A minimal Python library for RT Struct manipulation
RT-Utils is motivated to allow physicians and other users to view the results of segmentation performed on a series of DICOM images. RT-Utils allows you to create or load RT Structs, extract 3d masks from RT Struct ROIs, easily add one or more regions of interest, and save the resulting RT Struct in just a few lines!
How it works
RT-Utils provides a builder class to faciliate the creation and loading of an RT Struct. From there, you can add ROIs through binary masks and optionally input the colour of the region along with the region name.
The format for the ROI mask is an nd numpy array of type bool. It is an array of 2d binary masks, one plane for each slice location within the DICOM series. The slices should be sorted in ascending order within the mask. Through these masks, we extract the contours of the regions of interest and place them within the RT Struct file. Note that there is currently only support for the use of one frame of reference UID and structered set ROI sequence. Also note that holes within the ROI may be handled poorly.
Installation
pip install rt_utils
Creating new RT Structs
from rt_utils import RTStructBuilder
# Create new RT Struct. Requires the DICOM series path for the RT Struct.
rtstruct = RTStructBuilder.create_new(dicom_series_path="./testlocation")
# ...
# Create mask through means such as ML
# ...
# Add the 3D mask as an ROI.
# The colour, description, and name will be auto generated
rtstruct.add_roi(mask=MASK_FROM_ML_MODEL)
# Add another ROI, this time setting the color, description, and name
rtstruct.add_roi(
mask=MASK_FROM_ML_MODEL,
color=[255, 0, 255],
name="RT-Utils ROI!"
)
rtstruct.save('new-rt-struct')Adding to existing RT Structs
from rt_utils import RTStructBuilder
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Load existing RT Struct. Requires the series path and existing RT Struct path
rtstruct = RTStructBuilder.create_from(
dicom_series_path="./testlocation",
rt_struct_path="./testlocation/rt-struct.dcm"
)
# Add ROI. This is the same as the above example.
rtstruct.add_roi(
mask=MASK_FROM_ML_MODEL,
color=[255, 0, 255],
name="RT-Utils ROI!"
)
rtstruct.save('new-rt-struct')Creation Results
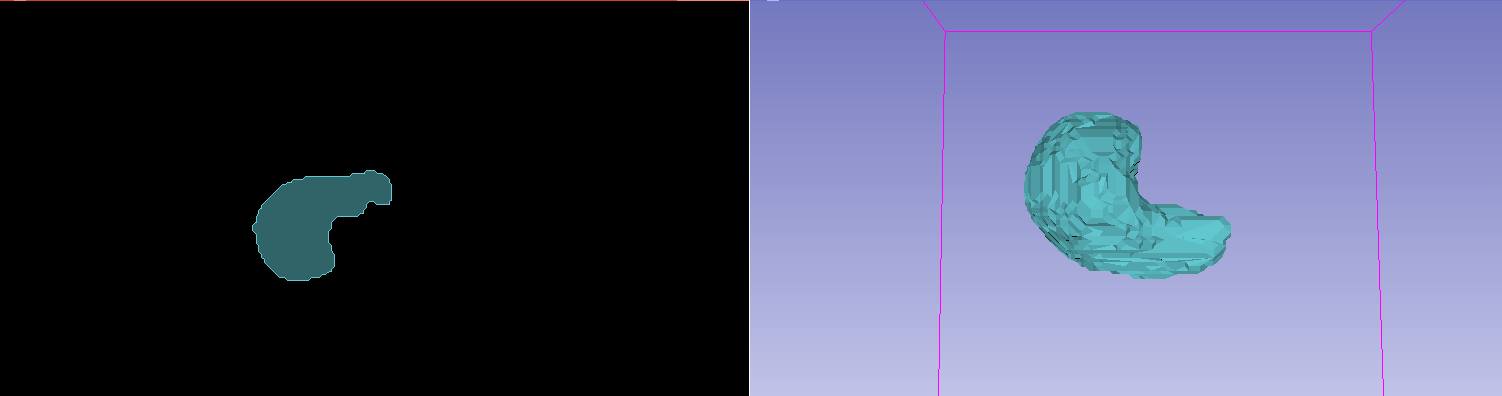
The results of a generated ROI with a dummy mask, as viewed in Slicer.
The results of a generated ROI with a liver segmentation model, as viewed in Slicer. (Note the underlying patient data has been hidden)
Loading an existing RT Struct contour as a mask
from rt_utils import RTStructBuilder
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Load existing RT Struct. Requires the series path and existing RT Struct path
rtstruct = RTStructBuilder.create_from(
dicom_series_path="./testlocation",
rt_struct_path="./testlocation/rt-struct.dcm"
)
# View all of the ROI names from within the image
print(rtstruct.get_roi_names())
# Loading the 3D Mask from within the RT Struct
mask_3d = rtstruct.get_roi_mask_by_name("ROI NAME")
# Display one slice of the region
first_mask_slice = mask_3d[:, :, 0]
plt.imshow(first_mask_slice)
plt.show()Loading Results
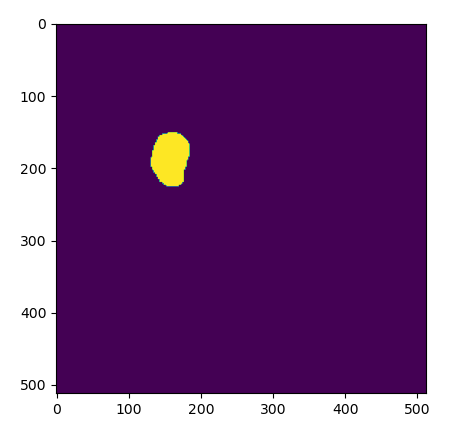
The results of a loading an exisiting ROI as a mask, as viewed in Python.
Additional Parameters
The add_roi method of our RTStruct class has a multitude of optional parameters available. Below is a comprehensive list of all these parameters and what they do.
- color: This parameter can either be a colour string such as '#ffffff' or a RGB value as a list such as '[255, 255, 255]'. This parameter will dictate the colour of your ROI when viewed in a viewing program. If no colour is provided, RT Utils will pick from our internal colour palette based on the ROI Number of the ROI.
- name: A str value that defaults to none. Used to set the name of the ROI within the RT Struct. If the name is none, RT Utils will set a name of ROI-{ROI Number}.
- description: A str value that sets the description of the ROI within the RT Struct. If no value is provided, the description is just left blank.
- use_pin_hole: A boolean value that defaults to false. If set to true, lines will be erased through your mask such that each separate region within your image can be encapsulated via a single contour instead of contours nested within one another. Use this if your RT Struct viewer of choice does not support nested contours / contours with holes.
- approximate_contours: A boolean value that defaults to True which defines whether or not approximations are made when extracting contours from the input mask. Setting this to false will lead to much larger contour data within your RT Struct so only use this if as much precision as possible is required.
- roi_generation_algorithm: An enum value that defaults to 0 which defines what ROI generation algorithm will be used. 0='AUTOMATIC', 1='SEMIAUTOMATIC', or 2='MANUAL'.