SICKAG / Sick_scan
Labels
Projects that are alternatives of or similar to Sick scan
sick_scan
This stack provides a ROS driver for the SICK lidar and radar sensors mentioned in the following list. The SICK MRS6124 is a multi-layer, multi-echo 3D laser scanner that is geared towards rough outdoor environments.
Table of Contents
- Supported Hardware
- Start node
- Bugs and feature requests
- Tools
- Troubleshooting
- SLAM-Support
- Radar
- Profiling
- Testing
- Creators
Supported Hardware
This driver should work with all of the following products.
ROS Device Driver for SICK lidar and radar sensors - supported scanner types:
| device name | part no. | description | tested? |
|---|---|---|---|
| MRS6124 | 6065086 | 24 layer max. range: 200 m, ang. resol. 0.13 [deg] hor., 0.0625 [deg] ver. | ✔ [stable] |
| Scan-Rate: 10 Hz | |||
| MRS1104 | 1081208 | 4 layer max. range: 64 m, ang. resol. 0.25 [deg] hor., 2.50 [deg] ver. | ✔ [stable] |
| Scan-Rate: 50 Hz, 4x12.5 Hz | |||
| LMS1104 | 1092445 | 1 layer max. range: 64 m, ang. resol. 0.25 [deg] | ✔ [stable] |
| Scan-Rate: 150 Hz, 4x37.5 Hz | |||
| TiM240 | prototype more info here | 1 layer max. range: 10 m, ang. resol. 1.00 [deg], 240 [deg] | ✔ [prototype] |
| Scan-Rate: 14.5 Hz | |||
| TiM433 | prototype | 1 layer range: 0.05 m ... 15 m, ang. resol. 0.33 [deg], 240 [deg] | ✔ [prototype] |
| Scan-Rate: 15.0 Hz | |||
| TiM443 | prototype | 1 layer range: 0.05 m ... 15 m, ang. resol. 0.33 [deg], 240 [deg] | ✔ [prototype] |
| Scan-Rate: 15.0 Hz | |||
| TiM551 | 1060445 | 1 layer max. range: 10 m, ang. resol. 1.00[deg] | ✔ [stable] |
| Scan-Rate: 15 Hz | |||
| TiM561 | 1071419 | 1 layer max. range: 10 m, ang. resol. 0.33 [deg] | ✔ [stable] |
| Scan-Rate: 15 Hz | |||
| TiM571 | 1079742 | 1 layer max. range: 25 m, ang. resol. 0.33 [deg] | ✔ [stable] |
| Scan-Rate: 15 Hz | |||
| TiM771S | 1105052 | 1 layer max. range: 25 m, ang. resol. 0.33 [deg] | ✔ [stable] |
| Scan-Rate: 15 Hz | |||
| TiM781 | 1096807 | 1 layer max. range: 25 m, ang. resol. 0.33 [deg] | ✔ [stable] |
| Scan-Rate: 15 Hz | |||
| TiM781S | 1096363 | 1 layer max. range: 25 m, ang. resol. 0.33 [deg] | ✔ [stable] |
| Scan-Rate: 15 Hz | |||
| LMS511-10100 PRO | e.g. 1046135 | 1 layer max. range: 80 m, ang. resol. 0.167 [deg] | ✔ [stable] |
| Scan-Rate: 100 Hz | |||
| LMS1xx-Family | e.g. 1041114 | 1 layer max. range: 28 m, ang. resol. 0.25 [deg] | ✔ [stable] |
| Scan-Rate: 15 Hz | |||
| NAV310 | e.g. 1052928 | 1 layer max. range: 250 m, ang. resol. 0.125 [deg] | ✔ [stable] |
| Scan-Rate: 8 Hz | |||
| NAV210+NAV245 | e.g. 1074308 | 1 layer max. range: 100 m, ang. resol. 0.25 [deg] | ✔ [stable] |
| Scan-Rate: 25 Hz | |||
| LMS4xxx-Family | e.g. 1091423 | 1 layer max. range: 3 m, ang. resol. 0,0833 [deg] | ✔ [stable] |
| Scan-Rate: 600 Hz | |||
| Opening angle: +/- 50 [deg] | |||
| RMS3xx | 8021530 | Radar Sensor | ✔ [stable] |
IMU Support
Devices of the MRS6xxx and MRS1xxx series are available with an optionally built-in IMU. Further information on the implementation and use of the experimental Imu support can be found on the Imu page.
Start Node
Use the following command to start ROS node:
- For MRS6124:
roslaunch sick_scan sick_mrs_6xxx.launch
- For MRS1104:
roslaunch sick_scan sick_mrs_1xxx.launch
- For LMS1104:
roslaunch sick_scan sick_lms_1xxx.launch
- For TiM240-prototype:
roslaunch sick_scan sick_tim_240.launch
- For TiM4xx-family:
roslaunch sick_scan sick_tim_4xx.launch
- For TiM5xx-family:
roslaunch sick_scan sick_tim_5xx.launch
- For TiM7xx-family (no safety scanner):
roslaunch sick_scan sick_tim_7xx.launch
- For TiM7xxS-family (safety scanner):
roslaunch sick_scan sick_tim_7xxS.launch
- For LMS1xx-family:
roslaunch sick_scan sick_lms_1xx.launch
- For LMS5xx-family:
roslaunch sick_scan sick_lms_5xx.launch
- For LMS4xxx-family:
roslaunch sick_scan sick_lms_4xxx.launch
- For NAV210:
roslaunch sick_scan sick_nav_2xx.launch
- For NAV245:
roslaunch sick_scan sick_nav_2xx.launch
- For NAV310:
roslaunch sick_scan sick_nav_3xx.launch
- For RMS3xx-family:
roslaunch sick_scan sick_rms_3xx.launch (under
opment)
Starting Scanner with Specific Ip Address
To start the scanner with a specific IP address, the launch command can be used for most launch files as follows. The hostname is the ip-address of the scanner:
roslaunch <launch-file> hostname:=<ip-address>
e.g.
roslaunch sick_scan sick_tim_5xx.launch hostname:=192.168.0.71
Start Multiple Nodes
Take the launchfile "sick_tim_5xx_twin.launch" as an example. Rempping the scan and cloud topics is essential to distinguish the scanndata and provide TF information.
Parameter
The use of the parameters can be looked up in the launch files. This is also recommended as a starting point.
Common parameters
-
scanner_typeName of the used scanner. Usually this is also the name of the launch file. This entry is used to differentiate between the various scanner properties within the software code. -
hostnameIP-address of the scanner (default: 192.168.0.1) -
portIP-port of the scanner (default: 2112) -
min_angStart angle in [rad] -
max_angEnd angle in [rad] -
use_binary_protocolSwitch between SOPAS Binary and SOPAS ASCII protocol -
intensityEnable or disable transport of intensity values -
intensity_resolution_16bitIf true, the intensity values is transferred as 16 bit value. If false, as 8 bit value. -
cloud_topicTopic name of the published pointcloud2 data -
frame_idFrame id used for the published data
Further useful parameters and features
-
timelimitTimelimit in [sec] for max. wait time of incoming sensor reply -
sw_pll_only_publishIf true, the internal Software PLL is fored to sync the scan generation time stamp to a system timestamp -
Angle compensation: For highest angle accuracy the NAV-Lidar series supports an angle compensation mechanism.
-
Field monitoring: The LMS1xx, LMS5xx, TiM7xx and TiM7xxS families have extended settings for field monitoring.
Sopas Mode
This driver supports both COLA-B (binary) and COLA-A (ASCII) communication with the laser scanner. Binary mode is activated by default. Since this mode generates less network traffic. If the communication mode set in the scanner memory is different from that used by the driver, the scanner's communication mode is changed. This requires a restart of the TCP-IP connection, which can extend the start time by up to 30 seconds. There are two ways to prevent this:
- [Recommended] Set the communication mode with the SOPAS ET software to binary and save this setting in the scanner's EEPROM.
- Use the parameter "use_binary_protocol" to overwrite the default settings of the driver.
- Setting "use_binary_protocol" to "False" activates COLA-A and disables COLA-B (default)
Bugs and Feature Requests
- Stability issues: Driver is experimental for the RMS3xx
- Sopas protocol mapping: -- All scanners: COLA-B (Binary)
- Software should be further tested, documented and beautified
- Setting of "topic" should not be hardcoded to /cloud in the future. This allows the simultaneous operation of several scanners. Each point cloud can then be converted using its own TF transformation.
Tools
Various tools exist in the repository to improve the operation of the scanners. It is also recommended to read the following section "Troubleshooting". Overview of the tools:
- Search for scanner in the network:
Use the Python3 tool "sick_generic_device_finder.py" in the tools/sick_generic_device_finder directory.
The tools will output the IP addresses of the connected scanners and some more information about the scanner.
Call it with python3, i.e.python3 sick_generic_device_finder.py - Setting new IP address: With the help of the parameter "new_IP" a new IP address can be assigned when calling the node sick_scan. The launch file sick_new_ip.launch in the launch directory shows an example of how to use this parameter.
- Converting of pointclouds to images: With the tool pcl_converter.cpp one can convert pointcloud2-data to image. That is especial convenient for 24-layers scanners like the MRS6124.
- Setting up a brand new scanner: To set up a brand new scanner, it is recommended to use the two tools "sick_generic_device_finder.py" to find the scanner in the network and the launch file sick_new_ip.launch to set a new IP address. If further settings are to be saved that cannot be made via ROS parameters, we recommend using the Windows tool "Sopas ET" from SICK.
Troubleshooting
- Check Scanner IP in the launch file.
- Check Ethernet connection to scanner with netcat e.g.
nc -z -v -w5 $SCANNERIPADDRESS 2112. For further details about setting up the correct ip settings see IP configuration - View node startup output wether the IP connection could be established
- Check the scanner status using the LEDs on the device. The LED codes are described in the above mentioned operation manuals.
- Further testing and troubleshooting informations can found in the file test/readme_testplan.txt
- If you stop the scanner in your debugging IDE or by other hard interruption (like Ctrl-C), you must wait until 60 sec. before
the scanner is up and running again. During this time the MRS6124 reconnects twice.
If you do not wait this waiting time you could see one of the following messages:
- TCP connection error
- Error-Message 0x0d
- Amplitude values in rviz: If you see only one color in rviz try the following: Set the min/max-Range of intensity display in the range [0...200] and switch on the intensity flag in the launch file
- In case of network problems check your own ip address and the ip address of your laser scanner (by using SOPAS ET).
- List of own IP-addresses: ifconfig|grep "inet addr"
- Try to ping scanner ip address (used in launch file)
- If the driver stops during init phase please stop the driver with ctrl-c and restart (could be caused due to protocol ASCII/Binary cola-dialect).
FAQ
- FAQ: doc/faq.md
Support
- In case of technical support please open a new issue. For optimal support, add the following information to your request:
- Scanner model name,
- Ros node startup log,
- Sopas file of your scanner configuration. The instructions at http://sickusablog.com/create-and-download-a-sopas-file/ show how to create the Sopas file.
- In case of application support please use https://supportportal.sick.com .
- Issue Handling: Issues, for which no reply was received from the questioner for more than 7 days, are closed by us because we assume that the user has solved the problem.
Installation
In the following instructions, replace <rosdistro> with the name of your ROS distro (e.g., indigo).
From Binaries
The driver is released at longer intervals as a binary package and can therefore be installed via the package manager. To be able to use all new functions of the driver, the driver should be built from the sources published in this reposity:
sudo apt-get install ros-<rosdistro>-sick-scan
From Source
source /opt/ros/<rosdistro>/setup.bash
mkdir -p ~/ros_catkin_ws/src/
cd ~/ros_catkin_ws/src/
git clone git://github.com/SICKAG/sick_scan.git
cd ..
catkin_make install
source ~/ros_catkin_ws/install/setup.bash
Development branch
A "devel" branch is also maintained for the very latest developments and tests. Add-ons and support for brand new scanners are usually first tested in this branch and can be checked out as needed as follows:
source /opt/ros/<rosdistro>/setup.bash
mkdir -p ~/ros_catkin_ws/src/
cd ~/ros_catkin_ws/src/
git clone -b devel --single-branch git://github.com/SICKAG/sick_scan.git
cd ..
catkin_make install
source ~/ros_catkin_ws/install/setup.bash
Quick Start
roslaunch sick_scan sick_mrs6xxx.launch
rosrun rviz rviz
publish to point cloud
Testing
The sick_scan_test program was developed for testing the driver. This program checks elementary properties of the scanner. In a first implementation stage, the shots per scan are checked. The test program works according to the following principle:
- The parameters from an original launch file are read.
- These parameters are modified according to the instructions in the test control file.
- The modified parameters including all other parameter settings from the original launch file are copied to a test launch file.
- The test launch file is started.
- The parameters are checked.
- The result of the check is transferred to a result file.
The basic procedure can be seen in the following figure:
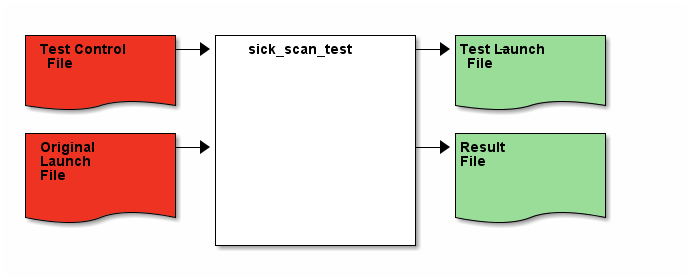 More information about the structure of the individual files in the test run can be found here:
More information about the structure of the individual files in the test run can be found here:
Keywords
MRS1000 MRS1104 LMS1000 LMS1104 MRS6000 MRS6124 RMS3xx RMS320 ROS LiDAR SICK LiDAR SICK Laser SICK Laserscanner SICK Radar LMS1xx MRS1xxx LMS1xxx MRS6xxx TiM5xx TiM551 TiM561 TiM571 TiM781 TiM781S LMS5xx LMS511 NAV210 NAV245 NAV310
Creators
Michael Lehning
on behalf of SICK AG


