tuxalin / Thst
Programming Languages
Projects that are alternatives of or similar to Thst
Hierarchical spatial trees
Templated hierarchical spatial trees designed for high-performance and hierarchical spatial partitioning use cases.
Features
There are two tree implementations, a multi-dimensional RTree and a two-dimensional QuadTree.
Some of the currently implemented features are:
- hierarchical, you can add values to the internal branch nodes or traverse them
- leaf and depth-first tree traversals for spatial partitioning, via custom iterators
- custom indexable getter similar to boost's
- hierarchical query
- nearest neighbour search
- conditional insert with custom predicates
- support for custom allocators for internal nodes
- estimation for node count given a number of items
- tagging of internal nodes
- the spatial trees have almost identical interfaces
- lightweight, resulting in faster compile times compared to boost(eg. benchmark compilation: 35,3 sec vs 1,4 sec)
- C++03 support
Installation
The implementation is header only, it's only requirement is at least (C++03) support.
Usage
How to create and insert items to the trees:
spatial::QuadTree<int, Box2<int>, 2> qtree(bbox.min, bbox.max);
spatial::RTree<int, Box2<int>, 2> rtree;
const Box2<int> kBoxes[] = {...};
qtree.insert(kBoxes, kBoxes + sizeof(kBoxes) / sizeof(kBoxes[0]));
rtree.insert(kBoxes, kBoxes + sizeof(kBoxes) / sizeof(kBoxes[0]));
Box2<int> box = {{7, 3}, {14, 6}};
qtree.insert(box);
rtree.insert(box);
Conditional insert:
const decltype(rtree)::bbox_type boxToAdd = {{7, 4}, {14, 6}};
bool wasAdded =
rtree.insert(boxToAdd, [&boxToAdd](const decltype(rtree)::bbox_type &bbox) {
return !bbox.overlaps(boxToAdd);
});
How to use the indexable getter:
struct Object {
spatial::BoundingBox<int, 2> bbox;
std::string name;
};
// helps to get the bounding of the items inserted
struct Indexable {
const int *min(const Object &value) const { return value.bbox.min; }
const int *max(const Object &value) const { return value.bbox.max; }
};
spatial::QuadTree<int, Object, 2, Indexable> qtree(bbox.min, bbox.max);
qtree.insert(objects.begin(), objects.end());
spatial::RTree<int, Object, 2, 4, 2, Indexable> rtree;
rtree.insert(objects.begin(), objects.end());
Leaf and depth traversal:
spatial::RTree<int, Object, 2, 4, 2, Indexable> rtree;
// gives the spatial partioning order within the tree
for (auto it = rtree.lbegin(); it.valid(); it.next()) {
std::cout << (*it).name << "\n";
}
assert(rtree.levels() > 0);
for (auto it = rtree.dbegin(); it.valid(); it.next()) {
// traverse current children of the parent node(i.e. upper level)
for (auto nodeIt = it.child(); nodeIt.valid(); nodeIt.next()) {
std::cout << "level: " << nodeIt.level() << " " << (*nodeIt).name
<< "\n";
}
// level of the current internal/hierachical node
std::cout << "level: " << it.level() << "\n";
}
How to use the search algorithms:
Box2<int> searchBox = {{0, 0}, {8, 31}};
std::vector<Box2<int>> results;
rtree.query(spatial::intersects<2>(searchBox.min, searchBox.max), std::back_inserter(results));
rtree.query(spatial::contains<2>(searchBox.min, searchBox.max), std::back_inserter(results));
// to be used only if inserted points into the tree
rtree.query(spatial::within<2>(searchBox.min, searchBox.max), std::back_inserter(results));
// hierachical query that will break the search if a node is fully contained
rtree.hierachical_query(spatial::intersects<2>(searchBox.min, searchBox.max), std::back_inserter(results));
// neatest neighbor search
rtree.nearest(point, radius, std::back_inserter(results));
Be sure to check the test and examples folders for more detailed info.
Benchmarks
Benchmark setup is based on spatial_index_benchmark by Mateusz Loskot and Adam Wulkiewicz.
Complete set of result logs in results directory.
Results
HW: Intel(R) Core(TM) i7-4870HQ CPU @ 2.50GHz, 16 GB RAM; OS: macOS Sierra 10.12.16
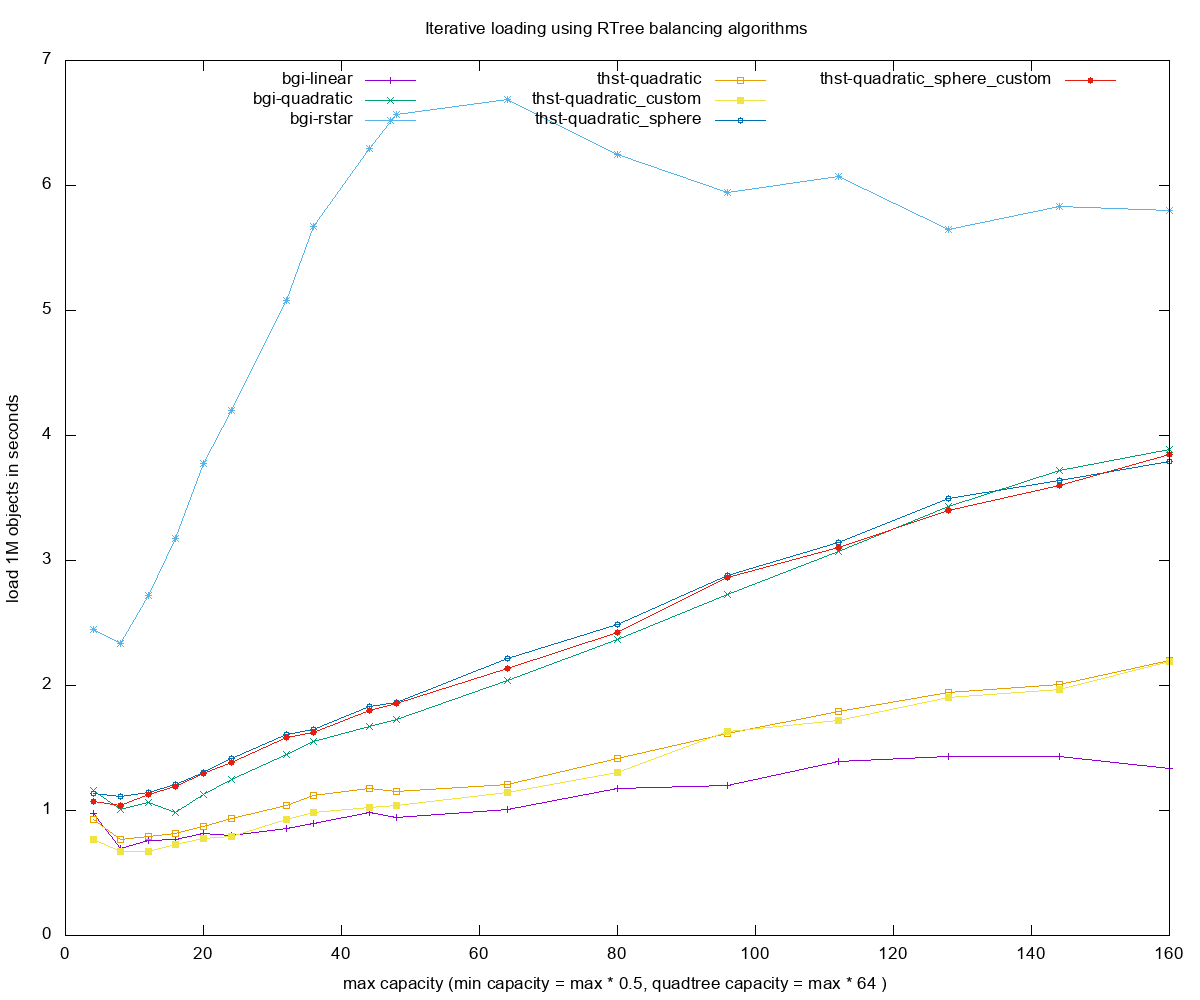
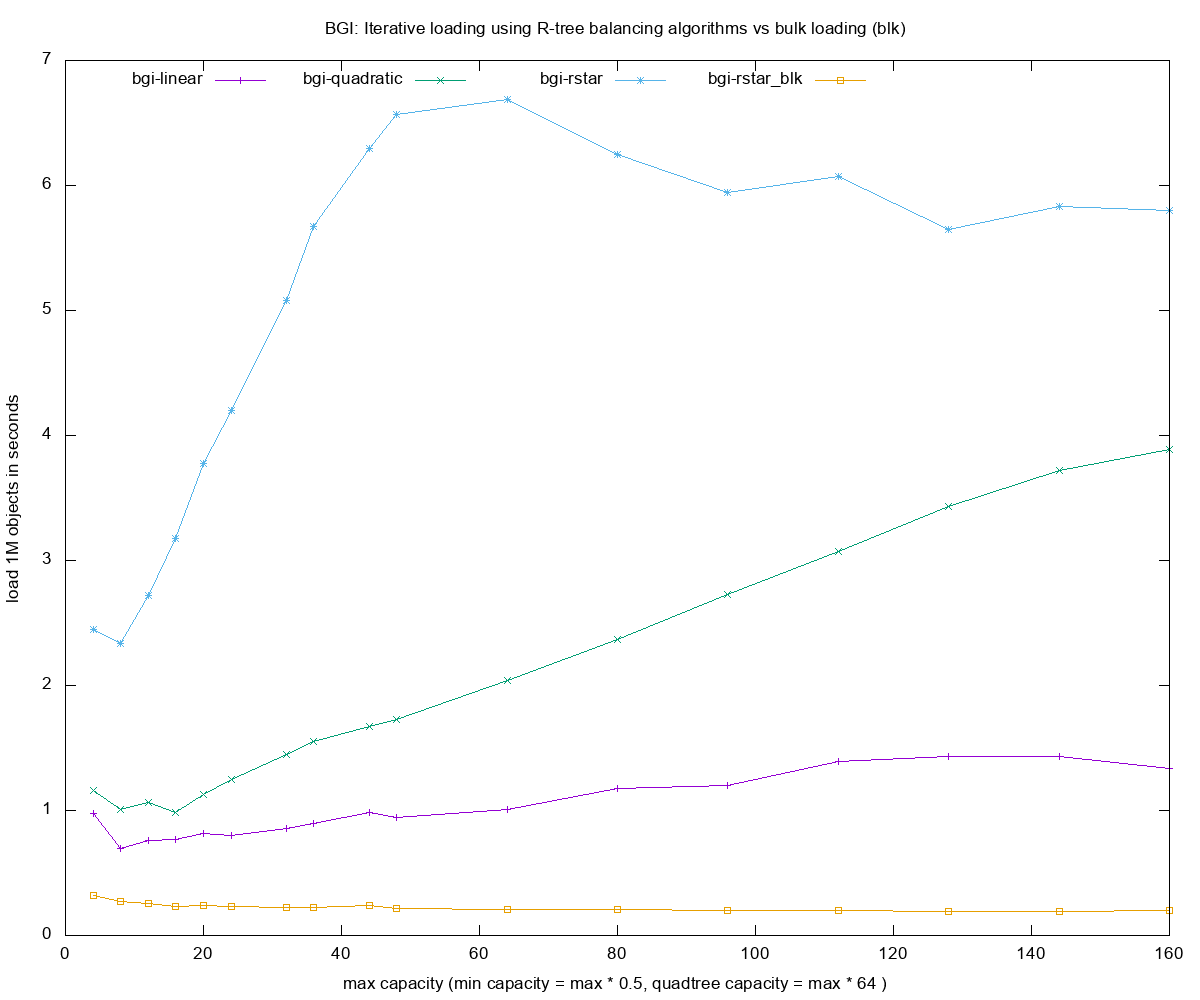
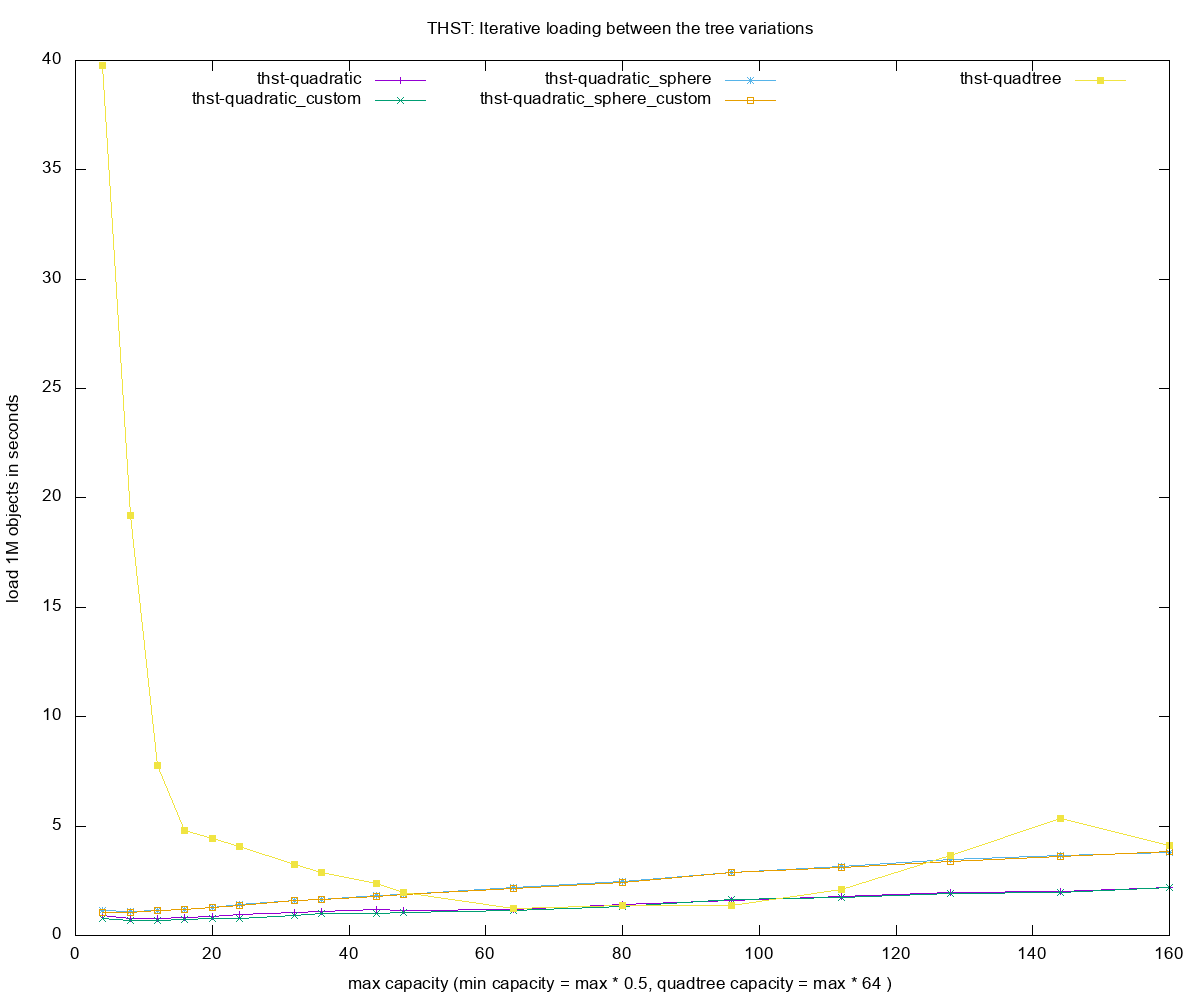
- Loading times for each of the R-tree construction methods
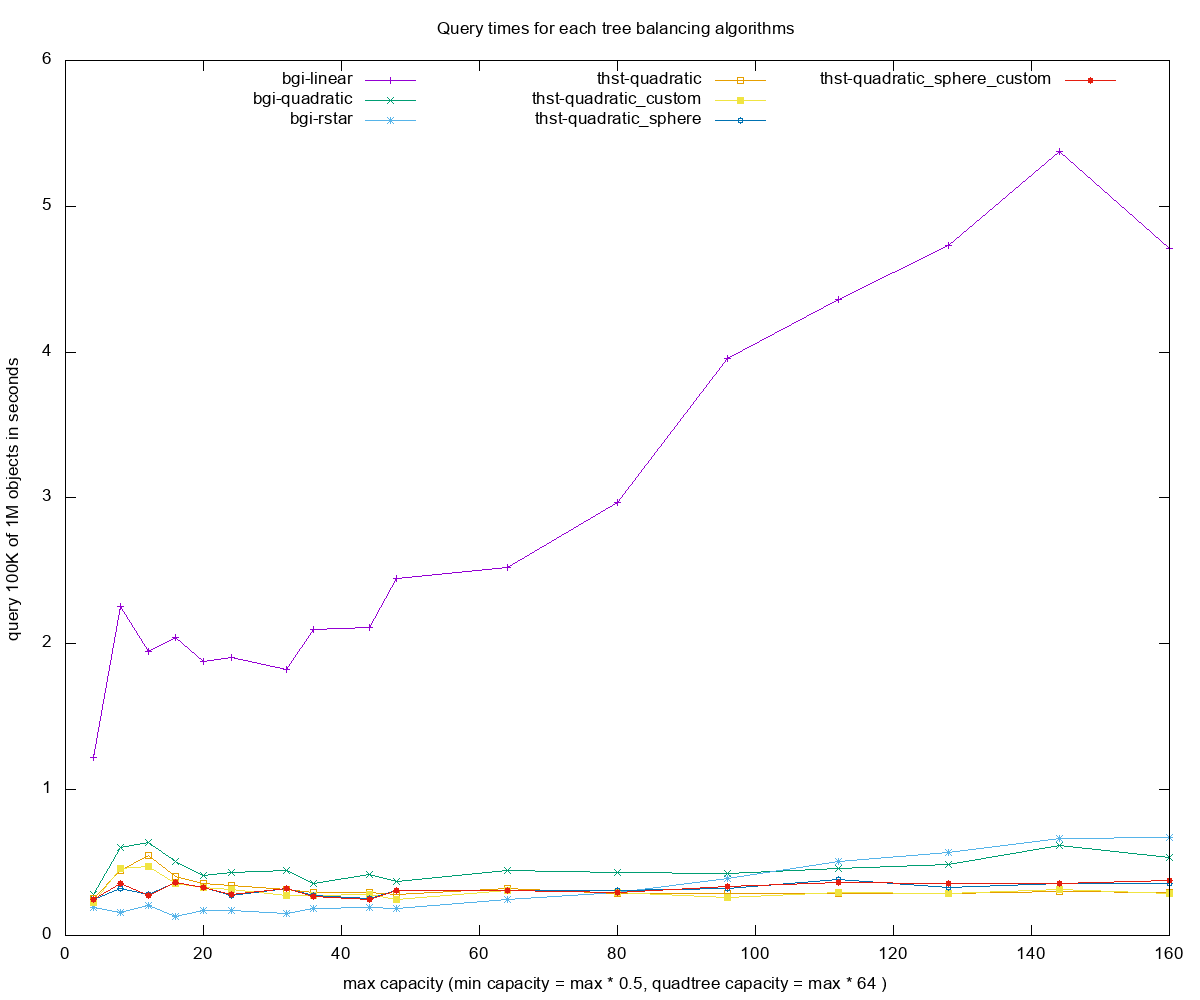
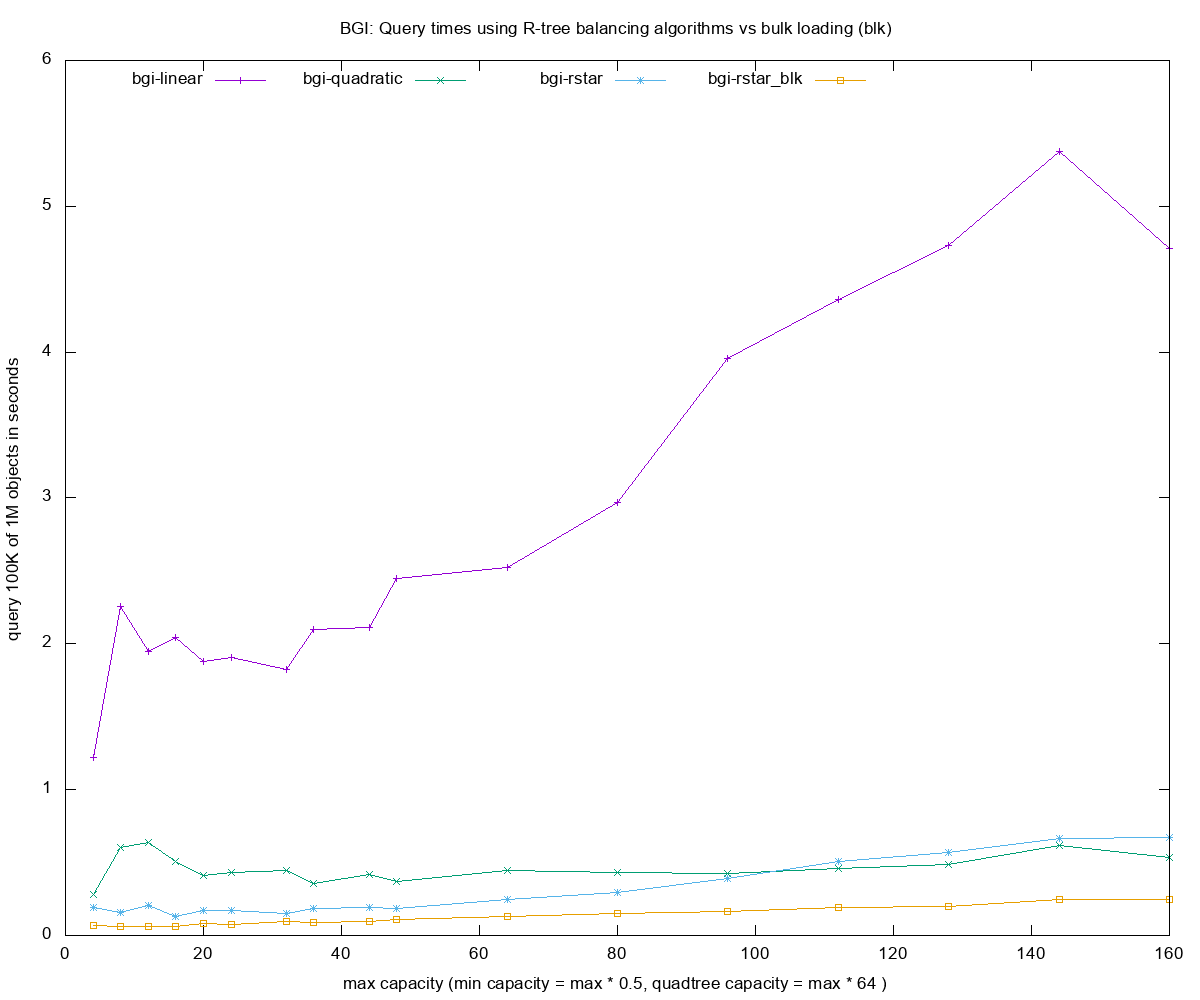
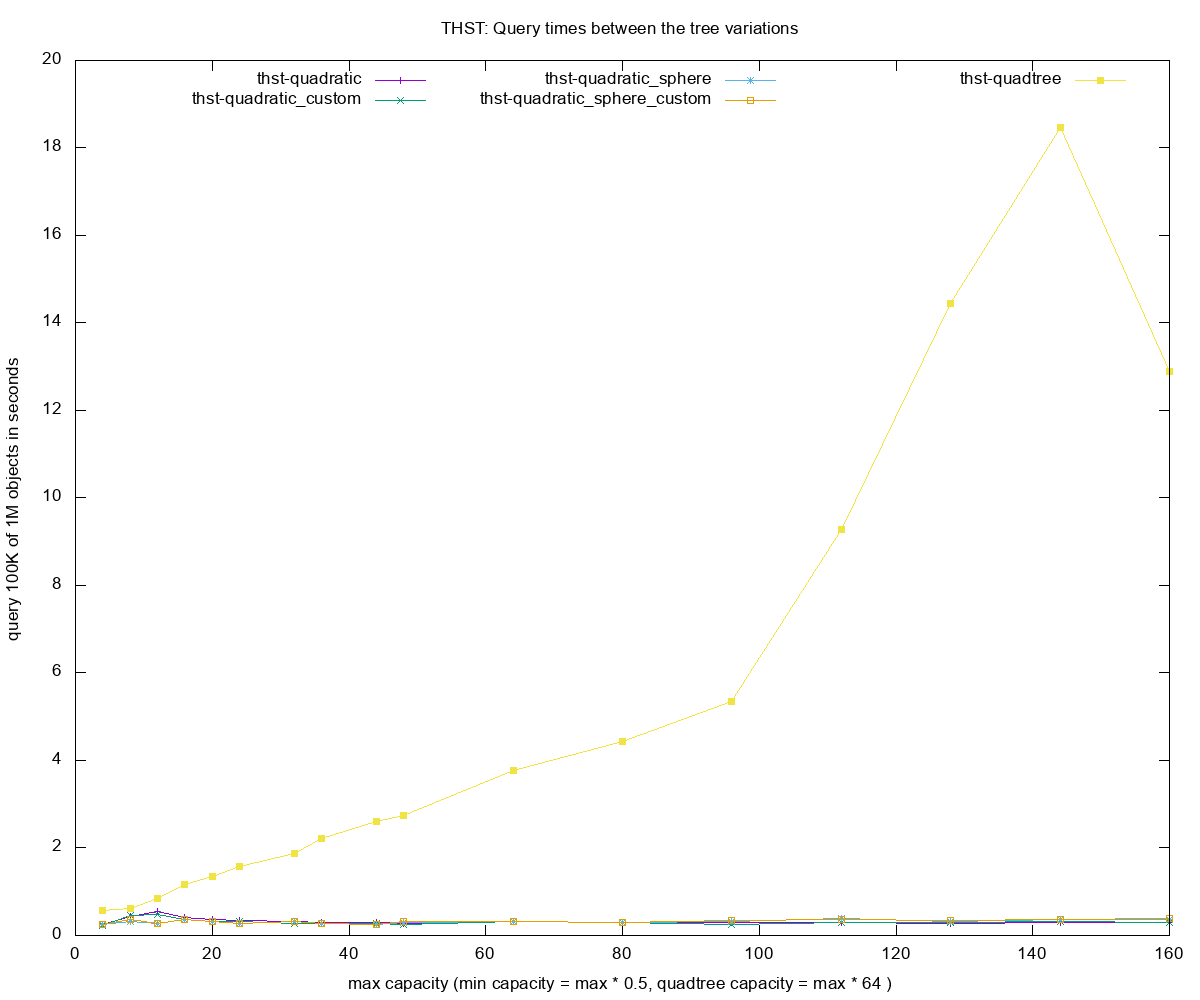
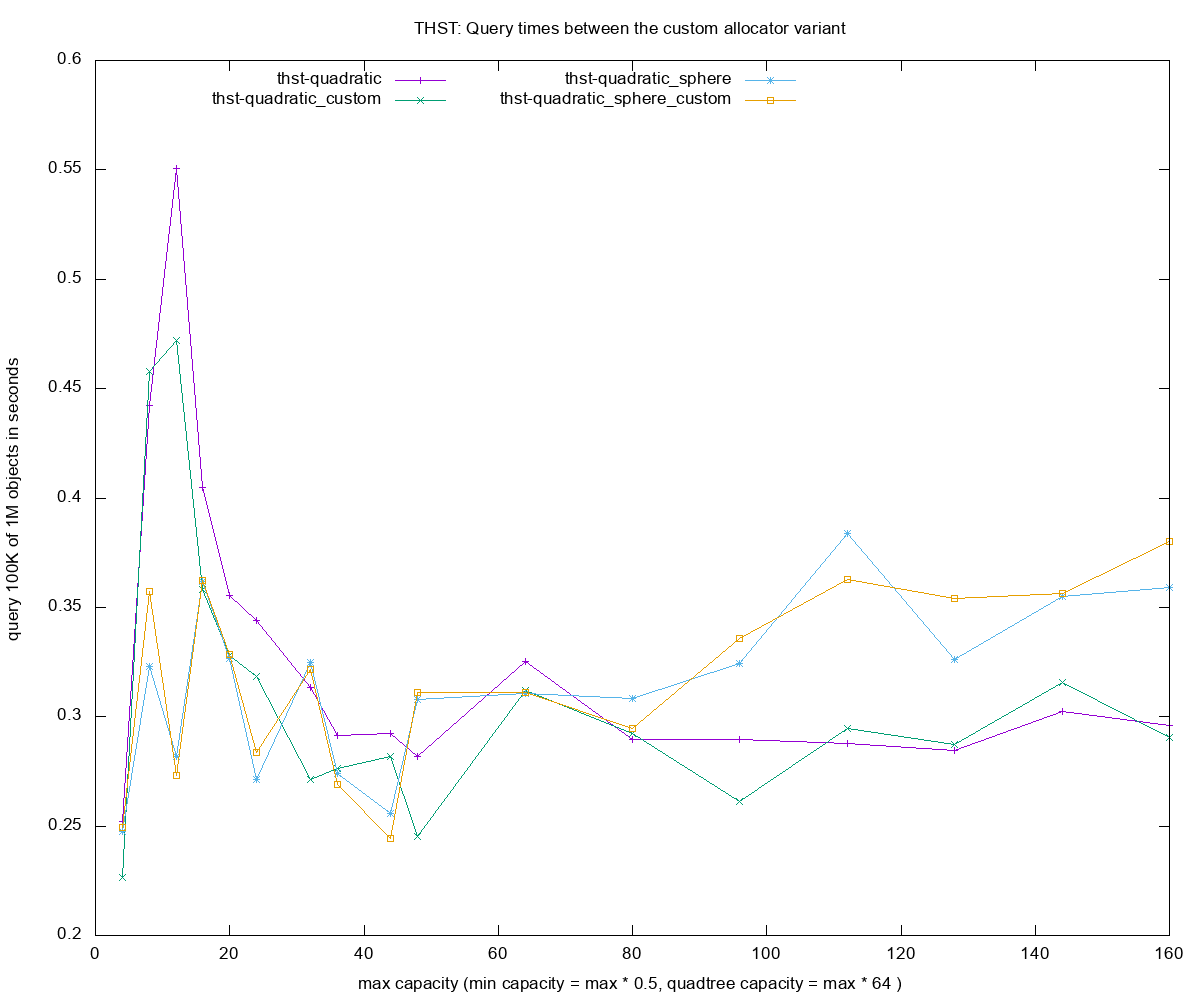
- Query times for each of the R-tree construction methods
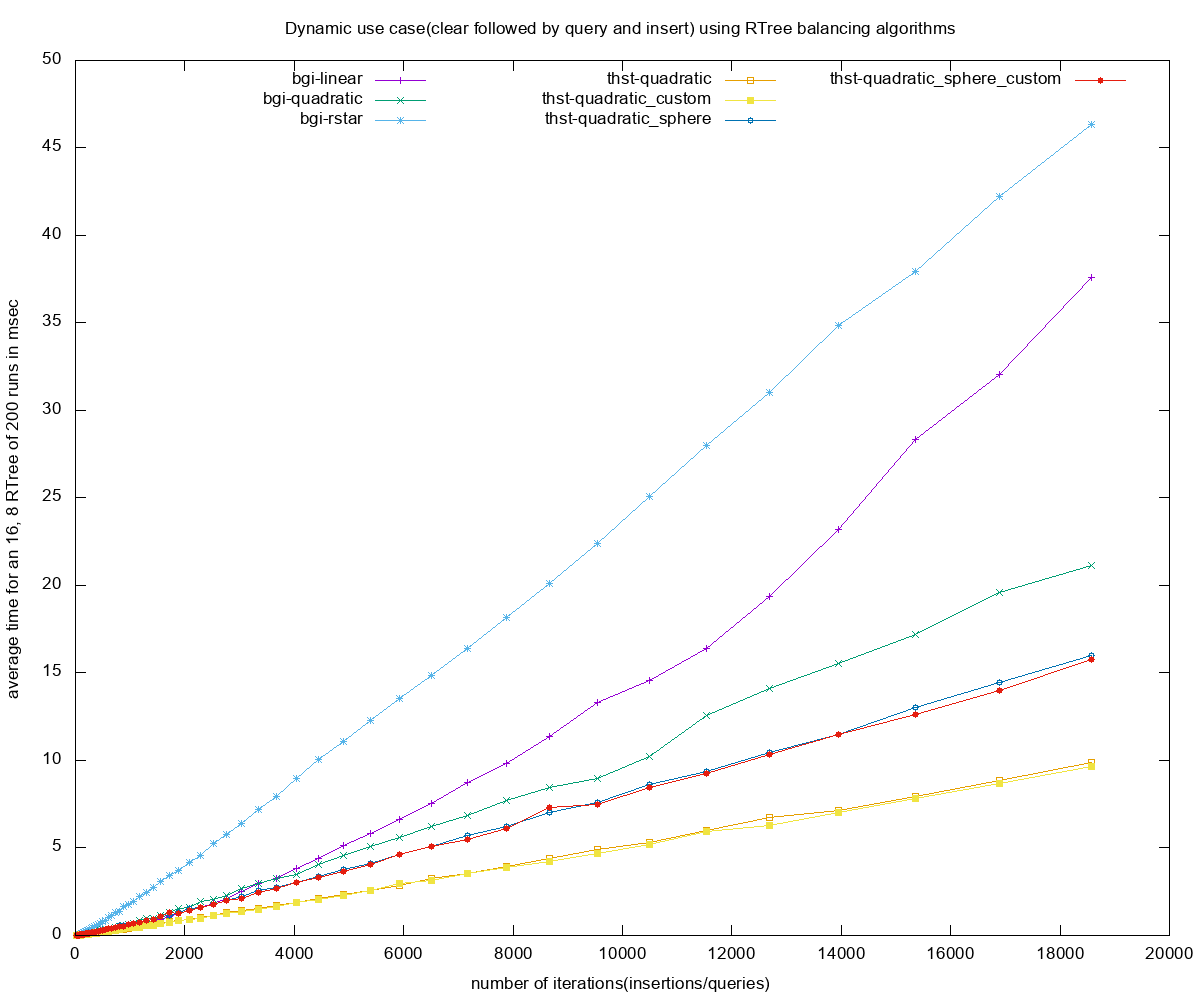
- Dynamic use case, average time for each of the R-tree construction methods
For more detailed benchmark results check the benchmark directory.
Legend
-
bgi- boost::geometry::index, compile time -
thst- thst -
ct- compile-time specification of rtree parameters -
rt(or non suffix) - Boost.Geometry-only, run-time specification of rtree parameters -
L- linear -
Q- quadratic -
QT- quadtree -
R- rstar -
itr (or no suffix)- iterative insertion method of building rtree -
blk- bulk loading method of building R-tree (custom algorithm forbgi) -
custom- custom allocator variant for thst(cache friendly, linear memory) -
sphere- sphere volume for computing the boxes's volume, better splitting but costlier - insert 1000000 - number of objects small random boxes
- query 100000 - number of instersection-based queries with random boxes 10x larger than those inserted
- dynamic 200 - number of runs composed of clear, instersection-based queries and insert with small random boxes
Future improvements
Possible improvements are:
- RTree bulk loading
- OCtree implementation
- reduced memory footprint for 1D and leaves
- support for multiple splitting heuristics
- SSE optimizations
Contributing
Based on:
- 1983 Original algorithm and test code by Antonin Guttman and Michael Stonebraker, UC Berkely
- ANCI C ported from original test code by Melinda Green
- Sphere volume fix for degeneracy problem submitted by Paul Brook
- Templated C++ port by Greg Douglas
- N-dimensional RTree implementation in C++ by nushoin (https://github.com/nushoin/RTree).
- Nearest neighbour search by Thinh Nguyen (http://andrewd.ces.clemson.edu/courses/cpsc805/references/nearest_search.pdf).
Bug reports and pull requests are welcome on GitHub at https://github.com/tuxalin/thst.
License
The code is available as open source under the terms of the MIT License.