cycloidio / Inframap
Projects that are alternatives of or similar to Inframap
InfraMap
Read your tfstate or HCL to generate a graph specific for each provider, showing only the resources that are most important/relevant.
Cloud Providers
We support certain providers. This allows us to better represent information that comes from these providers.
If your state file or HCL is from a provider we do not support, the resulting representation will simply be all resources present without any simplification or refinement.
We support Terraform 0.13 (and previous) and Terraform State version 4.
| Provider | State | HCL | Grouping1 | External Nodes2 | IAM3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
✔️ | ✔️ | WIP | ✔️ | ✖️ (https://github.com/cycloidio/inframap/issues/11) |
| ✔️ | ✔️ | ✖️ | ✖️ | ✖️ | |
| ✔️ | ✔️ | ✖️ | ✖️ | ✖️ | |
 |
✔️ | ✔️ | ✖️ | ✖️ | ✖️ |
 |
✔️ | ✔️ | ✖️ | ✖️ | ✖️ |
- Grouping: Group elements that belong to the same group like VPCs or regions
- External Nodes: Show the ingress of the Nodes if any
- IAM: Connections based on IAM (Identity Access Management)
Installation
Stable
To install the latest release of Inframap, you can pick one of this methods:
- pull the latest release from the Releases page
- pull the latest docker image from the Docker hub
- use your Linux package manager (only AUR at the moment)
Development
You can build and install with the latest sources, you will enjoy the new features and bug fixes. It uses Go Modules (1.13+)
$ git clone https://github.com/cycloidio/inframap
$ cd inframap
$ go mod download
$ make build
Install via brew
If you're macOS user and using Homebrew, you can install via brew command:
$ brew install inframap
Usage
The inframap --help will show you the basics.
The most important subcommands are:
-
generate: generates the graph from STDIN or file. -
prune: removes all unnecessary information from the state or HCL (not supported yet) so it can be shared without any security concerns
Example
Visualizing with dot
$ inframap generate state.tfstate | dot -Tpng > graph.png
or from the terminal itself
$ inframap generate state.tfstate | graph-easy
or from HCL
$ inframap generate config.tf | graph-easy
or HCL module
$ inframap generate ./my-module/ | graph-easy
using docker image (assuming that your Terraform files are in the working directory)
$ docker run --rm -v ${PWD}:/opt cycloid/inframap generate /opt/terraform.tfstate
Note: InfraMap will guess the type of the input (HCL or TFState) by validating if it's a JSON and if it fails then we fallback
to HCL (except if you send a directory on args, the it'll use HCL directly), to force one specific type you can use --hcl or --tfstate flags.
How is it different to terraform graph
Terraform Graph outputs a dependency graph of all the resources on the tfstate/HCL. We try to go one step further, by trying to make it human-readable.
If the provider is not supported, the output will be closer to the Terraform Graph version (without displaying provider / variable nodes)
Taking https://github.com/cycloid-community-catalog/stack-magento/ as a reference this is the difference in output:
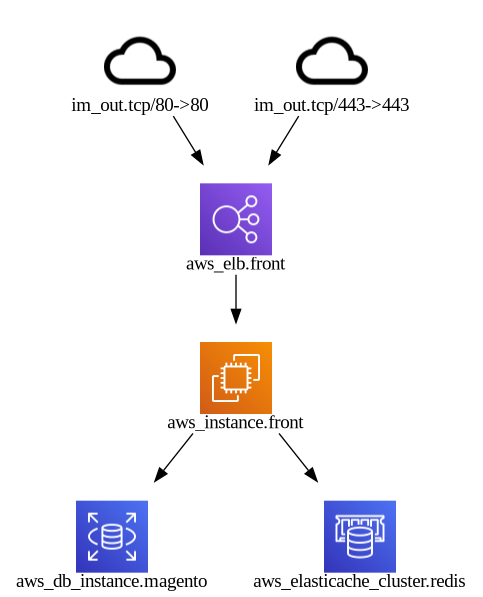
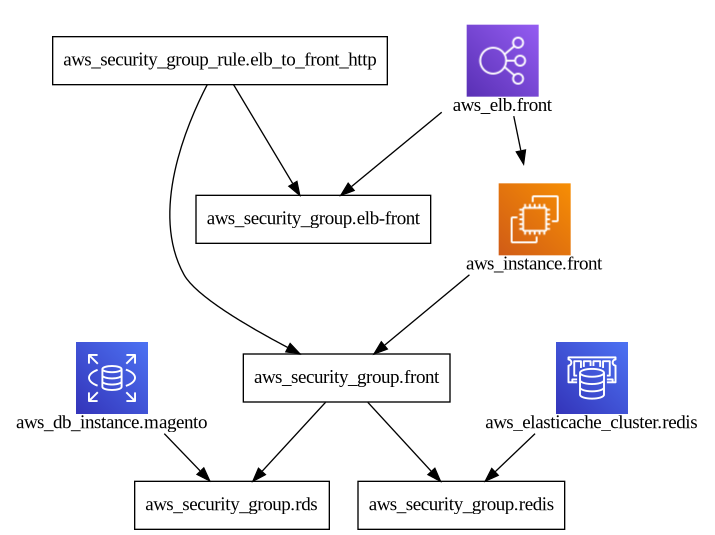
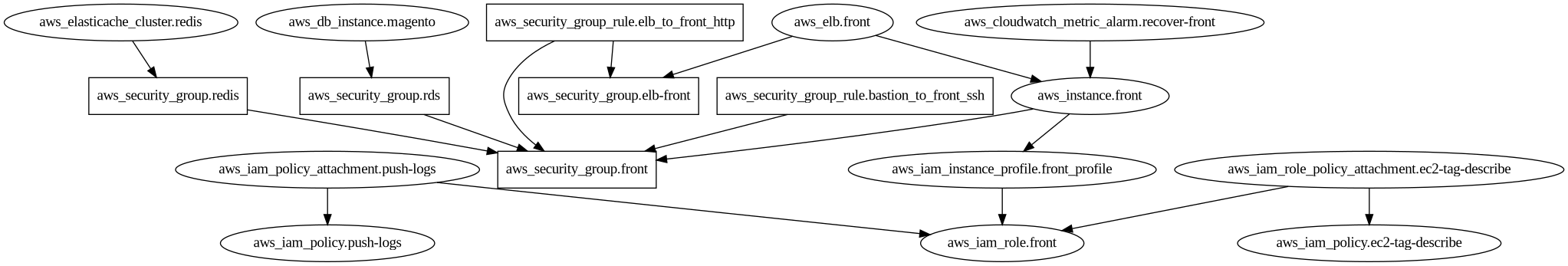
With terraform graph:
With inframap generate ./terraform/module-magento/ | dot -Tpng > inframap.png:
With inframap generate --connections=false ./terraform/module-magento/ | dot -Tpng > inframapconnections.png:
With inframap generate ./terraform/module-magento/ --raw | dot -Tpng > inframapraw.png:
How does it work?
For each provider, we support specific types of connections; we have a static list of resources that can be nodes or edges. Once we identify the edges, we try to create one unique edge from the resources they connect.
For a state file, we rely on the dependencies key (for the <0.13 we replace all depends_on for dependencies so we support them) and, for HCL we rely on interpolation to create the base graph one which we then
apply specific provider logic if supported. If not supported, then basic graph is returned.
FAQ
Why is my Graph generated empty?
If a graph is returned empty, it means that we support one of the providers you are using on your HCL/TFState but we do not recognize any connection or relevant node.
To show the configuration without any InfraMap applied logic you can use the --raw flag logic and print everything that we read.
If it works, it would be good to try to know why it was empty before so we can take a look
at it as it could potentially be an issue on InfraMap (open an issue if you want us to take a look).
By default unconnected nodes are removed, you can use --clean=false to prevent that.
Does InfraMap support Terraform backends ?
Terraform allows users to use backends (S3, Google Cloud Storage, Swift, etc.) in order to store the terraform.state. We currently do not support graph generation from tfstate stored in such backends. As mentioned in this issue, it is possible to play around stdin/out to generate graph from Terraform backends.
| backend | command |
|---|---|
| S3 | aws s3 cp s3://bucket/path/to/your/file.tfstate - | inframap generate |
| GCS | gsutil cat gs://bucket/path/to/your/file.tfstate | inframap generate |
What does the error Error: error while reading TFState: state snapshot was created by Terraform v0.13.0, which is newer than current v0.12.28; upgrade to Terraform v0.13.0 or greater to work with this state mean?
We use Terraform internally to read the TFStates and it has a built-in validation that checks that the version of Terraform used (specified as "version": "X.Y.Z", on the state) is the same or older than the one defined.
In this case it means that Terraform released a new version and InfraMap did not yet update to that version so we have to update to the latest version of Terraform. It'll not take more than a few days but if you update on the same day as the Terraform release then InfraMap will fail due to that.
You can open an issue to notify us just in case we missed it, similar to https://github.com/cycloidio/inframap/issues/47
License
Please see the MIT LICENSE file.
Changelog
All notable changes to this project will be documented in this file.
The format is based on Keep a Changelog, and this project adheres to Semantic Versioning.
About Cycloid
Cycloid is a European fully-remote company, building a product to simplify, accelerate and optimize your DevOps and Cloud adoption.
We built Cycloid, your DevOps framework to encourage Developers and Ops to work together with the respect of best practices. We want to provide a tool that eliminates the silo effect in a company and allows to share the same level of informations within all professions.
Cycloid supports you to factorize your application in a reproducible way, to deploy a new environment in one click. This is what we call a stack.
A stack is composed of 3 pillars:
Thanks to the flexible pipeline, all the steps and technologies are configurable.
To make it easier to create a stack, we build an Infrastructure designer named StackCraft that allows you to drag & drop Terraform resources and generate your Terraform files for you.
InfraMap is a brick that will help us to visualize running infrastructures.
The product comes also with an Open Source service catalog (all our public stacks are on Github) to deploy applications seamlessly. To manage the whole life cycle of an application, it also integrates the diagram of the infrastructure and the application, a cost management control to centralize Cloud billing, the monitoring, logs and events centralized with Prometheus, Grafana, ELK.