osrf / Rmf_core
rmf_core
The rmf_core packages provide the centralized functions of
the Robotics Middleware Framework (RMF). These include task
queuing, conflict-free resource scheduling, utilities to help
create robot fleet adapters, and so on.
All packages in this repo will be written in ROS 2.
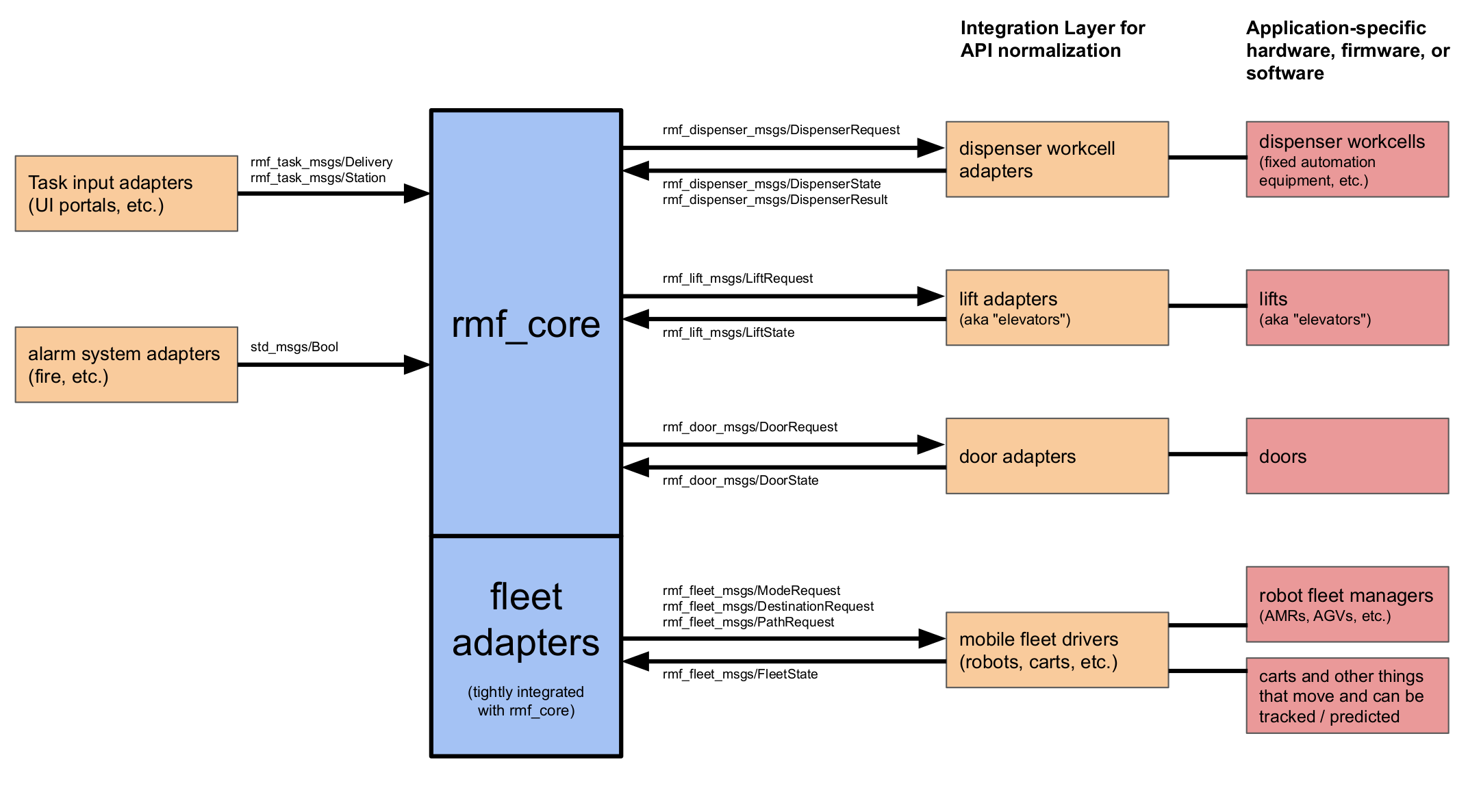
To create a useful deployment, rmf_core must be connected
to many other subsystems, as shown in the following diagram.
FAQ
Answers to frequently asked questions can be found here.
Roadmap
A near-term roadmap of the entire RMF project (including and beyond rmf_core) can be found in the user manual here.
Interfacing with rmf_core
There are several interface points with RMF core, as shown in the arrows
between the blue central box and the orange boxes in the diagram above. The
goal of these interfaces is to create a "narrow" and simple set of messages
that allow rmf_core to integrate with the following elements of a
deployment:
Robot fleet integration
The rmf_fleet_msgs package contains four messages and is
intended to carry the interactions between rmf_core and a vendor-provided
(typically proprietary) fleet manager for a collection of robots. It is
expected that a RMF deployment will consist of multiple robot fleets, often
operating at different levels of RMF integration: for example, one fleet may
only be willing to supply FleetState messages (observation-only) whereas
another fleet in the same facility may be willing to follow RMF
DestinationRequest messages. RMF is specifically designed to allow this
type of "mixed levels of control" and to plan accordingly.
-
rmf_fleet_msgs/FleetStateon topicfleet_states. This message consists of a list ofrmf_fleet_msgs/RobotStatemessages, each of which contains the state of a particular robot. This includes the level of the facility the robot is on, its X- and Y- offset (in meters) from the origin of that level's map, its current destination and path (if known), and so on. -
rmf_fleet_msgs/DestinationRequeston topicdestination_requestsis a request for a particular robot to go to a particular destination. -
rmf_fleet_msgs/ModeRequeston topicmode_requestsis a request for a particular robot to change modes, for example, fromMOVINGtoPAUSED, in order to preserve spatial separation between robots of different fleets. -
rmf_fleet_msgs/PathRequeston topicpath_requestsis a request for a particular robot to follow a particular path.
As mentioned above, several levels of integration are possible between RMF and
vendor-controlled Fleet Managers. The following table captures the required
messages for each integration feature. In general, the more integration
features that are available for a particular fleet, the more efficient the
combined system operations will be, because each integration feature gives
additional options for rmf_core to perform traffic management. For example, a
fleet that only supports the "state reporting" integration feature will always
require that rmf_core totally clear its predicted travel lane of all other
robots, whereas fleets that support "pause/resume motion" or "complete paths"
allow many other potential options for de-conflicting robot traffic.
| Integration Feature | Required Message | Default topic name |
|---|---|---|
| state reporting | rmf_fleet_msgs/FleetState |
fleet_states |
| set destinations | rmf_fleet_msgs/DestinationRequest |
destination_requests |
| pause/resume motion | rmf_fleet_msgs/ModeRequest |
mode_requests |
| set complete paths | rmf_fleet_msgs/PathRequest |
path_requests |
Door integration
The rmf_door_msgs package contains two messages. This interface allows
RMF to open and close motorized doors for robots as they move throughout a
facility.
-
rmf_door_msgs/DoorStatemessages are periodically sent by door controllers tormf_core. These messages express the current mode of the door asCLOSED,MOVING, orOPEN -
rmf_door_msgs/DoorRequestmessages are sent fromrmf_coreto doors when they need to open or close for robot operations.
Installation
Building rmf_core from source requires gcc version 8 or clang version 6 (or above)
mkdir ws_rmf/src -p
cd ws_rmf/src/
git clone https://github.com/osrf/rmf_core.git
cd ../
source /opt/ros/eloquent/setup.bash
rosdep update
rosdep install --from-paths src --ignore-src -yr
colcon build --cmake-args -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=RELEASE
To manually override the compiler version, prefix the colcon command with the CXX parameter.
sudo apt update && sudo apt install g++-8
CXX=g++-8 colcon build --cmake-args -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=RELEASE
Demonstrations
This repository holds a number of demonstrations and examples of working with rmf_core and the other packages in the RMF ecosystem.
Contributing
Guidelines on contributing to rmf_core and other RMF repositories can be found here.