vy / Hrrs
Programming Languages
Projects that are alternatives of or similar to Hrrs
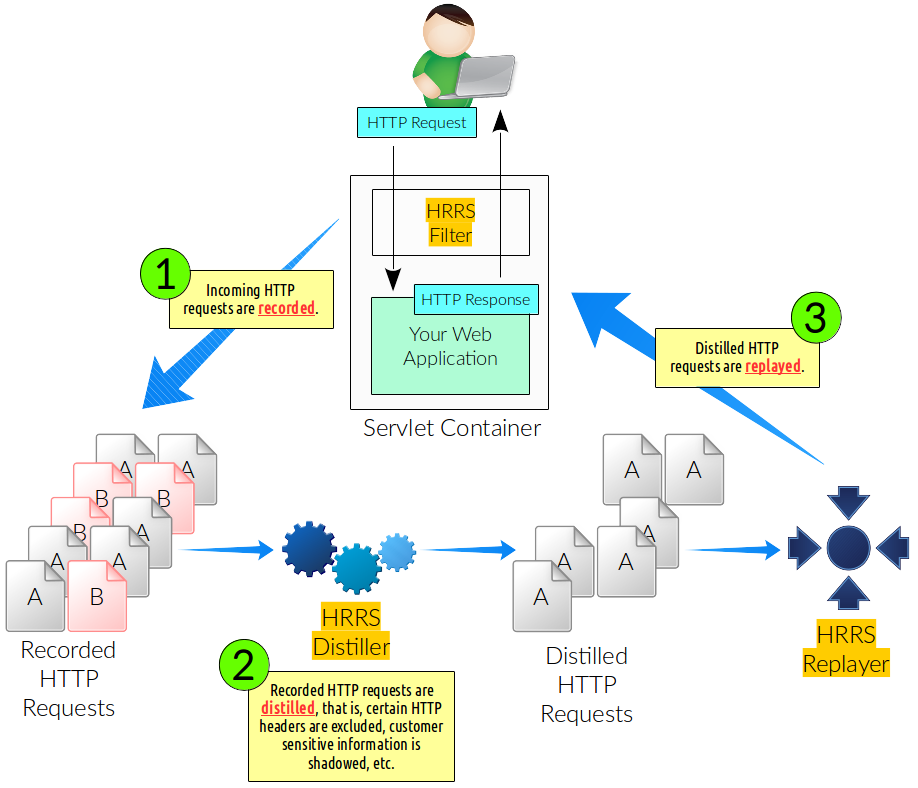
HRRS (HTTP Request Record Suite) is a set of tools that you can leverage to
record, transform, and replay HTTP requests in your Java EE and Spring web
applications written in Java 6 or higher. In essence, HRRS bundles a servlet
filter for recording (hrrs-servlet-filter) and standalone command-line
Java applications for transforming (hrrs-distiller) and replaying
(hrrs-replayer) the requests.
Table of Contents
- Rationale
- Overview
- Getting Started (setting up a Spring web application, running distiller and replayer)
- Recorder Configuration
- Recorder Performance
- Replayer Reports (Dropwizard Metrics and JMeter reports)
- Distiller & Replayer Debugging
- F.A.Q.
- Caveats
- License
Rationale
Why would someone want to record HTTP requests as is? There are two major problems that HRRS is aiming to solve:
-
Realistic performance tests: Artificially generated test data falls short of covering many production states. Testing with unrealistic user behaviour can cause caches to misbehave. Or benchmarks might have used JSON/XML for simplicity, while the actual production systems communicate over a binary protocol such as Protocol Buffers or Thrift. These short comings undermine the reliability of performance figures and renders regression reports unusable. HRRS lets the production load to be stored and reflected back to the test environment for more credible test results.
-
Diagnosing production problems: It might not always be a viable option to remotely debug an instance for production surfacing problems. HRRS can be leveraged to record the problem on production and replay it on development environment for further inspection.
-
Warming up standby service caches: Standby systems are an inevitable part of modern software architectures: reliability, separation of read & write clusters, etc. While replacing primaries with secondary systems, a cold replacement is anticipated to initially yield a degraded performance, which might not be desirable for certain systems. HRRS can be used to warm up the secondaries prior to deployment and alleviate this problem.
Overview
HRRS ships the following artifacts:
-
hrrs-api: Basic API models and interfaces like
HttpRequestHeader,HttpRequestRecord,HttpRequestRecordReader,HttpRequestRecordReaderSource, etc. - hrrs-servlet-filter: Basic servlet filter leveraging the functionality of the API interfaces.
- hrrs-replayer: The command line replayer application.
-
hrrs-distiller: A command line tool to transform and/or filter stored
HttpRequestRecords.
These artifacts provide interfaces for the potential concrete implementations. Fortunately, we provide one for you: File-based Base64 implementation. That is, HTTP request records are encoded in Base64 and stored in a plain text file. Following artifacts provide this functionality:
- hrrs-serializer-base64: The reader/writer implementation using Base64.
- hrrs-servlet-filter-base64: Servlet filter implementation using the Base64 serializer.
- hrrs-replayer-base64: The command line replayer implementation using the Base64 serializer.
- hrrs-distiller-base64: The command line distiller implementation using the Base64 serializer.
HRRS is designed with extensibility in mind. As of now, it only supports file sourced/targeted Base64 readers/writers. But all you need is a few lines of code to introduce your own serialization schemes powered by a storage backend (RDBMS, NoSQL, etc.) of your preference.
Source code also contains the following modules to exemplify the usage of HRRS with certain Java web frameworks:
- hrrs-example-jaxrs
- hrrs-example-spring
Getting Started
In order to start recording HTTP requests, all you need is to plug the HRRS
servlet filter into your Java web application. Below, we will use Base64
serialization for recording HTTP requests in a Spring web application. (See
examples directory for the actual sources and the JAX-RS example.)
Add the HRRS servlet filter Maven dependency to your pom.xml:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.vlkan.hrrs</groupId>
<artifactId>hrrs-servlet-filter-base64</artifactId>
<version>${hrrs.version}</version>
</dependency>
In the second and last step, you expose the HRRS servlet filter as beans so that Spring can inject them as interceptors:
@Configuration
public class HrrsConfig {
@Bean
public HrrsFilter provideHrrsFilter() throws IOException {
String tmpPathname = System.getProperty("java.io.tmpdir");
String file = new File(tmpPathname, "hrrs-spring-records.csv").getAbsolutePath();
String filePattern = new File(tmpPathname, "hrrs-spring-records-%d{yyyyMMdd-HHmmss-SSS}.csv").getAbsolutePath();
RotationConfig rotationConfig = RotationConfig
.builder()
.file(file)
.filePattern(filePattern)
.policy(DailyRotationPolicy.getInstance())
.build();
return new Base64HrrsFilter(rotationConfig);
}
@Bean
public ServletRegistrationBean provideHrrsServlet() {
HrrsServlet hrrsServlet = new HrrsServlet();
return new ServletRegistrationBean(hrrsServlet, "/hrrs");
}
}
And that's it! The incoming HTTP requests will be recorded into
writerTargetFile. (You can also run HelloApplication of examples/spring
in your IDE to see it in action.) All you need to do is instructing the HRRS
servlet to enable the recorder:
$ curl http://localhost:8080/hrrs
{"enabled": false}
$ curl -X PUT http://localhost:8080/hrrs?enabled=true
After a couple of GET /hello?name=<name> queries, let's take a quick look at
the contents of the Base64-serialized HTTP request records:
$ zcat records.csv.gz | head -n 3
iz4mjlt9_8f89s 20170213-224106.477+0100 hello POST ABYvaGVsbG8/bmFtZT1UZXN0TmFtZS0xAAAABQAEaG9zdAAObG9jYWxob3N0OjgwODAACnVzZXItYWdlbnQAC2N1cmwvNy40Ny4wAAZhY2NlcHQAAyovKgAMY29udGVudC10eXBlAAp0ZXh0L3BsYWluAA5jb250ZW50LWxlbmd0aAACMTMAAAAAAAAAAAAAAA9yYW5kb20tZGF0YS0x//8=
iz4mjlui_1l3bw 20170213-224106.522+0100 hello POST ABYvaGVsbG8/bmFtZT1UZXN0TmFtZS0zAAAABQAEaG9zdAAObG9jYWxob3N0OjgwODAACnVzZXItYWdlbnQAC2N1cmwvNy40Ny4wAAZhY2NlcHQAAyovKgAMY29udGVudC10eXBlAAp0ZXh0L3BsYWluAA5jb250ZW50LWxlbmd0aAACMTMAAAAAAAAAAAAAAA9yYW5kb20tZGF0YS0z//8=
iz4mjlty_sicli 20170213-224106.502+0100 hello POST ABYvaGVsbG8/bmFtZT1UZXN0TmFtZS0yAAAABQAEaG9zdAAObG9jYWxob3N0OjgwODAACnVzZXItYWdlbnQAC2N1cmwvNy40Ny4wAAZhY2NlcHQAAyovKgAMY29udGVudC10eXBlAAp0ZXh0L3BsYWluAA5jb250ZW50LWxlbmd0aAACMTMAAAAAAAAAAAAAAA9yYW5kb20tZGF0YS0y//8=
(If you can't see any content yet, you can enforce flushing via
curl -X POST http://localhost:8080/hrrs.)
Here each line corresponds to an HTTP request record and fields are separated
by \t character. A line first starts with plain text id, timestamp, group
name, and method fields. There it is followed by a Base64-encoded field
containing the URL (including request parameters), headers, and payload. This
simple representation makes it easy to employ well-known command line tools
(grep, sed, awk, etc.) to extract a certain subset of records.
$ zcat records.csv.gz | head -n 1 | awk '{print $5}' | base64 --decode | hd
00000000 00 16 2f 68 65 6c 6c 6f 3f 6e 61 6d 65 3d 54 65 |../hello?name=Te|
00000010 73 74 4e 61 6d 65 2d 31 00 00 00 05 00 04 68 6f |stName-1......ho|
00000020 73 74 00 0e 6c 6f 63 61 6c 68 6f 73 74 3a 38 30 |st..localhost:80|
00000030 38 30 00 0a 75 73 65 72 2d 61 67 65 6e 74 00 0b |80..user-agent..|
00000040 63 75 72 6c 2f 37 2e 34 37 2e 30 00 06 61 63 63 |curl/7.47.0..acc|
00000050 65 70 74 00 03 2a 2f 2a 00 0c 63 6f 6e 74 65 6e |ept..*/*..conten|
00000060 74 2d 74 79 70 65 00 0a 74 65 78 74 2f 70 6c 61 |t-type..text/pla|
00000070 69 6e 00 0e 63 6f 6e 74 65 6e 74 2d 6c 65 6e 67 |in..content-leng|
00000080 74 68 00 02 31 33 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |th..13..........|
00000090 00 0f 72 61 6e 64 6f 6d 2d 64 61 74 61 2d 31 ff |..random-data-1.|
000000a0 ff |.|
000000a1
Once you start recording HTTP requests, you can setup logrotate to periodically rotate and compress the record output file. You can even take one step further and schedule a cron job to copy these records to a directory accessible by your test environment. There you can replay HTTP request records using the replayer provided by HRRS:
$ java \
-jar /path/to/hrrs-replayer-base64-<version>.jar \
--targetHost localhost \
--targetPort 8080 \
--threadCount 10 \
--maxRequestCountPerSecond 1000 \
--inputUri file:///path/to/records.csv.gz
Below is the list of parameters supported by the replayer.
| Parameter | Required | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
--help, -h
|
N | false | display this help and exit |
--inputUri, -i
|
Y | input URI for HTTP records (Base64 replayer can accept input URIs with .gz suffix.) |
|
--jtlOutputFile, -oj
|
N | Apache JMeter JTL output file for test results | |
--localAddress, -l
|
N | address to bind to when making outgoing connections | |
--loggerLevelSpecs, -L
|
N | *=warn,com.vlkan.hrrs=info |
comma-separated list of loggerName=loggerLevel pairs |
--maxRequestCountPerSecond, -r
|
N | 1 | number of concurrent requests per second |
--metricsOutputFile, -om
|
N | output file to dump Dropwizard metrics | |
--metricsOutputPeriodSeconds, -mp
|
N | 10 | Dropwizard metrics report frequency in seconds |
--rampUpDurationSeconds, -d
|
N | 1 | ramp up duration in seconds to reach to the maximum number of requests |
--redirectStrategy, -rs
|
N | DEFAULT |
redirect strategy (NONE, DEFAULT, or LAX) |
--requestTimeoutSeconds, -t
|
N | 10 | HTTP request connect/write/read timeout in seconds |
--replayOnce, -1
|
N | false | exit once all the records are replayed |
--targetHost, -th
|
Y | remote HTTP server host | |
--targetPort, -tp
|
Y | remote HTTP server port | |
--threadCount, -n
|
N | 2 | HTTP request worker pool size |
--totalDurationSeconds, -D
|
N | 10 | total run duration in seconds |
It is not always desired to replay recorded HTTP requests as is. One might need to exclude certain HTTP headers, remove promotion codes from the URL, sanitize payload by shadowing sensitive customer information, etc. You can use distiller provided by HRRS for this purpose:
$ java \
-jar /path/to/hrrs-distiller-base64-<version>.jar
--inputUri file:///path/to/input-records.csv.gz
--outputUri file:///path/to/output-records.csv.gz
--scriptUri file:///path/to/transform.js
Distiller passes each read input record to the transform() function defined
in the JavaScript file pointed by --scriptUri parameter. transform()
receives a single argument of type HttpRequestRecord and returns an
HttpRequestRecord. (Returning null lets the distiller to exclude that
record.) Consider the following example:
var formatter = new java.text.SimpleDateFormat("yyyyMMdd-HHmmss.SSSZ");
var loTimestamp = formatter.parse("20170415-204551.527+0200");
var hiTimestamp = formatter.parse("20170415-204551.700+0200");
/**
* Remove `Host` and `Content-Length` headers.
*/
function sanitizeHeaders(oldHeaders) {
var newHeaders = [];
for (var oldHeaderIndex = 0; oldHeaderIndex < oldHeaders.length; oldHeaderIndex++) {
var oldHeader = oldHeaders[oldHeaderIndex];
var oldHeaderName = oldHeader.getName();
var allowed =
!oldHeaderName.equalsIgnoreCase("host") &&
!oldHeaderName.equalsIgnoreCase("content-length");
if (allowed) {
newHeaders.push(oldHeader);
}
}
return newHeaders;
}
function transform(input) {
var timestamp = input.getTimestamp();
if (timestamp.after(loTimestamp) && timestamp.before(hiTimestamp)) { // Check the timestamp.
var newHeaders = sanitizeHeaders(input.getHeaders()); // Sanitize headers.
return input.toBuilder().setHeaders(newHeaders).build(); // Reconstruct record with new headers.
}
return null; // Out of time range, ignore the record.
}
Below is the list of parameters supported by the distiller.
| Parameter | Required | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
--help, -h
|
N | false | display this help and exit |
--inputUri, -i
|
Y | input URI for HTTP records | |
--loggerLevelSpecs, -L
|
N | *=warn,com.vlkan.hrrs=info |
comma-separated list of loggerName=loggerLevel pairs |
--outputUri, -o
|
Y | output URI for HTTP records | |
--scriptUri, -s
|
Y | input URI for script file |
For a more detailed walk-through see README.md in examples/spring.
Recorder Configuration
By default, HRRS servlet filter records every HTTP request along with its
payload. This certainly is not a desired option for many applications. For such
cases, you can override certain methods of the HrrsFilter to have a more
fine-grained control over the recorder.
public abstract class HrrsFilter implements Filter {
// ...
public static final long DEFAULT_MAX_RECORDABLE_PAYLOAD_BYTE_COUNT = 10 * 1024 * 1024;
/**
* Checks if the given HTTP request is recordable.
*/
protected boolean isRequestRecordable(HttpServletRequest request) {
return true;
}
/**
* Maximum amount of bytes that can be recorded per request.
* Defaults to {@link HrrsFilter#DEFAULT_MAX_RECORDABLE_PAYLOAD_BYTE_COUNT}.
*/
public long getMaxRecordablePayloadByteCount() {
return DEFAULT_MAX_RECORDABLE_PAYLOAD_BYTE_COUNT;
}
/**
* Create a group name for the given request.
*
* Group names are used to group requests and later on are used
* as identifiers while reporting statistics in the replayer.
* It is strongly recommended to use group names similar to Java
* package names.
*/
protected String createRequestGroupName(HttpServletRequest request) {
String requestUri = createRequestUri(request);
return requestUri
.replaceFirst("\\?.*", "") // Replace query parameters.
.replaceFirst("^/", "") // Replace the initial slash.
.replaceAll("/", "."); // Replace all slashes with dots.
}
/**
* Creates a unique identifier for the given request.
*/
protected String createRequestId(HttpServletRequest request) {
return ID_GENERATOR.next();
}
/**
* Filters the given record prior to writing.
* @return the modified record or null to exclude the record
*/
protected HttpRequestRecord filterRecord(HttpRequestRecord record) {
return record;
}
// ...
}
Recorder Performance
HRRS provided servlet filter wraps the input stream of the HTTP request model. Whenever user consumes from the input, we store the read bytes in a seperate buffer, which later on gets Base64-encoded at request completion. There are two issues with this approach:
- Duplication increases the memory usage.
- Encoding and storing the requests adds an extra processing overhead.
It is possible to use a fixed (thread local?) memory pool to avoid extra memory allocations for each request. Further, encoding and storing can also be performed in a separate thread to not block the request handler thread. These being said, HRRS is successfully deployed on a 6-node Java EE application cluster (each node handles approximately 600 reqs/sec and requests generally contain a payload close to 50KB) without any noticeable memory or processing overhead.
Additionally, you can override isRequestRecordable() and
getMaxRecordablePayloadByteCount() methods in HrrsFilter to have a more
fine-grained control over the recorded HTTP requests.
Replayer Reports
If you have ever used HTTP benchmarking tools like
JMeter or Gatling, then
you should be familiar with the reports generated by these tools. Rather than
generating its own eye candy reports, HRRS optionally (--jtlOutputFile)
dumps a JMeter JTL file with the
statistics (timestamp, latency, etc.) of each executed request. A quick peek
at the JMeter JTL file looks as follows:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<testResults version="1.2">
<httpSample t="108" lt="108" ts="1486330510795" s="true" rc="200" lb="hello" tn="RateLimitedExecutor-0"/>
<httpSample t="6" lt="6" ts="1486330510802" s="true" rc="200" lb="hello" tn="RateLimitedExecutor-1"/>
<httpSample t="3" lt="3" ts="1486330510828" s="true" rc="200" lb="hello" tn="RateLimitedExecutor-0"/>
<!-- ... -->
</testResults>
For an overview or to track the progress, you can also command HRRS to
periodically dump Dropwizard metrics (--metricsOutputFile and
--metricsOutputPeriodSeconds) to a file as well. HRRS uses ConsoleReporter
of Dropwizard metrics to dump the statistics, which look as follows:
__all__
count = 10
mean rate = 1.01 calls/second
1-minute rate = 1.00 calls/second
5-minute rate = 1.00 calls/second
15-minute rate = 1.00 calls/second
min = 3.00 milliseconds
max = 108.00 milliseconds
mean = 16.15 milliseconds
stddev = 29.46 milliseconds
median = 8.00 milliseconds
75% <= 9.00 milliseconds
95% <= 108.00 milliseconds
98% <= 108.00 milliseconds
99% <= 108.00 milliseconds
99.9% <= 108.00 milliseconds
__all__.200
count = 10
mean rate = 1.01 calls/second
1-minute rate = 1.00 calls/second
5-minute rate = 1.00 calls/second
15-minute rate = 1.00 calls/second
min = 3.00 milliseconds
max = 108.00 milliseconds
mean = 16.15 milliseconds
stddev = 29.46 milliseconds
median = 8.00 milliseconds
75% <= 9.00 milliseconds
95% <= 108.00 milliseconds
98% <= 108.00 milliseconds
99% <= 108.00 milliseconds
99.9% <= 108.00 milliseconds
hello
count = 10
mean rate = 1.01 calls/second
1-minute rate = 1.00 calls/second
5-minute rate = 1.00 calls/second
15-minute rate = 1.00 calls/second
min = 3.00 milliseconds
max = 108.00 milliseconds
mean = 16.15 milliseconds
stddev = 29.46 milliseconds
median = 8.00 milliseconds
75% <= 9.00 milliseconds
95% <= 108.00 milliseconds
98% <= 108.00 milliseconds
99% <= 108.00 milliseconds
99.9% <= 108.00 milliseconds
hello.200
count = 10
mean rate = 1.01 calls/second
1-minute rate = 1.00 calls/second
5-minute rate = 1.00 calls/second
15-minute rate = 1.00 calls/second
min = 3.00 milliseconds
max = 108.00 milliseconds
mean = 16.15 milliseconds
stddev = 29.46 milliseconds
median = 8.00 milliseconds
75% <= 9.00 milliseconds
95% <= 108.00 milliseconds
98% <= 108.00 milliseconds
99% <= 108.00 milliseconds
99.9% <= 108.00 milliseconds
Here HRRS updates a Dropwizard timer with label <groupName>.<responseCode>
for each executed request. It also updates the metrics of a pseudo group,
called __all__, which covers all the existing groups.
Distiller & Replayer Debugging
Sometimes it becomes handy to have more insight into the distiller and replayer
internals. For such cases, you can increase the logging verbosity of certain
packages. As a starting point, adding --loggerLevelSpecs "*=info,com.vlkan.hrrs=trace"
to the command line arguments is generally a good idea. Note that, you don't
want to have such a level of verbosity while executing the actual performance
tests.
F.A.Q.
-
What's wrong with JMeter, Gatling, etc.? There is nothing wrong with them. In fact, they are fantastic tools. I use them on a daily basis for performance tests. Though they do not provide any integration solutions for recording the HTTP traffic of a web application.
-
Then why not just using JMeter, Gatling, etc. as a replayer? I first started my pursuit by trying to make JMeter replay the HTTP request records that I collected. After wrestling with JMeter and its BeanShell Pre-Processor for days, I implemented a custom fully-fledged replayer using Apache HTTP Client in a single day. Though it is a lot easier to pull that out using Gatling compared to JMeter. Long story short, I needed JMeter JTL files to integrate my test results in our test infrastructure at work, and a simple replayer did the trick. Though, I welcome any patches for replacing the custom replayer with JMeter and/or Gatling.
-
You could have sniffed HTTP from the raw network traffic. That would be great! Actually, that is a fantastic idea! Then HRRS would be totally programming language and framework agnostic. Though many Java network packet capturing solutions (Pcap4j, jNetPcap, etc.) require the native libpcap library to be installed on the system. This might be a bold assumption for many deployment environments. Further, deploying a separate executable along with your application might not always be a viable option. As a matter of fact, many deployment environments that I know in the industry still do expect a single JAR/WAR file as a deployable unit. Thus sticking close to the web application itself in Java serves a purpose here.
-
Are you recording the entire HTTP request payload, even if it is not used? Short answer is no. First, the
InputStreamof a request is wrapped and recorded only ifHrrsFilter#isRequestRecordable(HttpServletRequest)returnstrue. Second, the payload is recorded as long as it is consumed. If the request handler does not consume the payload, then HRRS will not record it either. Additionally,HrrsFilter#getMaxRecordablePayloadByteCount()provides a hardcoded upper bound on the maximum number of bytes HRRS is allowed to record. The only exception to this isx-www-form-urlencodedrequests, see Caveats section below. -
Is it possible to query the state of the recorder and enable/disable it at runtime? Yes, see the usage of
HrrsServletabove, which provides an HTTP API for that purpose. An MBean exposure is being worked on as well. [TODO] -
Is using plain text files a good idea for the HTTP records? Yes and no. Yes, because it suits our needs. It is easier to copy between production and test environments. It is easier to reason about. And you can leverage command line tools (
grep,sed,awk, etc.) to manipulate or take a subset of the records. That being said, you can easily implement your own serializers (for instance, using anRDBMS) according to your needs. -
What if the state of the services (e.g., database contents) differ in test and production environments? We also suffer from the same issue, but that is a totally different problem domain. In our case, the magnitude of the misalignment between production and test environment states are at negligible margins. In the tests, we do expect a stable rate in the HTTP 4XX and 5XX response codes and that works fine for us.
-
Sounds cool! How can I contribute? Awesome! Just send a pull request over GitHub. In terms of coding conventions, just try to stick to the style in the source code.
Caveats
-
What is up with the
x-www-form-urlencodedrequests? Long story short, serialization ofx-www-form-urlencodedrequests is an expensive operation andHrrsFilter#getMaxRecordablePayloadByteCount()limit is subject to violation.In section SRV.3.1.1 of Servlet spec, it has been stated that any access to request parameters (e.g.
HttpServletRequest#getParameterMap()) can trigger the early consumption of the requestInputStreambefore it reaches to the handler. If you recall HRRS just wraps the internalInputStreamto tap the consumed content, this servlet caveat should not constitute a problem. Though parameter parsing methods in Tomcat access theInputStreamthrough an internal reference and discard the one that is passed by HRRS. (See the relevant mailing-list discussion.) Hence, to be on the safe side, HRRS re-constructs the request payload by serializing form parameters back to a byte stream. Additionally, to be able to do that, it also needs to parse and deserialize query parameters and exclude them from the servlet parameters, which is a mixture of both query and form parameters by definition. And unfortunately this nasty operation is relatively more expensive then just cloning anInputStreamin a regularPOSTrequest and is not subject to any maximum recordable payload size limits.
License
Copyright © 2017-2018 Volkan Yazıcı
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.