greenpau / Ndmtk
Programming Languages
Labels
Projects that are alternatives of or similar to Ndmtk
Network Discovery and Management Toolkit
Network Discovery and Management Toolkit (ndmtk) makes Ansible "work" for
both Traditional and Software-Defined Network (SDN) network management.
Table of Contents
Overview
The future of network management lies in the area of Artificial Intelligence. Any network-enabled device will be able to build connectivity to a remote peer on-demand, without human intervention. The restraint on that ability are the AI-enabled systems acting as gatekeepers. AI is impossible without ongoing data collection, data analysis, probing, and modeling. As such, networks of the future need tools to perform the above tasks.
This toolkit is designed to accomplish the data collection piece of the AI puzzle. Specifically, the toolkit is designed to:
- discover data on network devices and capture the entirety of available data
- configure network devices via SSH, telnet, console, or terminal server
- collect, analyze, and store the data via command-line interactions; it performs data analysisn and, if necessary, it performs additional data collection and/or device configuration tasks.
The intended audience of this toolkit are system and network engineers and designers, as well as the researchers dealing with AI.
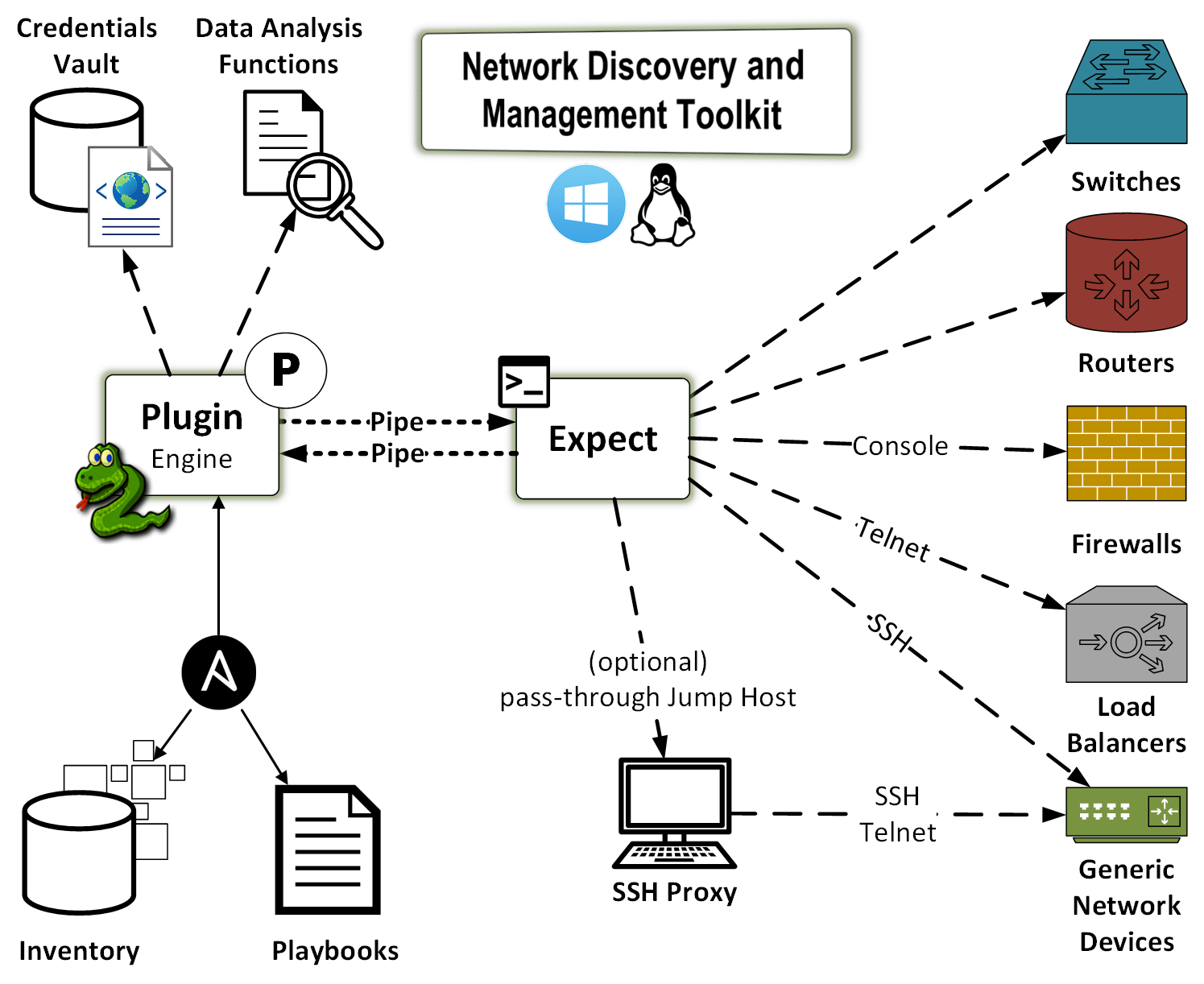
The toolkit is delivered in a form of an Ansible plugin. However, it could work well with Chef, or any other orchestration tool. The reason Ansible became a framework of choice is its modularity. The toolkit itself is modular. It allows extended existing functionality. For example, the plugin does not blindly run pre-defined commands. Rather, it first collects all of the commands forming the understanding of the function of a particular device in a network. Once the plugin receives the data, it runs it through its algorithms and determines whether there are any additional command required to further gather data. That process continues until the algorithms determine that the collection is complete.
Importantly, once the plugin completes its tasks it produces a number of reports in JSON, YAML, and JUnit formats. These reports provide a map of what was done, where the collected data reside, and what that data is.
The plugin has no required arguments and parameters, because there are a number of default commands available for various operating systems, e.g. Cisco Nexus OS, Arista EOS, Linux, etc.
Workflow Diagram
Getting Started
First, a user installs ndmtk with pip:
pip install ndmtk
Second, the user creates Ansible playbook, e.g. playbooks/collect_all.yml:
---
- name: generic data collection
hosts:
- ny-fw01
- ny-sw01
- ny-sw02
gather_facts: no
tasks:
- name: data collection from three network devices
action: ndmtk output="/tmp/ndmtk-%Y%m%d%H%M%S" debug=no no_host_key_check=yes on_error=continue
The above playbook collect the data from three devices: ny-fw01, ny-sw01, and
ny-sw02.
Third, the user must create a hosts file:
controller ansible_connection=local
[test:children]
cisco-asa-firewalls
arista-eos-switches
[arista-eos-switches]
ny-sw01 os=arista_eos host_overwrite=localhost host_port=8224
ny-sw02 os=arista_eos host_overwrite=localhost host_port=8225
[cisco-asa-firewalls]
ny-fw01 os=cisco_asa host_overwrite=192.168.1.1
[all:vars]
ansible_connection=local
The switches are Arista vEOS switches running on top of Virtual Box. The firewall is a physical Cisco ASA 5505.
Additionally, the user must create Ansible configuration file in either:
-
.ansible.cfgin the user's home directory, or -
ansible.cfgin the user's current directory
The configuration file contains the following directives:
[defaults]
inventory = ./hosts
forks = 100
local_tmp = $HOME/.ansible/tmp
retry_files_enabled = True
retry_files_save_path = $HOME/.ansible/retries/
log_path = $HOME/.ansible/log/ansible.log
transport = local
Fourth, the user must create Ansible Vault ~/.ansible.vault.yml and structure
it according to ndmtk's documentation. Then, for convinience, the user may
store the password to the vault in ~/.ansible.vault.key plain-text file.
For example .ansible.vault.key has a single line for the password:
NX23nKz!
While the vault itself has the following content:
--
credentials:
- regex: ny-fw0[1-9]
username: admin
password: 'NX23nKz!'
password_enable: '3nKz!NX2'
priority: 1
description: NY-FW01 password
- default: yes
username: greenpau
password: 'My#DefaultPass'
password_enable: 'Enabled#By$Default'
priority: 1
description: my default password
The toolkit accesses ny-fw01 with the first set of credentials because its
name matches the regular expression in that set. For the witches, the later,
default password is used.
At any point of time, the user could edit or view the vault using the following commands:
ansible-vault edit ~/.ansible.vault.yml --vault-password ~/.ansible.vault.key
ansible-vault view ~/.ansible.vault.yml --vault-password ~/.ansible.vault.key
Finally, the user runs the playbook:
ansible-playbook playbooks/collect_all.yml
Documentation
Please read the toolkit's documentation at Read the Docs and review the demo directory containing sample configuration files.
- User Guide
- Rules Engine
- Reports and Structured Data
- Access Credentials Management
- Frequently Asked Questions
Questions
Please open issues and ask questions in Github Issues.
Contribution
Please contribute using the following Guidelines.