stevengj / Sobol.jl
Programming Languages
Labels
Projects that are alternatives of or similar to Sobol.jl
The Sobol module for Julia
This module provides a free Julia-language Sobol low-discrepancy-sequence (LDS) implementation. This generates "quasi-random" sequences of points in N dimensions which are equally distributed over an N-dimensional hypercube.
The advantage of an LDS over truly random (or pseudo-random) numbers is that an LDS (which is not random) tends to be more evenly distributed for finite numbers of points. This is used in quasi-Monte Carlo methods in order to accelerate convergence compared to traditional Monte Carlo methods employing random sequences.
It can be installed using the Julia package manager via Pkg.add("Sobol").
Algorithm
This is an independent implementation, originally by Steven G. Johnson, of the algorithm for generation of Sobol sequences in up to 21201 dimensions described in:
- P. Bratley and B. L. Fox, Algorithm 659: Implementing Sobol's quasirandom sequence generator, ACM Trans. Math. Soft. 14 (1), pp. 88-100 (1988), doi:10.1145/42288.214372.
- S. Joe and F. Y. Kuo, Remark on algorithm 659: Implementing Sobol's quasirandom sequence generator, ACM Trans. Math. Soft 29 (1), 49-57 (2003), doi:10.1145/641876.641879.
Originally implemented in C in 2007 as part of the NLopt library for nonlinear optimization, the code was subsequently converted by Ken-B into pure Julia with roughly the same performance.
It is important to emphasize that SGJ's implementation was based on the mathematical description of the algorithms only, and was done without reference to the Fortran code from the Trans. Math. Soft. (TOMS) papers. The reason is that TOMS code is not free/open-source software (it falls under restrictive ACM copyright terms). (SGJ did re-use a table of primitive polynomials and coefficients from the TOMS code, but since this is merely a tabulation of mathematical facts it is not copyrightable.) SGJ's implementation in NLopt, along with this Julia translation, is free/open-source software under the MIT ("expat") license.
Direction numbers used were derived from the file http://web.maths.unsw.edu.au/~fkuo/sobol/new-joe-kuo-6.21201
Technically, we implement a 32-bit Sobol sequence. After 232-1 points, the sequence terminates, and subsequently our implementation returns pseudo-random numbers generated by the Mersenne Twister algorithm. In practical applications, however, this point is rarely reached.
Usage
To initialize a Sobol sequence s in N dimensions (0 < N < 21201), use
the SobolSeq constructor:
using Sobol
s = SobolSeq(N)
Then
x = next!(s)
returns the next point (a Vector{Float64}) in the sequence; each point
lies in the hypercube [0,1]N. You can also compute the next
point in-place with
next!(s, x)
where x should be a Vector of length N of some floating-point type (e.g. Float64, Float32, or BigFloat).
You can also use a SobolSeq as an iterator in Julia:
for x in SobolSeq(N)
...
end
Note, however, that the loop will never terminate unless you explicitly
call break (or similar) in the loop body at some point of your choosing.
We also provide a different SobolSeq constructor to provide
an N-dimensional Sobol sequence rescaled to an arbitrary hypercube:
s = SobolSeq(lb, ub)
where lb and ub are arrays (or other iterables) of length N, giving
the lower and upper bounds of the hypercube, respectively. For example,
SobolSeq([-1,0,0],[1,3,2]) generates points in the box [-1,1]×[0,3]×[0,2]. (Although the generated points are Float64 by default, in general the precision is determined by that of lb and ub.)
If you know in advance the number n of points that you plan to
generate, some authors suggest that better uniformity can be attained
by first skipping the initial portion of the LDS (and in particular,
the first power of two smaller than n; see Joe and Kuo, 2003). This
facility is provided by:
skip(s, n)
Skipping exactly n elements is also possible:
skip(s, n, exact=true)
Example
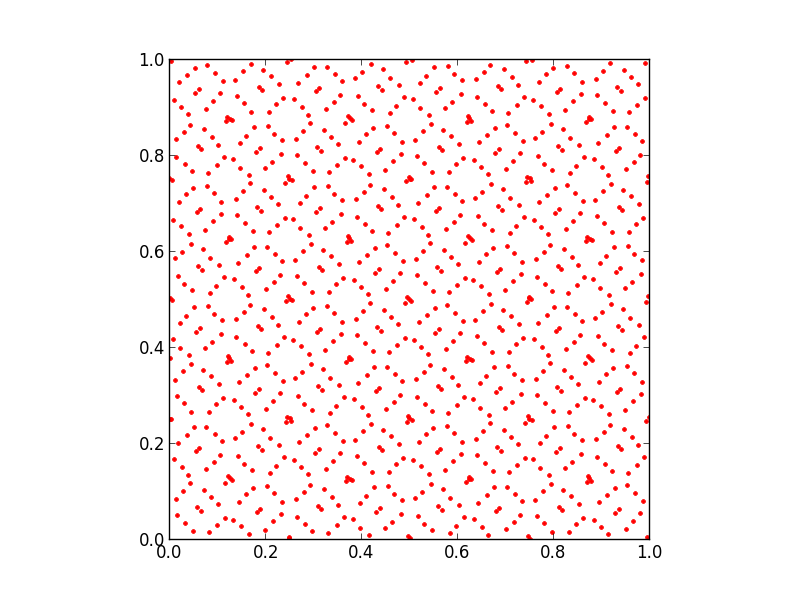
Here is a simple example, generating 1024 points in two dimensions and plotting them with the PyPlot package. Note the highly uniform, nonrandom distribution of points in the [0,1]×[0,1] unit square!
using Sobol
using PyPlot
s = SobolSeq(2)
p = hcat([next!(s) for i = 1:1024]...)'
subplot(111, aspect="equal")
plot(p[:,1], p[:,2], "r.")
Author
This module was written by Steven G. Johnson.