tidyverse / Readr
Programming Languages
Projects that are alternatives of or similar to Readr
readr 
Overview
The goal of readr is to provide a fast and friendly way to read rectangular data (like csv, tsv, and fwf). It is designed to flexibly parse many types of data found in the wild, while still cleanly failing when data unexpectedly changes. If you are new to readr, the best place to start is the data import chapter in R for data science.
Installation
# The easiest way to get readr is to install the whole tidyverse:
install.packages("tidyverse")
# Alternatively, install just readr:
install.packages("readr")
# Or the the development version from GitHub:
# install.packages("devtools")
devtools::install_github("tidyverse/readr")
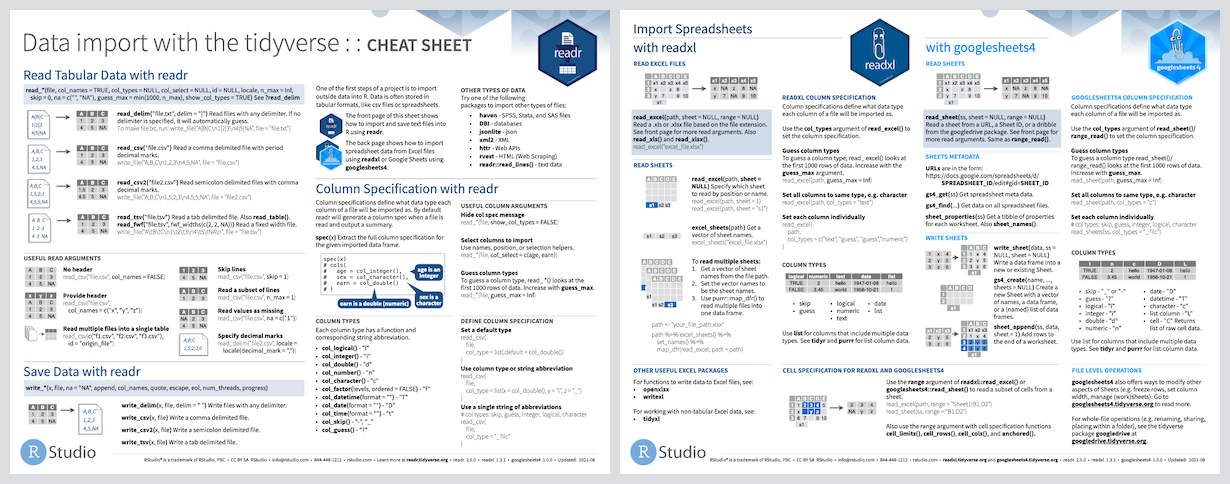
Cheatsheet
Usage
readr is part of the core tidyverse, so load it with:
library(tidyverse)
#> ── Attaching packages ─────────────────────────────────────── tidyverse 1.3.0 ──
#> ✔ ggplot2 3.3.2 ✔ purrr 0.3.4
#> ✔ tibble 3.0.3 ✔ dplyr 1.0.2.9000
#> ✔ tidyr 1.1.2 ✔ stringr 1.4.0
#> ✔ readr 1.3.1.9000 ✔ forcats 0.5.0
#> ── Conflicts ────────────────────────────────────────── tidyverse_conflicts() ──
#> ✖ dplyr::filter() masks stats::filter()
#> ✖ dplyr::lag() masks stats::lag()
To accurately read a rectangular dataset with readr you combine two pieces: a function that parses the overall file, and a column specification. The column specification describes how each column should be converted from a character vector to the most appropriate data type, and in most cases it’s not necessary because readr will guess it for you automatically.
readr supports seven file formats with seven read_ functions:
-
read_csv(): comma separated (CSV) files -
read_tsv(): tab separated files -
read_delim(): general delimited files -
read_fwf(): fixed width files -
read_table(): tabular files where columns are separated by white-space. -
read_log(): web log files
In many cases, these functions will just work: you supply the path to a file and you get a tibble back. The following example loads a sample file bundled with readr:
mtcars <- read_csv(readr_example("mtcars.csv"))
#>
#> ── Column specification ────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
#> cols(
#> mpg = col_double(),
#> cyl = col_double(),
#> disp = col_double(),
#> hp = col_double(),
#> drat = col_double(),
#> wt = col_double(),
#> qsec = col_double(),
#> vs = col_double(),
#> am = col_double(),
#> gear = col_double(),
#> carb = col_double()
#> )
Note that readr prints the column specification. This is useful because it allows you to check that the columns have been read in as you expect, and if they haven’t, you can easily copy and paste into a new call:
mtcars <- read_csv(readr_example("mtcars.csv"), col_types =
cols(
mpg = col_double(),
cyl = col_integer(),
disp = col_double(),
hp = col_integer(),
drat = col_double(),
vs = col_integer(),
wt = col_double(),
qsec = col_double(),
am = col_integer(),
gear = col_integer(),
carb = col_integer()
)
)
vignette("readr") gives more detail on how readr guesses the column
types, how you can override the defaults, and provides some useful tools
for debugging parsing problems.
Alternatives
There are two main alternatives to readr: base R and data.table’s
fread(). The most important differences are discussed below.
Base R
Compared to the corresponding base functions, readr functions:
-
Use a consistent naming scheme for the parameters (e.g.
col_namesandcol_typesnotheaderandcolClasses). -
Are much faster (up to 10x).
-
Leave strings as is by default, and automatically parse common date/time formats.
-
Have a helpful progress bar if loading is going to take a while.
-
All functions work exactly the same way regardless of the current locale. To override the US-centric defaults, use
locale().
data.table and fread()
data.table has a function
similar to read_csv() called fread. Compared to fread, readr
functions:
-
Are slower (currently ~1.2-2x slower. If you want absolutely the best performance, use
data.table::fread(). -
Use a slightly more sophisticated parser.
-
Forces you to supply all parameters, where
fread()saves you work by automatically guessing the delimiter, whether or not the file has a header, and how many lines to skip. -
Are built on a different underlying infrastructure. Readr functions are designed to be quite general, which makes it easier to add support for new rectangular data formats.
fread()is designed to be as fast as possible.
Acknowledgements
Thanks to:
-
Joe Cheng for showing me the beauty of deterministic finite automata for parsing, and for teaching me why I should write a tokenizer.
-
JJ Allaire for helping me come up with a design that makes very few copies, and is easy to extend.
-
Dirk Eddelbuettel for coming up with the name!
Code of Conduct
Please note that the readr project is released with a Contributor Code of Conduct. By contributing to this project, you agree to abide by its terms.