coolpup.py
.cool file pile-ups with python.
Introduction
.cool format
A versatile tool to perform pile-up analysis on Hi-C data in .cool format (https://github.com/mirnylab/cooler). And who doesn't like cool pupppies?
.cool is a modern and flexible format to store Hi-C data.
It uses HDF5 to store a sparse representation of the Hi-C data, which allows low memory requirements when dealing with high resolution datasets. Another popular format to store Hi-C data, .hic, can be converted into .cool files using hic2cool (https://github.com/4dn-dcic/hic2cool).
See for details:
Abdennur, N., and Mirny, L. (2019). Cooler: scalable storage for Hi-C data and other genomically-labeled arrays. Bioinformatics. 10.1093/bioinformatics/btz540
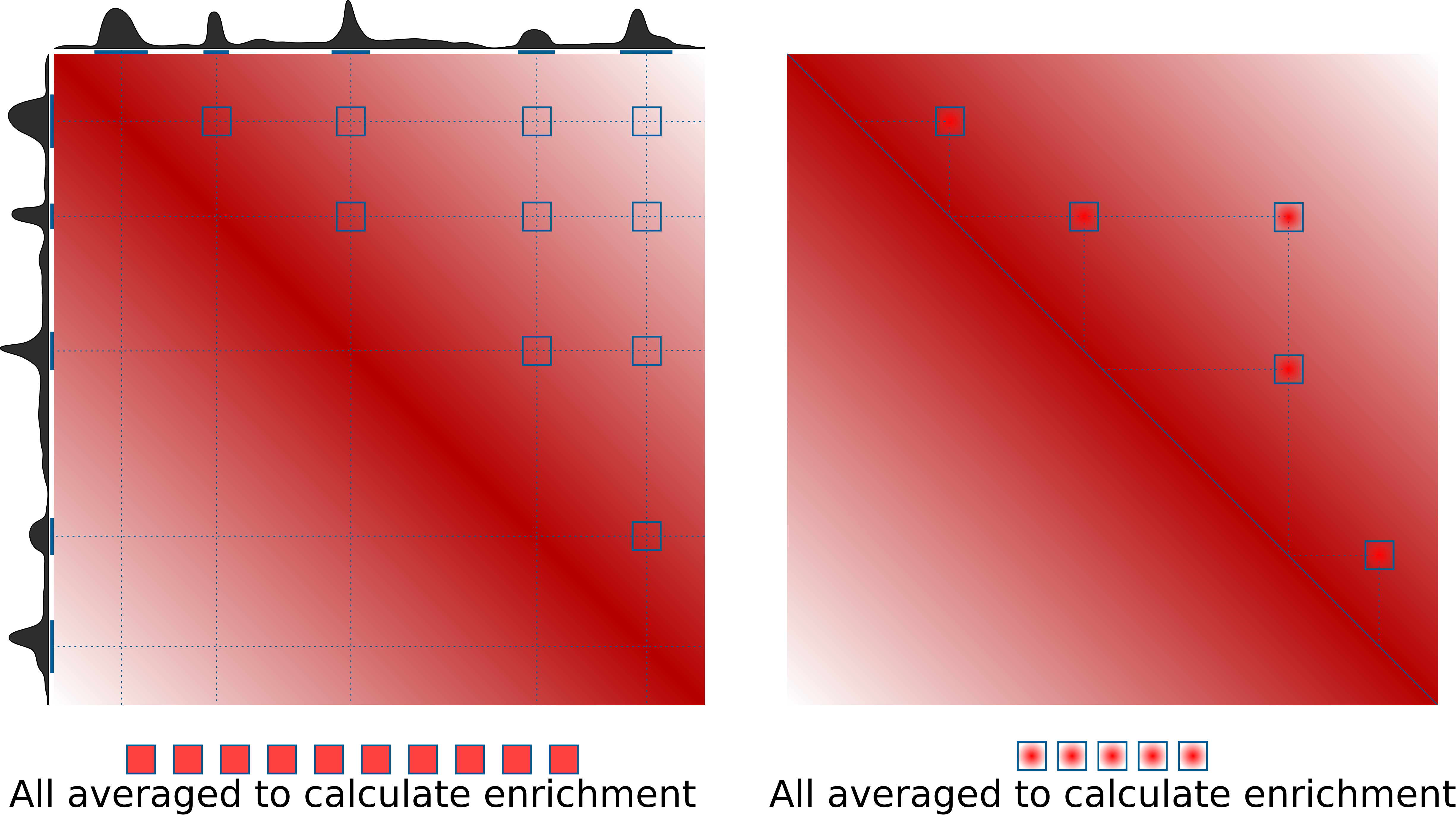
What are pileups?
This is the idea of how pileups work to check whether certain regions tend to interacts with each other:
What's not shown here is normalization to the expected values. This can be done in two ways: either using a provided file with expected values of interactions at different distances (output of cooltools compute-expected), or directly from Hi-C data by dividing the pileups over randomly shifted control regions. If neither expected normalization approach is used (just set --nshifts 0), this becomes essentially identical to the APA approach (Rao et al., 2014), which can be used for averaging strongly interacting regions, e.g. annotated loops. For weaker interactors, decay of contact probability with distance can hide any focal enrichment that could be observed otherwise.
coolpup.py is particularly well suited performance-wise for analysing huge numbers of potential interactions, since it loads whole chromosomes into memory one by one (or in parallel to speed it up) to extract small submatrices quickly. Having to read everything into memory makes it relatively slow for small numbers of loops, but performance doesn't decrease until you reach a huge number of interactions.
Getting started
Installation
All requirements apart are available from PyPI or conda.
Before installing everything you need to obtain cython using either pip or conda. Then for coolpuppy (and other dependencies) simply do:
pip install coolpuppy
or
pip install https://github.com/open2c/coolpuppy/archive/master.zip
to get the latest version from GitHub. This will make coolpup.py callable in your terminal, and importable in python as coolpuppy.
Usage
Some examples to get you started are available here: Examples
A guide walkthrough to pile-up analysis is available here (WIP): Walkthrough
Docs for the command line interface are available here: CLI docs
Currently, coolpup.py doesn't support inter-chromosomal pileups, but this is an addition that is planned for the future.
Plotting results
For flexible plotting, I suggest to use matplotlib or another library. However simple plotting capabilities are included in this package. Just run plotpup.py with desired options and list all the output files of coolpup.py you'd like to plot.
Citing coolpup.py
Ilya M Flyamer, Robert S Illingworth, Wendy A Bickmore (2020). Coolpup.py: versatile pile-up analysis of Hi-C data. Bioinformatics, 36, 10, 2980–2985.
https://academic.oup.com/bioinformatics/article/36/10/2980/5719023
doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btaa073
This tool has been used in the following publications
Please let me know if I've missed any and you'd like your paper ot be mentioned here!
McLaughlin, K., Flyamer, I.M., Thomson, J.P., Mjoseng, H.K., Shukla, R., Williamson, I., Grimes, G.R., Illingworth, R.S., Adams, I.R., Pennings, S., et al. (2019). DNA Methylation Directs Polycomb-Dependent 3D Genome Re-organization in Naive Pluripotency. Cell Reports 29, 1974-1985.e6.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2211124719313312?via%3Dihub
Boyle, S., Flyamer, I.M., Williamson, I., Sengupta, D., Bickmore, W.A., and Illingworth, R.S. (2019). A Central Role for Canonical PRC1 in Shaping the 3D Nuclear Landscape. Genes & Development 2020
http://genesdev.cshlp.org/content/early/2020/05/21/gad.336487.120.abstract
Rhodes, J.D.P., Feldmann, A., Hernández-Rodríguez, B., Díaz, N., Brown, J.M., Fursova, N.A., Blackledge, N.P., Prathapan, P., Dobrinic, P., Huseyin, M.K., et al. (2020). Cohesin Disrupts Polycomb-Dependent Chromosome Interactions in Embryonic Stem Cells. Cell Reports 30, 820-835.e10.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2211124719317140?via%3Dihub