cyring / Corefreq
Programming Languages
Projects that are alternatives of or similar to Corefreq
CoreFreq
Purpose
CoreFreq, a CPU monitoring software with BIOS like functionalities, is designed for the 64-bits Processors of architecture Intel Atom, Core2, Nehalem, SandyBridge and superiors; AMD Families from 0Fh ... up to 17h (Zen , Zen+ , Zen2), 18h (Hygon Dhyana), 19h (Zen3)
CoreFreq provides a framework to retrieve CPU data with a high degree of precision:
- Core frequencies & ratios; SpeedStep (EIST), Turbo Boost, Hyper-Threading (HTT) and Base Clock
- Performance counters including Time Stamp Counter (TSC), Unhalted Core Cycles (UCC), Unhalted Reference Cycles (URC)
- Number of instructions per cycle or second, IPS, IPC, or CPI
- CPU C-States C0 C1 C3 C6 C7 - C1E - Auto/UnDemotion of C1 C3
- DTS Temperature and Tjunction Max, Thermal Monitoring TM1 TM2 state, Vcore
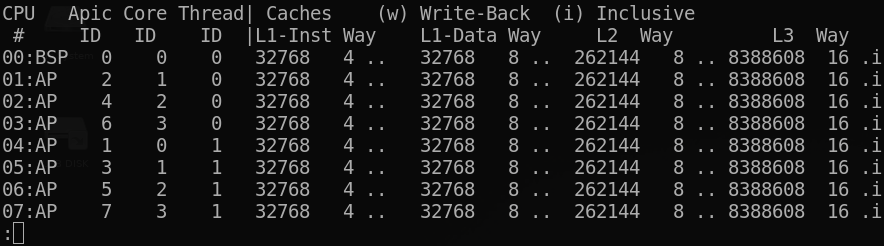
- Topology map including Caches for boostrap & application CPU
- Processor features, brand & architecture strings
- In progress: Uncore, Memory Controller channels & geometry, DIMM timings,
Stress tools, Power & Energy (RAPL, P-State, HWP, TDP), Overclocking, cpuidle & cpufreq driver, ClockSource, Mitigation Mechanisms
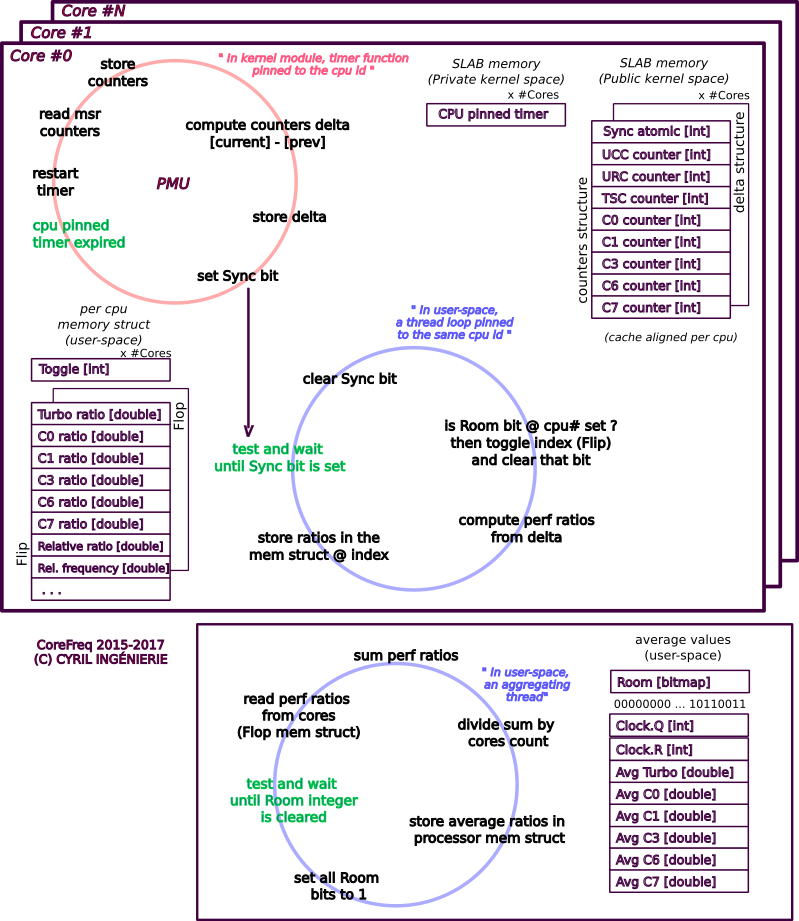
To reach this goal, CoreFreq implements a Linux Kernel module which employs the followings:
- asm code to keep as near as possible the readings of the performance counters;
- per-CPU, implements slab data memory and high-resolution timer;
- compliant with suspend / resume and CPU Hot-Plug;
- a shared memory to protect kernel from the user-space part of the software;
- atomic synchronization of threads to avoid mutexes and deadlock.
Build & Run
Prerequisites
a- Intel only: For a better accuracy, disable the Kernel NMI Watchdog
Add the below parameter in the kernel boot loader { Grub, SysLinux } ...
nmi_watchdog=0
... and build with the fixed performance counters
make MSR_CORE_PERF_UC=MSR_CORE_PERF_FIXED_CTR1 MSR_CORE_PERF_URC=MSR_CORE_PERF_FIXED_CTR2
b- AMD and Intel: Some Virtualization
VMs don't provide access to the registers that the CoreFreq driver employs :
- Fixed Performance Counters
- Model Specific Registers
- PCI Registers
However CoreFreq is making use of the virtualized performance counter :
- HV_X64_MSR_VP_RUNTIME(0x40000010)
c- Rendering
The UI renders best with an ASCII console or a Xterm with VT100 support and ANSI colors
If bold and bright colors are not rendered then use the following terminal options:
Ubuntu Terminal
In the Preferences - Colors tab, select Show bold text in bright colors
alacritty terminal
Uncomment and set draw_bold_text_with_bright_colors: true in <config-file>
Dependencies
- The Linux Kernel with a minimum version 3.3
- The GNU C Library
Build
- Software needed:
- GNU C Compiler with GNU extensions
- GNU Make tool
- Linux Kernel Header files to build modules
- Mandatory :
CONFIG_MODULES, CONFIG_SMP, CONFIG_X86_MSR - Optionally:
CONFIG_HOTPLUG_CPU, CONFIG_CPU_IDLE, CONFIG_CPU_FREQ, CONFIG_PM_SLEEP, CONFIG_DMI, CONFIG_XEN, CONFIG_AMD_NB, CONFIG_HAVE_PERF_EVENTS, CONFIG_SCHED_MUQSS, CONFIG_SCHED_BMQ, CONFIG_SCHED_PDS
- Mandatory :
-
Clone the source code into a working directory.
git clone https://github.com/cyring/CoreFreq.git -
Build the programs.
cd CoreFreq
make
cc -Wall -pthread -c corefreqd.c -o corefreqd.o
cc -Wall -c corefreqm.c -o corefreqm.o
cc corefreqd.c corefreqm.c -o corefreqd -lpthread -lm -lrt
cc -Wall -c corefreq-cli.c -o corefreq-cli.o
cc -Wall -c corefreq-ui.c -o corefreq-ui.o
cc corefreq-cli.c corefreq-ui.c -o corefreq-cli -lm -lrt
make -C /lib/modules/x.y.z/build M=/workdir/CoreFreq modules
make[1]: Entering directory '/usr/lib/modules/x.y.z/build'
CC [M] /workdir/CoreFreq/corefreqk.o
Building modules, stage 2.
MODPOST 1 modules
CC /workdir/CoreFreq/corefreqk.mod.o
LD [M] /workdir/CoreFreq/corefreqk.ko
make[1]: Leaving directory '/usr/lib/modules/x.y.z/build'
- (Optionally) Sign the driver
If module signature verification is enabled into Kernel, you will have to sign the
corefreqk.kodriver.
- See module-signing.rst from the Kernel documentation
- See the Gentoo Wiki
Install
Manual
- Copying CoreFreq into the binaries directory
make install
Distribution package
- Although CoreFreq is released in the ArchLinux AUR ; other sources of distribution may require to reload the systemd daemons:
systemctl daemon-reload
Start
- When built from source code:
- Load the kernel module, from current directory, as root.
insmod corefreqk.ko - Start the daemon, as root.
corefreqd - Start the client, as a user (in another terminal or console).
corefreq-cli
- When manually installed or from a distribution package:
- Load the kernel module, as root.
modprobe corefreqk - Start the daemon, as root.
systemctl start corefreqd - Start the client, as a user.
corefreq-cli
Stop
-
Press Ctrl+x or Ctrl+c to stop the client.
-
Press Ctrl+c to stop the daemon (in foreground) or kill its background job.
-
Unload the kernel module
rmmod corefreqk.ko
Try
Download the CoreFreq Live CD from the Wiki

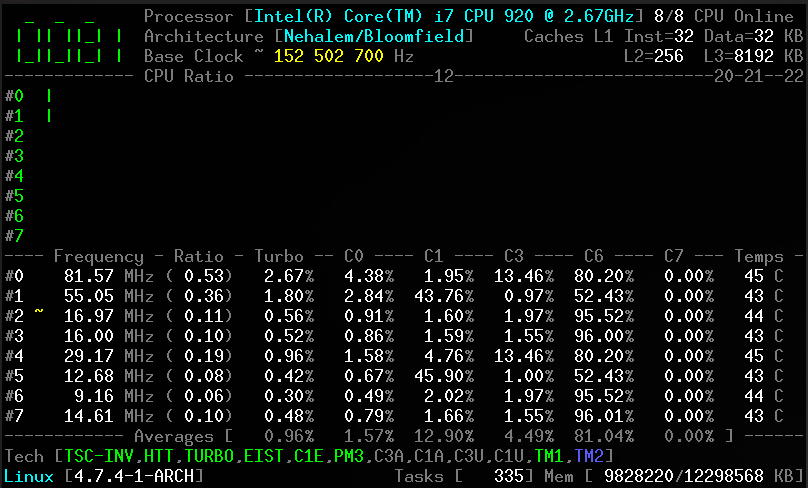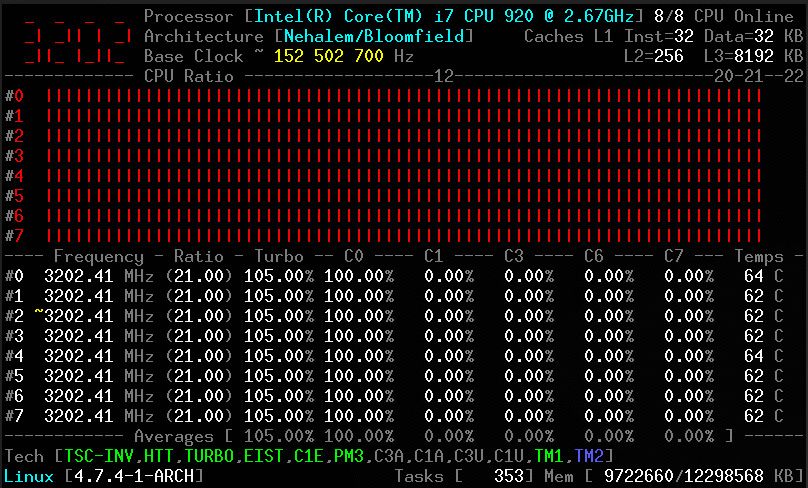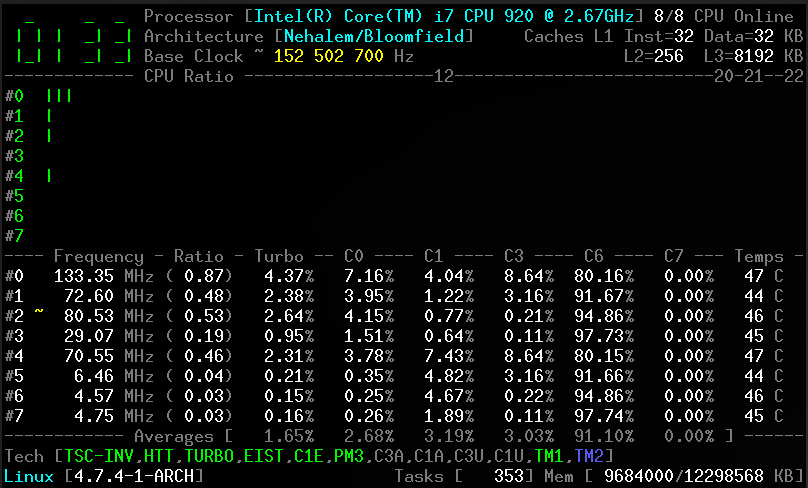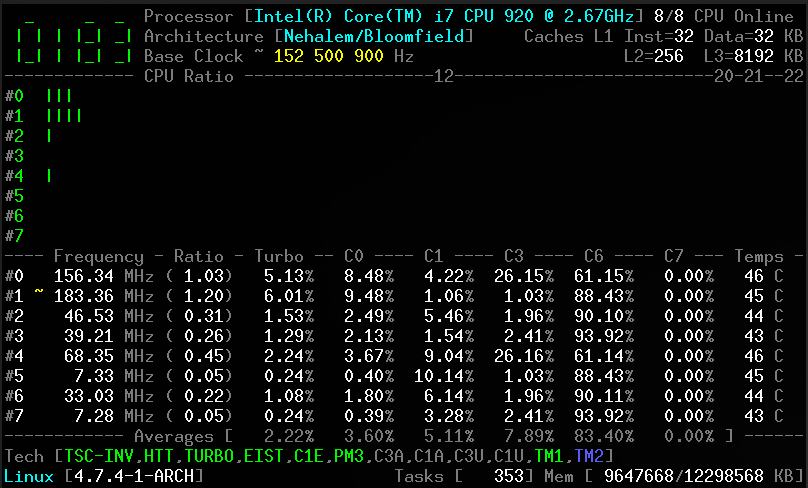
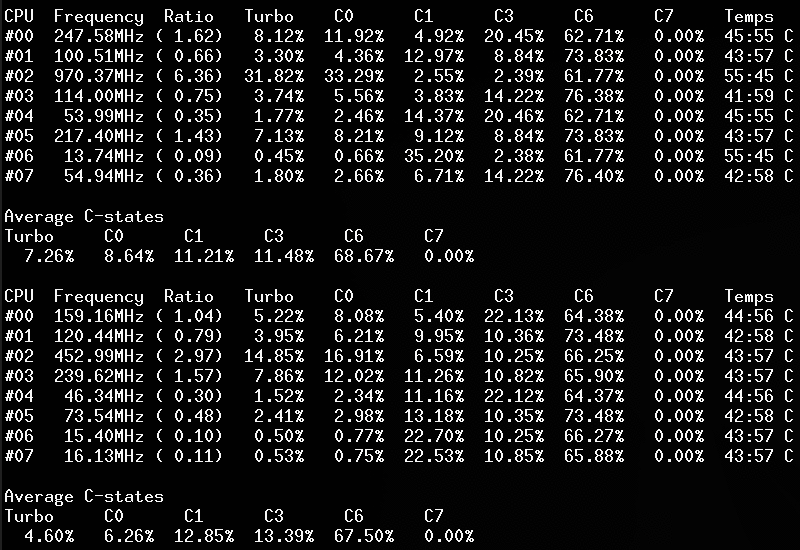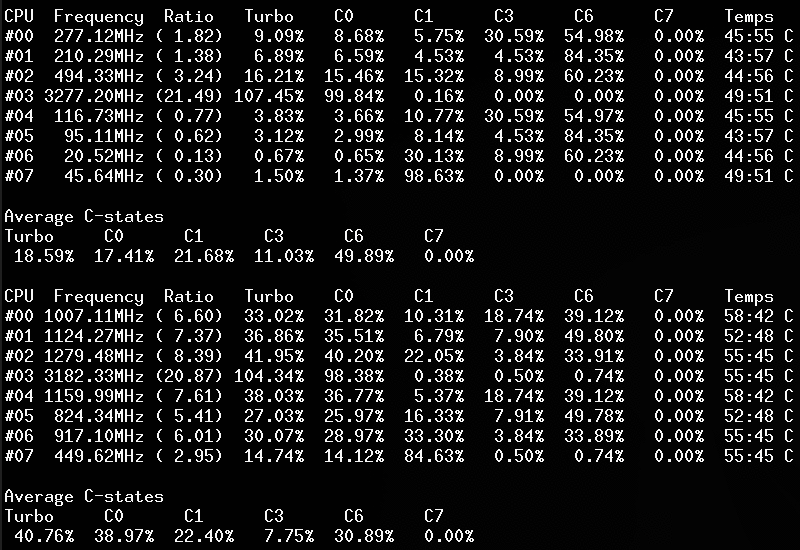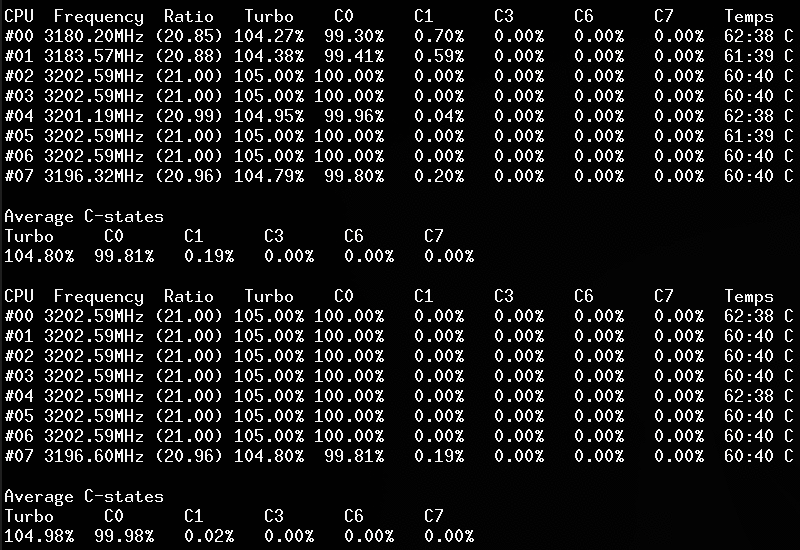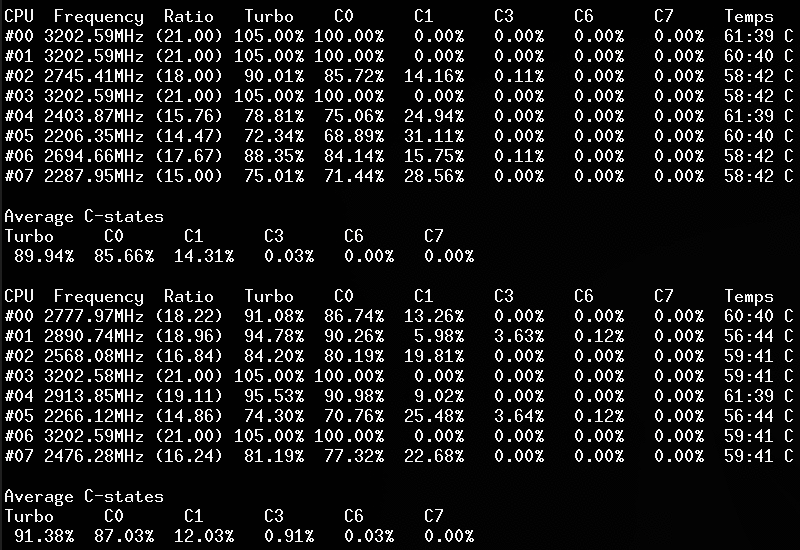
Screenshots
Linux kernel module
Use lsmod, dmesg or journalctl -k to check if the module is started:
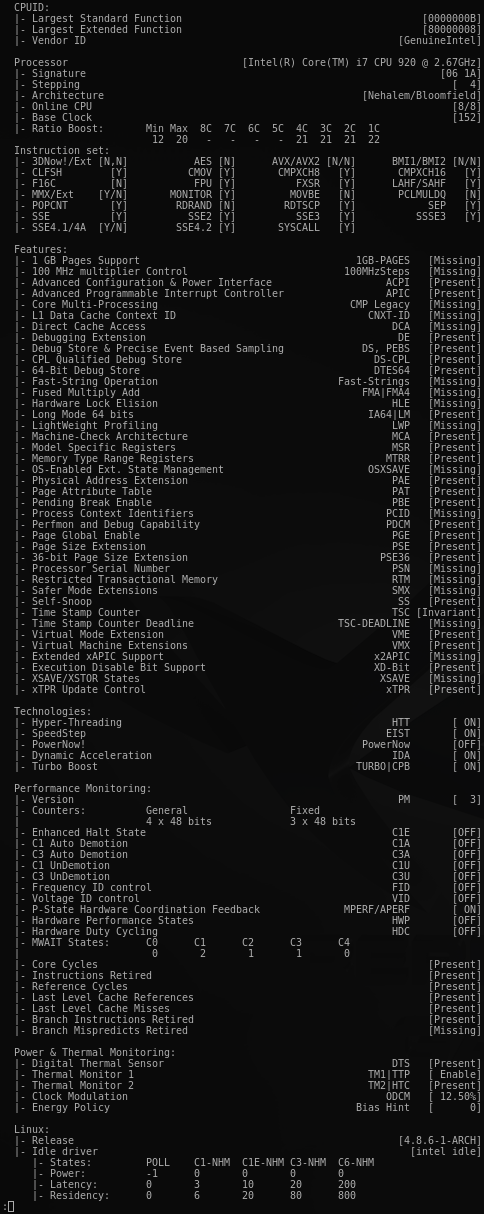
CoreFreq: Processor [06_1A] Architecture [Nehalem/Bloomfield] CPU [8/8]
Daemon
CoreFreq Daemon. Copyright (C) 2015-2021 CYRIL INGENIERIE
Processor [Intel(R) Core(TM) i7 CPU 920 @ 2.67GHz]
Architecture [Nehalem/Bloomfield] 8/8 CPU Online.
Client
Without arguments, the corefreq-cli program displays Top Monitoring

Remark: Drawing will stall if the terminal width is lower than 80 columns, or its height is less than required.
-
With the option '-i' corefreq-cli traces the number of instructions per second / cycle
CPU IPS IPC CPI
#00 0.000579/s 0.059728/c 16.742698/i
#01 0.000334/s 0.150569/c 6.641471/i
#02 0.000598/s 0.161326/c 6.198641/i
#03 0.000294/s 0.233535/c 4.282013/i
#04 0.000240/s 0.042931/c 23.293141/i
#05 0.000284/s 0.158661/c 6.302765/i
#06 0.000128/s 0.128031/c 7.810631/i
#07 0.000088/s 0.150406/c 6.648674/i
- Use the option '-s' to show the Processor information (BSP)
ArchLinux
corefreq-git can be installed from the Arch User Repository.
Debian, Ubuntu
- Installing the DKMS package will pull the Kernel development packages
apt-get install dkms - Or, install selectively the development packages prerequisites.
apt-get install libpthread-stubs0-dev
Red Hat, CentOS
- Development packages prerequisites.
yum install kernel-devel
yum group install "Development Tools"
Q&A
-
Q: How many CPUs are supported by CoreFreq ?
A: Up to 1024 CPUs can be built using the
makeCORE_COUNToption. 256 as a default. -
Q: Turbo Technology is activated however CPUs don't reach those frequencies ?
-
Q: The CPU ratio does not go above its minimum value ?
-
Q: The UI shows erratic counters values !
A: In the kernel boot command argument line, disable the NMI Watchdog
nmi_watchdog=0 -
Q: The Processor does not enter the C-States ?
A1: Check if at least one Idle driver is running.
Accordingly to the Processor specs, provide a max_cstate value in the kernel argument as below.
intel_idle.max_cstate=valueA2: CoreFreq can also register itself as a cpuidle driver.
This time, any idle driver will have to be blacklisted in the kernel command line; such as:
modprobe.blacklist=intel_cstate idle=halt intel_idle.max_cstate=0
Start the CoreFreq driver with theRegister_CPU_Idleparameter:
insmod corefreqk.ko Register_CPU_Idle=1 -
Q: The CoreFreq UI refreshes itself slowly, with a delay after the actual CPUs usage ?
A: The sampling time to read the counters can be reduced or increased using a CoreFreq module argument:
insmod corefreqk.ko SleepInterval=value
where<value>is supplied in milliseconds between a minimum of 100 ms and a maximum of 4500 ms. 1000 ms is the default value. -
Q: The base clock reports a wrong frequency value ?
A: CoreFreq uses various algorithms to estimate the base clock.
- The delta of two TimeStamp counters during a defined interval
- The value provided in the Processor brand string divided by the maximum ratio (without Turbo)
- A static value advertised by the manufacturer specs.
- The MSR_FSB_FREQ bits provided with the Core, Core2 and Atom architectures.
The CoreFreq module can be started as follow to ignore the first algorithm (frequency estimation):
insmod corefreqk.ko AutoClock=0Remark: algorithms # 2, 3 and 4 will not return any under/over-clock frequency.
-
Q: The CPU temperature is wrong ?
A: CoreFreq employs two MSR registers to calculate the temperature.
MSR_IA32_TEMPERATURE_TARGET - MSR_IA32_THERM_STATUS [DTS]Remark: if the MSR_IA32_TEMPERATURE_TARGET is not provided by the Processor, a default value of 100 degree Celsius is considered as a target.
-
Q: The menu option "Memory Controller" does not open any window ?
A: Although Uncore and IMC features are under development, they can be activated with the Experimental driver argument:
insmod corefreqk.ko Experimental=1 -
Q: The Instructions and PMC0 counters are stuck to zero ?
-
Q: The Daemon crashes whenever its stress tools are executing !
A: The
PCEbit of control registerCR4allows RDPMC in ring3
echo "2" > /sys/devices/cpu/rdpmc
or using systemd, create file/etc/tmpfiles.d/boot.confand add line:
w /sys/devices/cpu/rdpmc - - - - 2Next, load the driver with the
RDPMC_Enableargument to override theCR4register:
insmod corefreqk.ko RDPMC_Enable=1 -
Q: How to solely control the P-States or the HWP Performance States ?
A1: Without the Kernel
cpufreqframework (akaCONFIG_CPU_FREQ), CoreFreq will take the full control over P-States.
This allow the User to select a capped frequency from the UI, either per Core, either for the whole Processor.A2: With
cpufreqbuilt into Kernel, allow CoreFreq to register as a cpufreq driver.
In the Kernel boot command line, two ways:
-
disable
cpufreqwith the Kernel parameter
cpufreq.off=1 -
blacklist any P-state driver; such as:
modprobe.blacklist=acpi_cpufreq,pcc_cpufreq intel_pstate=disable -
load the CoreFreq driver with its
Register_CPU_Freqparameter:
insmod corefreqk.ko Register_CPU_Freq=1
-
Q: The CPU freezes or the System crashes.
A1: Changing the
Maxratio frequency (aka P0 P-State) makes the Kernel TSC clock source unstable.- Boot the Kernel with these command line parameters
notsc nowatchdog - Optionally, build the CoreFreq driver with its
udelay()TSC implementation
make DELAY_TSC=1 - Allow CoreFreq to register a new TSC clock source using driver arguments:
insmod corefreqk.ko TurboBoost_Enable=0 Register_ClockSource=1 - Switch the current system clock source to
corefreq
echo "corefreq" > /sys/devices/system/clocksource/clocksource0/current_clocksource
A2:
[AMD][Zen]CCD temperatures:
CoreFreq driver can be forced to use the Kernel functionamd_smn_read()
make LEGACY=2
Howeveramd_smn_read()serializes the SMU access through a mutex.
CoreFreq CPU monitoring loops are executed in an interrupt context where any blocking call like Mutex will freeze the kernel.
As a recommendation, don't use this option and make sure no other SMU driver is running.A3: This Processor is not or partially implemented in CoreFreq.
Please open an issue in the CPU support Wiki page. - Boot the Kernel with these command line parameters
-
Q: No voltage is showing up with Nehalem or Westmere processors ?
A: Build CoreFreq as below if one of those chips is present:
make HWM_CHIPSET=W83627
or
make HWM_CHIPSET=IT8720 -
Q:
[AMD][Zen]How to read the idle states ?A: As a workarround to the missing documentation of the hardware counters, CoreFreq implements virtual counters based on the TSC
Those VPMC are estimated each time the Kernel is entering an idle state level.
The prerequisities are:- Boot the Kernel without its idle drivers and no
TSCdefault clock source set
modprobe.blacklist=acpi_cpufreq idle=halt tsc=unstable - Build CoreFreq with its
TSCimplementation
make DELAY_TSC=1 - Load and register the CoreFreq kernel module as the system handler
insmod corefreqk.ko Register_ClockSource=1 Register_Governor=1 Register_CPU_Freq=1 Register_CPU_Idle=1 Idle_Route=1 - Define CoreFreq as the System clock source
echo "corefreq" > /sys/devices/system/clocksource/clocksource0/current_clocksource - Start the Daemon then the Client

- Boot the Kernel without its idle drivers and no
-
Q: What are the build options for CoreFreq ?
A: Enter
make helpto display them:
o---------------------------------------------------------------o
| make [all] [clean] [info] [help] [install] [module-install] |
| |
| CC=<COMPILER> |
| where <COMPILER> is cc, gcc [clang partial support] |
| |
| WARNING=<ARG> |
| where default argument is -Wall |
| |
| KERNELDIR=<PATH> |
| where <PATH> is the Kernel source directory |
| |
| CORE_COUNT=<N> |
| where <N> is 64, 128, 256, 512 or 1024 builtin CPU |
| |
| LEGACY=<L> |
| where level <L> is 1 or 2 |
| 1: assembly level restriction such as CMPXCHG16 |
| 2: kernel level restriction like amd_smn_read() |
| |
| UBENCH=<N> |
| where <N> is 0 to disable or 1 to enable micro-benchmark |
| |
| TASK_ORDER=<N> |
| where <N> is the memory page unit of kernel allocation |
| |
| FEAT_DBG=<N> |
| where <N> is 0 or 1 for FEATURE DEBUG level |
| |
| DELAY_TSC=<N> |
| where <N> is 1 to build a TSC implementation of udelay() |
| |
| OPTIM_LVL=<N> |
| where <N> is 0, 1, 2 or 3 of the OPTIMIZATION level |
| |
| MAX_FREQ_HZ=<freq> |
| where <freq> is at least 4850000000 Hz |
| |
| HWM_CHIPSET=<chipset> |
| where <chipset> is W83627 or IT8720 or COMPATIBLE |
| |
| Performance Counters: |
| ------------------------------------------------------- |
| | MSR_CORE_PERF_UCC | MSR_CORE_PERF_URC | |
| |----------- REG -----------|----------- REG -----------| |
| | MSR_IA32_APERF | MSR_IA32_MPERF | |
| | MSR_CORE_PERF_FIXED_CTR1 | MSR_CORE_PERF_FIXED_CTR2 | |
| | MSR_PPERF | MSR_PPERF | |
| | MSR_AMD_F17H_APERF | MSR_AMD_F17H_MPERF | |
| ------------------------------------------------------- |
| |
| User Interface Layout: |
| NO_HEADER=<F> NO_FOOTER=<F> NO_UPPER=<F> NO_LOWER=<F> |
| when <F> is 1 don't build and display this area part |
| |
| Example: |
| make CC=gcc OPTIM_LVL=3 FEAT_DBG=1 |
| MSR_CORE_PERF_UCC=MSR_CORE_PERF_FIXED_CTR1 |
| MSR_CORE_PERF_URC=MSR_CORE_PERF_FIXED_CTR2 |
| HWM_CHIPSET=W83627 MAX_FREQ_HZ=5350000000 |
| CORE_COUNT=1024 NO_FOOTER=1 NO_UPPER=1 |
| clean all |
o---------------------------------------------------------------o
-
Q: What are the parameters of the CoreFreq driver ?
A: Use the
modinfocommand to list them:
$ modinfo corefreqk.ko
parm: ArchID:Force an architecture (ID) (int)
parm: AutoClock:Estimate Clock Frequency 0:Spec; 1:Once; 2:Auto (int)
parm: SleepInterval:Timer interval (ms) (uint)
parm: TickInterval:System requested interval (ms) (uint)
parm: Experimental:Enable features under development (int)
parm: Target_Ratio_Unlock:1:Target Ratio Unlock; 0:Lock (short)
parm: Clock_Ratio_Unlock:1:MinRatio; 2:MaxRatio; 3:Both Unlock (short)
parm: Turbo_Ratio_Unlock:1:Turbo Ratio Unlock; 0:Lock (short)
parm: Uncore_Ratio_Unlock:1:Uncore Ratio Unlock; 0:Lock (short)
parm: ServiceProcessor:Select a CPU to run services with (int)
parm: RDPMC_Enable:Enable RDPMC bit in CR4 register (ushort)
parm: NMI_Disable:Disable the NMI Handler (ushort)
parm: Override_SubCstate:Override Sub C-States (array of ushort)
parm: PkgCStateLimit:Package C-State Limit (short)
parm: IOMWAIT_Enable:I/O MWAIT Redirection Enable (short)
parm: CStateIORedir:Power Mgmt IO Redirection C-State (short)
parm: L1_HW_PREFETCH_Disable:Disable L1 HW Prefetcher (short)
parm: L1_HW_IP_PREFETCH_Disable:Disable L1 HW IP Prefetcher (short)
parm: L2_HW_PREFETCH_Disable:Disable L2 HW Prefetcher (short)
parm: L2_HW_CL_PREFETCH_Disable:Disable L2 HW CL Prefetcher (short)
parm: SpeedStep_Enable:Enable SpeedStep (short)
parm: C1E_Enable:Enable SpeedStep C1E (short)
parm: TurboBoost_Enable:Enable Turbo Boost (short)
parm: C3A_Enable:Enable C3 Auto Demotion (short)
parm: C1A_Enable:Enable C3 Auto Demotion (short)
parm: C3U_Enable:Enable C3 UnDemotion (short)
parm: C1U_Enable:Enable C1 UnDemotion (short)
parm: CC6_Enable:Enable Core C6 State (short)
parm: PC6_Enable:Enable Package C6 State (short)
parm: ODCM_Enable:Enable On-Demand Clock Modulation (short)
parm: ODCM_DutyCycle:ODCM DutyCycle [0-7] | [0-14] (short)
parm: PowerMGMT_Unlock:Unlock Power Management (short)
parm: PowerPolicy:Power Policy Preference [0-15] (short)
parm: PState_FID:P-State Frequency Id (int)
parm: PState_VID:P-State Voltage Id (int)
parm: HWP_Enable:Hardware-Controlled Performance States (short)
parm: HWP_EPP:Energy Performance Preference (short)
parm: HDC_Enable:Hardware Duty Cycling (short)
parm: R2H_Disable:Disable Race to Halt (short)
parm: Clear_Events:Clear Thermal and Power Events (uint)
parm: ThermalScope:[0:None; 1:SMT; 2:Core; 3:Package] (int)
parm: VoltageScope:[0:None; 1:SMT; 2:Core; 3:Package] (int)
parm: PowerScope:[0:None; 1:SMT; 2:Core; 3:Package] (int)
parm: Register_CPU_Idle:Register the Kernel cpuidle driver (short)
parm: Register_CPU_Freq:Register the Kernel cpufreq driver (short)
parm: Register_Governor:Register the Kernel governor (short)
parm: Register_ClockSource:Register Clock Source driver (short)
parm: Idle_Route:[0:Default; 1:I/O; 2:HALT; 3:MWAIT] (short)
parm: Mech_IBRS:Mitigation Mechanism IBRS (short)
parm: Mech_STIBP:Mitigation Mechanism STIBP (short)
parm: Mech_SSBD:Mitigation Mechanism SSBD (short)
parm: Mech_IBPB:Mitigation Mechanism IBPB (short)
parm: Mech_L1D_FLUSH:Mitigation Mechanism Cache L1D Flush (short)