easystats / Modelbased
Programming Languages
modelbased 
modelbased is a lightweight package helping with model-based
estimations, used in the computation of marginal means, contrast
analysis and model predictions.
Installation
Run the following to install the stable release of modelbased from CRAN:
install.packages("modelbased")
Or this one to install the latest development version:
install.packages("remotes")
remotes::install_github("easystats/modelbased")
Documentation
Click on the buttons above to access the package documentation and the easystats blog, and check-out these vignettes:
- Visualisation matrix
- Marginal means
- Contrast analysis
- Use a model to make predictions
- Describe non-linear curves
Features
The package is built around 5 main functions:
-
estimate_means(): Estimates the average values at each factor levels -
estimate_contrasts(): Estimates and tests contrasts between different factor levels -
estimate_slopes(): Estimates the slopes of numeric predictors at different factor levels -
estimate_response(): Predict the response variable using the model -
estimate_smooth(): Describes a non-linear term (e.g. in GAMs) by its linear parts
These functions are powered by the
visualisation_matrix()
function, a smart tool for guessing the appropriate reference grid.
The package currently only supports rstanarm models, but will be
expanded to cover a large variety of frequentist and Bayesian models.
Examples
Create smart grids to represent complex interactions
Check-out this vignette to create this plot:
Estimate marginal means
Check-out this vignette to create this plot:
library(rstanarm)
model <- stan_glm(Sepal.Width ~ Species, data = iris)
estimate_means(model)
## Species | Mean | 95% CI
## --------------------------------
## setosa | 3.43 | [3.34, 3.52]
## versicolor | 2.77 | [2.68, 2.87]
## virginica | 2.97 | [2.89, 3.07]
Contrast analysis
Check-out this vignette to create this plot:
estimate_contrasts(model)
## Level1 | Level2 | Difference | 95% CI | pd | % in ROPE | Std_Difference
## -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
## setosa | versicolor | 0.66 | [ 0.53, 0.80] | 100% | 0% | 1.51
## setosa | virginica | 0.45 | [ 0.33, 0.59] | 100% | 0% | 1.04
## versicolor | virginica | -0.20 | [-0.34, -0.07] | 99.83% | 6.68% | -0.47
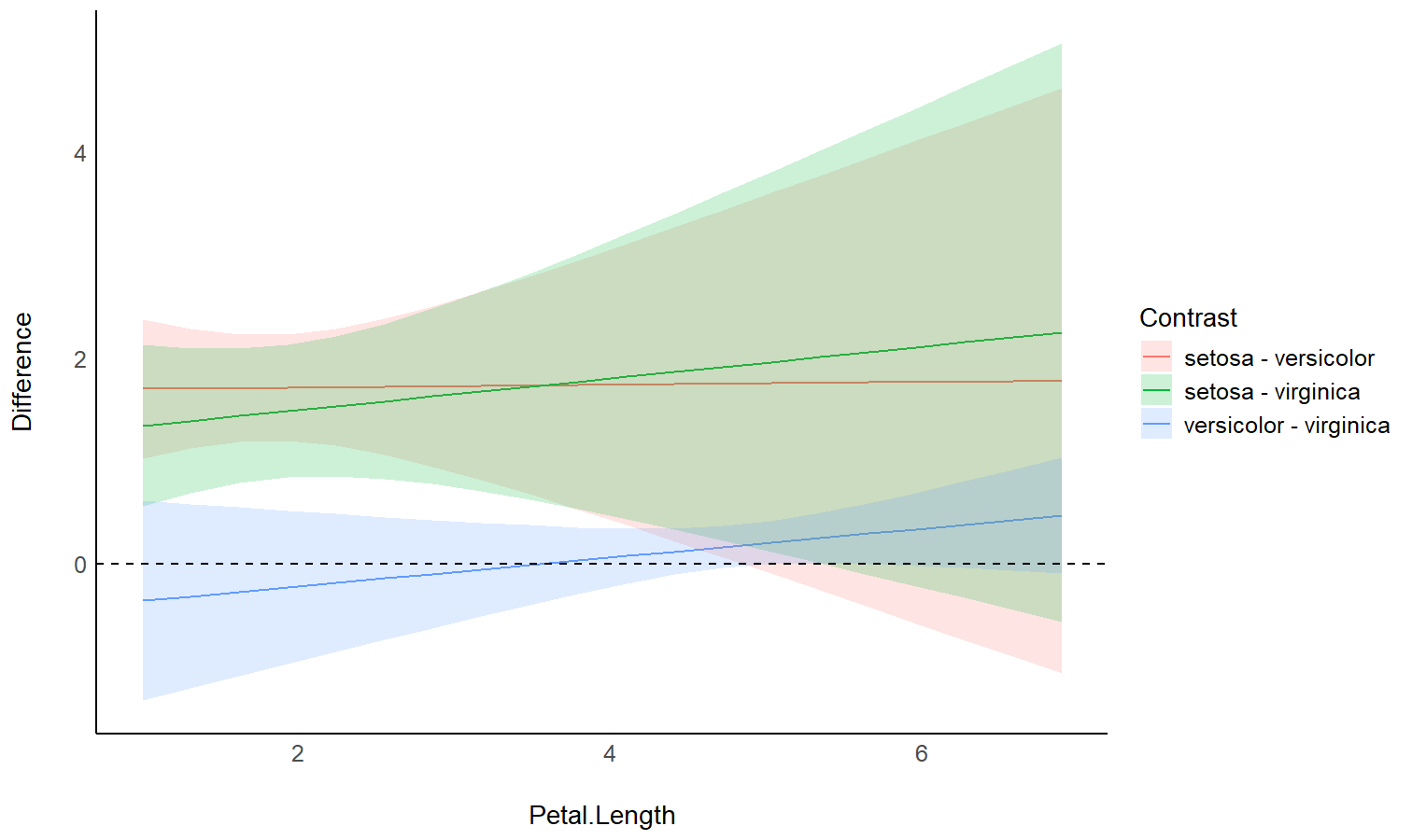
Check the contrasts at different points of another linear predictor
model <- stan_glm(Sepal.Width ~ Species * Petal.Length, data = iris)
estimate_contrasts(model, modulate = "Petal.Length", length = 3)
## Level1 | Level2 | Petal.Length | Difference | 95% CI | pd | % in ROPE | Std_Difference
## ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
## setosa | versicolor | 1.00 | 1.67 | [ 1.05, 2.27] | 100% | 0% | 3.84
## setosa | virginica | 1.00 | 1.34 | [ 0.59, 2.07] | 100% | 0.02% | 3.07
## versicolor | virginica | 1.00 | -0.33 | [-1.27, 0.57] | 75.48% | 13.60% | -0.76
## setosa | versicolor | 3.95 | 1.61 | [ 0.66, 2.54] | 99.92% | 0.07% | 3.70
## setosa | virginica | 3.95 | 1.66 | [ 0.69, 2.68] | 99.90% | 0.15% | 3.81
## versicolor | virginica | 3.95 | 0.05 | [-0.23, 0.34] | 63.50% | 47.48% | 0.12
## setosa | versicolor | 6.90 | 1.54 | [-0.54, 3.60] | 93.00% | 2.73% | 3.54
## setosa | virginica | 6.90 | 2.00 | [-0.02, 4.00] | 97.35% | 1.27% | 4.58
## versicolor | virginica | 6.90 | 0.44 | [-0.08, 0.96] | 94.62% | 8.80% | 1.01
Find a predictor’s slopes at each factor level
estimate_slopes(model)
## Species | Median | 95% CI | pd | % in ROPE | Std. Median
## ----------------------------------------------------------------------
## setosa | 0.34 | [-0.05, 0.69] | 96.00% | 8.48% | 1.37
## versicolor | 0.36 | [ 0.18, 0.54] | 99.98% | 0.18% | 1.46
## virginica | 0.23 | [ 0.07, 0.38] | 99.88% | 5.78% | 0.93
Generate predictions from your model to compare it with original data
Check-out this vignette to create this plot:
estimate_response(model)
| Sepal.Length | Species | Predicted | CI_low | CI_high |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5.1 | setosa | 1.47 | 0.98 | 1.98 |
| 4.9 | setosa | 1.45 | 0.92 | 1.97 |
| 4.7 | setosa | 1.41 | 0.88 | 1.96 |
| 4.6 | setosa | 1.42 | 0.92 | 1.98 |
| 5.0 | setosa | 1.46 | 0.90 | 1.96 |
| 5.4 | setosa | 1.51 | 1.00 | 2.11 |
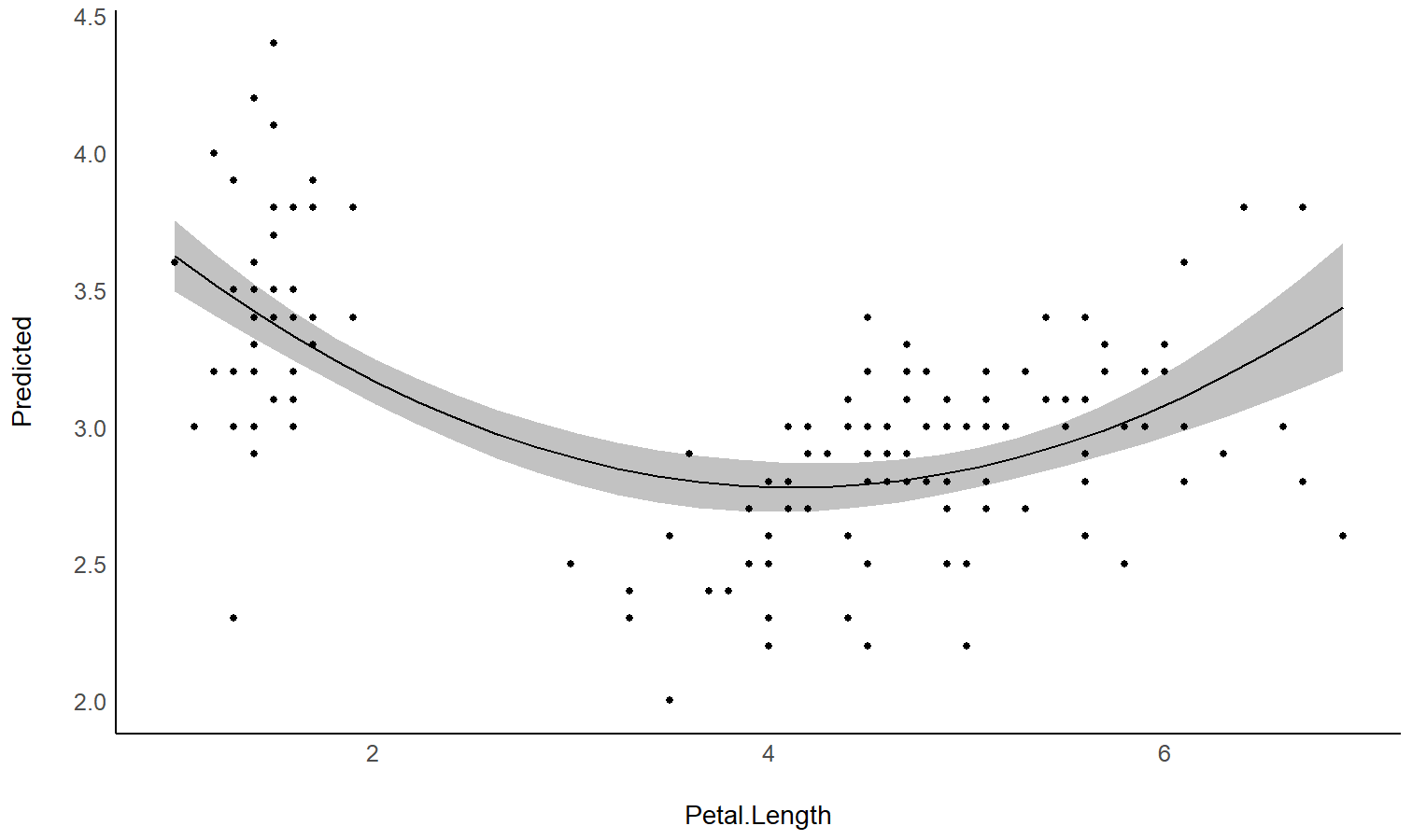
Estimate the link between the response and a predictor
See this
vignette
to create this plot:

model <- stan_glm(Sepal.Width ~ poly(Petal.Length, 2), data = iris)
estimate_link(model)
| Petal.Length | Predicted | CI_low | CI_high |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1.00 | 3.62 | 3.49 | 3.75 |
| 1.98 | 3.18 | 3.09 | 3.26 |
| 2.97 | 2.90 | 2.81 | 2.99 |
| 3.95 | 2.78 | 2.69 | 2.87 |
| 4.93 | 2.83 | 2.77 | 2.91 |
| 5.92 | 3.05 | 2.94 | 3.16 |
| 6.90 | 3.44 | 3.20 | 3.68 |
Describe the smooth term by its linear parts
estimate_smooth(model)
## Part | Start | End | Size | Trend | Linearity
## ------------------------------------------------
## 1 | 1.00 | 3.62 | 50.00% | -0.19 | 0.96
## 2 | 3.62 | 6.90 | 50.00% | 0.08 | 0.81