joanllenas / Ngx Remotedata
Programming Languages
Projects that are alternatives of or similar to Ngx Remotedata
RemoteData
Slaying a UI Antipattern with Angular.
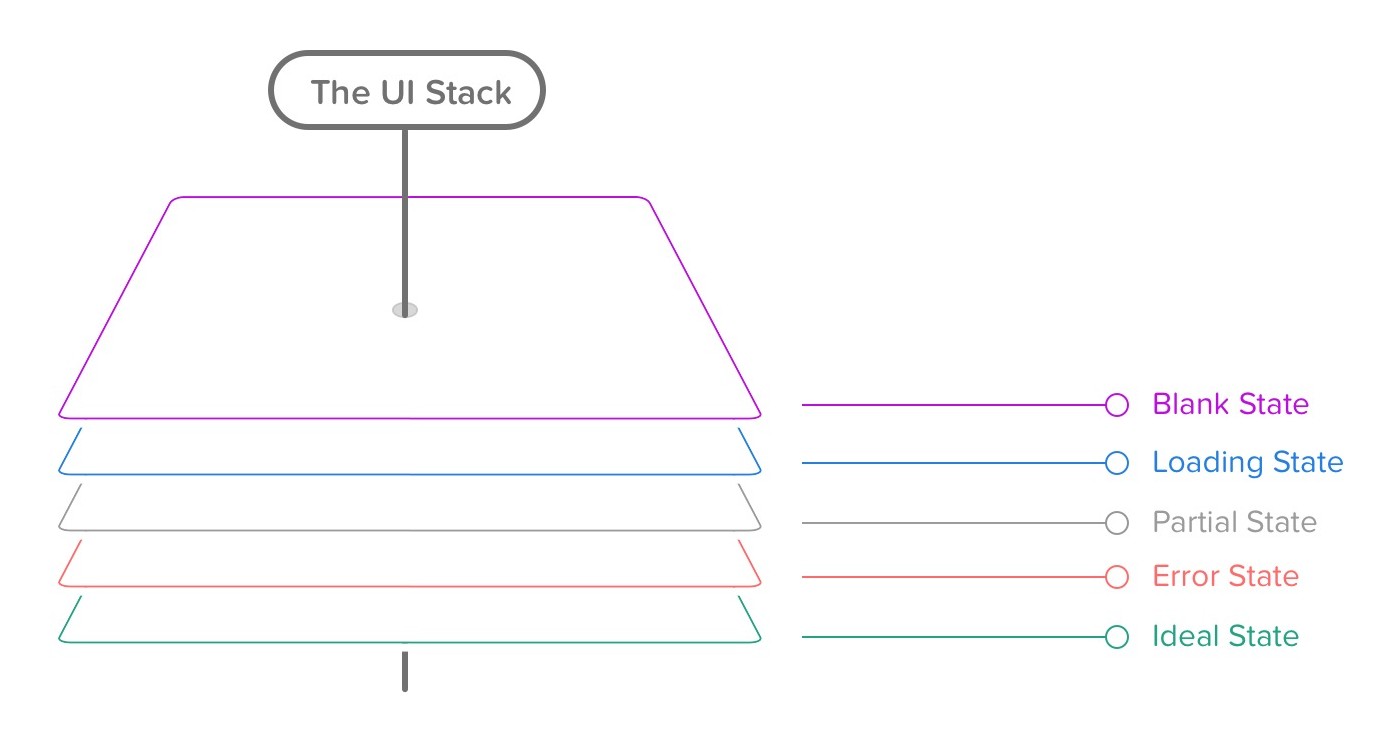
Library inspired by Kris Jenkins blog post about How Elm slays a UI antipattern, which mixes pretty well with another article written by Scott Hurff about what he calls the UI Stack.
Table Of Contents
What we are trying to solve
We are making an API request and want to display different things based on the request's status.
The traditional approach
export interface SunriseSunset {
isInProgress: boolean;
error: string;
data: {
sunrise: string;
sunset: string;
};
}
Let us see what each property means:
-
isInProgress: It istruewhile the data is being fetched. -
error: It is eithernull(no errors) or anystring(there are errors). -
data: Eithernull(no data) or the result payload (there is data).
There are a few problems with this approach, the main one being that it is possible to create invalid states such as:
{
"isInProgress": true,
"error": "Fatal error",
"data": {
"sunrise": "I am good data.",
"sunset": "I am good data too!"
}
}
Our html template will have to use complex *ngIf statements to make sure we are displaying the correct information.
The RemoteData approach ™
Instead of using a complex data structures we use a single data type to express all possible request states:
type RemoteData<T, E> = NotAsked | InProgress<T> | Failure<E, T> | Success<T>;
This approach makes it impossible to create invalid states.
Installation
npm install --save ngx-remotedata
Basic Usage
// app.module.ts
import { RemoteDataModule } from 'ngx-remotedata';
@NgModule({
imports: [
// (...)
RemoteDataModule
]
})
// app.component.ts
import {
RemoteData,
inProgress,
notAsked,
success,
failure
} from 'ngx-remotedata';
@Component({
selector: 'app-root',
templateUrl: './app.component.html'
})
export class AppComponent {
remoteData: RemoteData<string> = notAsked();
setNotAsked() {
this.remoteData = notAsked();
}
setInProgress() {
this.remoteData = inProgress('In progress...');
}
setSuccess() {
this.remoteData = success('Success!');
}
setFailure() {
this.remoteData = failure('Wrong!');
}
}
<!-- app.component.html -->
<ul>
<li><button (click)="setNotAsked()">Not Asked</button></li>
<li><button (click)="setInProgress()">InProgress</button></li>
<li><button (click)="setSuccess()">Success</button></li>
<li><button (click)="setFailure()">Failure</button></li>
</ul>
<hr />
<h4 *ngIf="remoteData | isNotAsked">Not Asked</h4>
<h4 *ngIf="remoteData | isInProgress">InProgress...</h4>
<h4 *ngIf="remoteData | isSuccess" style="color: green">
{{ remoteData | successValue }}
</h4>
<h4 *ngIf="remoteData | isFailure" style="color: red">
{{ remoteData | failureValue }}
</h4>
Examples
Demo
Source code
Api
RemoteData
RemoteData<T, E>
RemoteData is used to annotate your request variables. It wraps all possible request states into one single union type. Use the parameters to specify:
-
T: The success value type. -
E: The error value type (stringby default). -
Type guard function:
isRemoteData = <T, E>(value: unknown): value is RemoteData<T, E>.
NotAsked
- Constructor function:
notAsked<T, E>(): RemoteData<T, E>. - Type guard function:
isNotAsked<T, E>(value: unknown): value is NotAsked.
When a RemoteData is a NotAsked instance, it means that the request hasn't been made yet.
type User = { email: string };
const myRemoteData: RemoteData<User> = notAsked();
// (...)
if (isNotAsked(myRemoteData)) {
// Here myRemoteData is narrowed to NotAsked
}
InProgress
- Constructor function:
inProgress<T, E>(value?: T): RemoteData<T, E>. - Type guard function:
isInProgress<T, E>(value: unknown): value is InProgress<T>.
When a RemoteData is an InProgress instance, it means that the request has been made, but it hasn't returned any data yet.
The InProgress instance can contain a value of the same T type as Success. Useful when you want to use the last Success value while the new data is being fetched.
type User = { email: string };
const myRemoteData: RemoteData<User> = inProgress({ email: '[email protected]' });
// (...)
if (isInProgress(myRemoteData)) {
// Here myRemoteData is narrowed to InProgress
console.log(`I have some data: ${myRemoteData.value().email}`);
}
Success
- Constructor function:
success<T, E>(value: T): RemoteData<T, E>. - Type guard function:
isSuccess<T, E>(value: unknown): value is Success<T>.
When a RemoteData is a Success instance, it means that the request has completed successfully and the new data (of type T) is available.
type User = { email: string };
const myRemoteData: RemoteData<User> = success({ email: '[email protected]' });
// (...)
if (isSuccess(myRemoteData)) {
// Here myRemoteData is narrowed to Success
console.log(`I have some data: ${myRemoteData.value().email}`);
}
Failure
- Constructor function:
failure<T, E>(err: E, val?: T): RemoteData<T, E>. - Type guard function:
isFailure<T, E>(value: unknown): value is Failure<E, T>.
When a RemoteData is a Failure instance, it means that the request has failed. You can get the error information (of type E) from the payload.
The Failure instance can contain a value of the same T type as Success. Useful when you want to use the last Success value while displaying the failure message.
type User = { email: string };
const myRemoteData: RemoteData<User> = failure('Something went wrong.', {
email: '[email protected]'
});
// (...)
if (isFailure(myRemoteData)) {
// Here myRemoteData is narrowed to Failure
console.log(`This is the failure: ${myRemoteData.error()}`);
console.log(`I have some data: ${myRemoteData.value().email}`);
}
The default type for errors is string, but you can also provide other types like Error:
type User = { email: string };
const myRemoteData: RemoteData<User, Error> = failure(
new Error('Something went wrong.')
);
Unwrapping RemoteData values
getOrElse
getOrElse<T, E>(rd: RemoteData<T, E>, defaultValue: T): T;
getOrElse unwraps and returns the value of Success instances or the defaultValue when it's any other RemoteData variant.
let myRemoteData = success('ok!');
console.log(getOrElse(myRemoteData, 'The default value')); // ok!
myRemoteData = failure('There has been an error');
console.log(getOrElse(myRemoteData, 'The default value')); // The default value
fold
fold<T, E>(
onNotAsked: () => T,
onInProgress: (value: T | undefined) => T,
onFailure: (error: E, value: T | undefined) => T,
onSuccess: (value: T) => T,
rd: RemoteData<T, E>
): T;
With fold you unwrap the RemoteData value by providing a function for each of the type variants.
Transforming RemoteData values
map
map<A, B, E>(
fn: (a: A) => B,
rd: RemoteData<A, E>
): RemoteData<B, E>;
With map you provide a transformation function that is applied to a RemoteData only when it's a Success instance.
const scream = (s: string) => s.toUpperCase();
const hello = success('hello!');
const helloScreaming = map(scream, hello);
console.log(helloScreaming); // success('HELLO!')
mapFailure
mapFailure<A, E, F>(
fn: (e: E) => F,
rd: RemoteData<A, E>
): RemoteData<A, F>;
With mapFailure you provide a transformation function that is applied to a RemoteData only when it's a Failure instance.
const scream = (s: string) => s.toUpperCase();
const error = failure('wrong!');
const wrongScreaming = mapFailure(scream, error);
console.log(wrongScreaming); // failure('WRONG!')
Pipes
isNotAsked
transform<T, E>(rd: RemoteData<T, E>): boolean;
Returns true when RemoteData is a NotAsked instance.
anyIsNotAsked
transform<T, E>(
rds$: Observable<RemoteData<T, E>>[]
): boolean;
Returns true when any RemoteData<T, E>[] items is a NotAsked instance.
isInProgress
transform<T, E>(rd: RemoteData<T, E>): boolean;
Returns true when RemoteData is an InProgress instance.
anyIsInProgress
transform<T, E>(
rds$: Observable<RemoteData<T, E>>[]
): boolean;
Returns true when any RemoteData<T, E>[] item is an InProgress instance.
isFailure
transform<T, E>(rd: RemoteData<T, E>): boolean;
Returns true when RemoteData is a Failure instance.
isSuccess
transform<T, E>(rd: RemoteData<T, E>): boolean;
Returns true when RemoteData is a Success instance.
hasValue
transform<T, E>(rd: RemoteData<T, E>): boolean;
Returns true when RemoteData is a Success instance or is an InProgress or Failure instance with a value that is not null or undefined.
successValue
transform<T, E>(
rd: RemoteData<T, E>,
defaultValue?: T
): T | undefined;
Returns the Success payload (of type T) when the RemoteData is a Success instance, otherwise it returns the defaultValue when provided or undefined when not.
inProgressValue
transform<T, E>(
rd: RemoteData<T, E>,
defaultValue?: T | undefined
): T | undefined;
Returns the InProgress payload (of type T) when RemoteData is an InProgress instance, otherwise it returns the provided defaultValue or undefined when not.
remoteDataValue
transform<T, E>(rd: RemoteData<T, E>): T | E | undefined;
Returns the InProgress, Failure or Success payload (of type T) when RemoteData is an InProgress, Failure or Success instance. Returns undefined otherwise.
failureError
transform<T, E>(rd: RemoteData<T, E>): E | undefined
Returns the Failure error payload (of type E) when RemoteData is a Failure instance or undefined otherwise.
failureValue
transform<T, E>(rd: RemoteData<T, E>): T | undefined
Returns the Failure payload (of type T) when RemoteData is a Failure instance or undefined otherwise.