sz128 / Slot_filling_and_intent_detection_of_slu
Programming Languages
Projects that are alternatives of or similar to Slot filling and intent detection of slu
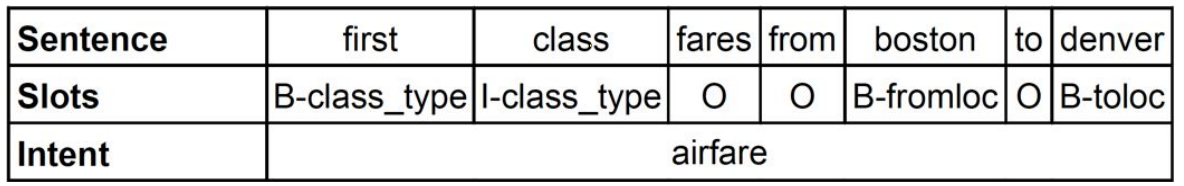
Slot filling and intent detection tasks of spoken language understanding
- Basic models for slot filling and intent detection:
- An implementation for "focus" part of the paper "Encoder-decoder with focus-mechanism for sequence labelling based spoken language understanding" (Su Zhu and Kai Yu, 2016).
- An implementation of BLSTM-CRF based on jiesutd/NCRFpp
- An implementation of joint training of slot filling and intent detection tasks (Bing Liu and Ian Lane, 2016).
- Basic models + ELMo / BERT / XLNET
- Tutorials on datasets:
- ATIS
- SNIPS
- The Facebook’s multilingual dataset (English/Spanish/Thai)
- MIT_Restaurant_Movie_corpus (w/o intent)
- E-commerce Shopping Assistant (ECSA) from Alibaba (w/o intent, in Chinese)
- CoNLL-2003 NER (w/o intent)
| Section | Description |
|---|---|
| Setup | Required packages |
| Evaluation of intent detection for multiple intents | How to report performance of intent detection on ATIS dataset |
| Tutorials A: with pretrained word embeddings | Tutorials A: Slot filling and intent detection with pretrained word embeddings |
| Tutorials B: with ELMo | Tutorials B: Slot filling and intent detection with ELMo |
| Tutorials C: with BERT | Tutorials C: Slot filling and intent detection with BERT |
| Tutorials D: with XLNET | Tutorials D: Slot filling and intent detection with XLNET |
| Results | Results of different methods on certain datasets |
| Inference Mode | Inference Mode |
| Reference | How to cite? |
Setup
- python 3.6.x
- pytorch 1.4.0
- pip install gpustat [if gpu is used]
- embeddings: pip install embeddings
- ELMo in allennlp: pip install allennlp
- BERT/XLNET in transformers: pip install transformers (2.5.0)
About the evaluations of intent detection on ATIS and SNIPS datasets
As we can know from the datasets, ATIS may have multiple intents for one utterance while SNIPS has only one intent for one utterance. For example, "show me all flights and fares from denver to san francisco <=> atis_flight && atis_airfare". Therefore, there is a public trick in the training and evaluation stages for intent detection of ATIS dataset.
NOTE!!!
: Impacted by the paper "What is left to be understood in ATIS?", almost all works about ATIS choose the first intent as the label to train a "softmax" intent classifier. In the evaluation stage, it will be viewed as correct if the predicted intent is one of the multiple intents.
TODO:
- Add char-embeddings
Tutorials A: Slot filling and intent detection with pretrained word embeddings
- Pretrained word embeddings are borrowed from CNN-BLSTM language models of ELMo where word embeddings are modelled by char-CNNs. We extract the pretrained word embeddings for ATIS, SNIPS, the Facebook’s multilingual dataset and MIT_Restaurant_Movie_corpus(w/o intent) datasets by:
python3 scripts/get_ELMo_word_embedding_for_a_dataset.py \
--in_files data/atis-2/{train,valid,test} \
--output_word2vec local/word_embeddings/elmo_1024_cased_for_atis.txt
python3 scripts/get_ELMo_word_embedding_for_a_dataset.py \
--in_files data/snips/{train,valid,test} \
--output_word2vec local/word_embeddings/elmo_1024_cased_for_snips.txt
python3 scripts/get_ELMo_word_embedding_for_a_dataset.py \
--in_files data/MIT_corpus/{movie_eng,movie_trivia10k13,restaurant}/{train,valid,test} \
--output_word2vec local/word_embeddings/elmo_1024_cased_for_MIT_corpus.txt
, or use Glove and KazumaChar embeddings which are also exploited in the TRADE dialogue state tracker:
python3 scripts/get_Glove-KazumaChar_word_embedding_for_a_dataset.py \
--in_files data/atis-2/{train,valid,test} \
--output_word2vec local/word_embeddings/glove-kazumachar_400_cased_for_atis.txt
python3 scripts/get_Glove-KazumaChar_word_embedding_for_a_dataset.py \
--in_files data/snips/{train,valid,test} \
--output_word2vec local/word_embeddings/glove-kazumachar_400_cased_for_snips.txt
python3 scripts/get_Glove-KazumaChar_word_embedding_for_a_dataset.py \
--in_files data/multilingual_task_oriented_data/en/{train,valid,test} \
--output_word2vec local/word_embeddings/glove-kazumachar_400_cased_for_multilingual_en.txt
python3 scripts/get_Glove-KazumaChar_word_embedding_for_a_dataset.py \
--in_files data/MIT_corpus/{movie_eng,movie_trivia10k13,restaurant}/{train,valid,test} \
--output_word2vec local/word_embeddings/glove-kazumachar_400_cased_for_MIT_corpus.txt
, or use word embeddings in the pretrained BERT model:
python3 scripts/get_BERT_word_embedding_for_a_dataset.py \
--in_files data/multilingual_task_oriented_data/es/{train,valid,test} \
--output_word2vec local/word_embeddings/bert_768_cased_for_multilingual_es.txt \
--pretrained_tf_type bert --pretrained_tf_name bert-base-multilingual-cased
python3 scripts/get_BERT_word_embedding_for_a_dataset.py \
--in_files data/multilingual_task_oriented_data/es/{train,valid,test} \
--output_word2vec local/word_embeddings/bert_768_cased_for_multilingual_es.txt \
--pretrained_tf_type bert --pretrained_tf_name bert-base-multilingual-cased
- Run scripts of training and evaluation at each epoch.
- BLSTM model (slot_tagger)
- BLSTM-CRF model (slot_tagger_with_crf)
- Enc-dec focus model (BLSTM-LSTM) (slot_tagger_with_focus), the same as Encoder-Decoder NN (with aligned inputs)(Liu and Lane, 2016)
slot_intent_model=slot_tagger # slot_tagger, slot_tagger_with_crf, slot_tagger_with_focus
bash run/atis_with_pretrained_word_embeddings.sh --task_slot_filling ${slot_intent_model}
bash run/snips_with_pretrained_word_embeddings.sh --task_slot_filling ${slot_intent_model}
bash run/MIT_corpus_with_pretrained_word_embeddings.sh --task_slot_filling ${slot_intent_model} --dataroot data/MIT_corpus/movie_eng --dataset mit_movie_eng
bash run/multilingual_en_with_pretrained_word_embeddings.sh --task_slot_filling ${slot_intent_model}
bash run/multilingual_es_with_pretrained_word_embeddings.sh --task_slot_filling ${slot_intent_model}
bash run/multilingual_th_with_pretrained_word_embeddings.sh --task_slot_filling ${slot_intent_model}
Tutorials B: Slot filling and intent detection with ELMo
- Run scripts of training and evaluation at each epoch.
- ELMo + BLSTM/BLSTM-CRF/Enc-dec focus model (BLSTM-LSTM) models:
slot_intent_model=slot_tagger # slot_tagger, slot_tagger_with_crf, slot_tagger_with_focus
bash run/atis_with_elmo.sh --task_slot_filling ${slot_intent_model}
bash run/snips_with_elmo.sh --task_slot_filling ${slot_intent_model}
bash run/MIT_corpus_with_elmo.sh --task_slot_filling ${slot_intent_model} --dataroot data/MIT_corpus/movie_eng --dataset mit_movie_eng
Tutorials C: Slot filling and intent detection with BERT
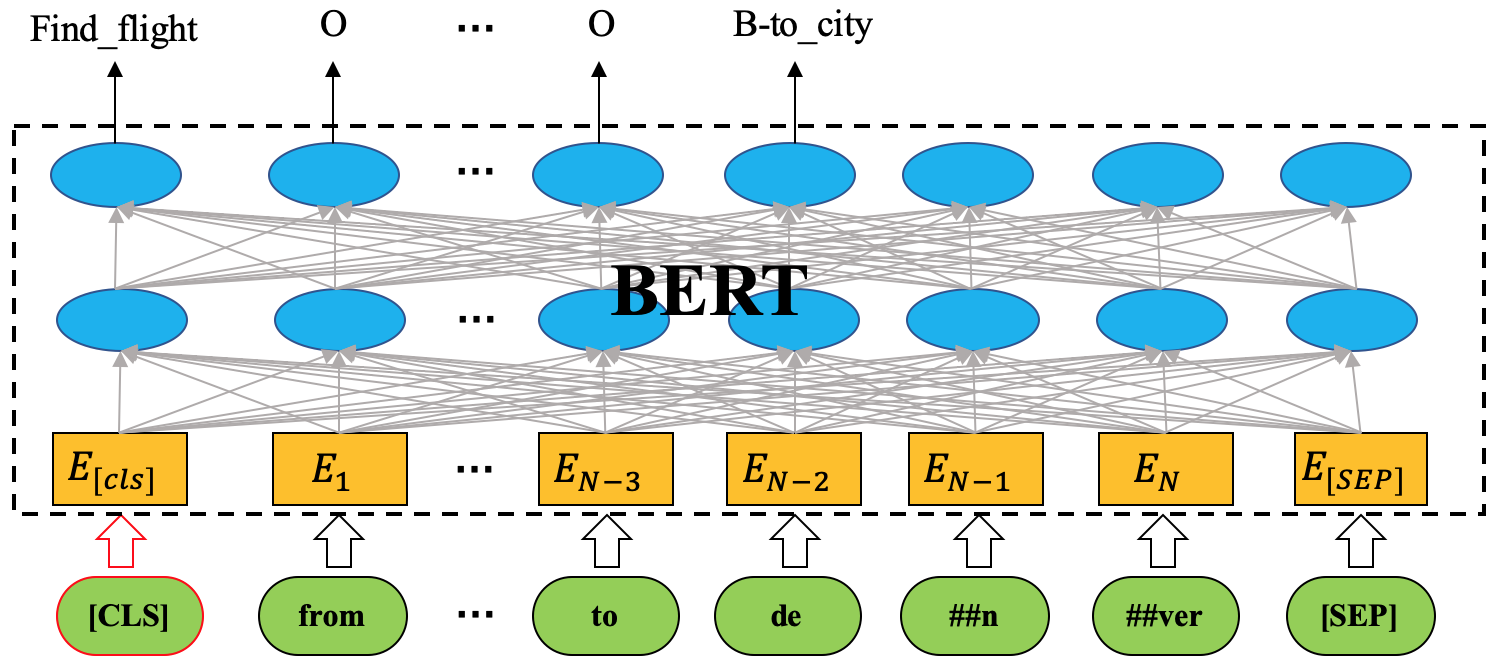
- Model architectures:
- Joint BERT or "with pure BERT":
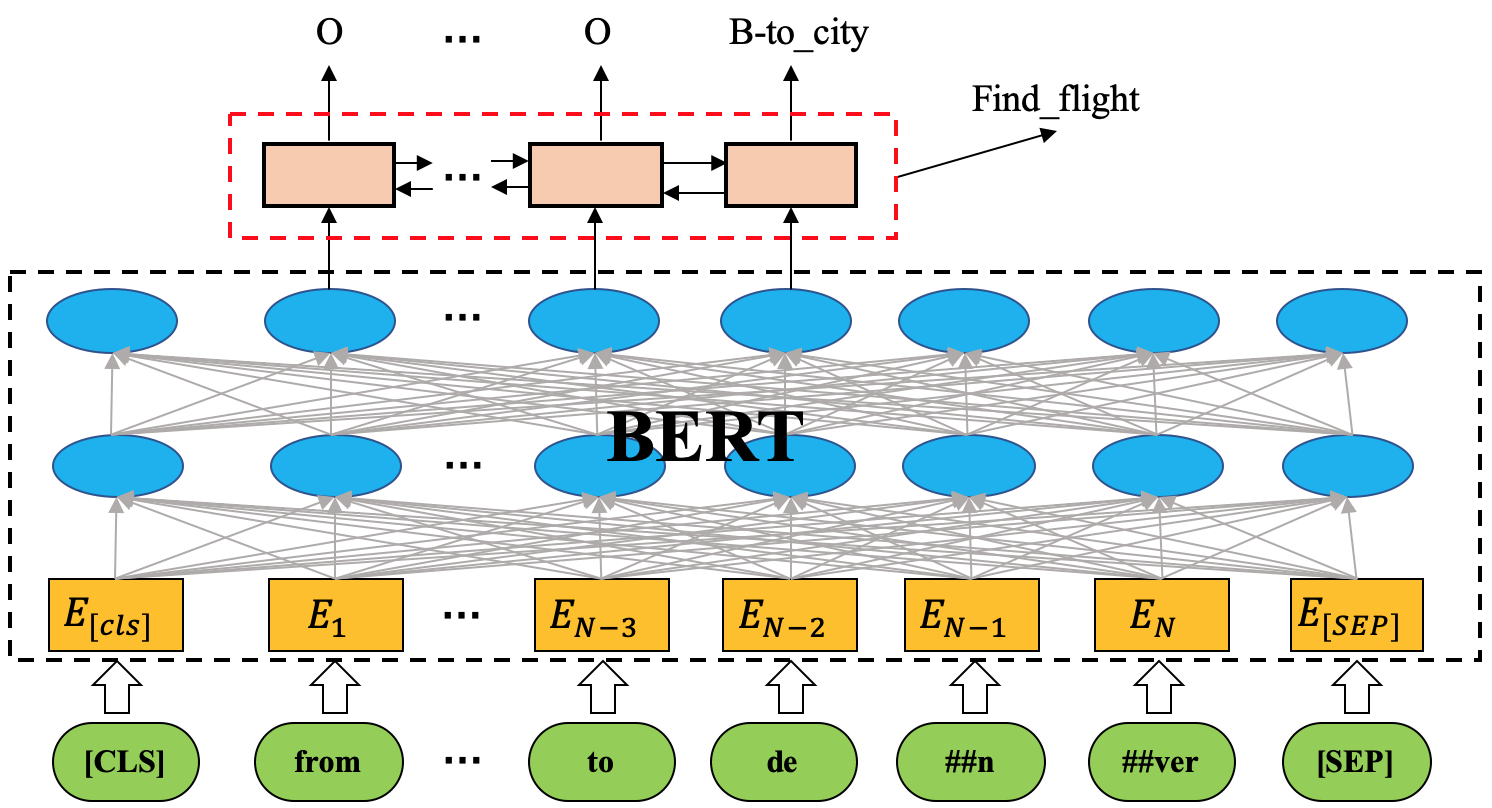
- Our BERT + BLSTM (BLSTM-CRF\Enc-dec focus):
- Run scripts of training and evaluation at each epoch.
- Pure BERT (without or with crf) model:
slot_model=NN # NN, NN_crf
intent_input=CLS # none, CLS, max, CLS_max
bash run/atis_with_pure_bert.sh --task_slot_filling ${slot_model} --task_intent_detection ${intent_input}
bash run/snips_with_pure_bert.sh --task_slot_filling ${slot_model} --task_intent_detection ${intent_input}
bash run/MIT_corpus_with_pure_bert.sh --task_slot_filling ${slot_model} --task_intent_detection ${intent_input} --dataroot data/MIT_corpus/movie_eng --dataset mit_movie_eng
bash run/multilingual_en_with_pure_bert.sh --task_slot_filling ${slot_model} --task_intent_detection ${intent_input}
bash run/multilingual_es_with_pure_bert.sh --task_slot_filling ${slot_model} --task_intent_detection ${intent_input}
bash run/multilingual_th_with_pure_bert.sh --task_slot_filling ${slot_model} --task_intent_detection ${intent_input}
bash run/ECSA_with_pure_bert.sh --task_slot_filling ${slot_model} --task_intent_detection ${intent_input}
bash run/CoNLL2003_NER_with_pure_bert.sh --task_slot_filling ${slot_model} --task_intent_detection ${intent_input}
- BERT + BLSTM/BLSTM-CRF/Enc-dec focus model (BLSTM-LSTM) models:
slot_intent_model=slot_tagger # slot_tagger, slot_tagger_with_crf, slot_tagger_with_focus
bash run/atis_with_bert.sh --task_slot_filling ${slot_intent_model}
bash run/snips_with_bert.sh --task_slot_filling ${slot_intent_model}
bash run/MIT_corpus_with_bert.sh --task_slot_filling ${slot_intent_model} --dataroot data/MIT_corpus/movie_eng --dataset mit_movie_eng
- For optimizer, you can try BertAdam and AdamW. In my experiments, I choose to use BertAdam.
Tutorials D: Slot filling and intent detection with XLNET
- Run scripts of training and evaluation at each epoch.
- Pure XLNET (without or with crf) model:
slot_model=NN # NN, NN_crf
intent_input=CLS # none, CLS, max, CLS_max
bash run/atis_with_pure_xlnet.sh --task_slot_filling ${slot_model} --task_intent_detection ${intent_input}
bash run/snips_with_pure_xlnet.sh --task_slot_filling ${slot_model} --task_intent_detection ${intent_input}
bash run/MIT_corpus_with_pure_xlnet.sh --task_slot_filling ${slot_model} --task_intent_detection ${intent_input} --dataroot data/MIT_corpus/movie_eng --dataset mit_movie_eng
- XLNET + BLSTM/BLSTM-CRF/Enc-dec focus model (BLSTM-LSTM) models:
slot_intent_model=slot_tagger # slot_tagger, slot_tagger_with_crf, slot_tagger_with_focus
bash run/atis_with_xlnet.sh --task_slot_filling ${slot_intent_model}
bash run/snips_with_xlnet.sh --task_slot_filling ${slot_intent_model}
bash run/MIT_corpus_with_xlnet.sh --task_slot_filling ${slot_intent_model} --dataroot data/MIT_corpus/movie_eng --dataset mit_movie_eng
- For optimizer, you can try BertAdam and AdamW.
Results:
- For "NLU + BERT/XLNET" models, hyper-parameters are not tuned carefully.
-
Results of ATIS:
models intent Acc (%) slot F1-score (%) [Atten. enc-dec NN with aligned inputs](Liu and Lane, 2016) 98.43 95.87 [Atten.-BiRNN](Liu and Lane, 2016) 98.21 95.98 [Enc-dec focus](Zhu and Yu, 2017) - 95.79 [Slot-Gated](Goo et al., 2018) 94.1 95.2 Intent Gating & self-attention 98.77 96.52 BLSTM-CRF + ELMo 97.42 95.62 Joint BERT 97.5 96.1 Joint BERT + CRF 97.9 96.0 BLSTM (A. Pre-train word emb. of ELMo) 98.10 95.67 BLSTM-CRF (A. Pre-train word emb. of ELMo) 98.54 95.39 Enc-dec focus (A. Pre-train word emb. of ELMo) 98.43 95.78 BLSTM (A. Pre-train word emb. of Glove & KazumaChar) 98.66 95.55 BLSTM-CRF (A. Pre-train word emb. of Glove & KazumaChar) 98.21 95.74 Enc-dec focus (A. Pre-train word emb. of Glove & KazumaChar) 98.66 95.86 BLSTM (B. +ELMo) 98.66 95.52 BLSTM-CRF (B. +ELMo) 98.32 95.62 Enc-dec focus (B. +ELMo) 98.66 95.70 BLSTM (C. +BERT) 99.10 95.94 BLSTM (D. +XLNET) 98.77 96.08 -
Results of SNIPS:
-
Cased BERT-base model gives better result than uncased model.
models intent Acc (%) slot F1-score (%) [Slot-Gated](Goo et al., 2018) 97.0 88.8 BLSTM-CRF + ELMo 99.29 93.90 Joint BERT 98.6 97.0 Joint BERT + CRF 98.4 96.7 BLSTM (A. Pre-train word emb. of ELMo) 99.14 95.75 BLSTM-CRF (A. Pre-train word emb. of ELMo) 99.00 96.92 Enc-dec focus (A. Pre-train word emb. of ELMo) 98.71 96.22 BLSTM (A. Pre-train word emb. of Glove & KazumaChar) 99.14 96.24 BLSTM-CRF (A. Pre-train word emb. of Glove & KazumaChar) 98.86 96.31 Enc-dec focus (A. Pre-train word emb. of Glove & KazumaChar) 98.43 96.06 BLSTM (B. +ELMo) 98.71 96.32 BLSTM-CRF (B. +ELMo) 98.57 96.61 Enc-dec focus (B. +ELMo) 99.14 96.69 BLSTM (C. +BERT) 98.86 96.92 BLSTM-CRF (C. +BERT) 98.86 97.00 Enc-dec focus (C. +BERT) 98.71 97.17 BLSTM (D. +XLNET) 98.86 97.05
-
Results of the Facebook’s multilingual dataset (note: cased BERT-base model gives better result than uncased model):
- English (en):
models intent Acc (%) slot F1-score (%) Cross-Lingual Transfer (only target) 99.11 94.81 BLSTM (no Pre-train word emb.) 99.19 95.37 Enc-dec focus (A. Pre-train word emb. of Glove & KazumaChar) 99.28 96.04 Pure BERT 99.34 96.23 - Spanish (es):
models intent Acc (%) slot F1-score (%) Cross-Lingual Transfer (only target) 97.26 80.95 Cross-Lingual Transfer (Cross-lingual + ELMo) 97.51 83.38 BLSTM (no Pre-train word emb.) (only target) 97.63 86.05 Enc-dec focus (A. Pre-train word emb. of BERT input layer) (only target) 97.67 88.67 Pure BERT (only target) 98.85 89.26 - Thai (th): (it seems "Enc-dec focus" gives better results than BLSTM)
models intent Acc (%) slot F1-score (%) Cross-Lingual Transfer (only target) 95.13 87.26 Cross-Lingual Transfer (Cross-lingual + Mult. CoVe + auto) 96.87 91.51 BLSTM (no Pre-train word emb.) (only target) 96.99 89.17 Enc-dec focus (no Pre-train word emb.) (only target) 96.75 91.31 Enc-dec focus (A. Pre-train word emb. of BERT input layer) (only target) 96.87 91.05 Pure BERT (only target) 97.34 92.51 -
Slot F1-scores of MIT_Restaurant_Movie_corpus(w/o intent):
models Restaurant Movie_eng Movie_trivia10k13 Dom-Gen-Adv 74.25 83.03 63.51 Joint Dom Spec & Gen-Adv 74.47 85.33 65.33 Data Augmentation via Joint Variational Generation 73.0 82.9 65.7 BLSTM (A. Pre-train word emb. of ELMo) 77.54 85.37 67.97 BLSTM-CRF (A. Pre-train word emb. of ELMo) 79.77 87.36 71.83 Enc-dec focus (A. Pre-train word emb. of ELMo) 78.77 86.68 70.85 BLSTM (A. Pre-train word emb. of Glove & KazumaChar) 78.02 86.33 68.55 BLSTM-CRF (A. Pre-train word emb. of Glove & KazumaChar) 79.84 87.61 71.90 Enc-dec focus (A. Pre-train word emb. of Glove & KazumaChar) 79.98 86.82 71.10 -
Slot F1-scores of E-commerce Shopping Assistant (ECSA) from Alibaba(w/o intent, in Chinese):
models slot F1-score (%) Basic BiLSTM-CRF 43.02 Pure BERT 46.96 Pure BERT-CRF 47.75 -
Entity F1-scores of CoNLL-2003 NER(w/o intent):
models F1-score (%) Pure BERT 91.36 Pure BERT-CRF 91.55
Inference Mode
An example here:
bash run/atis_with_pretrained_word_embeddings_for_inference_mode__an_example.sh
Reference
- Su Zhu and Kai Yu, "Encoder-decoder with focus-mechanism for sequence labelling based spoken language understanding," in IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing(ICASSP), 2017, pp. 5675-5679.
