Narasimha1997 / Pavlos
Projects that are alternatives of or similar to Pavlos
Pavlos
A light-weight container runtime for Linux with NVIDIA gpu support, allows developers to quicky setup development environments for dev and test. Pavlos can emulate any Linux rootfs image as a container. Pavlos is a greek word which means "small". Pavlos now ships with a package manager that manages all your rootfs and their configurations.
Building Pavlos from srouce :
You should be able to build pavlos easily on any Linux system provided you have offical golang installed. You mant also need nvidia-container-runtime if you want to use pavlos with GPUs.
Requirements:
- A Linux distro
- Official Go Programming Language properly setup and configured.
-
GOPATHandGOROOTdirectories.
Building pavlos core container-runner
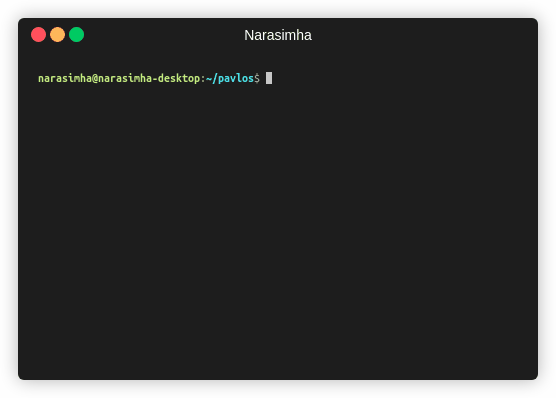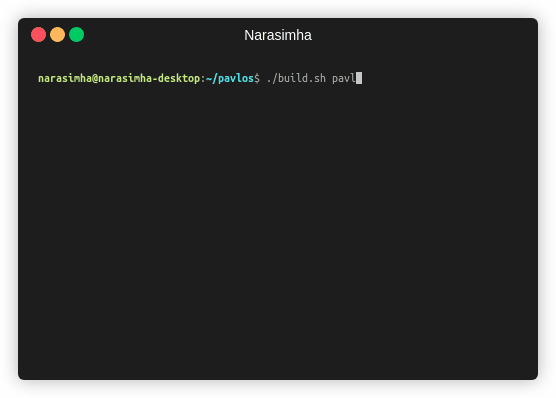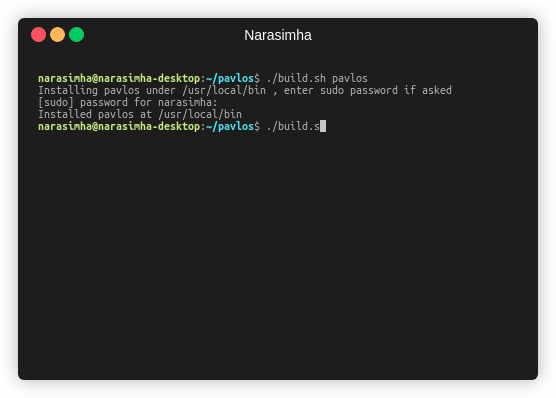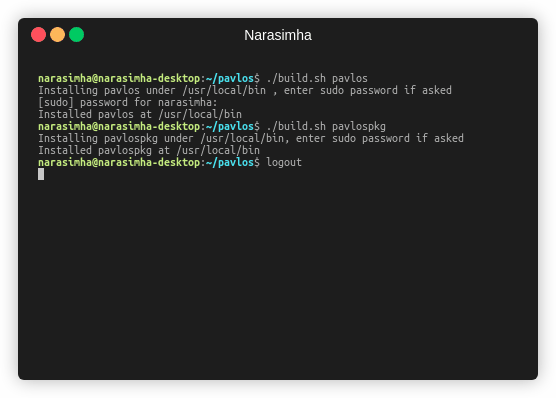
The build script build.sh automatically builds pavlos for you. You may need to be sudo if you want to install pavlos under /usr/local/bin so that it can be accessed anywhere.
To build pavlos:
./build.sh pavlos
Manually from project root:
GOPATH=$GOPATH:$(pwd)
GOBIN=$(pwd)/bin
go install github.com/Narasimha1997/pavlos
Building the package-manager (pavlospkg)
Pavlos package manager needs to be installed to manage rootfs packages. It acts as a source-registry for all the rootfs images. It is just like npm or pip which stores packages somewhere and manages it for you.
To build pavlospkg:
./build.sh pavlospkg
Manually from project root:
GOPATH=$GOPATH:$(pwd)
GOBIN=$(pwd)/bin
go install github.com/Narasimha1997/pavlospkg
How to emulate a rootfs with pavlos:
- Download and register the rootfs image using
pavlospkg
sudo pavlospkg rootfs create \
--name=alpine-linux \
--uri=http://dl-cdn.alpinelinux.org/alpine/v3.12/releases/x86_64/alpine-minirootfs-3.12.0-x86_64.tar.gz
- Register your configuration for
alpine-linux: We have provided examples underexamples/directory which contains example configs for CPU and GPU based containers with pavlos. We will be using CPU config for our rootfsalpine-linux:
sudo pavlospkg config create \
--name=alpine-linux \
--file=examples/example-cpu.json
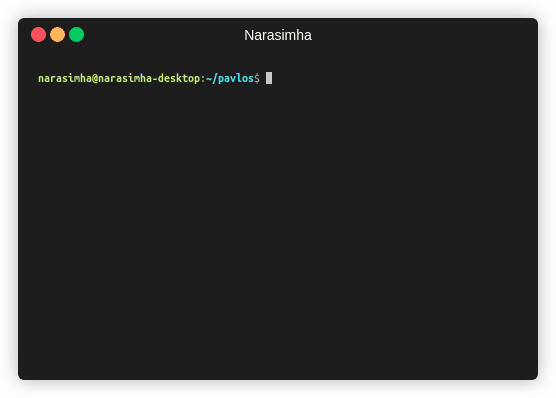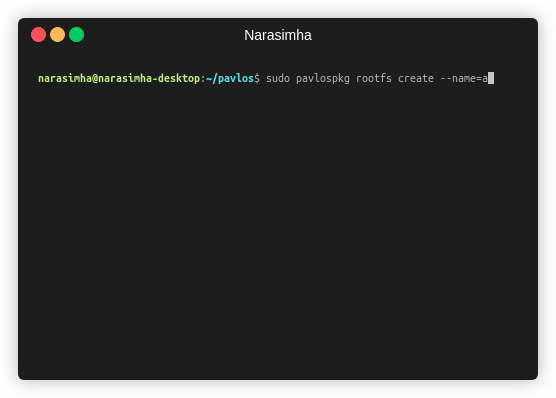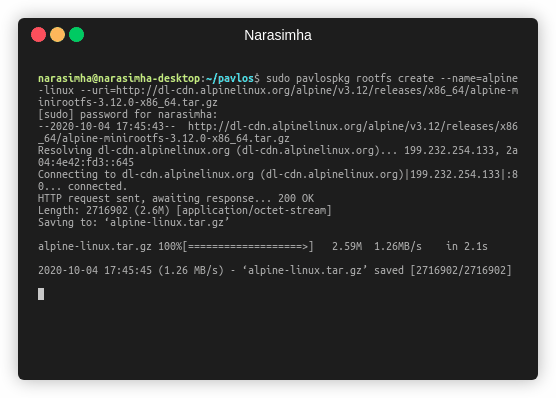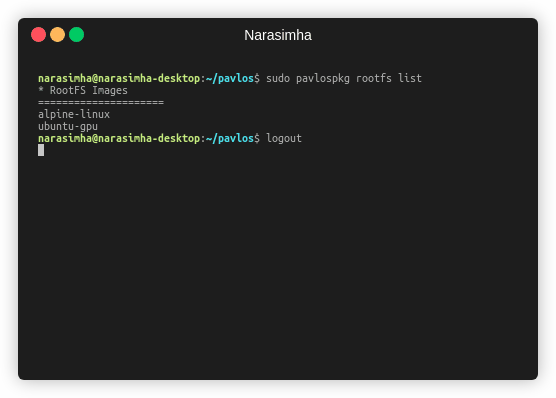
- Now you can list the available rootfs images:
sudo pavlospkg rootfs list
Output:
* RootFS Images
=====================
alpine-linux # our new rootfs
ubuntu-gpu
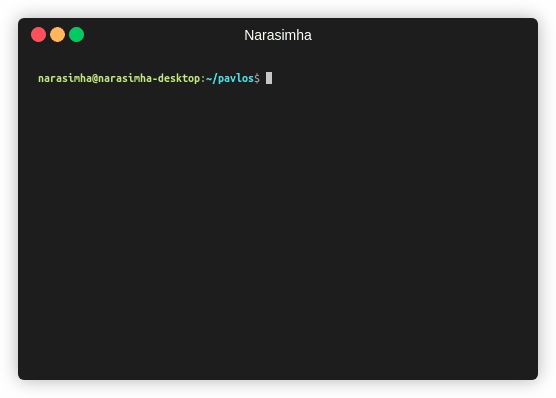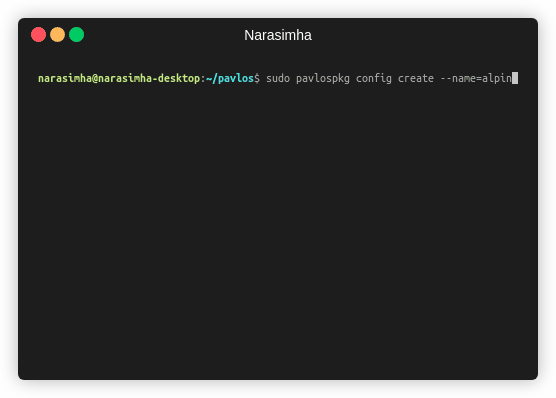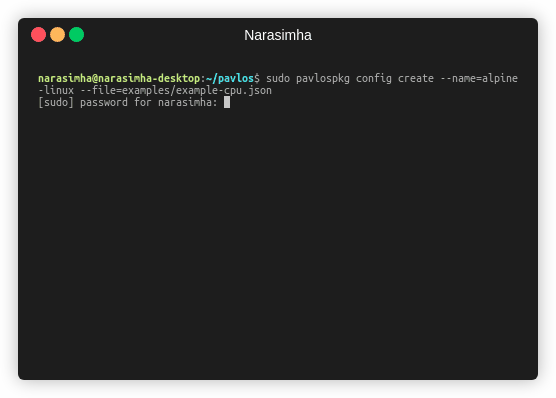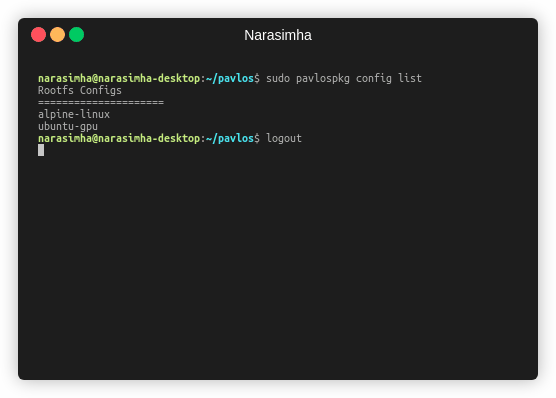
Also you can list the configs registered:
sudo pavlospkg config list
Output:
Rootfs Configs
=====================
alpine-linux
ubuntu-gpu
- Create the container out of the config:
sudo pavlos run --config=alpine-linux
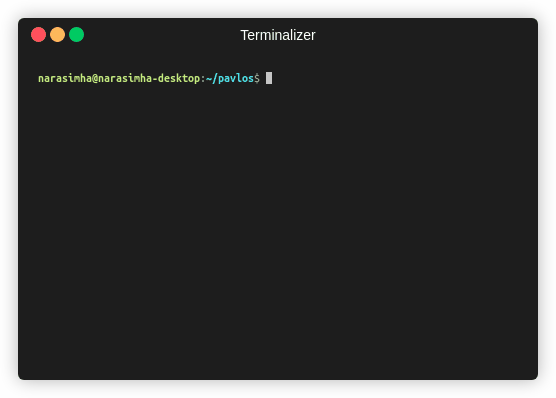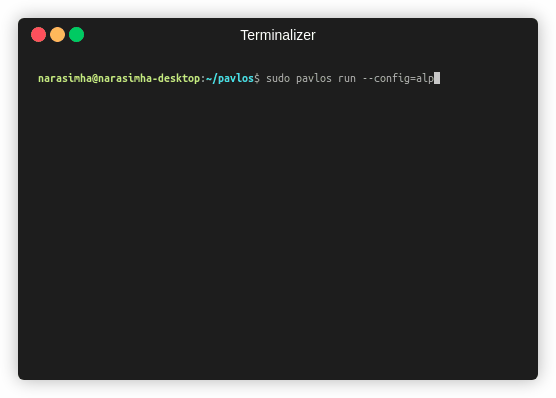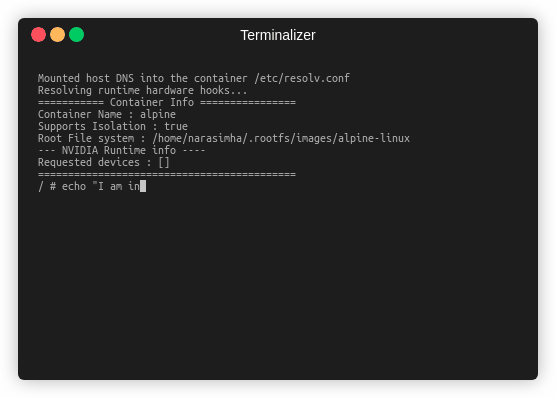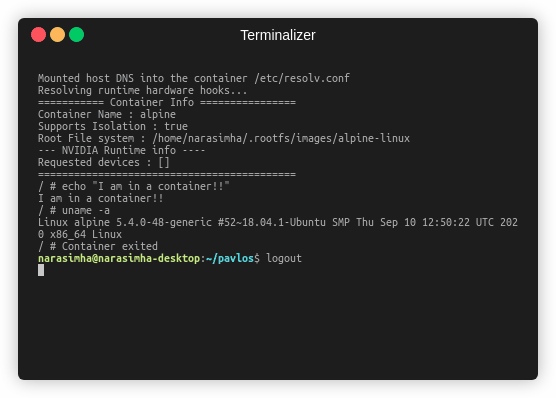
You will now get the container which you can use:
=========== Container Info ================
Container Name : alpine
Supports Isolation : true
Root File system : /home/narasimha/.rootfs/images/alpine-linux
--- NVIDIA Runtime info ----
Requested devices : []
===========================================
/ #
Editing configuration files:
pavlospkg has a support for editing config-files in place, to do so you have to call :
sudo pavlospkg config edit -n <config-name>
This will open basic vi editor by default, however you can use the editor of your choice, for thos purpose, pavlospkg looks at the env EDITOR during the start of edit command, if that env is empty, it invokes vi as the default editor, you can change the editor however by settign the EDITOR env to your favourite editor. Supported editors are vi, vim, nano, gedit and pico. For example, to invoke edit with nano, do :
export EDITOR=nano
sudo -E pavlospkg config edit -n <config-name>
Hooking GPUs at runtime:
Pavlos supports NVIDIA GPUs, that means, you can use pavlos container with nvidia gpus. Look at examples/example-gpu.json to understand how to configure your image to detect GPUs. Pavlos uses libnvidia-container for GPU support.
How GPU assignment works in pavlos??
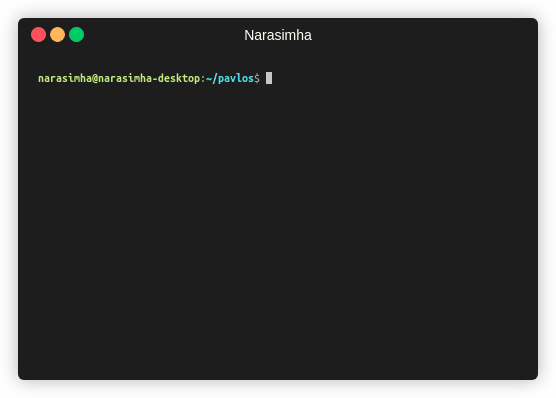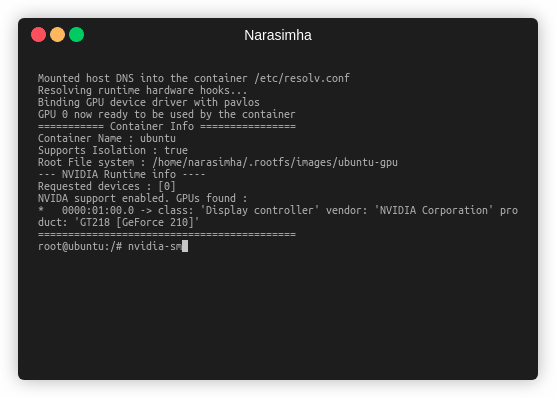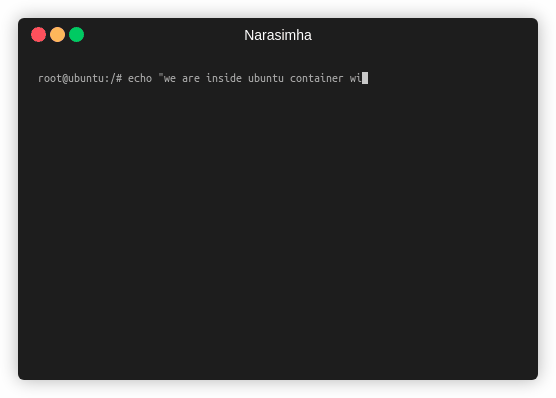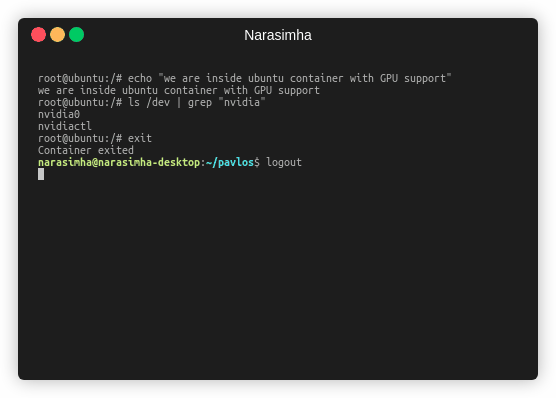
Pavlos scans PCI device tree to understand what GPUs are there on the host machine and then gives each GPU an integer ID and maintains the mapping internally, this is built in order to check for errors, if user hooks a GPU which is not present, pavlos throws error right away instead of creating a segmentation fault in libnvidia-container. If a GPU is found, then pavlos calls nvidia-container-cli and passes the device ID and other parameters to install the kernel module inside the container. Example of pavlos running GPU container is shown below:
Roadmap :
- SW defined container overaly networking (like CNI) (This functionality is broken as of now)
- Resource isolation using Linux - cgroups (Partial support is already implemented)
- Union File system like the one in Docker (Reduces storage space by reusing existing fs components)
- More advanced hardware discovery by traversing PCI Device tree (Partial functionality is already implemented to discover NVIDIA GPUs using jaypipe's GHW library)
- Encrypted file-system support (see dm_crypt and cryptmount) using Linux Kernel device-mapper driver.
- Volume mounting support like Docker - can mount encrypted volumes as well (See LVM encrypted volume mounting)