marty-suzuki / Fluxcapacitor
Programming Languages
Labels
Projects that are alternatives of or similar to Fluxcapacitor
FluxCapacitor
FluxCapacitor makes implementing Flux design pattern easily with protocols and typealias.
- Storable protocol
- Actionable protocol
- DispatchState protocol
Requirements
- Xcode 10.1 or later
- Swift 4.2 or later
- iOS 10.0 or later
Installation
CocoaPods
FluxCapacitor is available through CocoaPods. To install it, simply add the following line to your Podfile:
pod "FluxCapacitor"
Carthage
If you’re using Carthage, simply add FluxCapacitor to your Cartfile:
github "marty-suzuki/FluxCapacitor"
Usage
This is ViewController sample that uses Flux design pattern. If ViewController calls fetchRepositories method of RepositoryAction, it is reloaded automatically by observed changes of Constant in RepositoryStore after fetched repositories from Github. Introducing how to implement Flux design pattern with FluxCapacitor.
final class UserRepositoryViewController: UIViewController {
@IBOutlet weak var tableView: UITableView!
private let repositoryAction = RepositoryAction()
private let repositoryStore = RepositoryStore.instantiate()
private let userStore = UserStore.instantiate()
private let dustBuster = DustBuster()
private let dataSource = UserRepositoryViewDataSource()
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
dataSource.configure(with: tableView)
observeStore()
if let user = userStore.selectedUser.value {
repositoryAction.fetchRepositories(withUserId: user.id, after: nil)
}
}
private func observeStore() {
repositoryStore.repositories
.observe(on: .main, changes: { [weak self] _ in
self?.tableView.reloadData()
})
.cleaned(by: dustBuster)
}
}
Dispatcher
First of all, implementing DispatchState. It connects Action and Store, but it plays a role that don't depend directly each other.
extension Dispatcher {
enum Repository: DispatchState {
typealias RelatedStoreType = RepositoryStore
typealias RelatedActionType = RepositoryAction
case isRepositoryFetching(Bool)
case addRepositories([GithubApiSession.Repository])
case removeAllRepositories
}
}
Store
Implementing Store with Storable protocol. func reduce(with:_) is called when Dispatcher dispatches DispatchStateType. Please update store's value with Associated Values.
final class RepositoryStore: Storable {
typealias DispatchStateType = Dispatcher.Repository
let isRepositoryFetching: Constant<Bool>
private let _isRepositoryFetching = Variable<Bool>(false)
let repositories: Constant<[Repository]>
private let _repositories = Variable<[Repository]>([])
required init() {
self.isRepositoryFetching = Constant(_isRepositoryFetching)
self.repositories = Constant(_repositories)
}
func reduce(with state: Dispatcher.Repository) {
switch state {
case .isRepositoryFetching(let value):
_isRepositoryFetching.value = value
case .addRepositories(let value):
_repositories.value.append(contentsOf: value)
case .removeAllRepositories:
_repositories.value.removeAll()
}
}
}
If you want to use any store, please use XXXStore.instantiate(). That static method returns its reference or new instance.
If you want to unregister any store from Dispatcher, please call xxxStore.clear().
Action
Implementing Action with Actionable protocol. If you call invoke method, it can dispatch value related DispatchStateType.
final class RepositoryAction: Actionable {
typealias DispatchStateType = Dispatcher.Repository
private let session: ApiSession
init(session: ApiSession = .shared) {
self.session = session
}
func fetchRepositories(withUserId id: String, after: String?) {
invoke(.isRepositoryFetching(true))
let request = UserNodeRequest(id: id, after: after)
_ = session.send(request) { [weak self] in
switch $0 {
case .success(let value):
self?.invoke(.addRepositories(value.nodes))
case .failure:
break
}
self?.invoke(.isRepositoryFetching(false))
}
}
}
Observe changes with Constant<Element> / Variable<Element>
You can initialize a store with instantiate(). If reference of store is left, that method returns remained one. If reference is not left, that method returns new instance.
You can observe changes by Constant or Variable. When called observe, it returns Dust. So, clean up with DustBuster.
let dustBuster = DustBuster()
func observeStore() {
// Get store instance
let store = RepositoryStore.instantiate()
// Observer changes of repositories that is `Constant<[Github.Repository]>`.
store.repositories
.observe(on: .main) { value in
// do something
}
.cleaned(by: dustBuster)
}
Robert Zemeckis (1989) Back to the future Part II, Universal Pictures
Constant<Element> and Variable<Element>
Variable<Element> has getter and setter of Element.
let intVal = Variable<Int>(0)
intVal.value = 1
print(intVal.value) // 1
Constant<Element> has only getter of Element. So, you can initialize Constant with Variable.
Variable shares its value with Constant.
let variable = Variable<Int>(0)
let constant = Constant(variable)
variable.value = 1
print(variable.value) // 1
print(constant.value) // 1
In addition, Constant that initialize with some Variable, it can use same observation.
let variable = Variable<Int>(0)
let constant = Constant(variable)
_ = variable.observe { value in
print(value) // 0 -> 10
}
_ = constant.observe { value in
print(value) // 0 -> 10
}
variable.value = 10
with RxSwift
You can use FluxCapacitor with RxSwift like this link.
Or implement func asObservable() like this.
// Constant
extension PrimitiveValue where Trait == ImmutableTrait {
func asObservable() -> Observable<Element> {
return Observable.create { [weak self] observer in
let dust = self?.observe { observer.onNext($0) }
return Disposables.create { dust?.clean() }
}
}
}
Example
To run the example project, clone the repo, and run pod install and carthage update from the Example directory first. In addition, you must set Github Personal access token.
// ApiSessionType.swift
extension ApiSession: ApiSessionType {
static let shared: ApiSession = {
let token = "" // Your Personal Access Token
return ApiSession(injectToken: { InjectableToken(token: token) })
}()
}
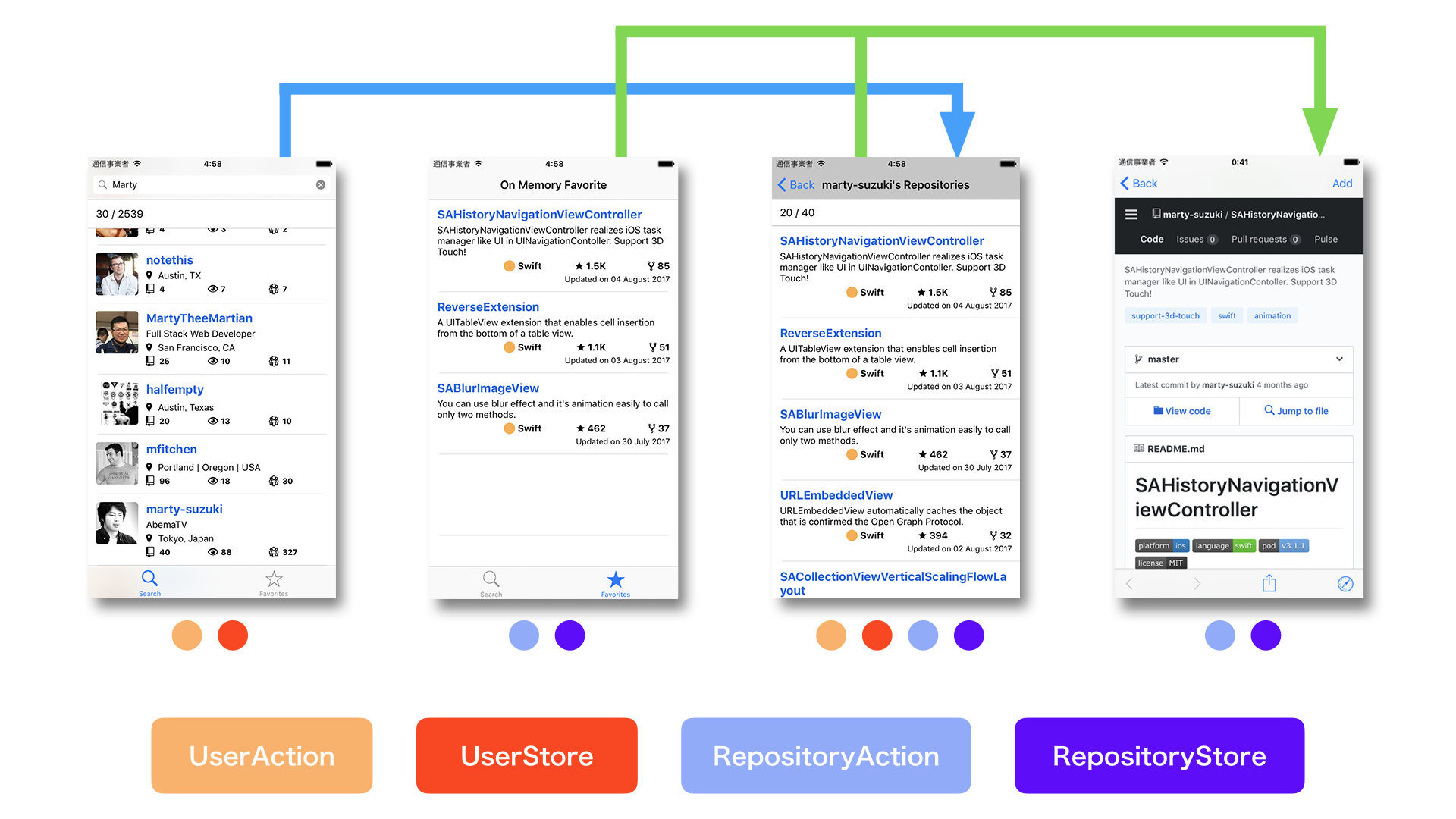
Application structure is like below.
- SearchViewController (with RxSwift) You can search Github user.
- FavoriteViewController You can stock favorites on memory.
- UserRepositoryViewController You can display a user's repositories.
- RepositoryViewController You can display webpage of repository, and add favorites on memory.
GithubKitForSample is used in this sample project.
Additional
Flux + MVVM Sample is here.
Migration Guide
FluxCapacitor 0.10.0 Migration Guide
Author
marty-suzuki, [email protected]
License
FluxCapacitor is available under the MIT license. See the LICENSE file for more info.