matsui528 / Rii
Licence: mit
Fast and memory-efficient ANN with a subset-search functionality
Stars: ✭ 96
Programming Languages
python
139335 projects - #7 most used programming language
Labels
Projects that are alternatives of or similar to Rii
adventures-with-ann
All the code for a series of Medium articles on Approximate Nearest Neighbors
Stars: ✭ 40 (-58.33%)
Mutual labels: nearest-neighbor-search
Smile
Statistical Machine Intelligence & Learning Engine
Stars: ✭ 5,412 (+5537.5%)
Mutual labels: nearest-neighbor-search
Fast Near Duplicate Image Search
Fast Near-Duplicate Image Search and Delete using pHash, t-SNE and KDTree.
Stars: ✭ 54 (-43.75%)
Mutual labels: nearest-neighbor-search
lbvh
an implementation of parallel linear BVH (LBVH) on GPU
Stars: ✭ 67 (-30.21%)
Mutual labels: nearest-neighbor-search
Lopq
Training of Locally Optimized Product Quantization (LOPQ) models for approximate nearest neighbor search of high dimensional data in Python and Spark.
Stars: ✭ 530 (+452.08%)
Mutual labels: nearest-neighbor-search
Ngt
Nearest Neighbor Search with Neighborhood Graph and Tree for High-dimensional Data
Stars: ✭ 636 (+562.5%)
Mutual labels: nearest-neighbor-search
graphgrove
A framework for building (and incrementally growing) graph-based data structures used in hierarchical or DAG-structured clustering and nearest neighbor search
Stars: ✭ 29 (-69.79%)
Mutual labels: nearest-neighbor-search
Annoy
Approximate Nearest Neighbors in C++/Python optimized for memory usage and loading/saving to disk
Stars: ✭ 9,262 (+9547.92%)
Mutual labels: nearest-neighbor-search
Soundfingerprinting
Open source audio fingerprinting in .NET. An efficient algorithm for acoustic fingerprinting written purely in C#.
Stars: ✭ 554 (+477.08%)
Mutual labels: nearest-neighbor-search
Deep Mihash
Code for papers "Hashing with Mutual Information" (TPAMI 2019) and "Hashing with Binary Matrix Pursuit" (ECCV 2018)
Stars: ✭ 13 (-86.46%)
Mutual labels: nearest-neighbor-search
Mlpack
mlpack: a scalable C++ machine learning library --
Stars: ✭ 3,859 (+3919.79%)
Mutual labels: nearest-neighbor-search
N2
TOROS N2 - lightweight approximate Nearest Neighbor library which runs fast even with large datasets
Stars: ✭ 457 (+376.04%)
Mutual labels: nearest-neighbor-search
Pointcloudutilities
Utilities for point cloud processing. read ply, write ply, search nearest neighbors using octree ...
Stars: ✭ 17 (-82.29%)
Mutual labels: nearest-neighbor-search
pgvector
Open-source vector similarity search for Postgres
Stars: ✭ 482 (+402.08%)
Mutual labels: nearest-neighbor-search
Awesome Cbir Papers
📝Awesome and classical image retrieval papers
Stars: ✭ 1,114 (+1060.42%)
Mutual labels: nearest-neighbor-search
docarray
The data structure for unstructured data
Stars: ✭ 561 (+484.38%)
Mutual labels: nearest-neighbor-search
Milvus
An open-source vector database for embedding similarity search and AI applications.
Stars: ✭ 9,015 (+9290.63%)
Mutual labels: nearest-neighbor-search
Gann
gann(go-approximate-nearest-neighbor) is a library for Approximate Nearest Neighbor Search written in Go
Stars: ✭ 75 (-21.87%)
Mutual labels: nearest-neighbor-search
Ggnn
GGNN: State of the Art Graph-based GPU Nearest Neighbor Search
Stars: ✭ 63 (-34.37%)
Mutual labels: nearest-neighbor-search
Falconn
FAst Lookups of Cosine and Other Nearest Neighbors (based on fast locality-sensitive hashing)
Stars: ✭ 919 (+857.29%)
Mutual labels: nearest-neighbor-search

Reconfigurable Inverted Index (Rii): IVFPQ-based fast and memory efficient approximate nearest neighbor search method with a subset-search functionality.
Reference:
- Y. Matsui, R. Hinami, and S. Satoh, "Reconfigurable Inverted Index", ACM Multimedia 2018 (oral). [paper] [project]
Summary of features
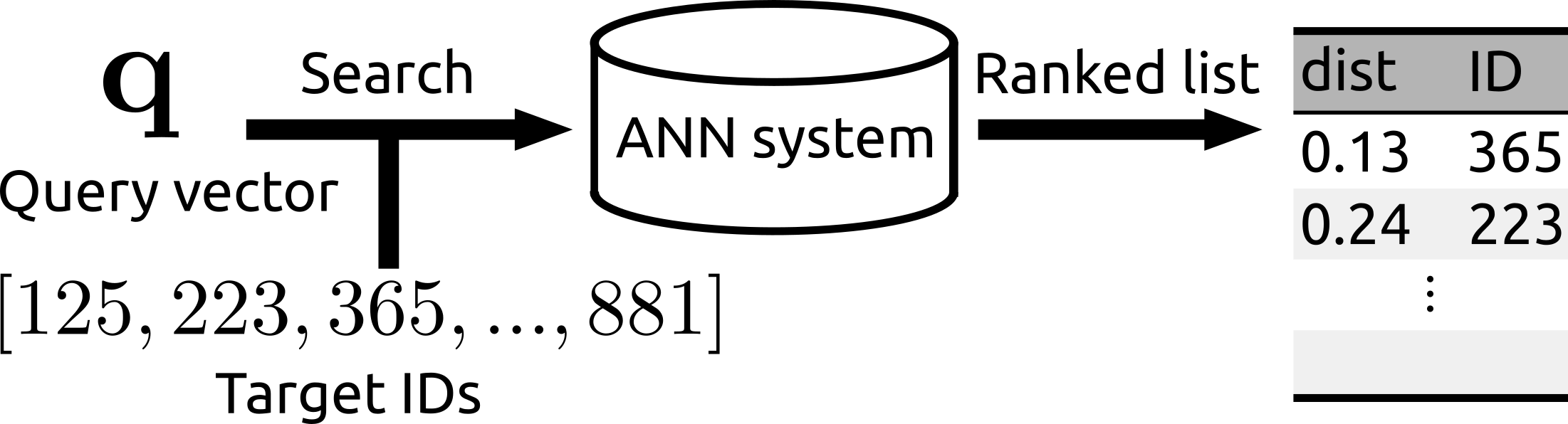 |
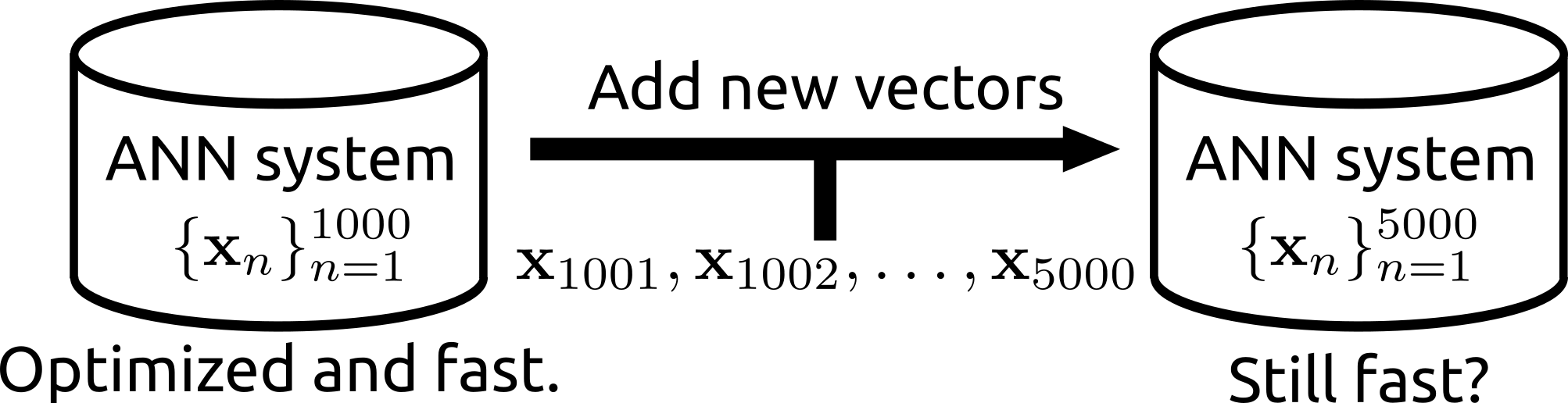 |
|---|---|
| The search can be operated for a subset of a database. | Rii remains fast even after many new items are added. |
- Fast and memory efficient ANN. Rii enables you to run billion-scale search in less than 10 ms.
- You can run the search over a subset of the whole database
- Rii Remains fast even after many vectors are newly added (i.e., the data structure can be reconfigured)
Installing
You can install the package via pip. This library works with Python 3.5+ on linux.
pip install rii
Documentation
Usage
Basic ANN
import rii
import nanopq
import numpy as np
N, Nt, D = 10000, 1000, 128
X = np.random.random((N, D)).astype(np.float32) # 10,000 128-dim vectors to be searched
Xt = np.random.random((Nt, D)).astype(np.float32) # 1,000 128-dim vectors for training
q = np.random.random((D,)).astype(np.float32) # a 128-dim vector
# Prepare a PQ/OPQ codec with M=32 sub spaces
codec = nanopq.PQ(M=32).fit(vecs=Xt) # Trained using Xt
# Instantiate a Rii class with the codec
e = rii.Rii(fine_quantizer=codec)
# Add vectors
e.add_configure(vecs=X)
# Search
ids, dists = e.query(q=q, topk=3)
print(ids, dists) # e.g., [7484 8173 1556] [15.06257439 15.38533878 16.16935158]
Note that you can construct a PQ codec and instantiate the Rii class at the same time if you want.
e = rii.Rii(fine_quantizer=nanopq.PQ(M=32).fit(vecs=Xt))
e.add_configure(vecs=X)
Furthermore, you can even write them in one line by chaining a function.
e = rii.Rii(fine_quantizer=nanopq.PQ(M=32).fit(vecs=Xt)).add_configure(vecs=X)
Subset search
# The search can be conducted over a subset of the database
target_ids = np.array([85, 132, 236, 551, 694, 728, 992, 1234]) # Specified by IDs
ids, dists = e.query(q=q, topk=3, target_ids=target_ids)
print(ids, dists) # e.g., [728 85 132] [14.80522156 15.92787838 16.28690338]
Data addition and reconfiguration
# Add new vectors
X2 = np.random.random((1000, D)).astype(np.float32)
e.add(vecs=X2) # Now N is 11000
e.query(q=q) # Ok. (0.12 msec / query)
# However, if you add quite a lot of vectors, the search might become slower
# because the data structure has been optimized for the initial item size (N=10000)
X3 = np.random.random((1000000, D)).astype(np.float32)
e.add(vecs=X3) # A lot. Now N is 1011000
e.query(q=q) # Slower (0.96 msec/query)
# In such case, run the reconfigure function. That updates the data structure
e.reconfigure()
e.query(q=q) # Ok. (0.21 msec / query)
I/O by pickling
import pickle
with open('rii.pkl', 'wb') as f:
pickle.dump(e, f)
with open('rii.pkl', 'rb') as f:
e_dumped = pickle.load(f) # e_dumped is identical to e
Util functions
# Print the current parameters
e.print_params()
# Delete all PQ-codes and posting lists. fine_quantizer is kept.
e.clear()
# You can switch the verbose flag
e.verbose = False
# You can merge two Rii instances if they have the same fine_quantizer
e1 = rii.Rii(fine_quantizer=codec)
e2 = rii.Rii(fine_quantizer=codec)
e1.add_reconfigure(vecs=X1)
e2.add_reconfigure(vecs=X2)
e1.merge(e2) # Now e1 contains both X1 and X2
Examples
Author
Credits
- The logo is designed by @richardbmx (#4)
Note that the project description data, including the texts, logos, images, and/or trademarks,
for each open source project belongs to its rightful owner.
If you wish to add or remove any projects, please contact us at [email protected].
