endpoint over http or https, with optional TLS client authentication.
- Supports using Vault as a CA or an external CA for all components with TLS support.
- High availability mode using Raft, so that if the leader goes down, a follower can take over immediately.
- Peer discovery using Kubernetes services and endpoints and gossip to propagate peer changes across the cluster.
Prerequisites:
- Vault should be 0.6.3 and above.
- You must use Kubernetes 1.6.0 and above as we rely on init containers (in beta) to accept the token.
- For Kubernetes 1.5.x and below, please use an older versions of Kubernetes-Vault by referencing the compatibility table.
- You must generate a periodic token with the correct policy to generate
secret_ids using the AppRole backend. - The Kubernetes-Vault controller uses the Kubernetes service account to watch for new pods. This service account must have the appropriate permissions.
- Your app should use a Vault client to renew the token and any secrets you request from Vault.
- You should configure Vault to use HTTPS, so that the authentication token and any other secrets cannot be sniffed.
- If using RBAC, the Kubernetes-Vault controller needs the following permissions
-
getit's endpoint (headless service) -
listandwatchpodsin all namespaces.
-
Get started
To run Kubernetes-Vault on your cluster, follow the quick start guide.
Best practices
See our list of best practices.
Token format
The token information is encoded as JSON and written to a file called vault-token. Here's an example of what it looks like:
{
"clientToken":"91526d9b-4850-3405-02a8-aa29e74e17a5",
"accessor":"476ea048-ded5-4d07-eeea-938c6b4e43ec",
"leaseDuration":3600,
"renewable":true,
"vaultAddr":"https://vault:8200"
}
Your application should parse the JSON representation and renew the clientToken using the leaseDuration as a guide.
If you ask the init container to not login using the role_id and secret_id to retrieve the token by setting the
RETRIEVE_TOKEN environment variable of the init container to false, the secret_id and any related information is
encoded as JSON written to a file called vault-secret-id instead. Here's an example of what it looks like:
{
"roleId":"313b0821-4ff6-1df8-54dd-c3eea5d3b8b1",
"secretId":"3c3ebf1f-8fa5-8cce-e3e8-f769e386bd4b",
"accessor":"5c8b7cb5-5d8e-0dbf-be27-12604f5b64aa",
"vaultAddr":"https://vault:8200"
}
If you choose to use Kubernetes-vault in this mode, it will be your application's responsibility to use the secret_id
and role_id pair to login to the Vault server and retrieve an auth token.
Alternatively, you can choose to not have the init container unwrap the secret, and leave that responsibility up to your app. To do this, set UNWRAP_SECRET to false, and the wrapped secret_id and any related information will be encoded as JSON and written to a file called vault-wrapped-secret-id. Here's an example of what it looks like:
{
"roleId":"313b0821-4ff6-1df8-54dd-c3eea5d3b8b1",
"wrappedSecretId":"2179ad51-cfb5-03de-dad7-2c25746b38e3",
"vaultAddr":"https://vault:8200",
"ttl":60
}
CA bundle
If you are connecting to Vault over https (highly recommended for production), you will find the CA bundle for Vault in
the file ca.crt. Use the CA bundle when connecting to Vault using your application, so that the identity of Vault is
verified.
Configuration
The project consists of 2 containers, a controller container that watches the Kubernetes cluster and pushes secret_ids
to pods and an init container that receives the secret_id and exchanges it for an auth token. The controller is
configured using a YAML file and the init container uses environment variables. The init container also requires
configuration using Kubernetes annotations.
For full examples of configuration files, check out the ConfigMaps in the quick start and secured examples.
Kubernetes-Vault controller configuration
The Kubernetes-Vault is configured using a YAML file. We recommend using a ConfigMap to mount the file and any other files ( such as certificates and private keys, if using an external CA) into the controller's pod.
The controller automatically expands any environment variables used in the configuration specified using the $VARIABLE or
${VARIABLE} notation. For example, if you set raftDir: ${MY_DIR} and set the $MY_DIR environment variable to /tmp, it
expands to: raftDir: /tmp.
By default, the controller looks for configuration in kubernetes-vault.yml in the current working directory, but you
can override this by setting the -config flag with the absolute path to your config file.
The available configuration options in the config file are:
raftDir (optional)
The location where raft data should be stored. By default this is: /var/lib/kubernetes-vault/.
If you want to set a custom location:
raftDir: /my/custom/raft/dir
vault (required)
Settings for communicating with the Vault server. It contains nested properties:
-
addr (required) The address of the Vault server. For example,
http://vault:8200. -
token (required) A renewable and periodic Vault token to be used by the Kubernetes-Vault controller.
-
skipTokenRoleNameValidation (optional) If set to
truethen skip validation for token role name. By default, this is:false. -
tls (optional) If Vault is secured using TLS (https), then you need to set one of the following:
-
vaultCABackends (optional) If Vault uses itself as a certificate authority, provide the list of root PKI backends here.
-
caCert (optional) If Vault uses an external CA, provide the absolute path to a file containing the CA certificates in PEM format.
-
-
wrappingTTL (optional) The TTL for wrapped AppRole secret ids. By default, this is:
60s.
Example (using Vault as a CA):
vault:
addr: http://vault:8200
token: 91526d9b-4850-3405-02a8-aa29e74e17a5
tls:
vaultCABackends:
- root-ca
kubernetes (required)
Settings for talking to the Kubernetes API server.
-
watchNamespace (required) The namespace to watch for newly created pods. If you want to watch for pods across multiple namespaces, you can prefix it with
~followed by a regex pattern. For example, using~^(staging|default)$will watch for pods in both thestaginganddefaultnamespaces.IMPORTANT: If you are using regex to watch multiple namespaces, make sure
vault.addris set to the FULL DNS name of your Vault server. For example:https://vault.default:8200orhttps://vault.staging:8200. This is because the Vault address is pushed to the watched pods, and those pods will only be able to communicate with pods outside their own namespace using the FULL DNS name. -
serviceNamespace (required) The Kubernetes namespace the Kubernetes-Vault controller's service is in. This parameter and the
serviceparameter is used to discover other Kubernetes-Vault controllers to form a cluster. -
service (required) The Kubernetes service being used by the Kubernetes-Vault controller. Used in conjunction with
serviceNamespaceso that it can discover other Kubernetes-Vault controllers to form a cluster.
Example:
kubernetes:
# For watchNamespace, you can use a regex by prefixing it with ~. For example: ~^(staging|default)$
watchNamespace: default
# Note the use of an environment variable here, which will be expanded by the controller
serviceNamespace: ${KUBERNETES_NAMESPACE}
service: kubernetes-vault
prometheus (optional)
Configuration for the Prometheus endpoint.
-
tls (optional) TLS configuration for the Prometheus endpoint. You can use Vault as the CA or an external CA. If using Vault as the CA, you must set
vaultCertBackend,vaultCertRole,vaultCABackends. Otherwise, setcertFile,certKey, andcaCertif using an external CA.-
vaultCertBackend (optional) The Vault PKI backend to be used to issue certificates for securing the Prometheus metrics endpoint.
-
vaultCertRole (optional) The Vault PKI role to be used to issue certificates for securing the Prometheus metrics endpoint.
-
vaultCABackends (optional) If you want to enable client TLS authentication against the Prometheus scrappers, set the list of Vault PKI backend being used as a certificate authority for those scrappers here.
-
certFile (optional) If using an external CA, provide the absolute path to the certificate in PEM format here.
-
certKey (optional) If using an external CA, provide the absolute path to the key for the certificate in PEM format here.
-
caCert (optional) If you want to enable client TLS authentication against the Prometheus scrappers, provide the absolute path to the file containing the root certificates in PEM format here.
-
Example:
prometheus:
tls:
# Note that vaultCABackends is not set, so TLS client authentication for the scrappers will not be
# enabled.
vaultCertBackend: intermediate-ca
vaultCertRole: kubernetes-vault
Init container configuration
The init containers are configured using environment variables and Kubernetes annotations.
Environment variables
| Environment Variable | Description | Required | Default Value | Example |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CREDENTIALS_PATH | The location where the Vault token and CA Bundle (if it exists) will be written. | no |
/var/run/secrets/boostport.com |
/var/run/my/path |
| LOG_LEVEL | The log level. Valid values are debug and error. |
no |
debug |
debug |
| RETRIEVE_TOKEN | Whether to login using the secret_id and role_id to retrieve the auth token. |
no |
true |
false |
| UNWRAP_SECRET | Whether to unwrap the secret_id
|
no |
true |
false |
| TIMEOUT | Maximum amount of time to wait for the wrapped secret_id to be pushed. Valid time units are ns, us, ms, s, m and h. |
no |
5m |
120s |
| VAULT_ROLE_ID | The Vault role id. | yes |
none |
313b0821-4ff6-1df8-54dd-c3eea5d3b8b1 |
Pod annotations
| Annotation | Description | Required | Default Value | Example |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pod.boostport.com/vault-approle | The Vault role. | yes |
none |
sample-app |
| pod.boostport.com/vault-init-container | The name of the init container. | yes |
none |
install |
Metrics
Kubernetes-Vault uses Prometheus for metrics reporting. It exposes these metrics over the /metrics endpoint over http or https.
For more information about metrics, read the guide on metrics.
Sidekick container
UKHomeOffice/vault-sidekick is a sidekick container that runs in your pods to retrieve and renew credentials from Vault. The container has support for reading the token and other associated information from the token information that is created by the Kubernetes-Vault container.
In order to use vault-sidekick with Kubernetes-Vault, set the AUTH_FILE environment variable to the path of the token JSON
file written by the init container and the AUTH_FORMAT environment variable to kubernetes-vault.
Kubernetes version compatibility
| Kubernetes Version | Kubernetes-Vault Version |
|---|---|
| <= 1.5.x | <= 0.4.8 |
| >= 1.6.x and <= 1.7.x | any |
| >= 1.8.x | >= 0.5.0 |
Troubleshooting
See the troubleshooting guide.
Development
PRs are highly welcomed!
We use Go 1.11 and Go modules for dependency management.
Docker is used to build the binaries, so you need to have docker installed.
Production images can be built using multi-stage docker builds by building the respective dockerfile in each binary's folder.
For development, simply run build.sh to build the binaries. To build the development docker images, run build-dev-images.sh.
Running build-dev-images.sh also automatically runs build.sh.
The Dockerfile.dev files are used to build development/testing images, while the Dockerfile files are used to build
production images.
License
This project is licensed under the Apache 2 License.