FrancescoSaverioZuppichini / Mirror
Programming Languages
Projects that are alternatives of or similar to Mirror
Mirror
Pytorch CNN Visualisation Tool
Francesco Saverio Zuppichini
This is a raw beta so expect lots of things to change and improve over time.
An interactive version of this tutorial can be found here
Getting started
To install mirror run
pip install git+https://github.com/FrancescoSaverioZuppichini/mirror.git
Getting Started
A basic example
from mirror import mirror
from mirror.visualisations.web import *
from PIL import Image
from torchvision.models import resnet101, resnet18, vgg16, alexnet
from torchvision.transforms import ToTensor, Resize, Compose
# create a model
model = vgg16(pretrained=True)
# open some images
cat = Image.open("./cat.jpg")
dog_and_cat = Image.open("./dog_and_cat.jpg")
# resize the image and make it a tensor
to_input = Compose([Resize((224, 224)), ToTensor()])
# call mirror with the inputs and the model
mirror([to_input(cat), to_input(dog_and_cat)], model, visualisations=[BackProp, GradCam, DeepDream])
* Serving Flask app "mirror.App" (lazy loading)
* Environment: production
WARNING: Do not use the development server in a production environment.
Use a production WSGI server instead.
* Debug mode: off
* Running on http://0.0.0.0:5000/ (Press CTRL+C to quit)
It will automatic open a new tab in your browser
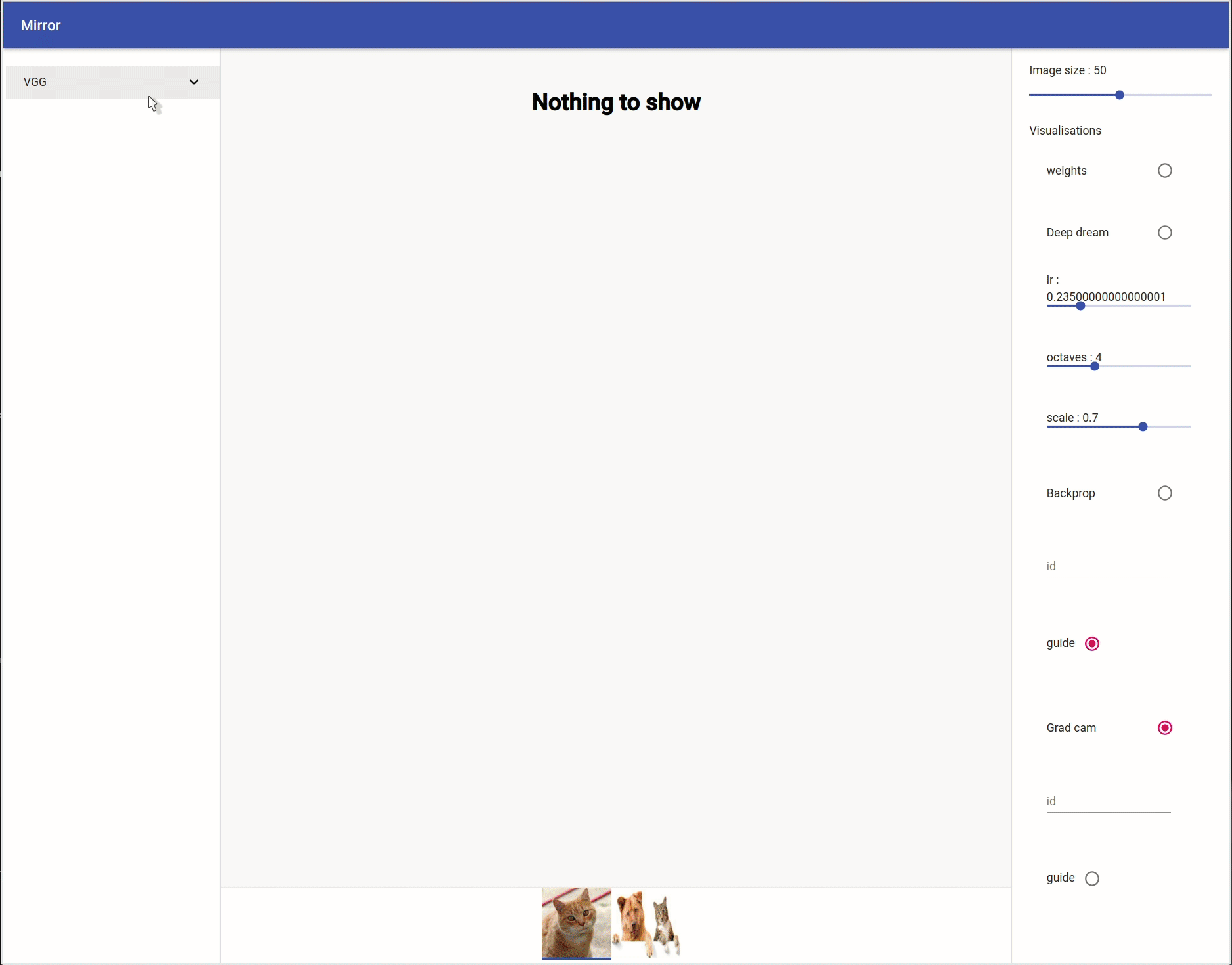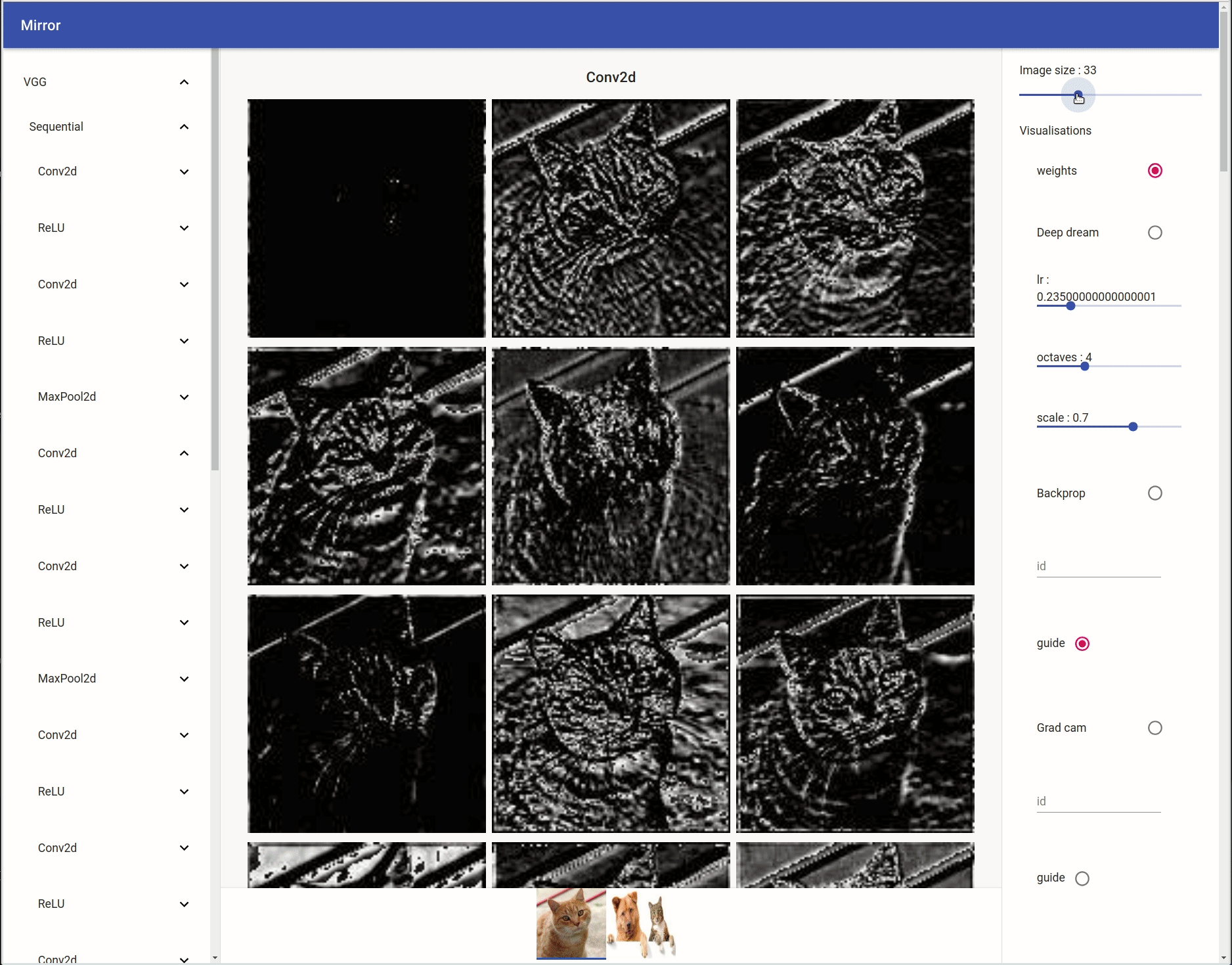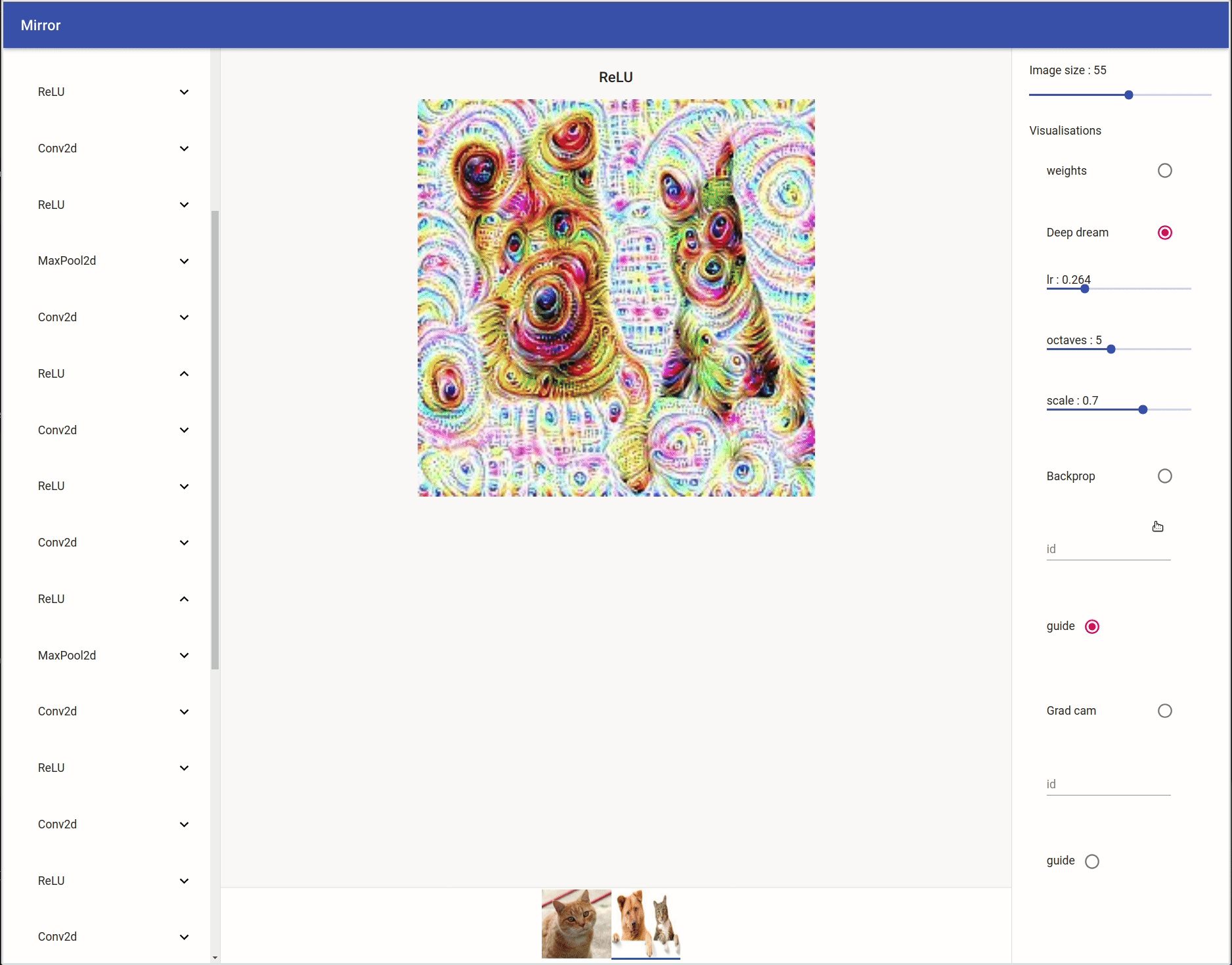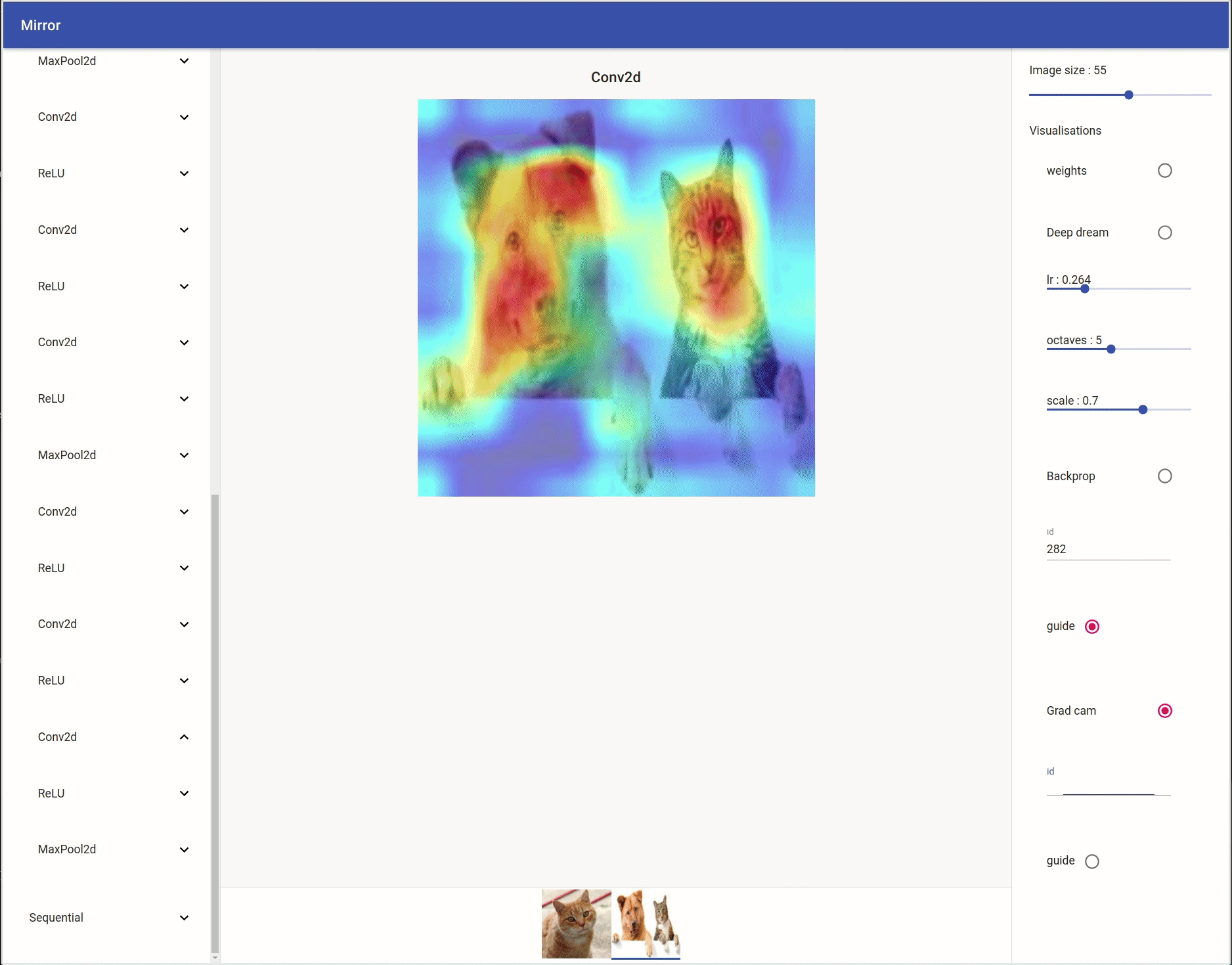
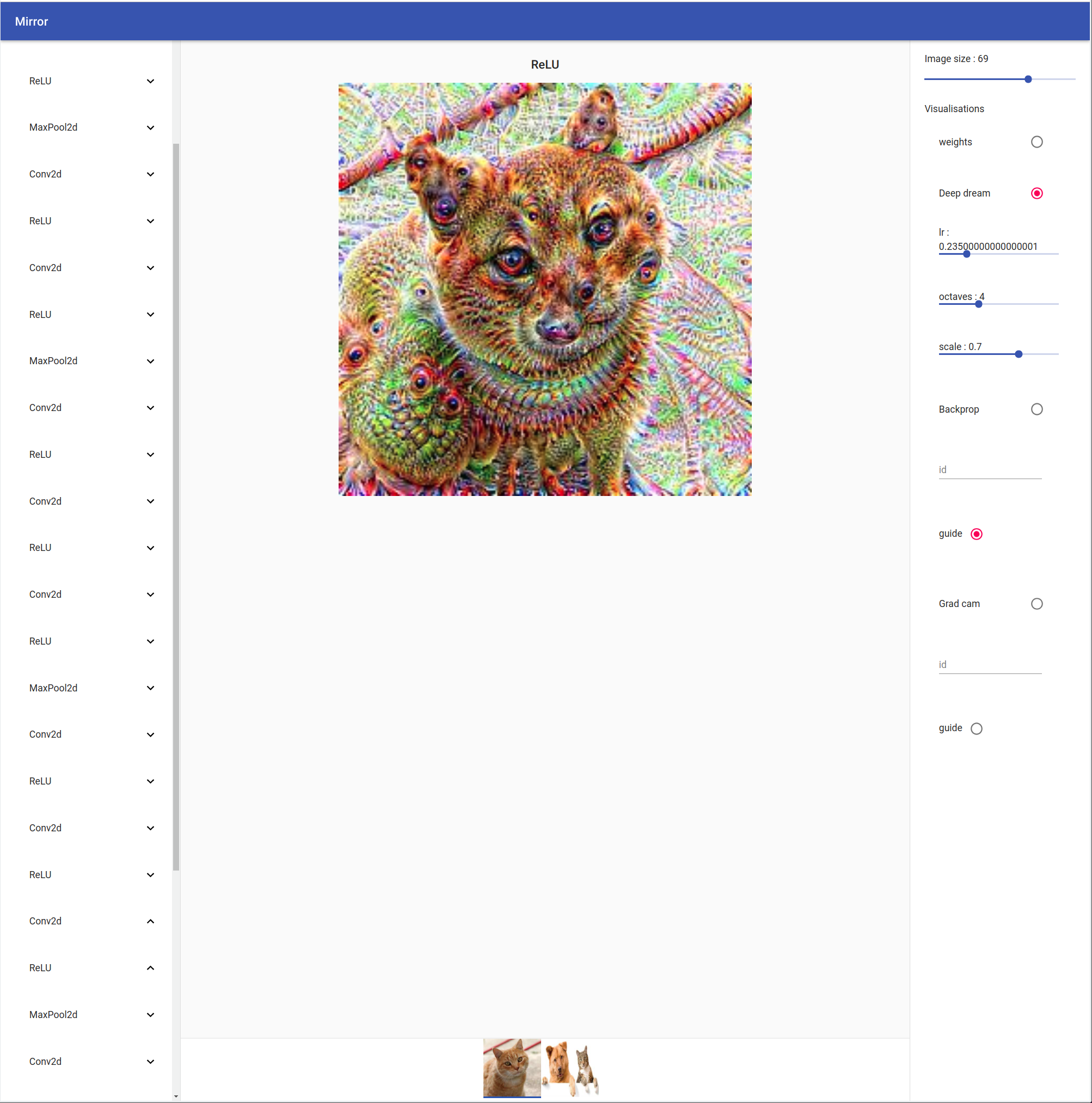
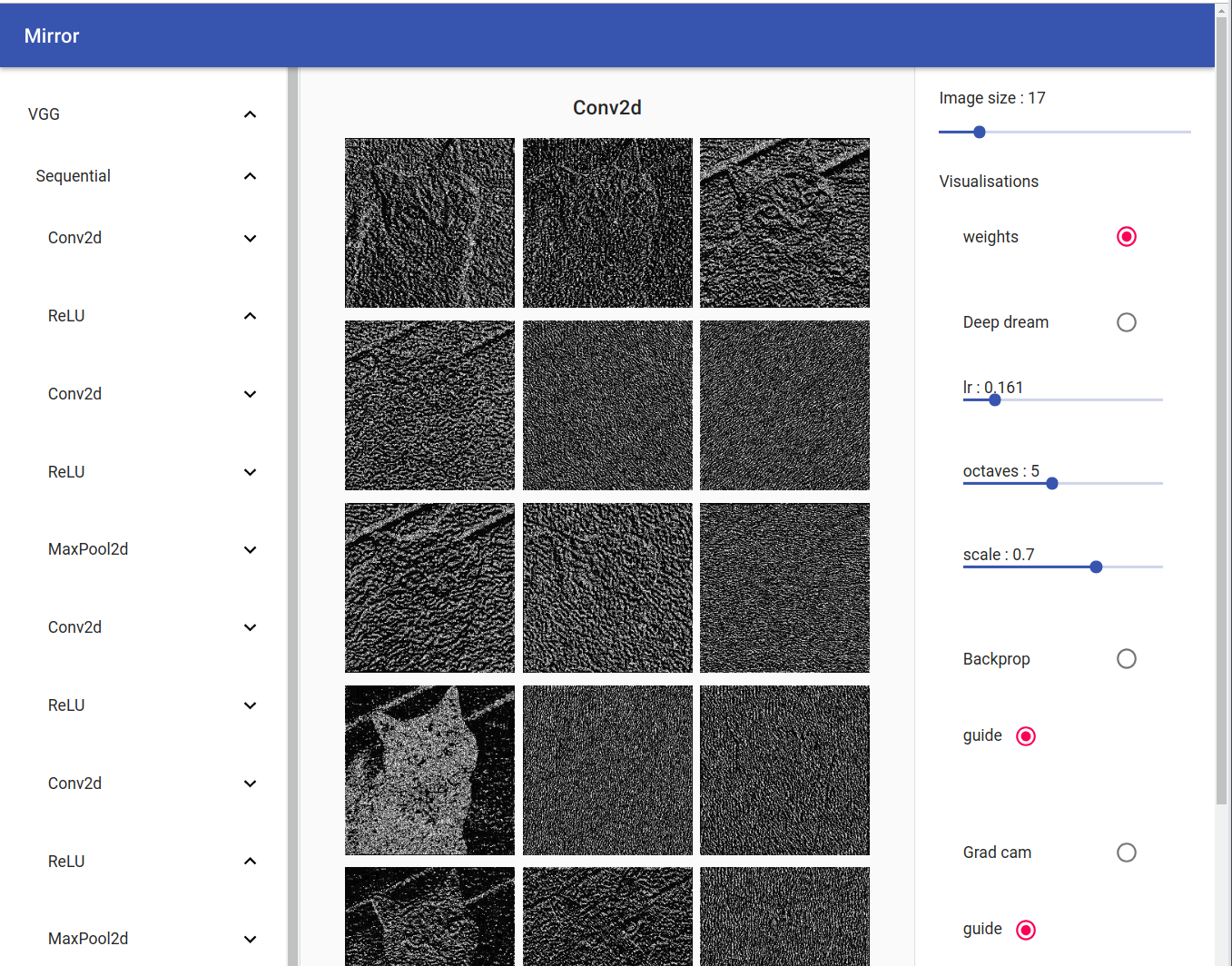
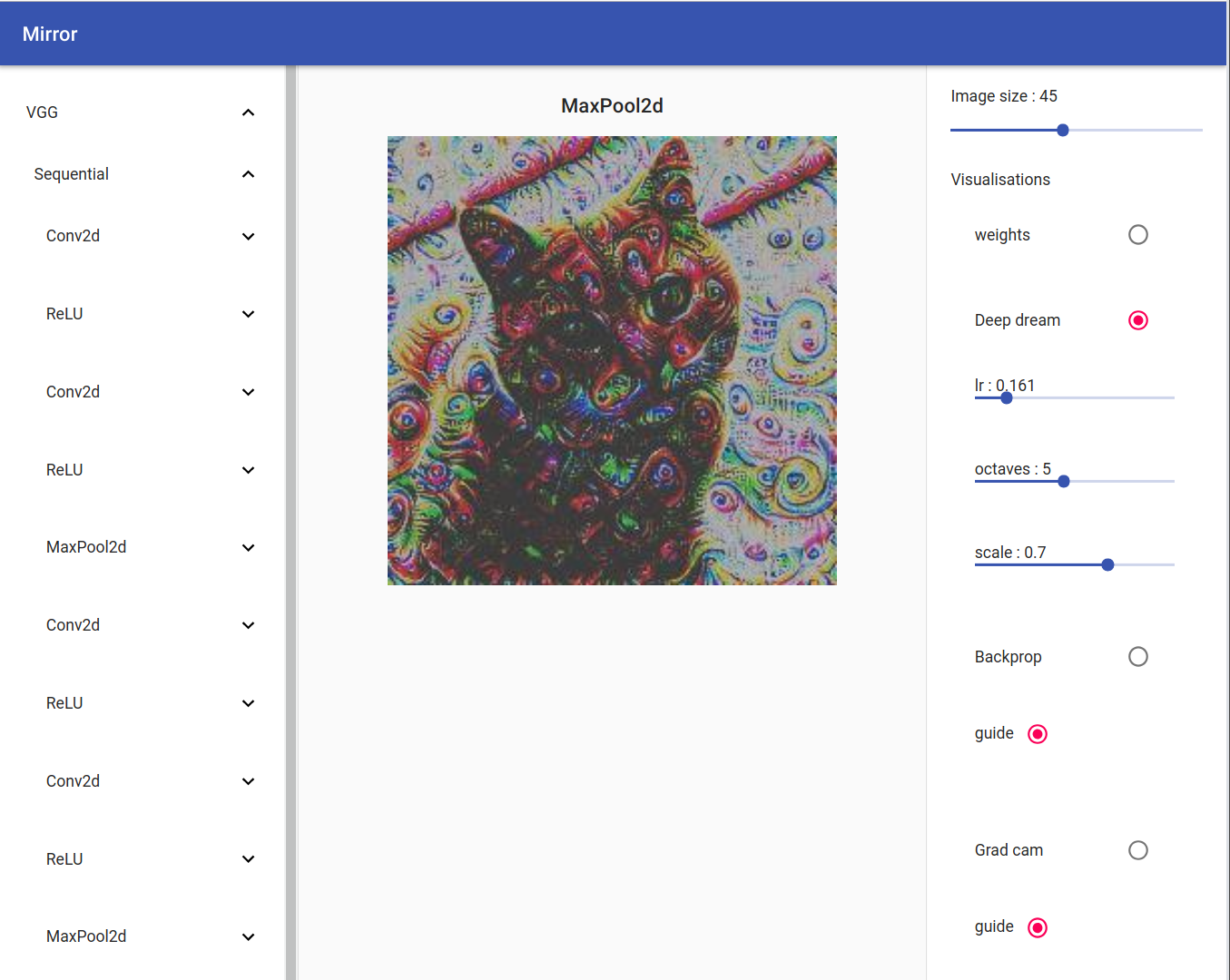
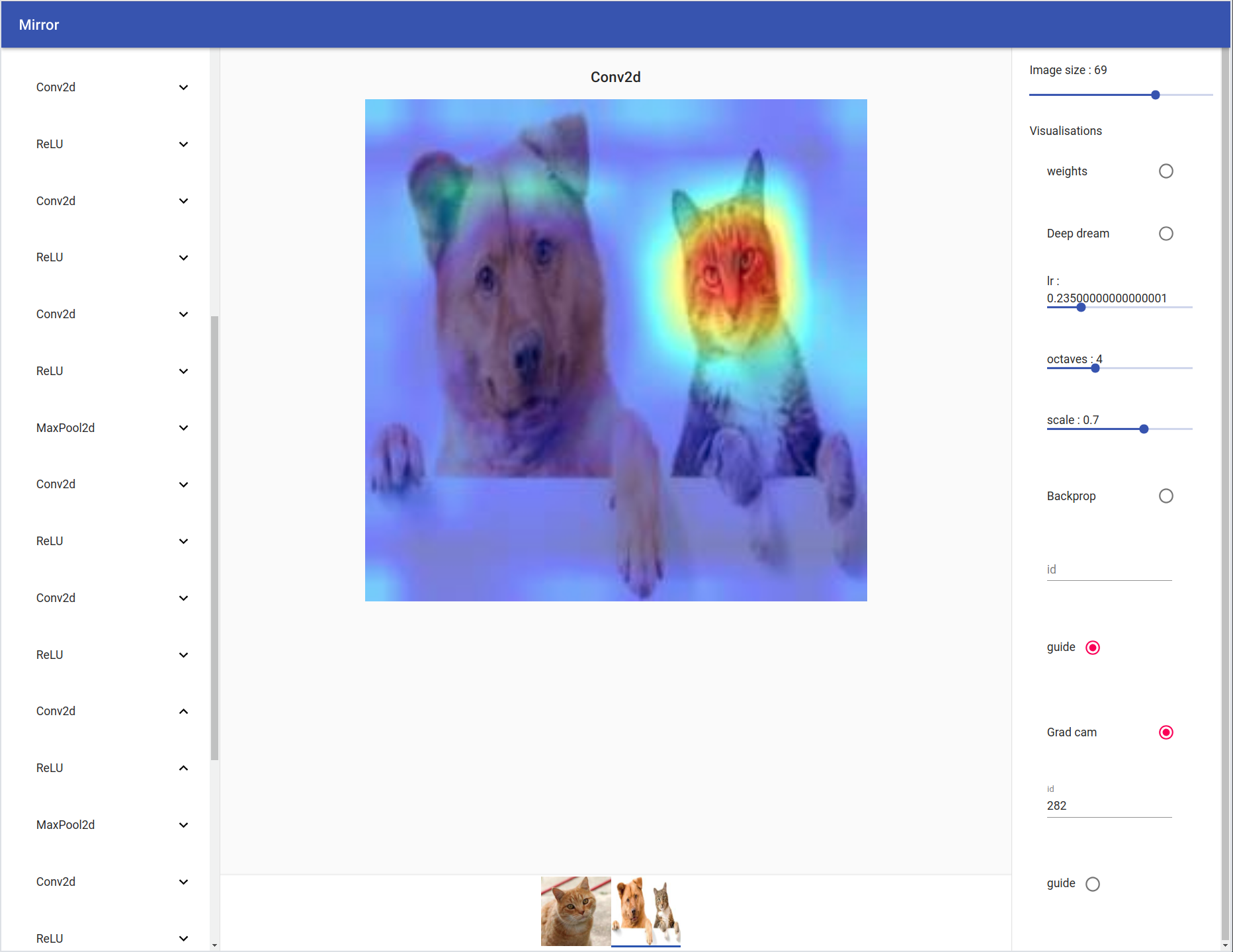
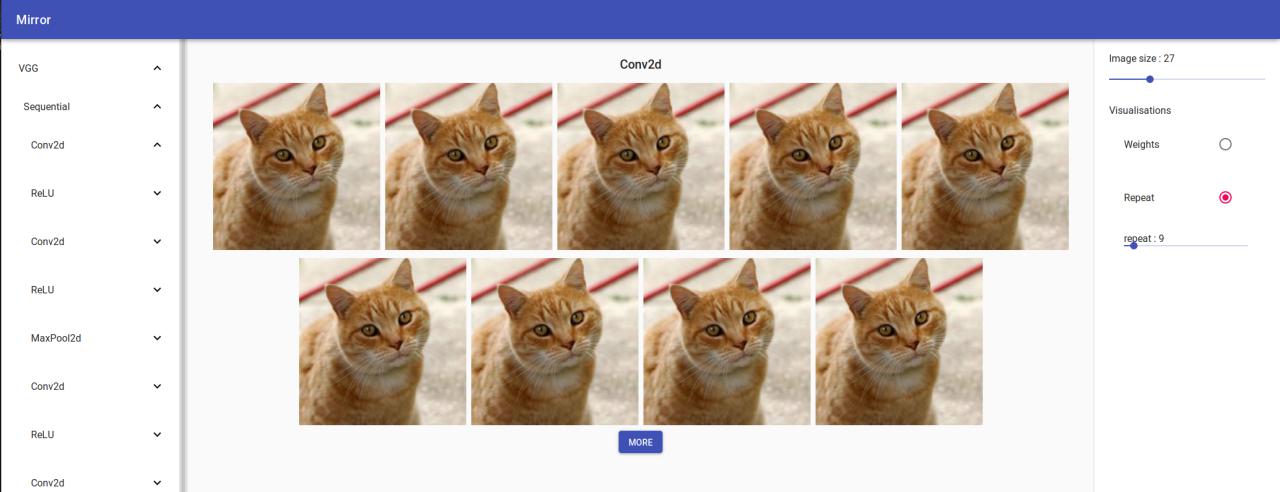
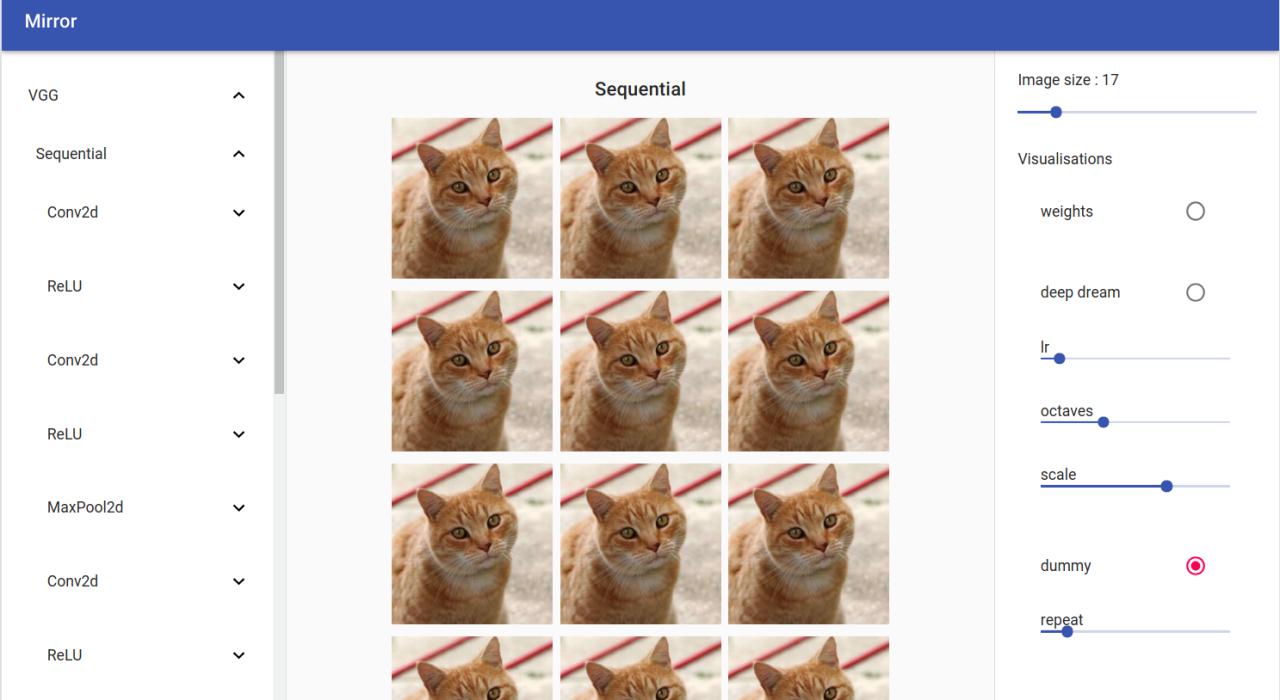
On the left you can see your model tree structure, by clicking on one layer all his children are showed. On the right there are the visualisation settings. You can select your input by clicking on the bottom tab.
Available Visualisations
All visualisation available for the web app are inside .mirror.visualisations.web.
Weights
Deep Dream
Back Prop / Guide Back Prop
By clicking on the radio button 'guide', all the relus negative output will be set to zero producing a nicer looking image
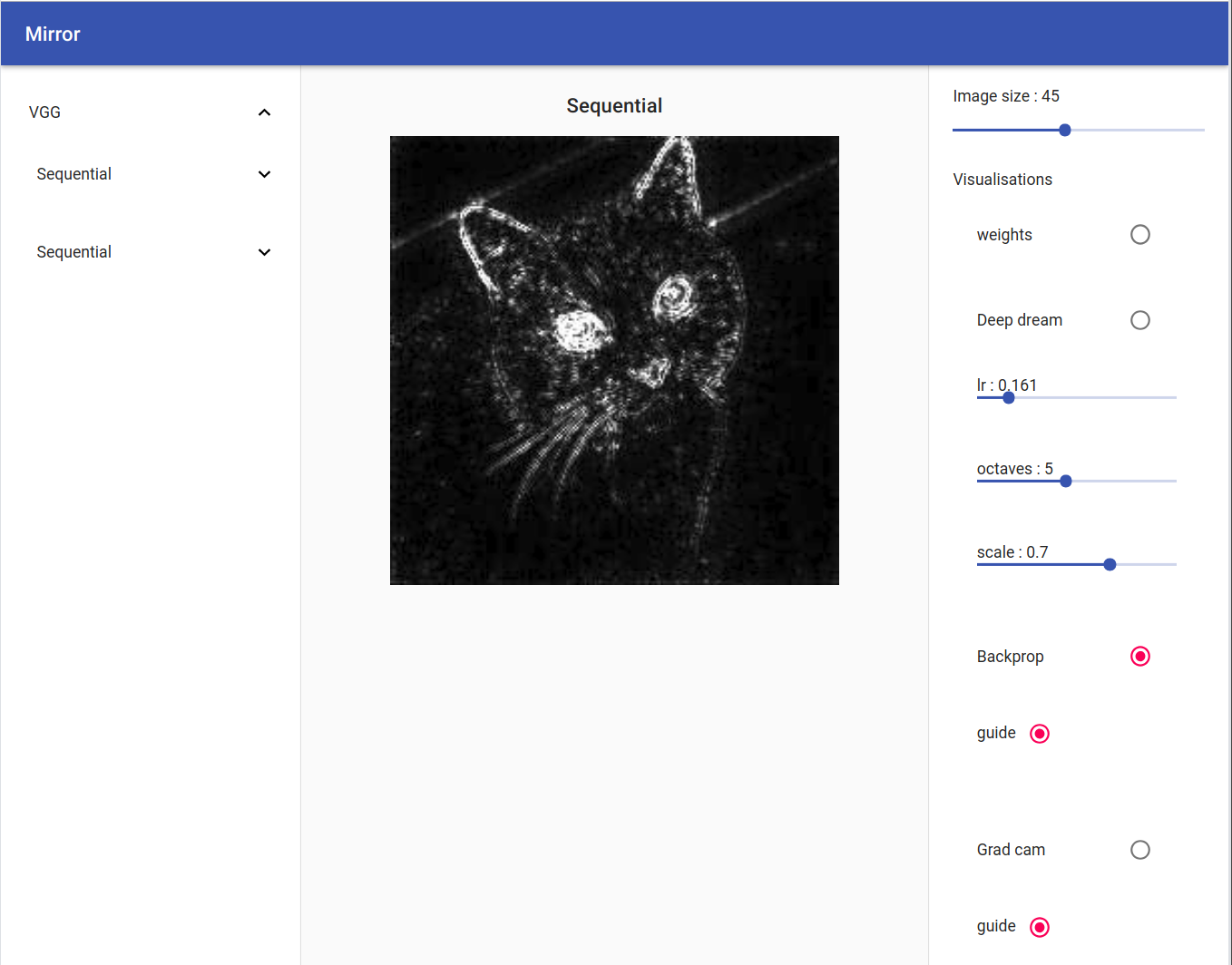
Grad Cam / Guide Grad Cam
Using with Tensors
If you want, you can use the vanilla version of each visualisation by importing them from .mirror.visualisation.core.
from mirror.visualisations.core import GradCam
# create a model
model = vgg16(pretrained=True)
# open some images
cat = Image.open("./cat.jpg")
dog_and_cat = Image.open("./dog_and_cat.jpg")
# resize the image and make it a tensor
to_input = Compose([Resize((224, 224)), ToTensor()])
cam = GradCam(model, device='cpu')
cam(to_input(cat).unsqueeze(0), None) # will return the output image and some additional information
Create a Visualisation
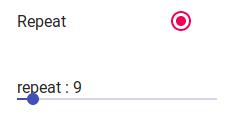
To create a visualisation you first have to subclass the Visualisation class and override the__call__ method to return an image and, if needed, additional informations. The following example creates a custom visualisation that just repeat the input repeat times. So
from mirror.visualisations.core import Visualisation
class RepeatInput(Visualisation):
def __call__(self, inputs, layer, repeat=1):
return inputs.repeat(repeat, 1, 1, 1), None
This class repeats the input for repeat times.
Connect to the web interface
To connect our fancy visualisation to the web interface, we have to create a WebInterface. Easily, we can use WebInterface.from_visualisation to generate the communication channel between our visualisation and the web app.
It follows and example
from mirror.visualisations.web import WebInterface
from functools import partial
params = {'repeat' : {
'type' : 'slider',
'min' : 1,
'max' : 100,
'value' : 2,
'step': 1,
'params': {}
}
}
visualisation = partial(WebInterface.from_visualisation, RepeatInput, params=params, name='Repeat')
First we import WebInterface and partial. Then, we create a dictionary where each they key is the visualisation parameter name. In our example, RepeatInput takes a parameter called repeat, thus we have to define a dictionary { 'repeat' : { ... }' }.
The value of that dictionary is the configuration for one of the basic UI elements: slider, textfield and radio.
The input is stored in the value slot.
Then we call WebInterface.from_visualisation by passing the visualisation, the params and the name. We need to wrap this function using partial since mirror will need to dynamically pass some others parameters, the current layer and the input, at run time.
Change the front-end
All the front-end is developed usin React and Material-UI, two very known frameworks, making easier for anybody to contribuite.
You can customise the front-end by changing the source code in mirror/client. After that, you need to build the react app and move the file to the server static folder.
I was not able to serve the static file directly from the /mirror/client/build folder if you know how to do it any pull request is welcome :)
cd ./mirror/mirror/client // assuming the root folder is called mirror
npm run build
Then you need to move the fiels from the mirror/mirror/client/build folder to mirror/mirror. You can remove all the files in mirror/mirro/static
mv ./build/static ../ && cp ./build/* ../static/
TODO
-
[x] Cache reused layer
-
[x] Make a generic abstraction of a visualisation in order to add more features
-
[x] Add dropdown as parameter
-
[x] Add text field
-
[x] Support multiple inputs
-
[x] Support multiple models
-
Add all visualisation present here https://github.com/utkuozbulak/pytorch-cnn-visualizations
- [x] Gradient visualization with vanilla backpropagation
- [x] Gradient visualization with guided backpropagation [1]
- [x] Gradient visualization with saliency maps [4]
- [x] CNN filter visualization [9]
- [x] Deep dream [10]
- [ ] Class specific image generation [4]
- [x] Grad Cam
-
[ ] Add a
output_transformationparams for each visualisation to allow better customisation -
[ ] Add a
input_transformationparams for each visualisation to allow better customisation