HKUST-Aerial-Robotics / Timeoptimizer
TimeOptimizer
1.Introduction
TimeOptimizer is a tool to do re-timing (time optimization) of an arbitrary piecewise polynomial-based trajectory (no matter monomial polynomial, Bezier curve, B-spline or others). The objective of this work is to map the original parametrization variable to a new variable (time), with which the trajectory can finish as fast as possible and respect all kinodynamic limits (velocity, acceleration). For details, we refer readers to our paper.
Authors:Fei Gao and Shaojie Shen from the HUKST Aerial Robotics Group.
Disclaimer
This is a research repo, any fitness for a particular purpose is disclaimed.
Related Paper
- Optimal Time Allocation for Quadrotor Trajectory Generation, Fei Gao, William Wu, Jie Pan, Boyu Zhou and Shaojie Shen, IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), 2018, Madrid, Spain. full text
Video of this paper can be found at:
If you use this planning framework for your academic research, please cite our related paper.
@inproceedings{Fei2018IROS,
Address = {Madrid, Spain},
Author = {F. Gao and W.Wu and J. Pan and B. Zhou and S. Shen},
Booktitle = {Optimal Time Allocation for Quadrotor Trajectory Generation},
Title = {Proc. of the {IEEE/RSJ} Intl. Conf. on Intell. Robots and Syst.({IROS})},
Month = Oct,
Year = {2018}}
}
Implementation
2.Prerequisities
- Our testing environment: Ubuntu 16.04, ROS Kinetic.
- If you want to directly set waypoints in Rviz for generating the spatial trajectory, please follow 5.2. Otherwise you should follow 5.1.
- Remember to approve a license from mosek following 4.
3.Build on ROS
Clone the repository to your catkin workspace and catkin_make. For example:
cd ~/catkin_ws/src
git clone https://github.com/HKUST-Aerial-Robotics/TimeOptimizer.git
cd ../
catkin_make
source ~/catkin_ws/devel/setup.bash
4.Install Mosek
We use mosek for solving second-order cone program(SOCP). To use mosek, you should approve an academic license in here. The academic license is free and is easy to approve. Then create a folder named 'mosek' in your home directory and put your license in it. All header and library files are already included in the 'third_party' folder under this repo, so you don't need to download mosek again.
5.Usage
The time optimizer can be applied to an arbitrary type pieciwise polynomial-based trajectory, and we proovide a simple demo using minimum-jerk monomial polynomials as an example. If you have done all above configuration, you can try the simple demo in two ways
1. We provide a clean launch file which has no dependence on other packages, suppose you do not want to configure the interactive tools we provide. In this way, you can write down you the coordinates of all waypoints in the traj.json file under the root directory of this package, and the program would read it after launching:
roslaunch time_optimizer clean_demo.launch
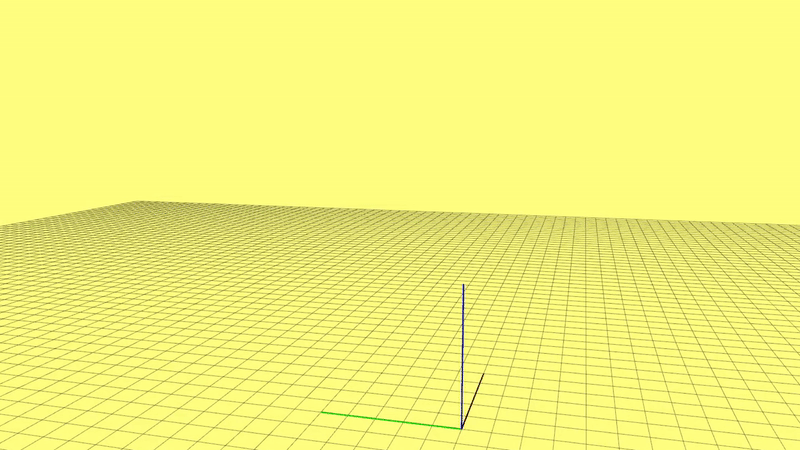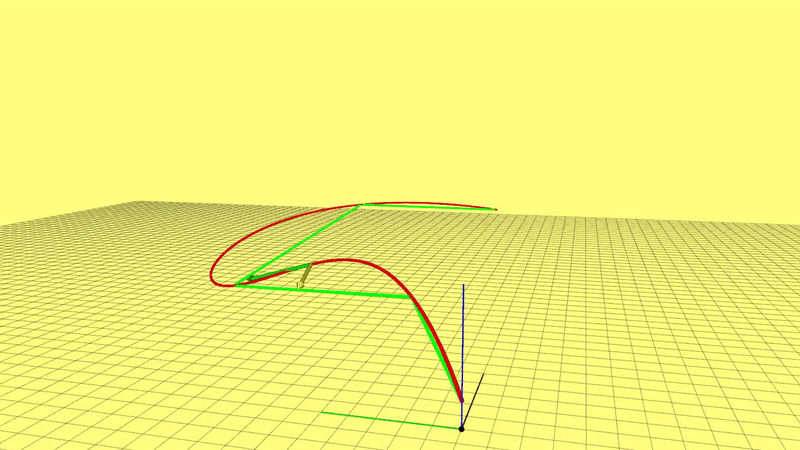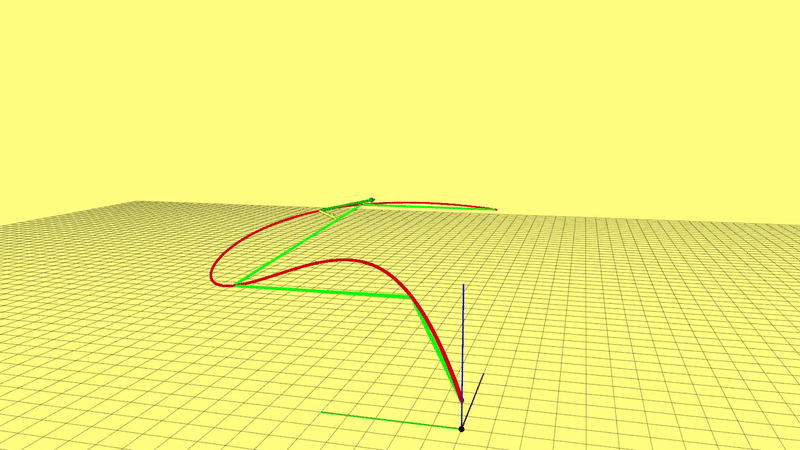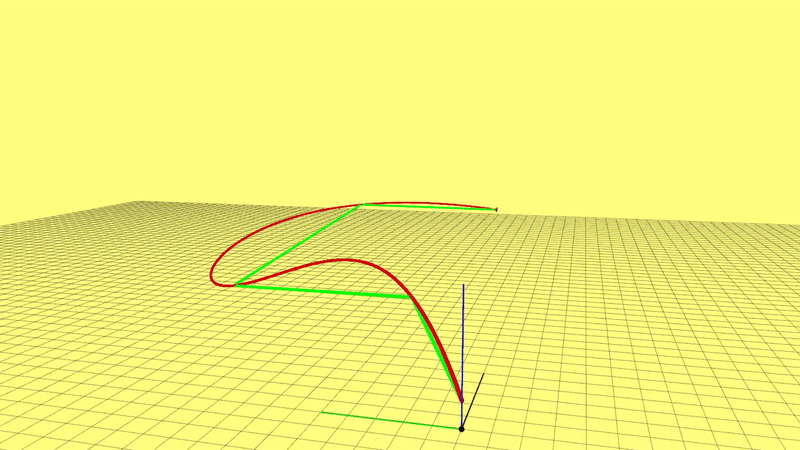
2. If you want to use the interactive tools we provide, you have to compile two additional ros-packages rviz_plugins and waypoint_generator in utils. By default these two packages will be compiled, if you want to skip them, please add a file named 'CATKIN_IGNORE' under each package's root directory.
Then run the following command:
roslaunch time_optimizer inte_demo.launch
In rviz, click 'Panels -> tools -> +' and select the plugin 'Goal3DTool'. If you have successfully compiled all packages from plan_utils, now you can see 3D Nav Goal in the tools panel.
We use 3D Nav Goal to send waypoints for the drone. To use it, click the tool (shortcut keyboard 'g' may conflict with 2D Nav Goal), then press on left mouse button on a position in rviz, click right mouse button to start to drag it slide up or down for a targeting height (don't lose left button at this time). Finally, you lose left mouse button, and a series of waypoints will be sent to the planner, done.
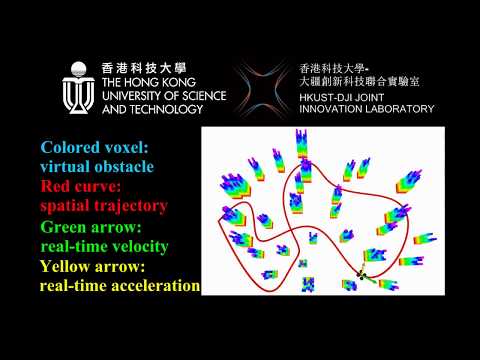
6.Visualization of Results
The entire pipeline is : setting waypoints -> generating spatial trajectory -> time optimization -> publishing commands (position, velocity, acceleration). Commands can be viewed in rviz. Then, if you want to plot all commands of the final trajectory, please run:
roscd time_optimizer
sudo chmod +x draw.py
python draw.py
8.Extension
To use the time optimizer with other kinds of spatial trajectory generator, you can follow 'demo.cpp' as an example. The simplest way is to implemente your own trajectory type as an inheritance of the class 'Trajectory' definded in 'trajectory_base.h'.
9.Acknowledgements
We use mosek for solving second-order cone program(SOCP).
10.Licence
The source code is released under GPLv3 license.
11.Notes
- The code has not been deeply tested, if you find any problems, do not hesitate to raise an issue or write an e-mail to me.